The Outer, Middle, & Inner Ear
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
outer, inner, middle
sections of the ear
outer ear
collects soundwaves from the environment
middle ear
transmits sounds collected from the outer ear to inner
inner ear
the sensory organ for hearing and balance
external auditory canal (ear canal)
opening of the ear
pinna
the part of the ear that sticks out from your head
funnel
the main function of the external ear is to act like a _______ to direct sound into the ear canal
→ it’s similar to cupping your hand up to your ear - sound gets louder when you do that because you’re directing more of the sound waves into the canal
head and torso amplification
sounds reaching a listener are affected by the body, head, and outer ear
several pinna cavities have resonance (sound enhancing) effects
each anatomical feature amplifies sounds at certain frequencies
directionality of the outer ear
the angle that sound approaches the ear has an effect on how much it is amplified AND in what frequency ranges
directionality
determining where a sound comes from in space involves localization and spatial orientation
localization
azimuth estimation
process of determining the direction on the horizontal plane
elevation estimation
process of determining the direction of the vertical plane (sounds from above and below)
spatial orientation
localization
distance estimation
process of determining how far we are from a sound source
monaural localization cues
the localization cues created by reflection and refraction of sound by the folds, cavities, and ridges of each outer ear
primary cues for estimating elevation
when a sound wave reaches the pinna, some of the original sound wave goes straight in the ear canal, and some of it gets reflected around by the pinna and “bounced” into the ear
think of a coin going around the swirly machine things at the mall
interaural (between ear)
just like your brain compares the spectrum of reflected sounds from one ear to help determine elevation, it can use _______ to help determine the location of sound in the horizontal plane
interaural intensity differences
intensity differences between the ears result in ______ ______ _____ (IID) cues
→ sound arriving from the left side will be louder in the left ear
interaural time difference
timing differences between ears results in ______ ___ _____ (ITD) cues
→ sound arriving from the left will be earlier in the left ear
→ another term for this is interaural phase difference (IPD) cues
ear canal
roughly 2.5 cm long
usually in diagrams it looks like a straight tube, but they’re usually curvy like an S-shape
has cartilaginous portion and osseous, the bony portion
tympanic membrane
the ear canal is basically like an open/closed tube: open at the meatus and closed at the TM
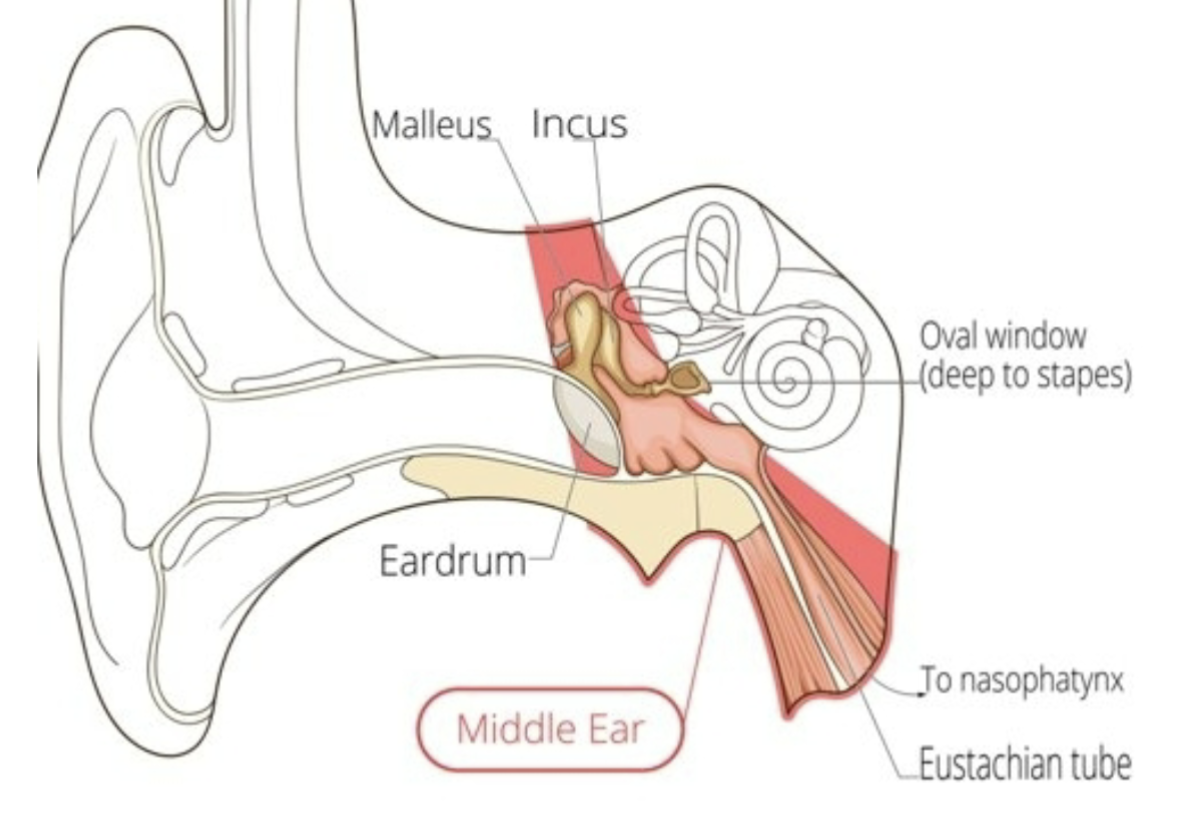
middle ear structures
tympanic membrane
ossicles
muscles
nerves
eustachian tube
tympanic membrane
also called the eardrum
slightly cone-shaped membrane
tip is called the umbo
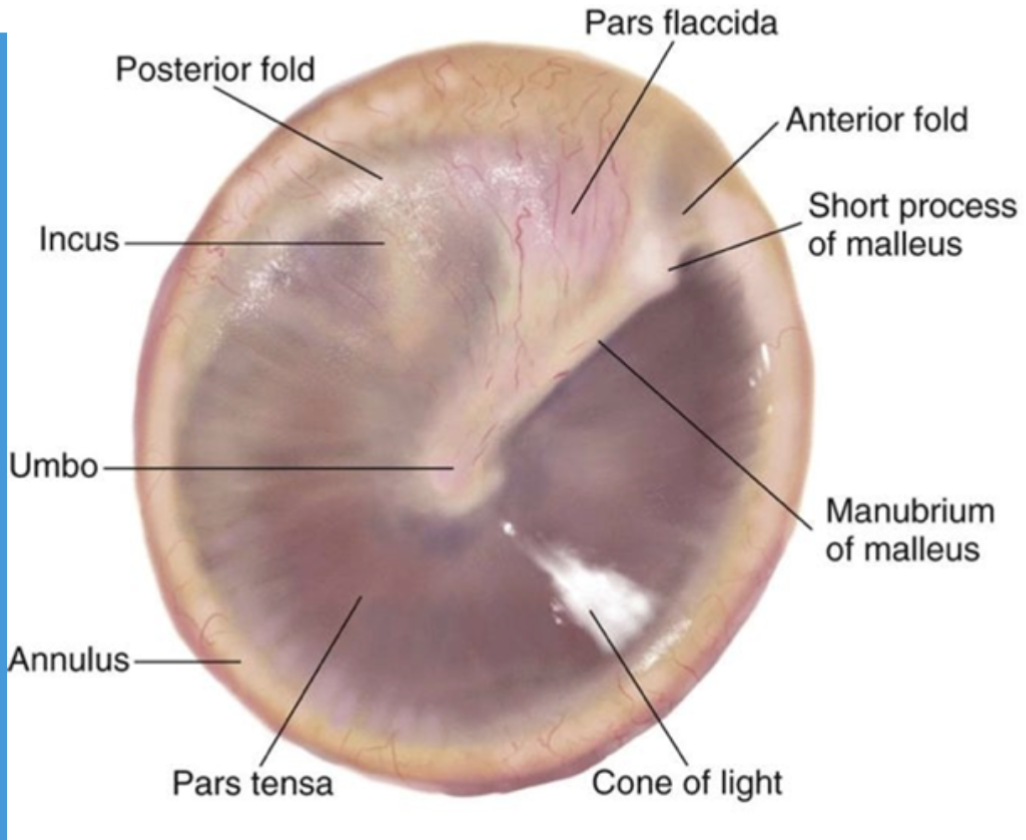
annulus
ring shaped ligament that holds the tympanic membrane in place
pars tensa
stretched (taut) part of the tympanic membrane
pars flaccida
loose (flaccid) part of the tympanic membrane
cone of light
a reflection of the light you’re using to look into the ear
otoscopy
the act of looking into the ear canal to observe the TM
device used = otoscope
left ear
if pac-man is facing the left or it’s 7:55, you are looking at the ____ ____
right ear
if pac-man is facing the right or it’s 5:05, you are looking at the ____ ___
tympanic cavity
the middle ear space, occupies 2 cm³ of space
ossicles
the middle ear bones
→ malleus
→ incus
→ stapes
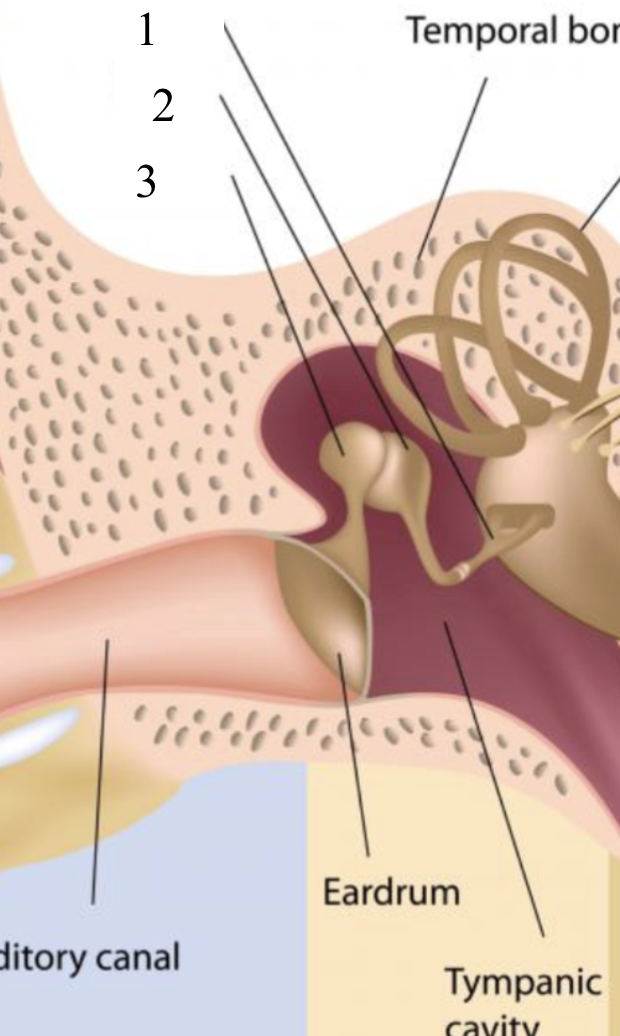
stapes
1
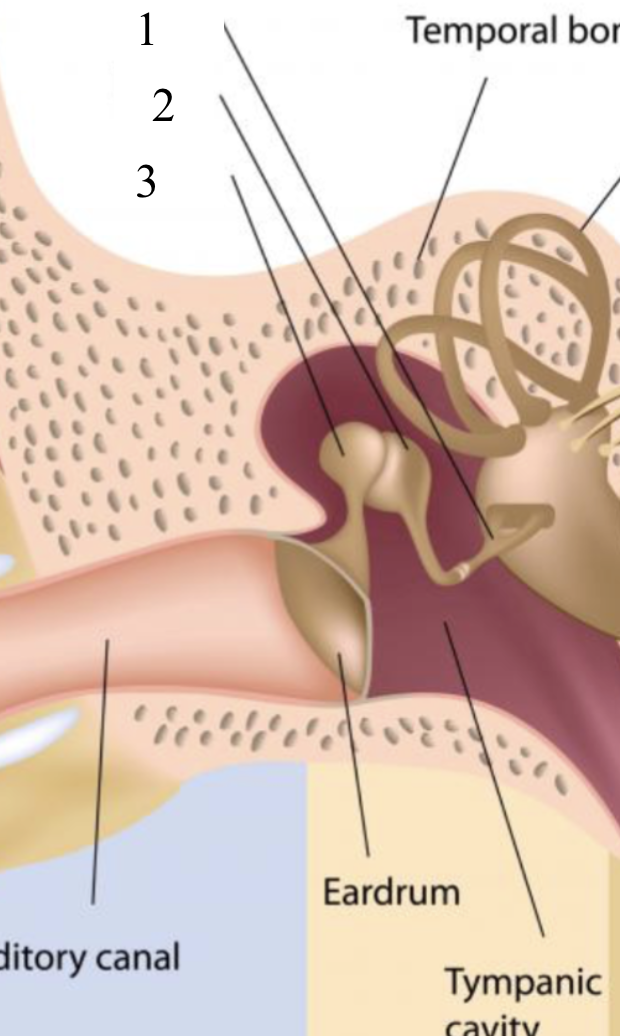
incus
2
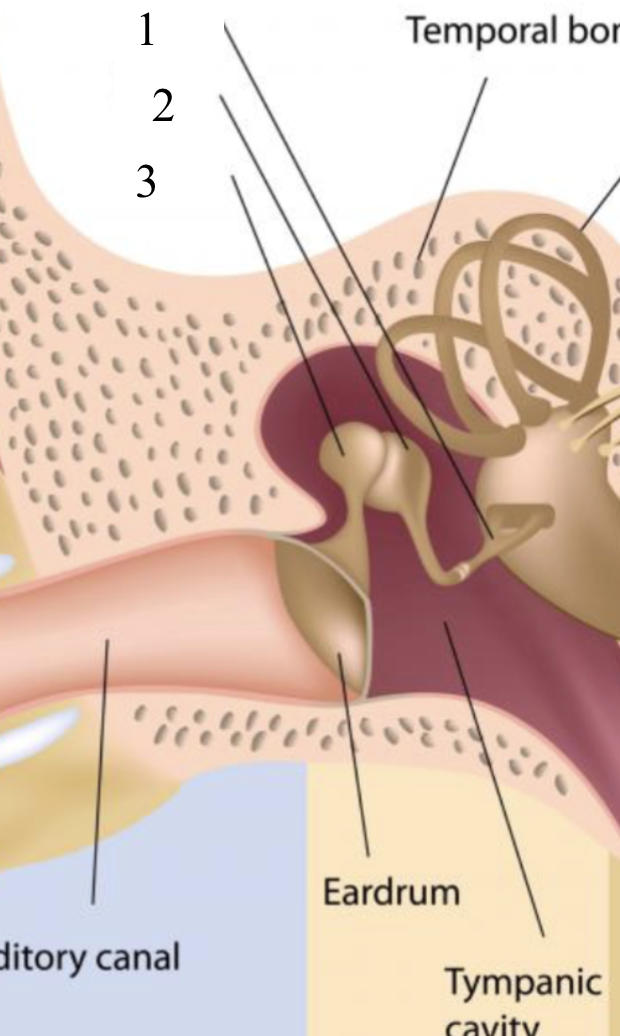
malleus
3
tegmen tympani
top plate of the cavity & has a thin layer of bone that separates the middle ear space from the brain cavity
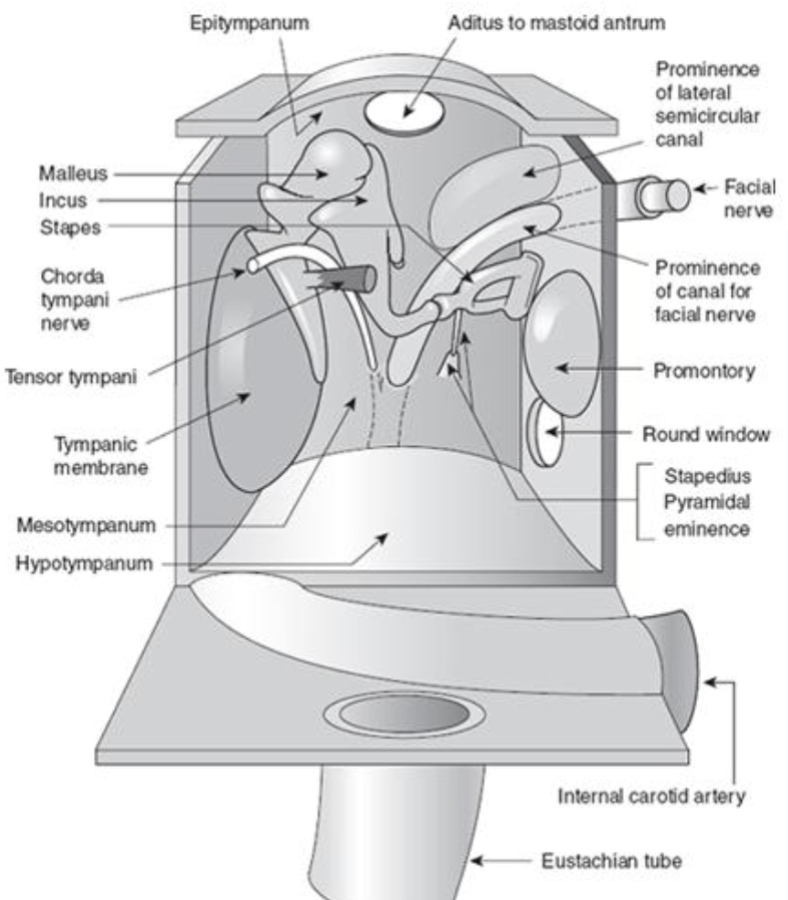
aditus ad antrum
hole in the top, which leads to a space in the mastoid portion of the temporal bone
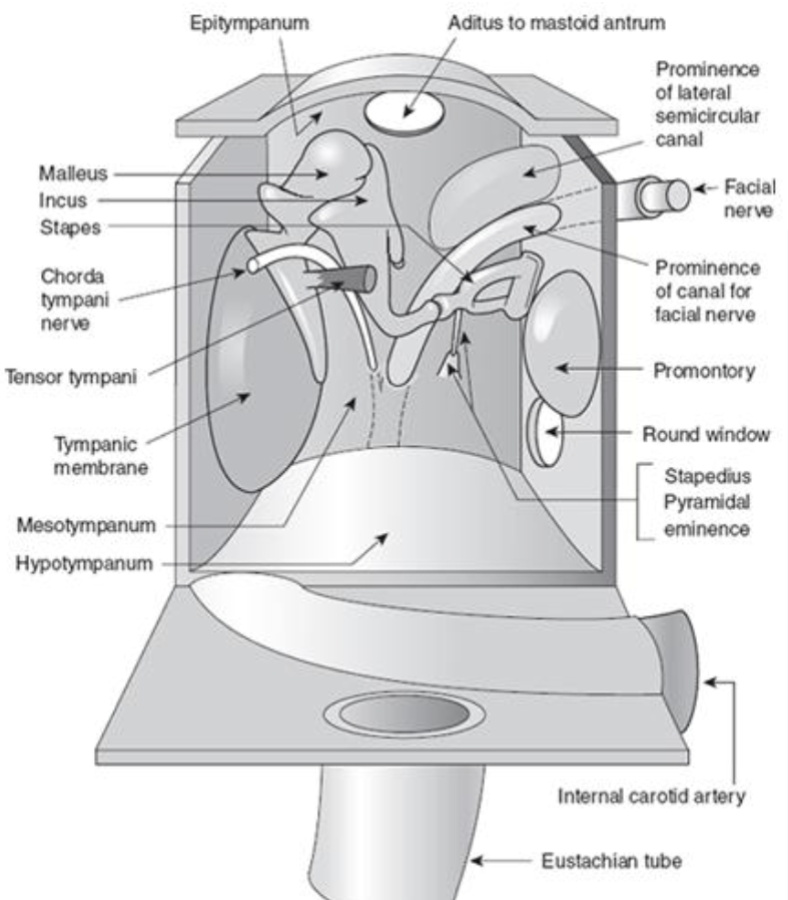
mastoid air cells
the antrum is a small chamber in the mastoid portion of the temporal bone and is surrounded by ______ ___ _____
manubrium
the _______ of the malleus attaches to the tympanic membrane
annular ligament
the stapes footplate is held in the oval window by a ring-shaped ligament called the ______ ______
anterior ligament of the malleus
the anterior process of the malleus is attached to the anterior wall of the tympanic cavity by the ______ ______ __ ___ ______
posterior ligament of the incus
the posterior process of the incus is attached to the _____ ______ __ ___ ______
tensor tympani
middle ear muscle
innervated by CN V
connects to malleus
stapedius
middle ear muscle
innervated by CN VII
connects to the stapes
tense up, prevent damage
what do the stapedius and tensor tympani do when you hear really loud sounds? what do they do this?
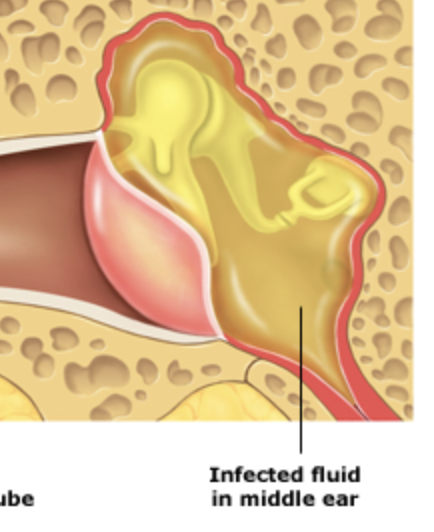
eustachian tube
connects the middle ear space to the back of the throat (nasopharynx)
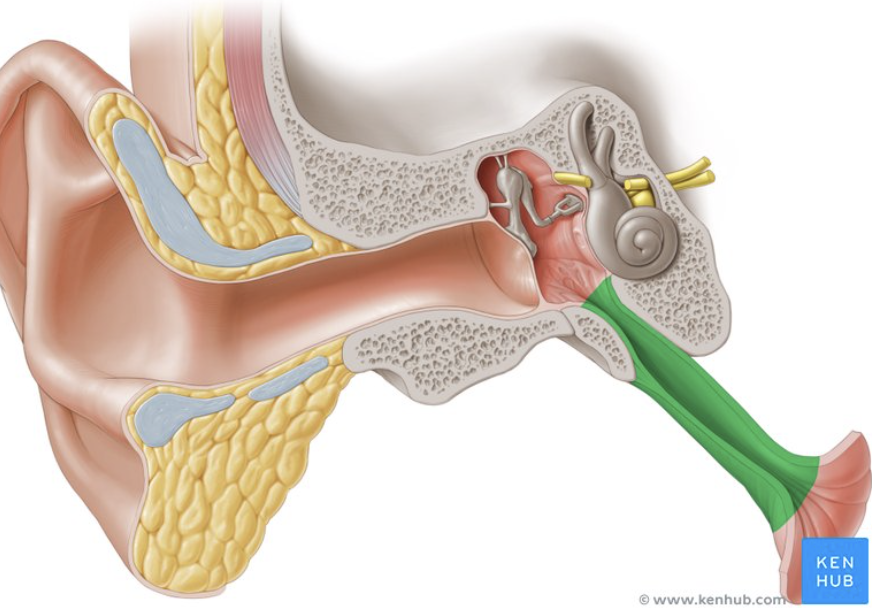
eustachian tube purposes
equalizes pressure in the middle ear
drain any fluid that might accumulate in the middle ear space
children
have much shorter and flat eustachian tubes, making them more susceptible to ear infections
otitis media
happens when eustachian tube gets blocked, inflammation of the middle ear
valsava maneuver
one way to try to open the eustachian tube
middle ear physiology
transfer acoustical energy (sound pressure fluctuations) into mechanical energy (vibrations) that are sent to the inner ear
transducer, impedance matching device
the middle ear acts as a ________ and an ________ _______ ______
area ratio, lever, buckling
the middle ear pressure transformer has three mechanisms:
the ___ ____ pressure transformer
the ossicular _____
the catenary lever (_____ effect)
area ratio pressure transformer
the most effective mechanism of the middle ear
the size of the TM is 17 times larger than the stapes footplate / oval window
this means that the pressure at the oval window is about 17 times (about 25 dB) greater than the pressure at the tympanic membrane
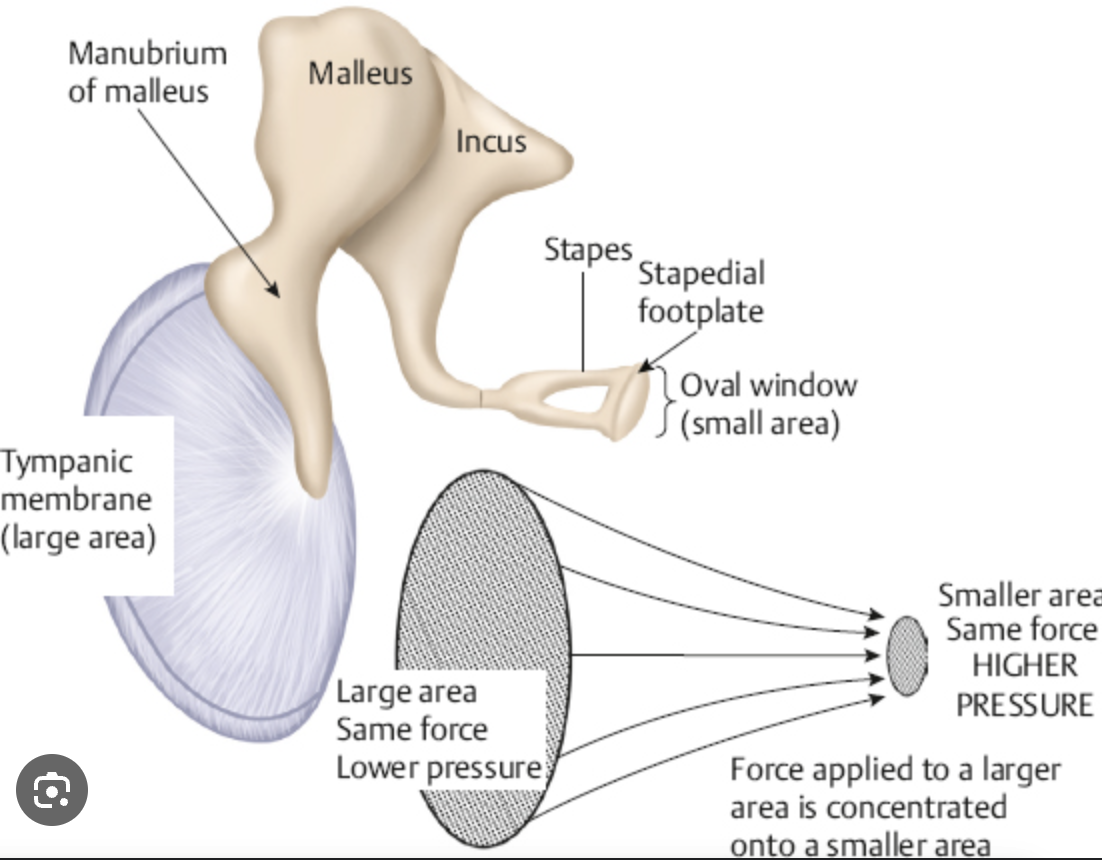
ossicular lever and catenary lever (bucking effect)
because the length of the malleus is greater than the length of the incus, an anatomic lever is created
this means that the pressure at the incus is about 1.15 times (about 1.2 dB) greater than the pressure at the malleus
because the umbo is displaced less than the rest of the tympanic membrane, an anatomic lever is created
this means that the pressure at the umbo is about two times (6 dB) greater than the pressure across the entire membrane
32 dB
combining the effects of all these mechanisms:
17 × 1.15 × 2 = 40
so, 40 times increased sound pressure at the stapes footplate, which results in roughly __ ___
250 and 6000 hz
together, the outer ear resonances and middle ear impedance matching work together to effectively transmits sounds between about ____ ___ _____ __
oval window
footplate of stapes is attached to the ____ _____
perilymph
fills the scala vestibuli and scala tympani
higher sodium concentration (K+)
endolymph
fills the scala media
higher potassium concentration (Na)
cochlea ‘unrolled’
basilar membrane
scala tympani
scala vestibuli
helicotrema
oval & round windows
endolymph vs. perilymph
apex
what part of the cochlea responds better to low frequencies?
base
what part of the cochlea responds better to high frequencies?
high frequency
because sound always goes high to low, these hairs are the most susceptible
analogy: if there was one door that allowed entrance, its path would become worn
organ of corti
houses hair cells
turns travelling waves into nerve impulses
embedded
outer hair cell stereocilia are ________
not embedded
inner hair stereocilia are ___ ________
afferent, efferent
______ neurons transmit sensory information from hair cells to the brain, while _____ neurons project from the brain back to the hair cells, primarily modulating their function
sensorineural hearing loss
difficulty hearing due to damage in the inner ear (cochlea) or the auditory nerve, leading to difficulty perceiving or transmitting sound signals
cochlea is affected, so bone & air conduction are both impacted, and gap is very small
conductive hearing loss
occurs due to problems in the outer or middle ear, preventing sound waves from reaching the inner ear
can be caused by infection, accident
presents normal bone conduction thresholds
ICF
model that measures the implication hearing loss will have on various individuals
balance organs
we have 5 - or 10 total
3 canals
2 otolith organs
semicircular canals
superior, posterior, and horizontal
houses hair cells
translates head movements into nerve impulses
otolith organs
utricle, saccule
maintain balance when moving head
house otoconia
responsible for forward & backward motion & up/down motion