Issues in a Newborn: First Half
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
37
Birth before __ weeks is considered premature
large, produce, apnea, hemorrhage, hypoglycemia, sepsis
Prematurity: Short Term Complications
-Hypothermia → ______ body surface area or an inability to _______ enough heat. This may be due in part to the hypothalamus needing to adjust to life outside of the uterus
-Respiratory abnormalities → RDS, _______, pulmonary hemorrhage
-Cardiovascular abnormalities → PDA, hypotension
-Neurologic abnormalities → intraventricular _____________
-Hypo/hyperglycemia → ____________ is more common due to metabolic immaturity
-GI abnormalities → necrotizing enterocolitis
-Infection → pneumonia, ______
-Retinopathy → neovascularization occurs
increased, cerebral palsy, growth, function
Prematurity: Long Term Complications
-__________ hospitalizations
-Neurodevelopment disabilities → impaired cognitive skills, motor deficits, _______ _____, sensory impairment, behavior/psych problems
-Chronic health issues → CKD, _______ impairment, impaired lung __________
distress, hypertension, meconium, sepsis
Respiratory Disease of the Newborn
-Preterm infant
Respiratory _________ syndrome, erythroblastosis fetalis, nonimmune hydrops, pulmonary hemorrhage
-Term infant
Primary pulmonary ___________, ________ aspiration syndrome, polycythemia, and amniotic fluid aspiration
-Preterm and term infants
Bacterial _______, transient tachypnea, spontaneous pneumothorax, congenital heart disease, pulmonary hypoplasia, viral infections, and inborn metabolic errors
preterm, surfactant, decrease, atelectasis, collapse, 20, II, cortisol
RDS: Background
-Most common cause of respiratory distress in ________ infants
-Deficiency in _________, a _________ in quality and quantity
-Physiology
Surfactant is a lipid/protein mixture
Prevents ____________ by reducing alveolar surface tension, facilitating alveolar expansion, reduces alveolar _________
Synthesis starts around __ weeks gestation by development of alveolar type __ cells
Quantity and quality based on fetal ___________ levels, which begins production between 32-34 weeks
surfactant, tension, alveoli, inflammation, hypoxia, acidosis
RDS: Pathophysiology
-Inadequate ___________ → high alveolar surface ________ → low lung volume and decreased compliance → collapse of _______ (atelectasis) and lung ___________/injury → respiratory distress and _______ and hypercarbia → respiratory __________ and respiratory failure
-Can cause pulmonary edema and difficulty breathing
minutes, tachypnea, retractions, cyanosis, edema
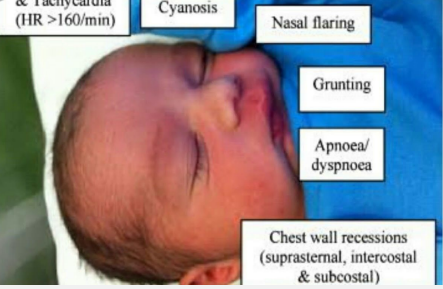
RDS: Symptoms
-Presents within a few _________ to hours after birth
-__________
-Nasal flaring
-Expiratory grunting
-Intercostal/subcostal ____________
-________/hypoxemia or pallor
-Decreased breath sounds
-Diminished peripheral pulses
-Possible peripheral ______
preterm, low, ground glass
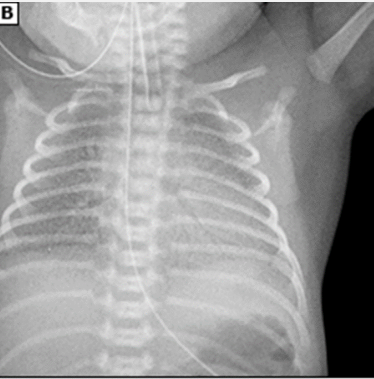
RDS: Diagnosis
-________ infant with progressive respiratory distress/failure shortly after birth
-CXR shows ___ lung volume, diffuse ______ _______ appearance with air bronchograms. This is a result of alveolar atelectasis contrasting with aerated airways
corticosteroids, 23-34, nCPAP, ventilation, acidosis, apnea
RDS: Treatment
-Antenatal _______________ therapy
Give to pregnant women at ___-___ weeks at risk of preterm delivery
Try to prevent the development of RDS
-Positive end expiratory pressure (PEEP)
Nasal continuous positive airway pressure (_____) preferred
Helps keep alveoli from closing
Preferred initial intervention after birth
-Exogenous surfactant
-Intubation and mechanical __________ with PEEP and indications of intubation
Respiratory _________
Hypoxemia despite supplemental oxygen or FiO2 > 0.40 on nCPAP
Severe ______
clearance, fluid, full, short, c-section, retractions
Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn
-Delayed __________ or slow resorption of fetal lung _____
-Epidemiology → ____ or late term following a _____ labor or __________ without labor
-Symptoms → tachypnea, mild ___________, hypoxia, and cyanosis
perihilar streaking, fluid, self limited, oxygen
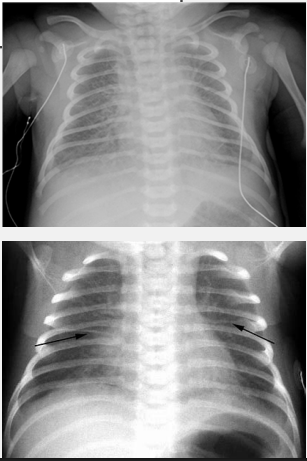
Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn: Diagnosis and Treatment
-CXR → central vascular markings (________ ___________) and ______ in lung fissures
-Treatment → _____ ________ (resolves within 12-48 hours), may need nCPAP and/or __________
meconium, amniotic, distress, pneumonia, term
Meconium Aspiration Syndrome: Background
-__________ stained _______ fluid
Sign of fetal ________ like asphyxia, hypoxia, and acidosis
-High risk of developing ___________ and pneumothorax
-Epidemiology → ____ and post-term deliveries
aspirated, after, obstruction, leaks, pneumonitis, hypoxia
Meconium Aspiration Syndrome: Patho and Signs/Symptoms
-Patho → __________ in utero by distressed, gasping fetus or immediately _____ delivery
Leads to small airway __________, air trapping, surfactant inactivation, alveolar air ______, atelectasis, or chemical ____________
-Signs/Symptoms → tachypnea, _________, hypercapnia, overdistention of the chest
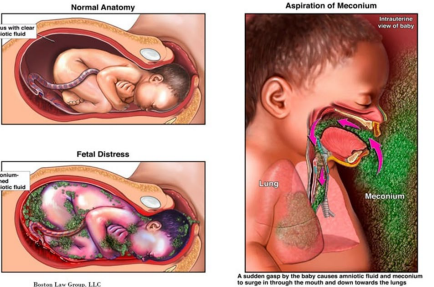
infiltrates, flattening, supportive, nitric oxide
Meconium Aspiration Syndrome: CXR and Treatment
-CXR → patchy ________, overdistention (increased AP diameter), and ________ of the diaphragm
-Treatment → _________ care and assisted ventilation. In the case of persistent severe hypoxia, you could try surfactant therapy, inhaled ______ ______, or ECMO
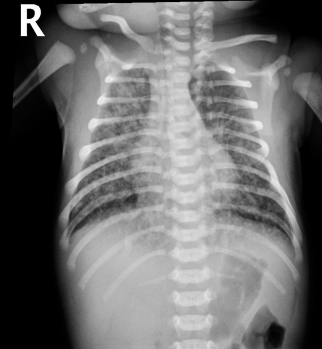
asphyxia, meconium, hypoplasia, vasoconstriction, smooth muscle, increased
Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of the Newborn: Background
-Epidemiology → post term, term, or near term infants
-Etiology → perinatal ________ (MC), _________ aspiration syndrome (MC), hyaline membrane disease, sepsis, and pulmonary __________
-Pathophysiology → _____________ due to perinatal hypoxia, prenatal increase in pulmonary vascular _______ ________ development, and decreased pulmonary vascular beds
-Overall result is __________ pulmonary vascular resistance instead of normal decrease after birth. Normally, there is a rapid fall in pulmonary vascular resistance and increase in systemic vascular resistance when the baby starts breathing outside the womb
hypoxia, oxygen, hypotension
PPHN: Symptoms
-Severe _________ → poor response to high concentrations of ___________
-Respiratory distress
-Systemic _____________
-Metabolic acidosis
normal, ECHO, elevated, oxygen, pressors, ECMO
PPHN: Diagnosis and Treatment
-CXR → usually ________, possible signs of pulmonary pathology
-________ (confirms diagnosis) → __________ pulmonary artery pressures and sites of right to left shunting
-Treatment → ___________, ventilation, fluids (first line)
Correct hypotension with fluids, _________ if needed
Inhaled nitric oxide
_____ if needed
40-45, diabetic, hyperinsulinemia, reduced, feeding, seizure
Hypoglycemia: Background
-Levels < ___-___ mg/dL after first feeding
-Risk Factors
________ mother → infant has abundant glucose stores, develops hypoglycemia due to ______________
Intrauterine growth restriction → _________ glucose stores
Preterm
-Symptoms
Lethargy, poor ________, irritability, tremors, ________, and apnea
Not specific to hypoglycemia
heelstick, blood draw, 45, dextrose
Hypoglycemia: Evaluation and Treatment
-Evaluation
Screen infants with risk factors
__________ and glucometer first
Confirm low or borderline values by ______ ______
-Target glucose is > __ mg/dL before feeding
-Treatment
__________ gel
IV 10% dextrose in water (D10W)
decreased, LGA, delayed, plethora, emesis, hematocrit, 65, transfusion, removal, 50-55
Polycythemia
-Hyperviscosity with ___________ perfusion of capillary beds
-Epidemiology
Most prevalent in SGA and ___ populations
_________ cord clamping is the most common cause of benign polycythemia
Other causes → twin-twin transfusion, maternal-fetal transfusion, and chronic intrauterine hypoxia
-Symptoms
________, respiratory distress, hypoglycemia, poor feeding, _______, irritability, and lethargy
-Diagnosis
Screen with capillary ___________ (heelstick) → if > 68% hct then do peripheral venous hct
If > __% hct = hyperviscosity
-Treatment
Isovolemic partial exchange ___________ with normal saline
Blood ________ through umbilical venous line
Desired hct of ___-___%
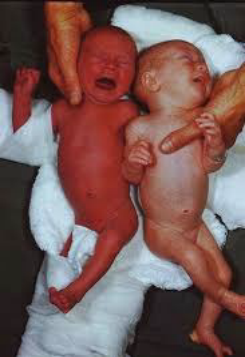
2-3, 1-2, increased, RBC, low
Anemia: Physiologic
-Normal
-Occurs at __-__ months of age in term infants and ___-___ months in preterm
-Does not result in illness
-Related to _________ tissue oxygenation, shortened ___ life span, and ___ erythropoietin levels
bone marrow, pallor, reticulocyte
Anemia: Decreased RBC Production
-_____ ________ failure syndromes, infection (like rubella), and congenital leukemia
-Sx include ______, low ____________ count, absence of erythroid precursors in the bone marrow
Rh, hydrops, hepatosplenomegaly, 24, ABO, mild
Anemia: Increased RBC Production
-Hemolysis in utero
__ blood group incompatibility. Can lead to erythroblastosis fetalis → _____
Asphyxia, _______________, pallor, jaundice within __ hours
-Hemolytic disease of the newborn
___ incompatibility
Causes anemia and ____ hyperbilirubinemia/jaundice
rupture, previa, pulses, heart
Anemia: Blood Loss
-Acute → fetal-maternal hemorrhage, _______ of umbilical cord, placenta _____, internal hemorrhage
Pallor, diminished peripheral _______, shock
-Chronic → chronic fetal-maternal hemorrhage, twin to twin transfusion
Pallor, ______ failure, hepatosplenomegaly, hypochromic microcytic anemia