Introduction to Bacteriology and Prokaryotic Cells
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
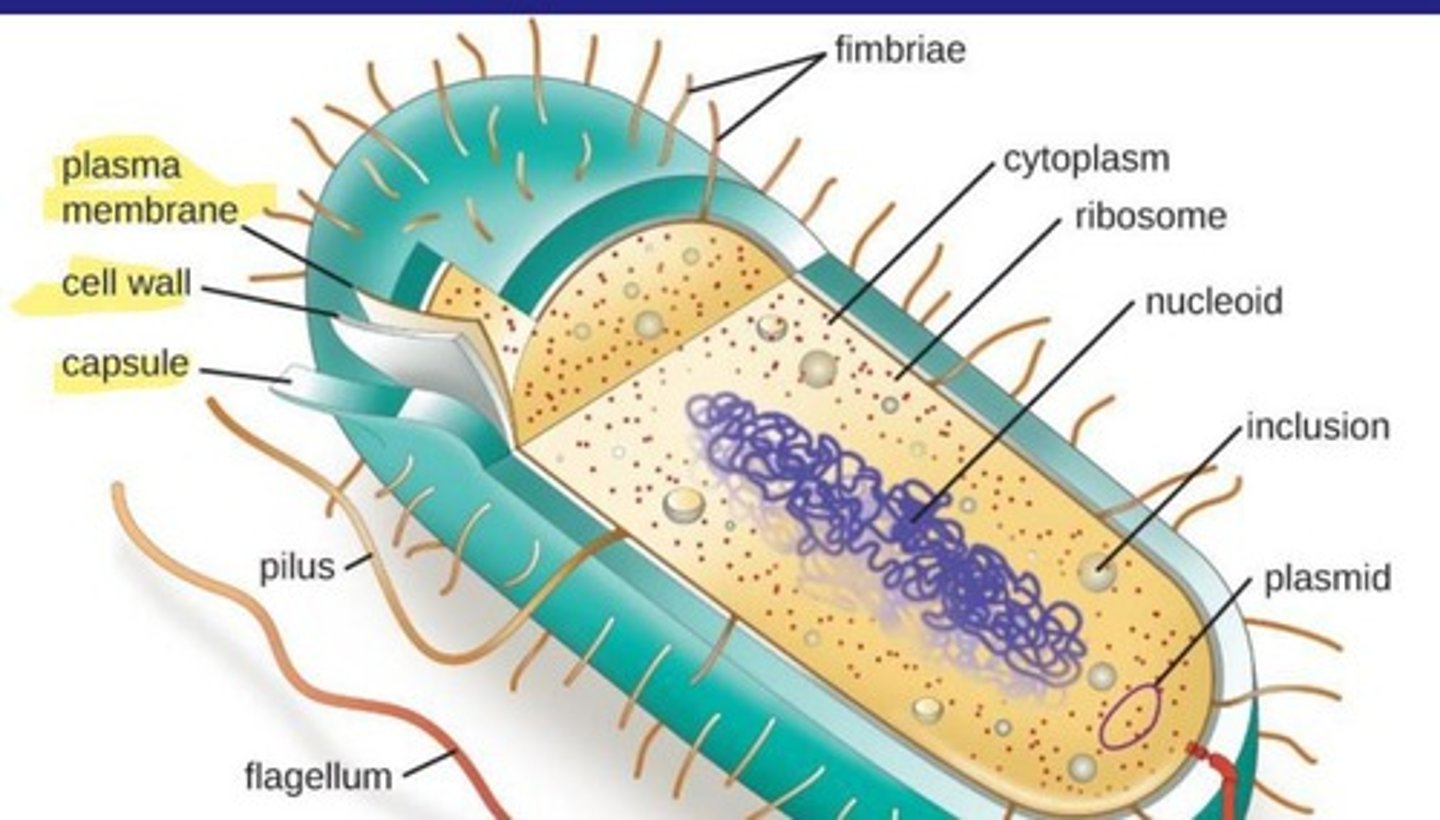
Prokaryotic cells
Cells without a nucleus, smaller than eukaryotic cells.
Binary fission
Asexual reproduction method for bacteria, involves cell division.
Generation time
Time taken for bacterial population to double.
Gram-positive bacteria
Bacteria with thick peptidoglycan cell wall.
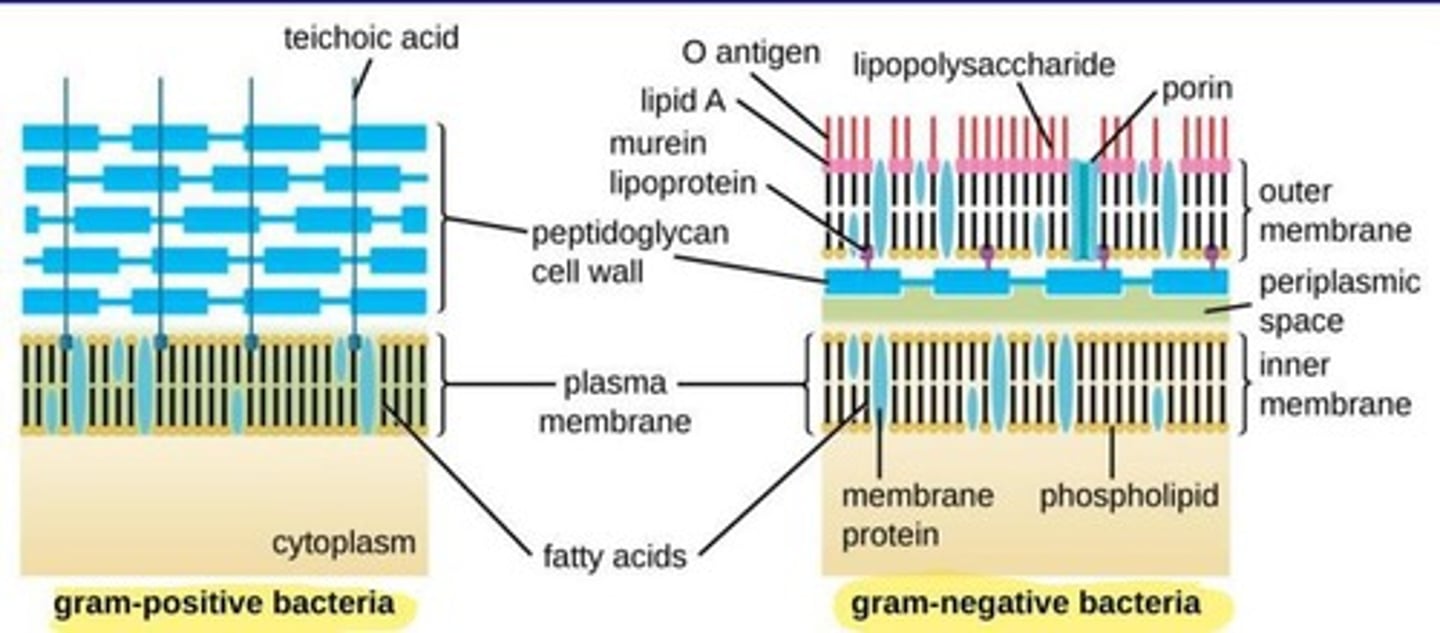
Gram-negative bacteria
Bacteria with thin peptidoglycan and lipopolysaccharide layer.
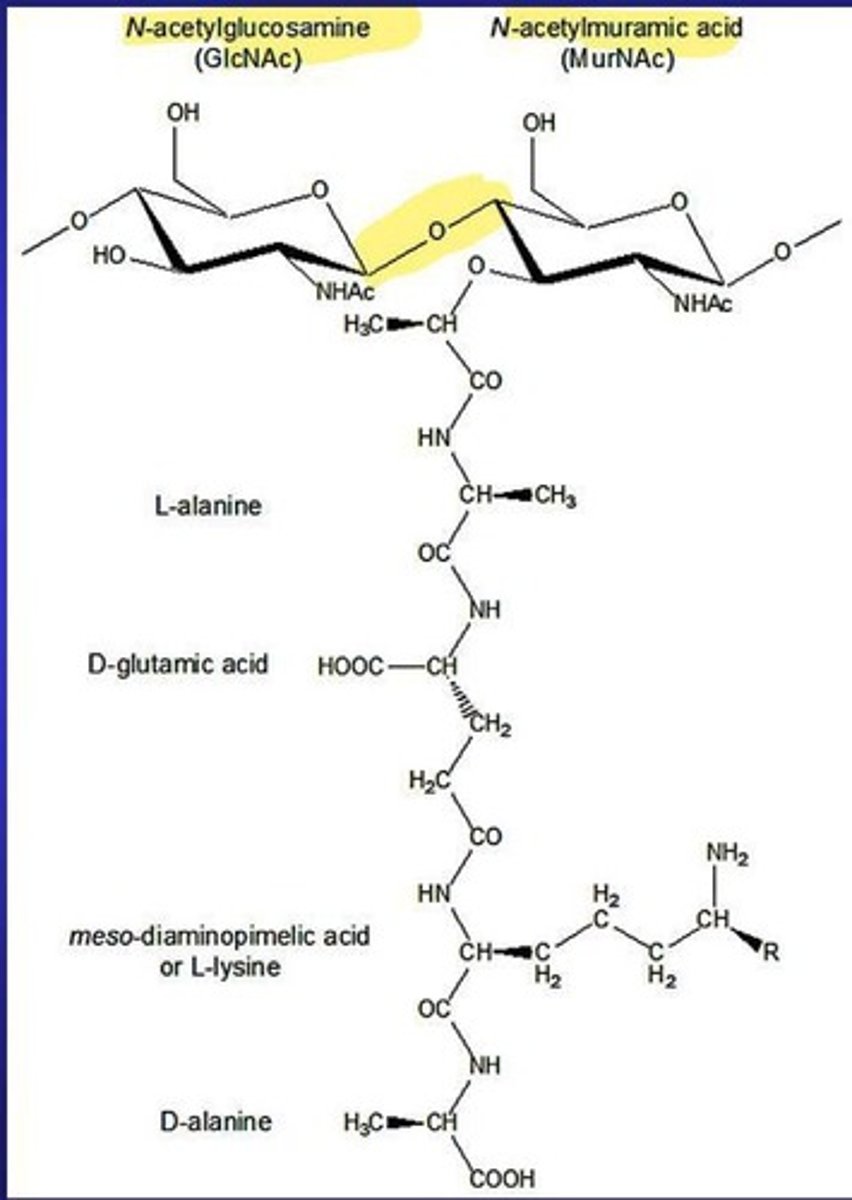
Peptidoglycan
Polymer forming bacterial cell walls, consists of NAM and NAG.
Pili
Hair-like structures aiding attachment and genetic transfer.
Flagella
Tail-like structure for bacterial motility.
Glycocalyces
Mucus layers aiding biofilm formation and protection.
Plasmids
Small DNA molecules providing genetic advantages, including resistance.
Endospore
Dormant, resistant structure formed under harsh conditions.
Inclusion bodies
Storage granules for nutrients like carbon and phosphorus.
70s ribosomes
Ribosomes found in prokaryotes, smaller than eukaryotic ribosomes.
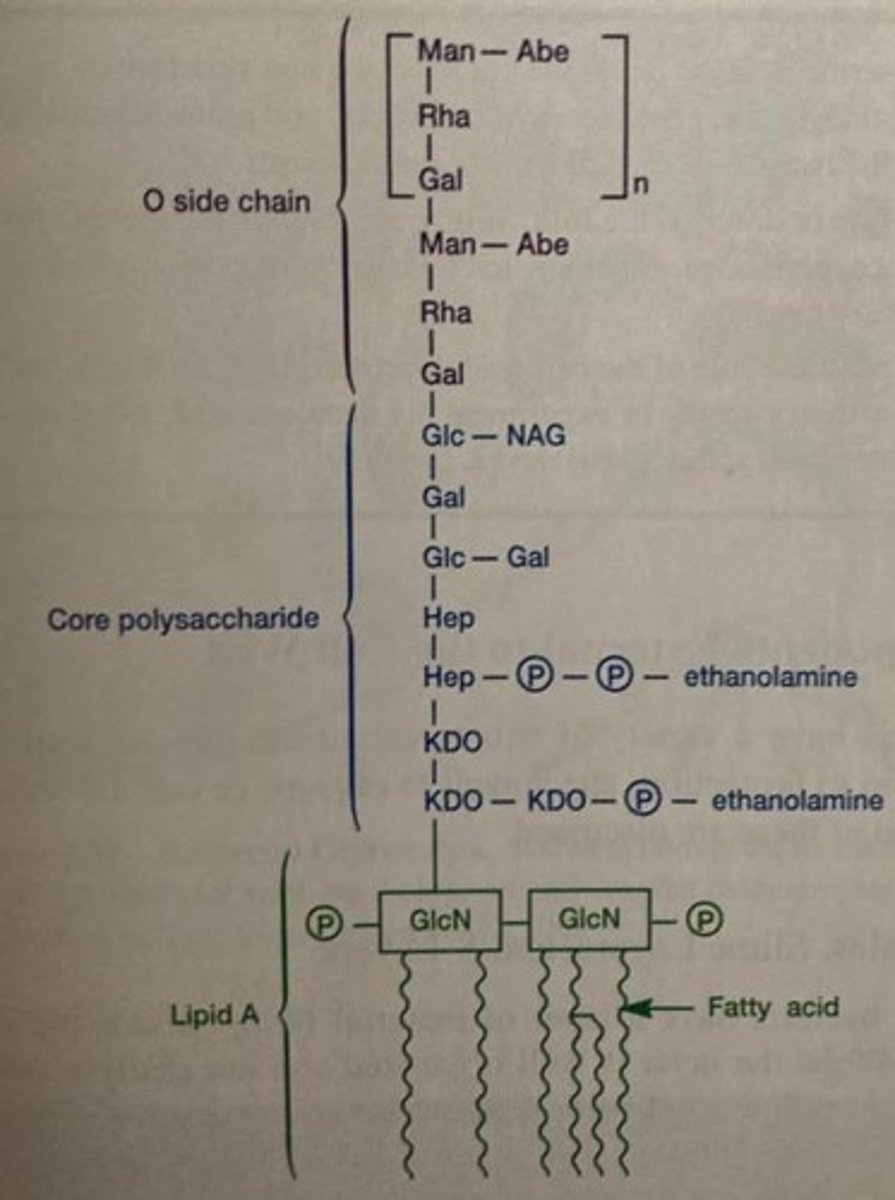
Lipid A
Component of LPS, can cause septic shock when released.
Selective drug toxicity
Targeting bacterial structures without harming human cells.
Exponential phase
Growth phase where bacteria double at a constant rate.
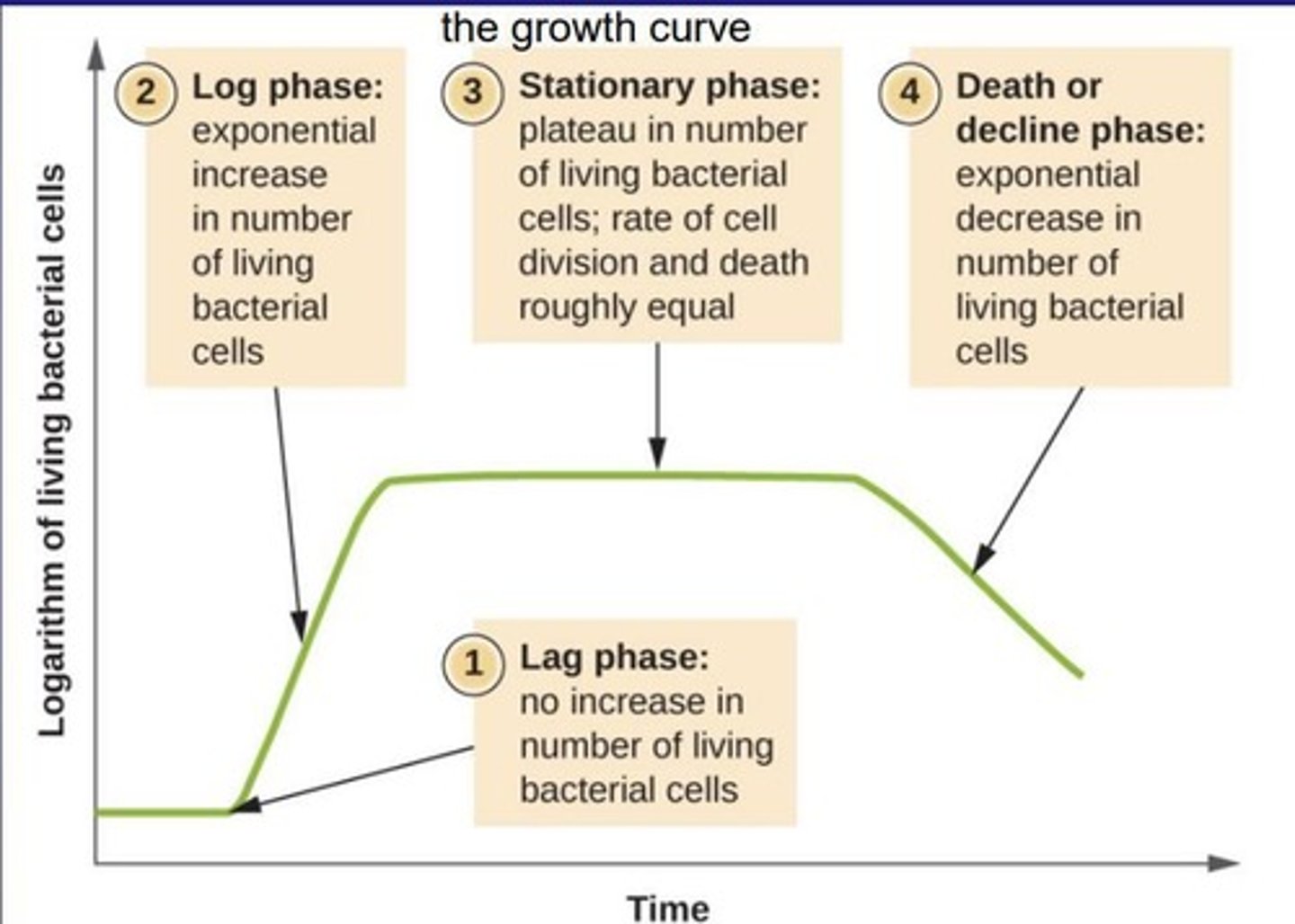
Stationary phase
Growth phase with limited nutrients and toxic accumulation.
Lag phase
Initial phase of bacterial growth, adaptation period.
Mean generation time formula
g = t / (log(Nt) - log(N0)),
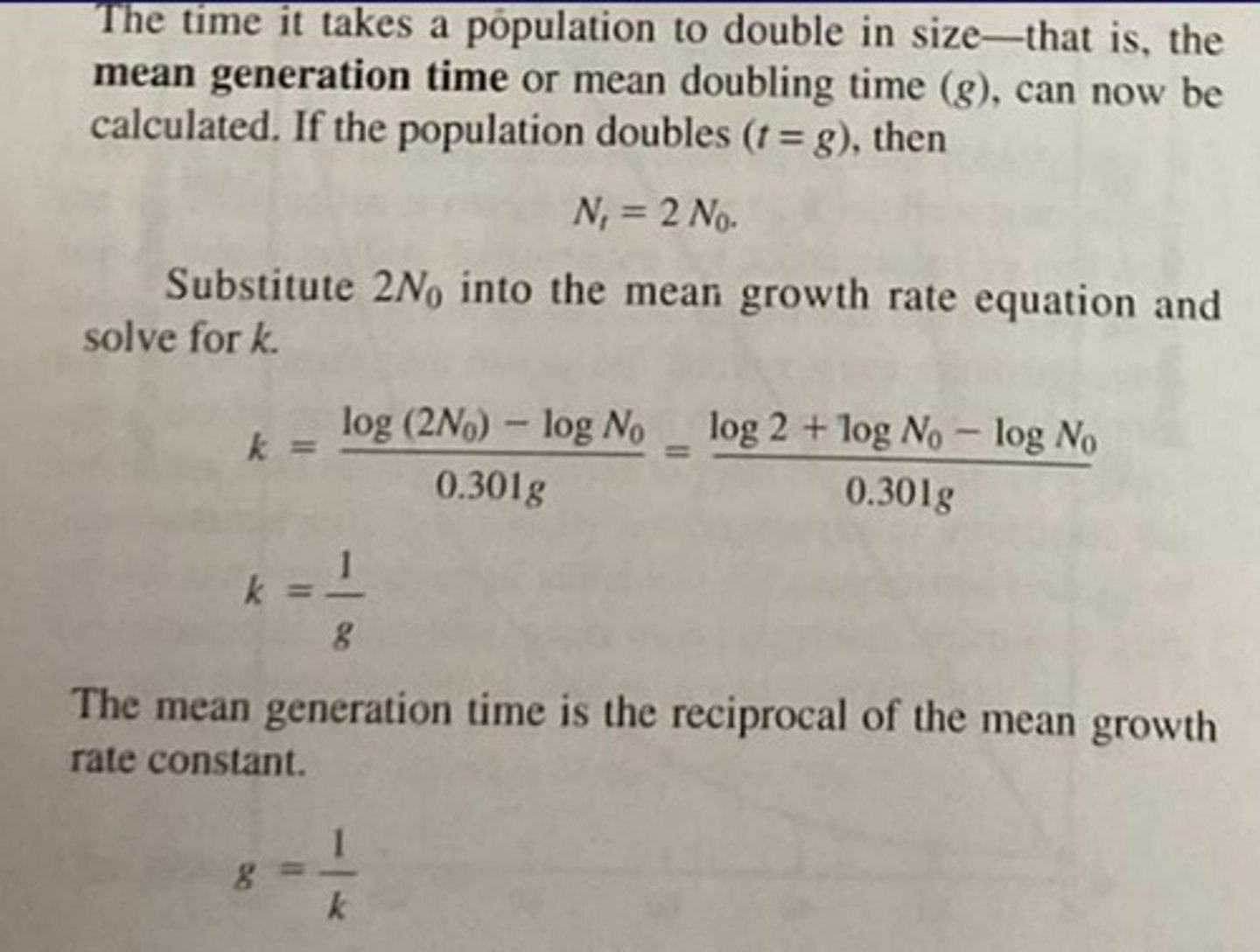
Antibiotic resistance
Ability of bacteria to survive despite antibiotic treatment.
Sepsis
Severe response to infection, often caused by Gram-negative bacteria.
Bacteriostatic drugs
Antibiotics that inhibit bacterial growth without killing.
Cell wall biosynthesis
Target for antibiotics, crucial for bacterial survival.
Antibiotic classes
Groups of drugs targeting specific bacterial functions.