Section 4
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
What’s significant about all valence orbitals of noble gases being filled?
maximized spin exchange stabilization energy (energy gained when e- with opposite spins are paired within same orbital)
due to stable e- configuration, noble gases are inert + don’t readily react with other elements
Many properties of elements depend upon?
Their valence shell e- configuraiton.
What is the 1st ionization energy?
energy required to remove the outer e- (highest energy) from an atom in the gas phase
X(g) + energy(light) ➡ X+(g) + e-
∆E = Eproducts - Ereactants
energy provided to reactants to eject an e-
What do ionization energies give direct measurements of?
Valence e- energies.
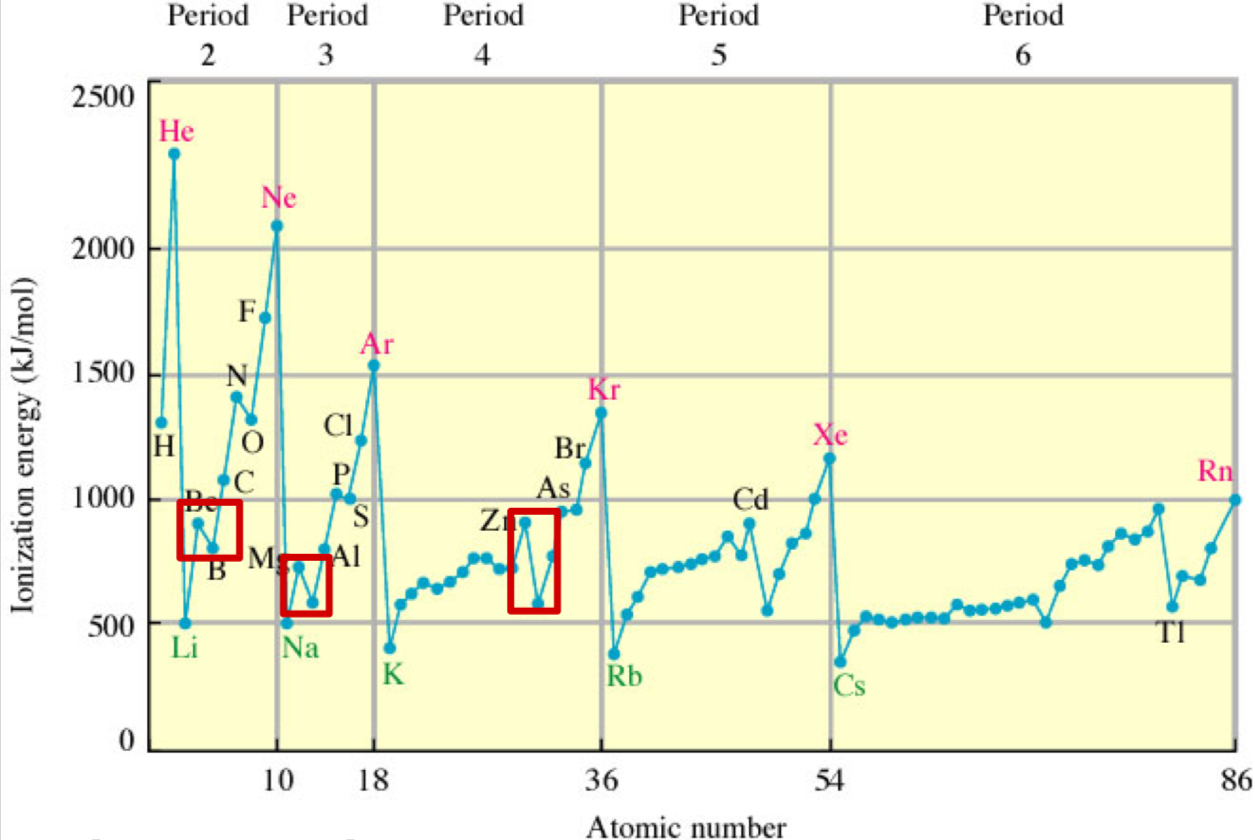
What are the 3 trends of ionization energy?
across a row (L to R): 1st IE increases
net (+) charge experienced by valence e- is due to Zeff increasing (more protons)
screening by e- in same shell less than core e-
valence e- don’t shield each other as effectively as core e- do, so increasing the (+) charge of nucleus more strongly is felt by the valence e-, making them being held more tightly
down a group: 1st IE decreases
principle QN increases ➡ E of orbital increases (e- in higher orbitals easier to remove than in lower orbitals)
# core e- increases down the group ➡ more screening + less Zeff
ionization potential drops s2 ➡ s2p + s2p3 ➡ s2p4
s2 ➡ s2p
adding 1st p-e- leads to drop in IE since p-orbitals are higher in energy + easier to remove than s-orbitals
s2p3 ➡ s2p4
p-orbitals are half-filled in s2p3 (stable due to symmetrical distribution + minimized e- repulsion)
but adding a 4th e- in s2p4 forces pairing within a p-orbital, increasing e- repulsion + lowering IE
What is atomic radii + 3 types of it?
distance from nucleus of an atom to the outermost e- shell: size
types
single bond (covalent): measure distance between nucleii (single bond) + divide by 2
van der Waals: outer e- in one atom is weakly attracted to another atom’s nucleus
½ distance between nucleii
ionic radii: ionic solids after gaining or losing e- compared to neutral atom
measure distance between nucleii + extrapolate to neutral atomic radii
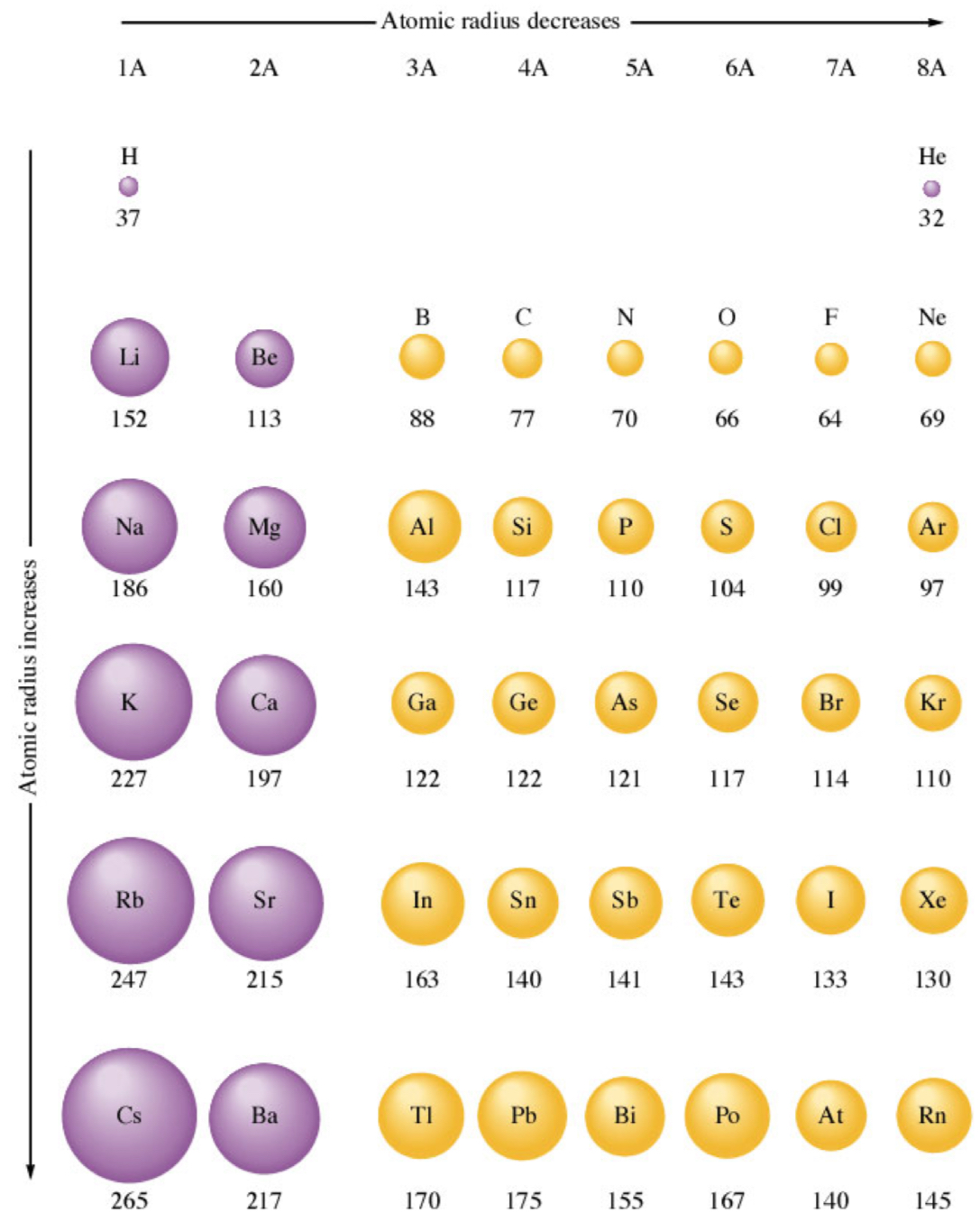
What are the 2 trends of atomic radii?
atomic radius increases down a group
principle QN increases ➡ energy of orbital increases + # core e- increases
more shells are being added
atomic radius generally decreases across a row (L to R)
# protons + # core e- increase left to right
Zeff increases left to right (more protons)
atom size decreases since e- are being pulled in more
What is the order of shielding ability for s, p, d + f-orbitals?
s > p > d > f
e- in f-orbitals are less effective at screening nuclear charge than e- in s + p-orbitals
d-orbitals: requires 10 e- to fill orbitals + 10 protons in nucleus
ex. between Ca + Ga the 3d orbitals are filled, but d-e- don’t shield nuclear charge effectively
thus Ga has a smaller atomic radius than Al even though Al is above it in period table (d-orbital contraction)
What is electronegativity?
Atom’s relative ability to attract e- in interactions with other atoms, solids, metals, molecules, covalent/ionic bonding.
What are the 2 trends for electronegativity?
EN increases L to R (along with Zeff)
EN decreases down a group (due to screening)