multifactorial inheritance
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
most common cause of major anomalies observed in newborn infant
multifactorial inheritance
these are examples of...
cleft lip and palate; pyloric stenosis; clubfoot; congenital dislocation of hip, neural tube defect; peridontal disease
multifactorial inheritance
what is multifactorial inheritance
a condition where a trait or disease is caused by a combination of multiple genetic and environmental factors, rather than a single gene
(how many factors and what kind you have can dec ur threshold for a disorder)
characteristics of multifactorial causation
familial (not distinctive)
inc risk the closer you are to relative
inc risk with more affected relatives
inc risk with more severe malformations/presentations
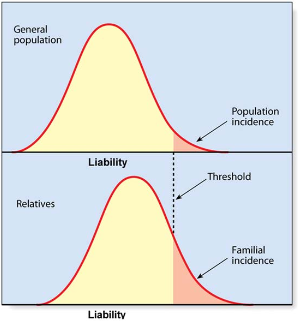
with multifactorial causation, if there is a sex difference and the less affected sex is affected, what is the effect on recurrence risk
increases.
the less-affected sex must have a greater "liability load"—a higher level of genetic and environmental risk factors—to develop the condition, indicating that the entire family has a higher concentration of risk factors
fourth most common congenital disorder in humans
cleft lip and palate
(less common than heart defects, genital or urinary tract) (more common than spina bifida)
incidence: about 1/700 – 1/1,000 births; 15 per day in the United States
cleft lip and palate
failure of union of frontonasal processes of face with lateral maxillary prominences at 3-4 weeks
cleft lip and palate
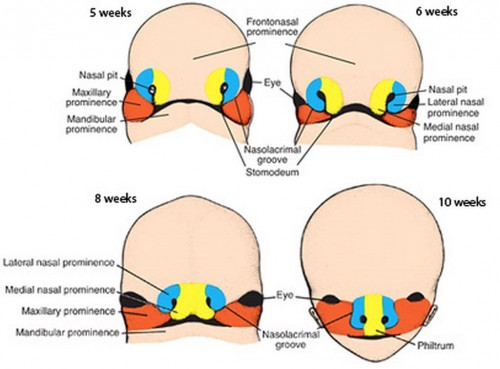
what union fails to form in cleft lip ± cleft palate
union of frontonasal process of face with lateral maxillary prominences at 3-4 weeks
how are midline facial clefts different from cleft lip and palate
facial clefts result from deficient frontonasal development normally induced by underlying brain
*associated with holoprosencephaly
these clefts are commonly associated with holoprosencephaly
midline facial clefts
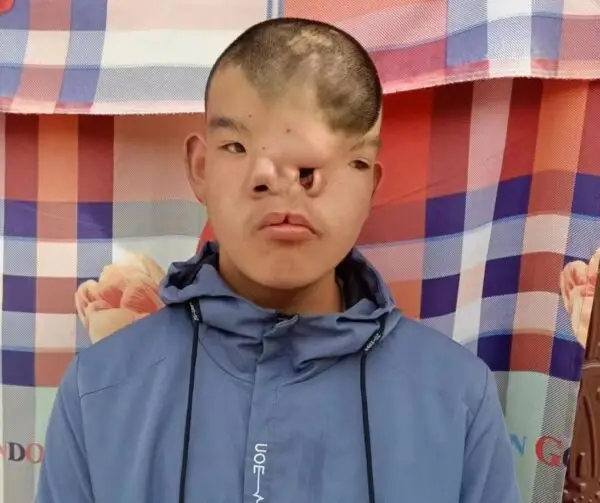

characteristic of a classic cleft palate
V shaped cleft

common types of cleft lip and palate
unilateral 80%
bilateral 20%
CL extending to palate 70% in unilateral cases and 85% in bilateral cases
isolated CP separate from CL and CP
do the palate and lip form at different stages
yes
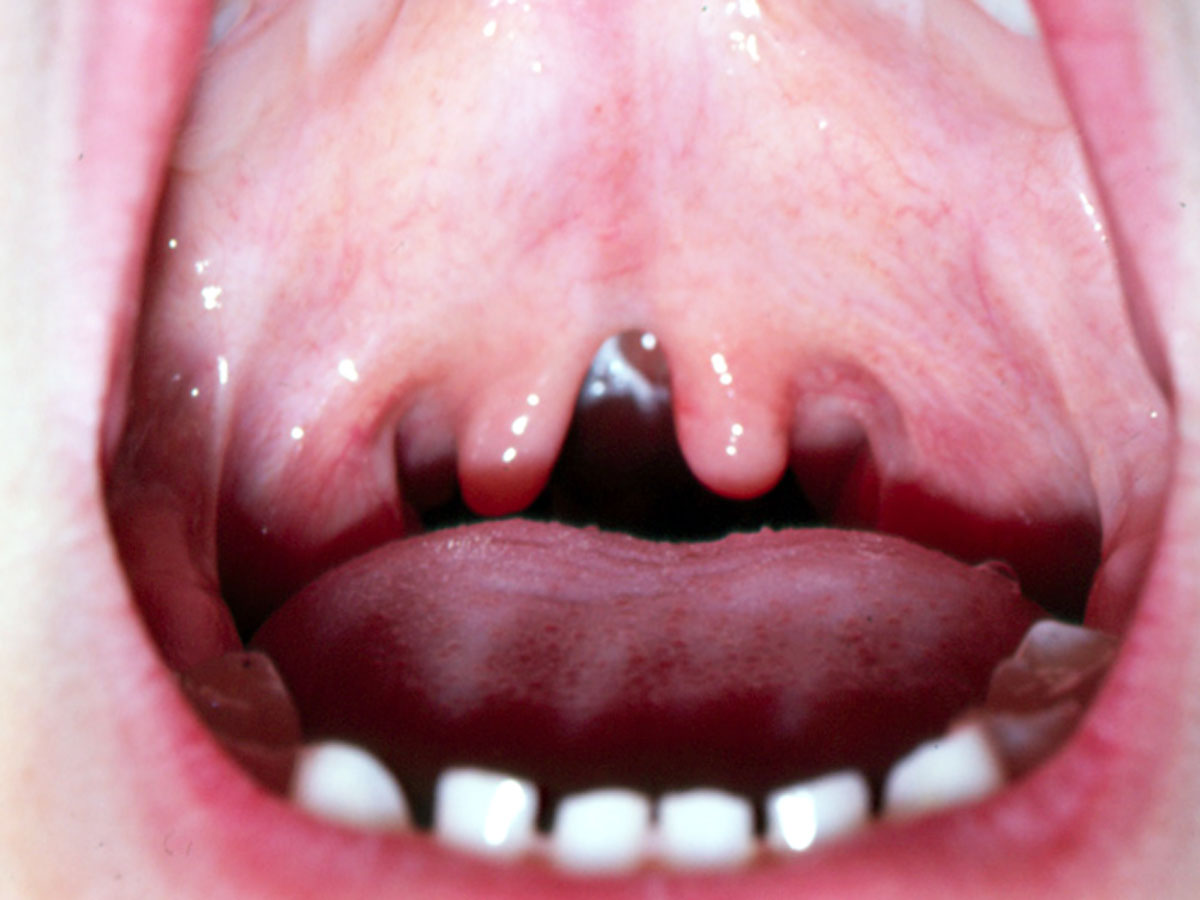
what is the submucous cleft palate
hard palatine shelves dont merge + soft tissue does not form that causes asymmetric movement of pharyngeal wall
can be isolated or occur as part of a syndrome such as deletion 22q syndrome
submucous cleft palate
common finding with submucous cleft palate
bifid or double uvula is frequent finding
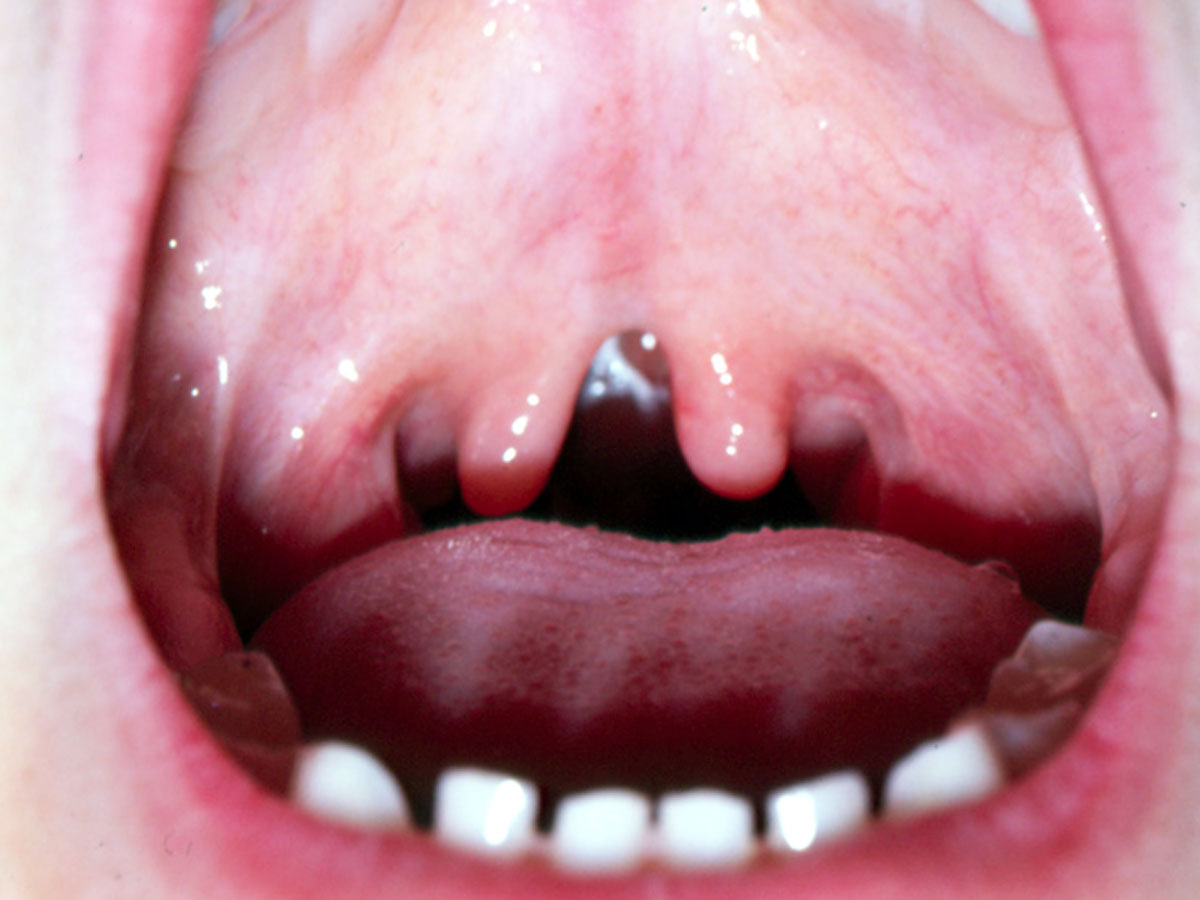
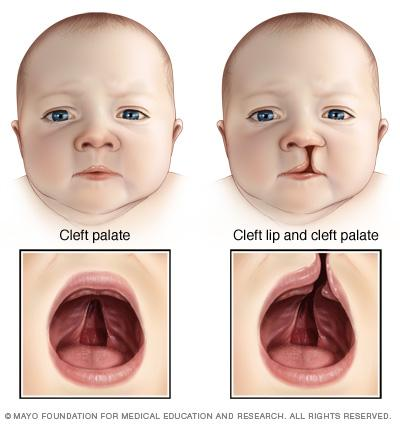
what syndrome can submucous cleft palate be apart of
deletion 22q11.2 di george
(may also be isolated)
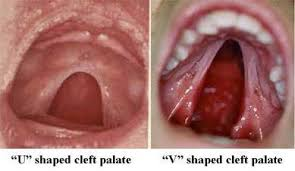
U shaped cleft palate
pierre robin malformation sequence
small recessed chin which causes obstruction by tongue
cleft is due to obstruction by the tongue
U shaped cleft palate (pierre robin malformation sequence)
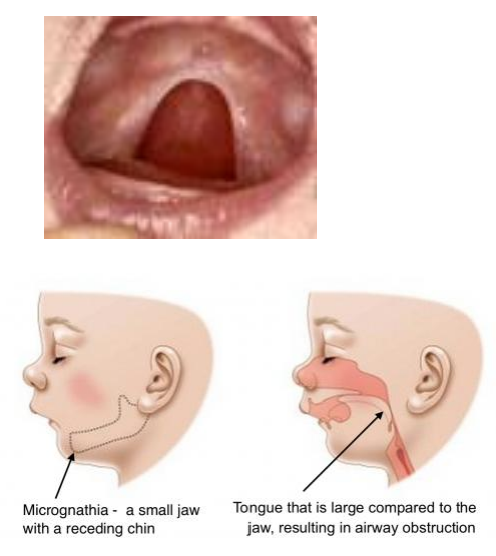
CP oten seen in Pierre Robin malformation sequence
U shaped cleft palate
___% of those with cleft lip/palate also have a related syndrome
30
*more are associated with cleft lip and palate but can just be associated with isolated cleft lip
most common chromosome anomalies associated with cleft lip and palate
13 and 18
Up to __% of those with cleft lip and/or cleft palate also have a related syndrome
• 7-13% with “isolated” CL are born with associated anomalies
• 11-14% with CL+CP are born with associated anomalies
• Over 300 syndromes associated with CL/CP
• Many chromosome anomalies associated, the most common are trisomies _____
30%
13 & 18
approx. 40-50% of those with only ___________ have a syndrome
*more common with this
cleft palate only
*different process
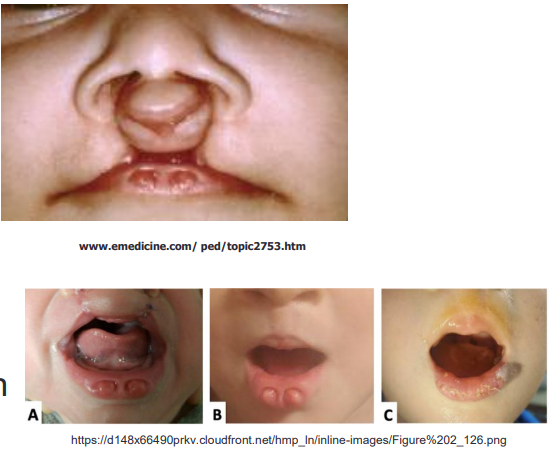
mode of inheritance of van der woude syndrome
autosomal dominant
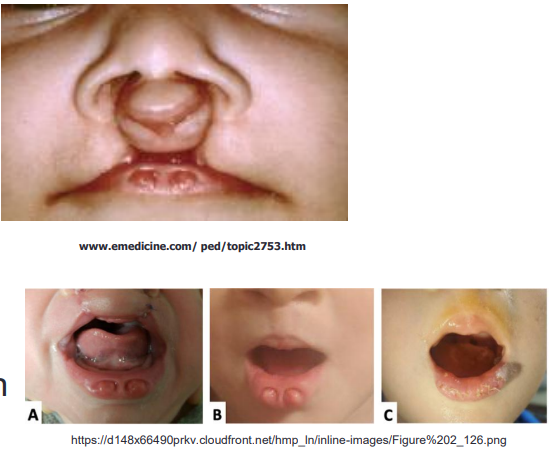
characterized by a cleft lip and/or palate and distinctive lower lip pits
Van der Woude Syndrome
what is van der woude syndrome
congenital lip pits
can have cleft lip or palate
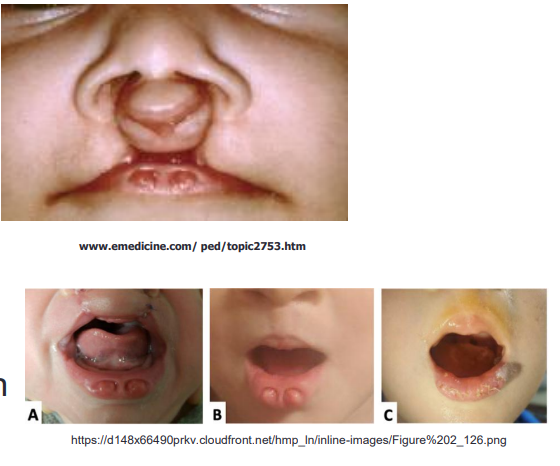
caused by mutations in IRF6
van der woude syndrome
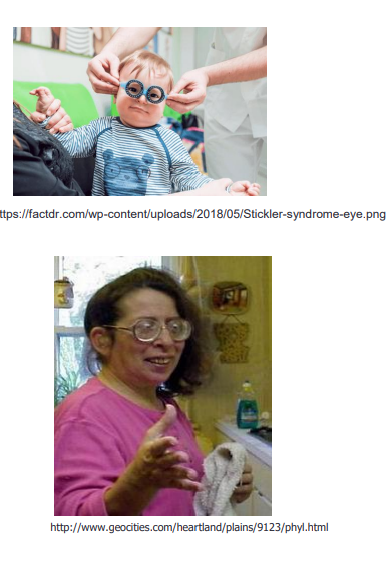
CT disorder with myopia, cataracts, retinal detachment
stickler syndrome
autosomal dominant + COL2A1 mutation
stickler syndrome
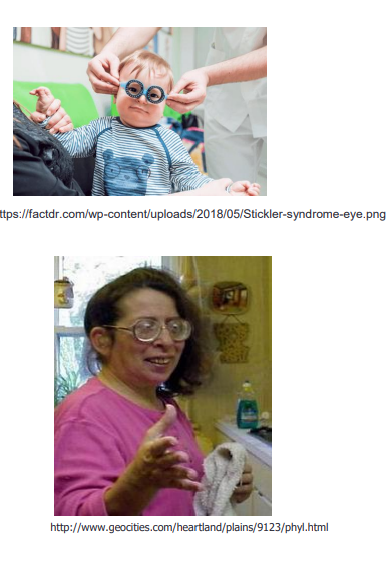
characteristics of stickler syndrome
cleft palate with small jaw causing critical airway disease
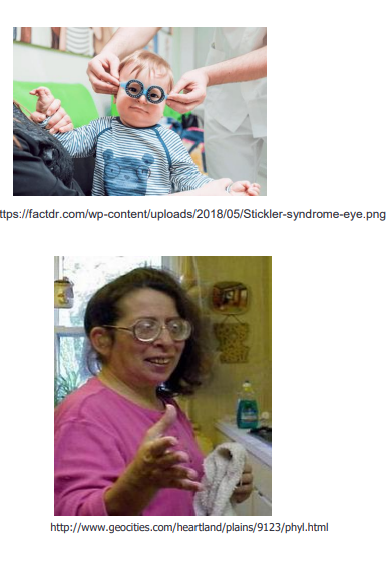
mutation in ______ causes stickler syndrome
COL2A1
22q, van der woude, and stickler all have a ___% recurrence risk if inherited
50
22q11.2 deletion syndrome (digeorge) is characterized by
a wide range of symptoms affecting multiple body systems, including congenital heart disease, impaired immunity due to an under-developed thymus, cleft palate, developmental delays, velopharyngeal Incompetence
the condition has a highly variable presentation
22q11.2 deletion can sometimes be visible by
chromosome analysis
how are non-syndromic CL/P a complex multifactorial trait
several genes are involved
level of penetrance varies
males and females different
environmental overlays
smaller deletions of 22q11.2 may be detected by
smaller deletions detected by FISH or microarray
empiric data for risk recurrence of non-syndromic CL/P is dependent on what 3 things
number of other affected family members and their relationship
type of cleft
severity of cleft
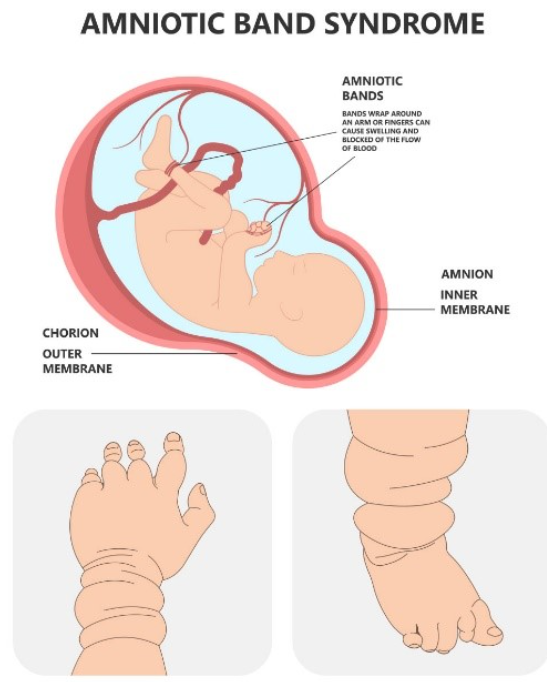
some environmental causes of cleft lip and palate
amniotic band sequence
teratogens (alc, anticonvulsants, methotrexate, maternal tobacco)
you are more likley to have a child with nonsyndromic CL/P if..
there is more family history
does having a child with a more severe CL/P inc the chances of having another child with it
yes

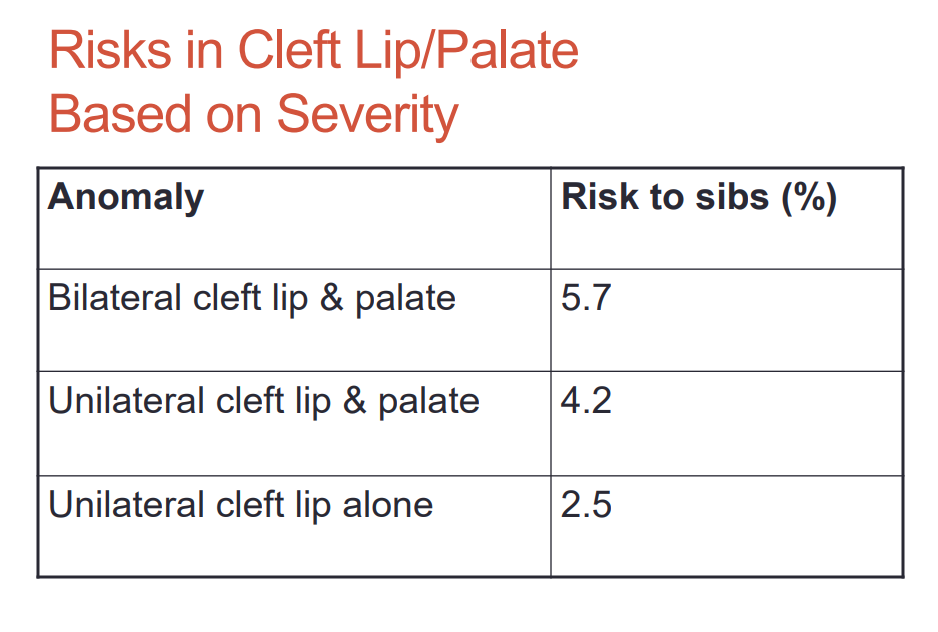
this cleft lip and palate anomaly has a greater risk to sibs
bilateral cleft lip and palate
CL+/-P is more common in males or females
males
cleft palate is more common in males or females
females
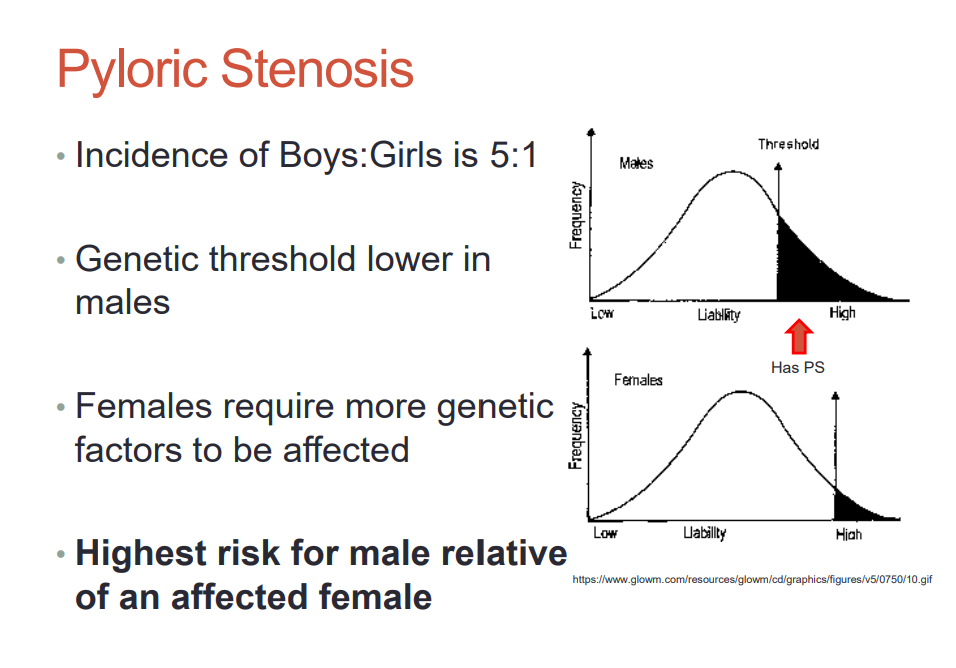
multifactorial disorder with hardening of the pyloric sphincter
pyloric stenosis
who is more affected with pyloric stenosis
males b/c genetic threshold is lower and females require more genetic factors to be affected
who has highest risk for pyloric stenosis
male relative of an affected female
when does the neural tube form
24-28 days (before pregnancy confirmation)
3 types of neural tube defects
spina bifida- 65
anencephaly- 25
encephalocele- 10
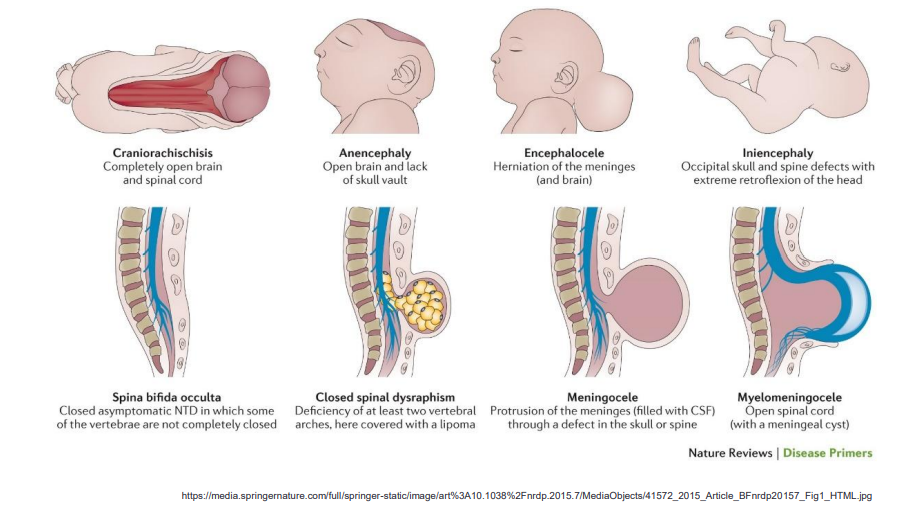
backbone and spinal canal do not form properly in the developing fetus
spina bifida
Meninges and spinal cord tissue incorporated into the overlying skin • Open or closed
Myelomeningocele
Myelomeningocele (spina bifida)
meninges and SPINAL CORD tissue incorporated into overlying skin
-can be open or closed
Surgery within 24 hrs in this spina bfida
myelominingocele
what determines the clinical features of spina bifida
degree related to LOCATION of defect
higher of the opening, the greater the impairment

Individuals can have many disabilities:
• Partial or complete paralysis of lower extremities
• Difficulty with control of bowel and bladder function
• Anal wink
• Hydrocephalus (excessive fluid on the brain)
• Normal intelligence in ~70%, some with intellectual disability
Spina Bifida
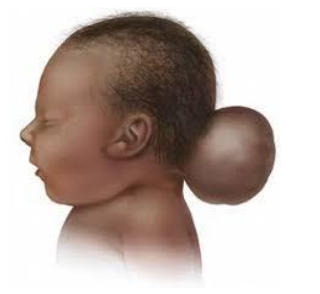
part of skull improperly formed, part of the brain is outside (often part of a syndrome)
encephalocele
effect of encephalocele is dependent on...
size (may have physical or mental handicaps) 30% mortality
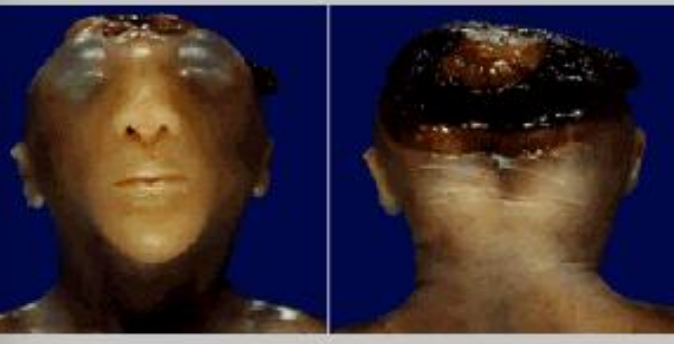
brain and skull not formed properly
anencephaly (50% miscarried or still born; if they live they die shortly after)
Tx of spina bifida
In-utero fetal surgery to minimize damage as soon as possible; long term neurological benefits
No significant difference in PROM, preterm delivery, perinatal death, maternal complications
but promising long term neurological benefits (ore likely to retain neurologic function)
spina bfida surgery
occurrence rate of ntds/spina bfida
95% with no history of neural tube defects
why are NTD a multifactorial cause
interactions between several genes and between genetic and environmental causes
may be several genes or gene combinations involved
seizure medications
• valproic acid (Depakene)
• carbamazepine (Tegretol)
are risk factors for
NTD
risk factors of NTD
seizure medications
insulin-dependent diabetes
maternal obesity, prolonged increased maternal temperature, race
Insulin-dependent diabetes
• Maternal obesity
• Prolonged increased maternal temperature •
?History of celiac and other malabsorption disorders
• ?History of gastric bypass
• Race/ethnicity: hispanic women, particularly of Mexican origin, have highest risk
risk factors for ?
NTD
antieplieptic drugs and NTD
valproate
6-7% risk for malformations
spectrum of defects is broad, could be related to dose
hyperthermia and NTD
inc risk of NTD
heart defects
*should not take hot baths when pregnant; treat fevers aggressively with tylenol
atrial septal defects, hypoplastic left heart may be results of NTDs due to
hyperthermia
which genes are linked to NTD
genes for folate and glucose metabolism
what is MTHFR
enzyme used to metabolize folate
gene variants of MTHFR
C677T and A1298C
*minimal effect on risk
what percent of population has two copies of C677T
10-20%
*so dont order this test to be done b/c effect is minimal and not a lot of ppl in the pop has it

people with two MTHFR variants were thought to be at risk of...
stroke, thrombosis, CAD, preeclamsia and placental abruption
*related to elevated homocysteine level
Having 2 mutations in ____ AND elevated_______ increases the risk of NTD’s
• About 20% of women who have a child with an NTD have abnormal ______ metabolism
• Having an adequate amount of folate reduces _______ back to normal levels
MTHFR
homocysteine
homocysteine
homocysteine
having 2 mutations in MTHFR and elevated homocysteine ...
inc risk of NTD's
effect of adequate amount of folate on homocysteine levels
returns it back to normal
why is folic acid important for spina bifida
daily intake (400ug) can reduce spina bifida up to 70%
prevents other birth defects, heart disease, CL/P, stroke, colon and cervical cancers. UTI defects
when should you take folic acid when conceiving
a month before
continuing through first few weeks of pregnancy
*FDA recommended you take it during childbearing years
foods high in folate
- LIVER
- green leafy vegetables
- grains
- legumes chickpeas
- oranges
- white bread
4 mg (milligrams) or 4000 mcg (micrograms) folic acid recommended ____________ to reduce risk of recurrence when there is a significant family history
PRECONCEPTIONALLY
folic acid reduces the recurrence of NTD's by ___%
75
*shouldnt overdose it
recurrence risk of NTD is higher if
you already have an affected child/children
multiple additive factors needed to reach disease threshold
multifactorial
locus heterogeneity
mutations in different genes can produce the same phenotype
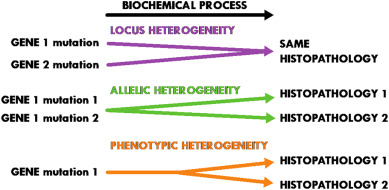
Examples of _______
• Osteogenesis imperfecta – can be caused by a mutation in COL1A1, COL1A2, IFITM5, SERPINF1, CRTAP, LEPRE1, PPIB, or FKBP10
• Noonan syndrome – can be caused by a mutation in PTPN11, SOS1, RAF1, KRAS, NRAS, BRAF, or MAP2K1
locus heterogeneity
does medical management change the outcomes of a multifactorial inheritance pattern or locus heterogeneity
locus heterogeneity
twins that originate from the same embryo. one zygote, a single fertilized egg (identical twins, same genetics)
monozygotic twins
twins that are great for studying the environmental effect on disease
monozygotic twins
two babies in one pregnancy who develop from two zygotes (fraternal, different genetics) double ovulation. born at the same time
dizygotic twins
what is high concordance in twins
when one twin has a trait the other will likely too (fingerprints, height, BMI, autism)
heritability equation in twins
2 x (MZ concordance - DZ concordance)
*if value is 1= highly genetic component!
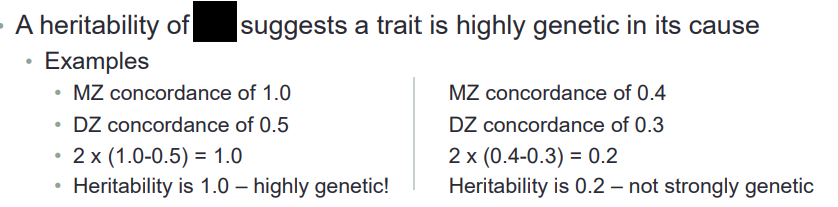
1.0
what accounts for differences in monozygotic twins
diff uterine environment, postnatal environments, somatic mutations, diff methylation patterns
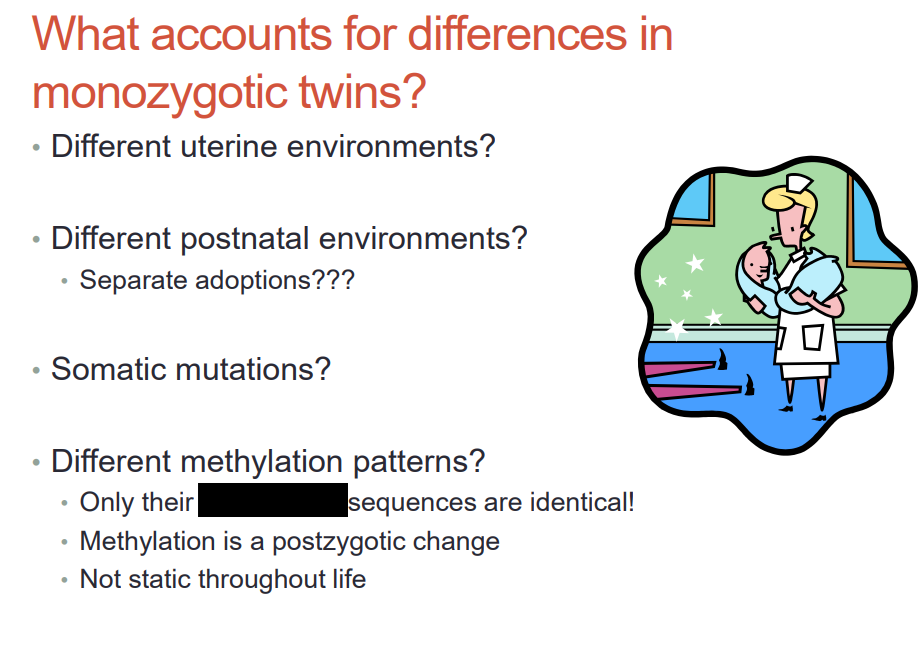
nucleic acid sequences
is methylation prezygotic or postzygotic change
postzygotic change (changes through life-- only twins nucleic acid sequences are identical)
psychiatric diseases are more prevalent in DZ or MZ twins
MZ
*hard to study, genetically heterogeneous, multiple suceptibility loci
multiple susceptibility loci found linked to brain-expressed proteins with glutamate receptor interactions in these disorders
psychiatric disorders
adoption studies show us that traits between child and biological parents are
less attributed to environment but more emphasis on shared genetics
why are multifactorial conditions harder to study than congenital defects
more variables and factors to look at
