zones of the ocean and coastline (littoral or intertidal zones)
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
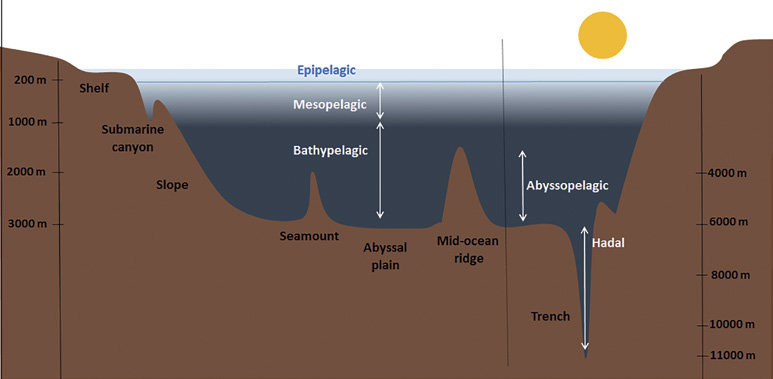
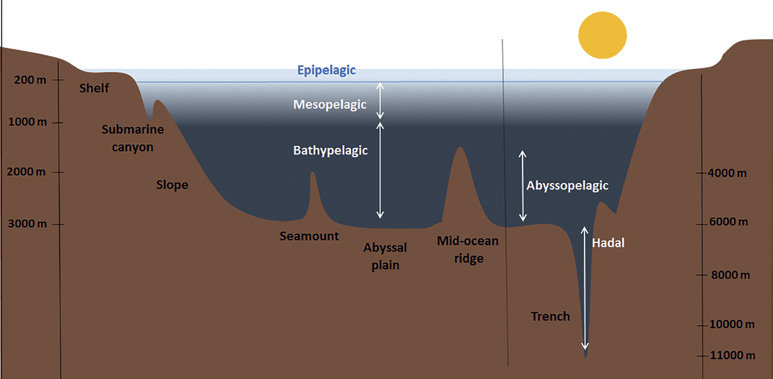
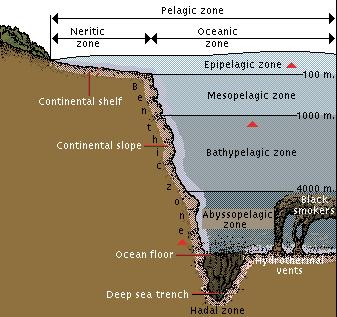
name the 5 zones of the ocean from surface level to deepest level (including meters)
epipelagic (0-200m)
mesopelagic (200-1,000m)
bathypelagic (1,000-4,000m)
abyssopelagic (4,000-6,000m)
hadopelagic (6,000-seafloor)
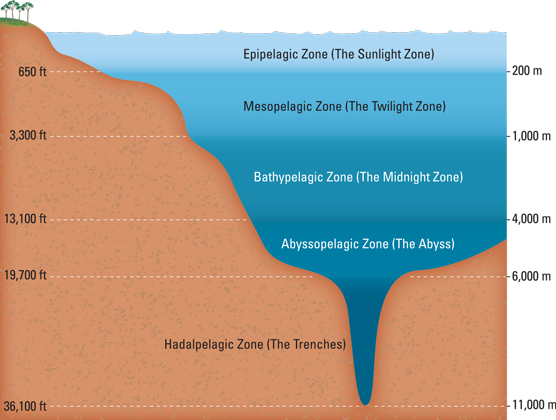
which zones of the ocean make up the deep sea?
bathypelagic
abyssopelagic
hadopelagic
what are the zones of the ocean divided on?
divided based on light penetration and depth
describe the epipelagic zone
AKA the photic zone
contains most light
contains planktonic organism
separated into two zones
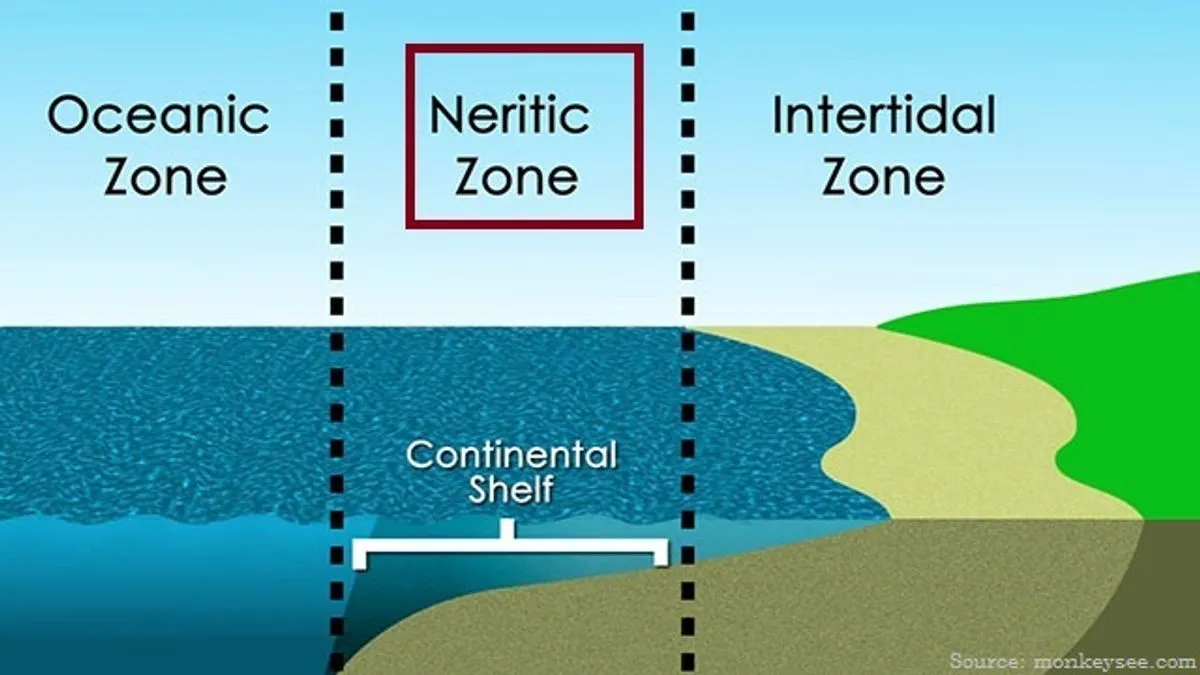
describe the neritic epipelagic zone
over coastline, near shore
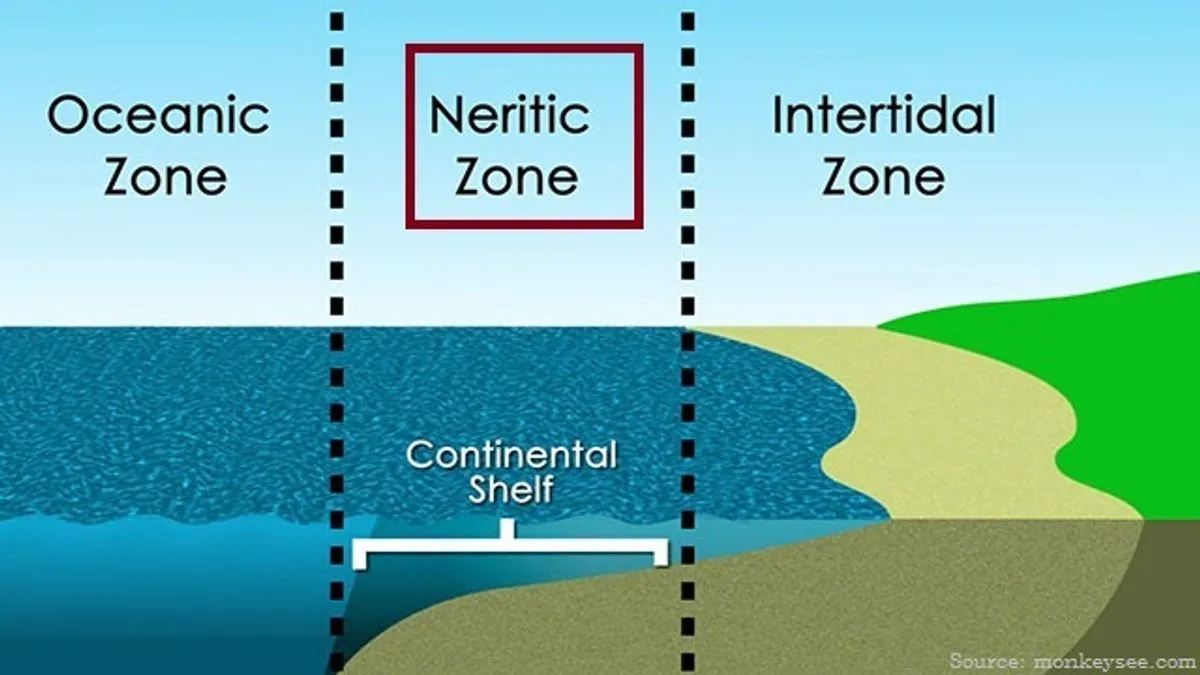
describe the oceanic epipelagic zone
beyond continental shelf
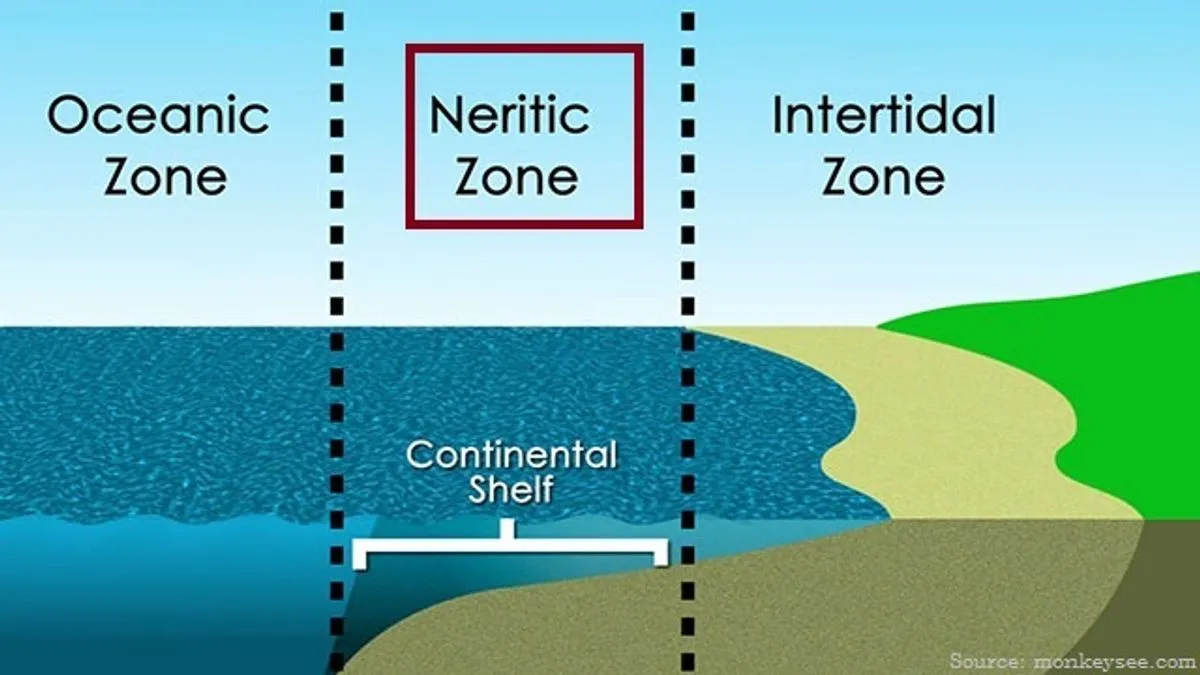
describe the mesopelagic zone
AKA twilight zone
light slowly degrades 200m-1,000m where it becomes completely absent
organisms have specialized adaptations here
in which zones do trenches occur in
hadopelagic zone
describe the deep sea
the largest habitat on planet
animals have are small, reduced eyes, hermaphroditic, some are bioluminescence
define an intertidal zone
area of land between high tide and low tide
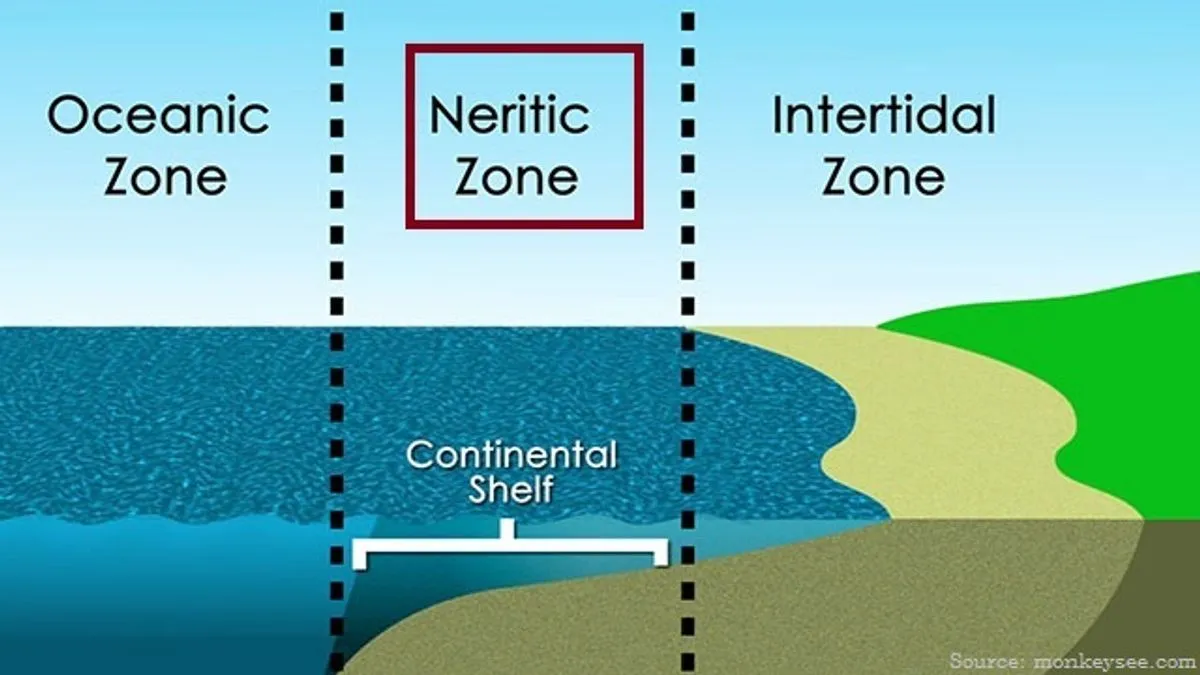
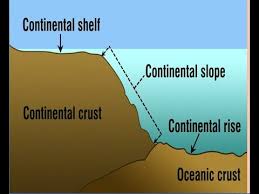
define a continental shelf
shallow part of the continental margin
gently sloping
covered in sediments
define a continental slope
begins at the shelf break (slope abruptly gets steeper) and descends down to the deep sea
define a continental rise
where the sediment from the slope collect and form a more gradual decline
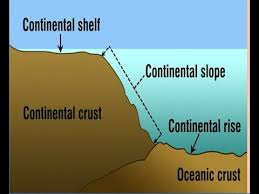
define a abyssal plain
a very gentle slope less than 1 degree toward the mid-ocean ridge
define a mid-ocean ridge
an underwater mountain range, formed by plate tectonics
what is used to map the seafloor?
side scan sonar
type of sonar that transmits sound pulses and the time interval between emission and return of pulse is recorded
describe benthic environments
low availability of food
no light (no photosynthesis)
falling remains of dead orgainsm (whale falls)
low temp (0-2 celsius)
high pressure
what did Dr Robert Ballard do?
in 1977 he did research a long Galapagos Rift and noticed temp spikes in data
discovered hydrothermal vents
what was launch ALVIN
HOV (human occupied vehicle)
launched to research vents
where are hydrothermal vents located?
in divergent centers, within mid-ocean ridges
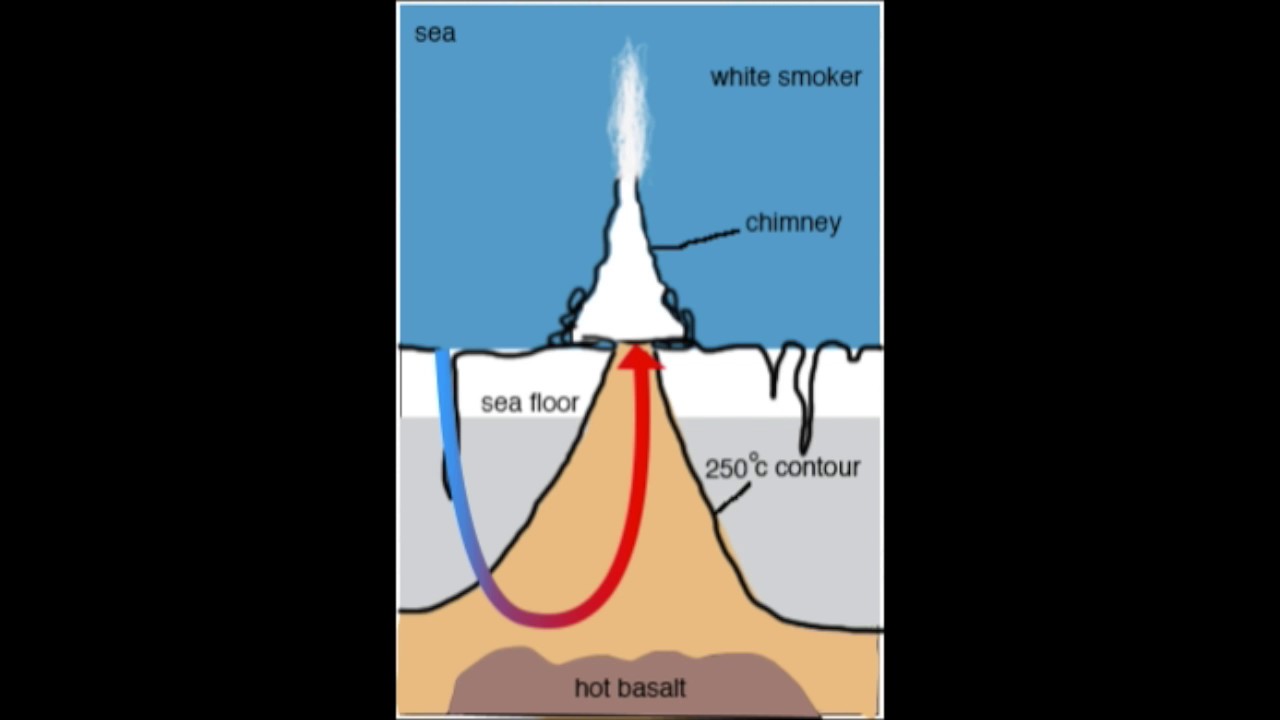
describe how hydrothermal vents are formed
cold water seeps into the crust and is geothermically heated (dissolves minerals from rocks, turning it black), the superheated water then escape the crust through a fissure above
these vents are hot, low in oxygen, and rich in metals and hydrogen sulfide
the chemicals contained from these vents are the basis for chemosynthesis
what are the three types of hydrothermal vents?
black smokers, white smokers, and seeps
characterized by different physical, chemical factors (minerals, temp, and flow)
describe a black smoker
hottest
darkest plumes
high in sulfur
can form chimneys (vents) up to 18 stories tall

describe a white smoker
rich in barium, calcium, and silicon (so they are lightly colored)
cooler plumes
smaller chimneys

describe seeps
coolest and weakest flow
the sometimes shimmer due to difference in water temp
can sometimes bubble due to presence of gases

define isostasy
means weighing the same
buoyant properties of layers of rocks due to density and thickness
explains why there are shallower seas above a continental plate than over an oceanic plate
what does the water depth of a continental shelf depend on?
isostatic changes in land height
changes in sea level
define the principle of isostatsy
if the crust in higher, then it is thicker/less dense
if the crust is lower, then it is thinner/more dense
which is more dense: continental crust or oceanic crust?
the oceanic crust is more dense (contains basalt) and the continental crust is less dense (contains granite)
define weathering
the breaking down of rocks
due to exposure to atmosphere
little movement of particles involved
describe chemical weathering
chemical composition changes through exposure to water/oxygen
describe physical weathering
broken into small pieces without changing chemical composition (temp change)
constant heating and cooling of rocks weaken structure, breaks apart
describe organic (biological) weathering
living organisms complete weathering process
ex: lichen release special compounds that beak down rock, aiding production of soil
define erosion
the movement and transportation of broken down material by natural agents to new locations
describe ice erosion
glaciers move over land, break rock, and carry them to new location
describe gravity erosion
ex: cliff rock fall; gravity helps move rock from cliff edge to ocean below
describe wind erosion
strong breeze picks up sediment, carries it to new location
describe water erosion
ex: river runoff carrying material to new location
define deposition
the delivery of particles in a new location
define sedimentation
the deposition of suspended particles from water; left there to accumulate
forms deltas Δ or fan shaped structure

define the littoral zone
the area where land meets sea
what impacts the nature of littoral zones
shape of the shore
wave action and erosion
the substrate that makes up the shore
the organisms that live there
define a rocky shore
any shoreline that has a rocky substrate but may vary in slope and composition of rocks
describe what can be found at a rocky shore
boulders, stones, pebbles
granite or igneous rocks (resistant to weathering)
sandstone (easily broken down)
very steep cliffs to horizontal flat rocks
rock pools
describe some characteristics of a rocky shore
most exposed type of shore
most resistant to erosion
very little sedimentation due to speed of water coming in
largest boulders at top of shore
HIGH biodiversity
stable substrate - large rocks and algae
describe the biodiversity of a rocky shore
high biodiversity
substrate provides many places for animals to live
what are the environmental factors that influence rocky shores?
desiccation (extreme drying) - species near tip of shore exposed to air for long periods
temp
wave action
light intensity
aspect (N, E, S, W)
slope
nature of substrate
describe the formation of sandy shores
by the erosion of sandstone and sedimentation of sand particles by waves
describes some characteristics of sandy shores
LOW biodiversity
erosion of sandstone
deposition of sand by sea - bc of wave action
slope gradually toward sea
VERY unstable - wind easily can remove fine sand that makes up shore
describe the biodiversity of sandy shores
no shelter for organisms at the surface so they have to burrow to survive
organisms have to adapt to environment
LOW BIODIVERSITY
describe a muddy shore
least exposed to erosion and weathering due to little to no wave action
allows for the deposition of silt particles
little slope and makes mud flats
what are the three types of muddy shores?
estuaries, deltas, mangroves
describe an estuary
form in semi enclosed body of water where fresh and saltwater meet (BRACKISH)
water is very murky as the slow flow of water allows for particles to settle
describe the formation of a delta
form at the mouth of a river where it meets the sea, river carries suspended sediment until it reaches a sea
describe how deltas use sedimentation
the flow rate decreases and sediments begin to settle at bottom of river
sediments deposit and accumulate into a fan shaped structure
over time the delta will form tributary channels of river
define a mangrove
trees, shrubs that live in tropical/subtropical saline environments between latitudes 25 N and 25 S
form woodland habitats
describe the conditions of a mangrove area
grow in saltwater with a large tidal range where deposition is more frequent than erosion due to calmer waters with reduced wave action
temp of region needs to be mild to warm year round
will grow best in areas with health coral reefs offshore due to protection provided by reefs
what are mangroves adapted to?
wide range of salinity
low oxygen concentrations
what are pneumatophores?
root like structures that obtain oxygen directly from air
describe the root systems of mangroves
extensive root systems
trap particles suspended in water
filters water
reduce water flow
increases deposition of sediments
dissipates wave energy
protects coastal area from erosion