selfishness and altruism
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Social behavior can be
Heritable
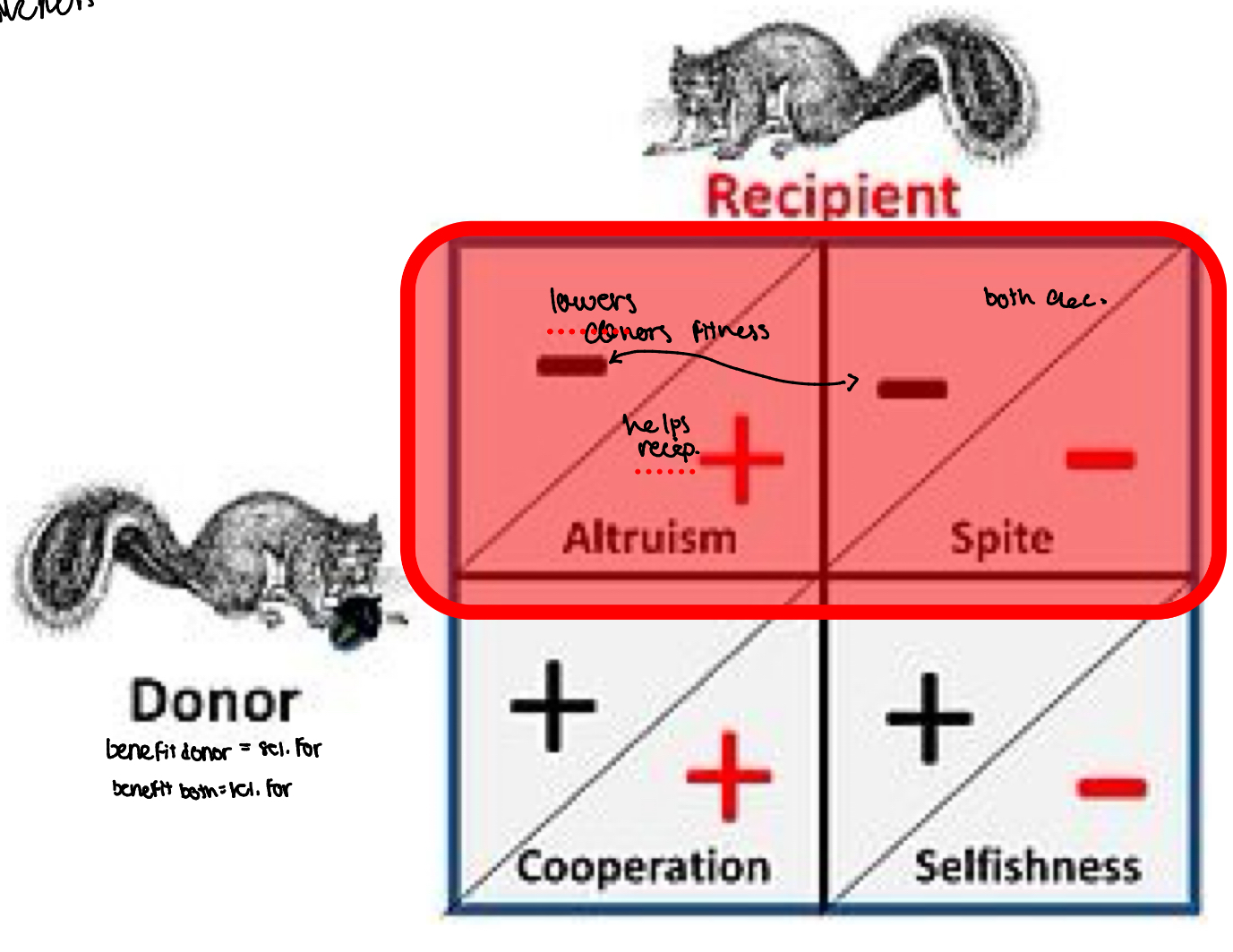
How can an action/phenotype that lowers the actor’s fitness be
“beneficial”?
Altruism ex. Caring for kids with resources instead of using the resources yourself because they carry your genes
Kin selection
Inclusive fitness – dependent on both direct and indirect fitness
Whether or not you act altruistic to someone depends on how closely related you are
Hamiltons rule
Br - C > 0
B is benefit to recipient
r relatedness between actor and recipient
C cost to actor
> 0 then should do the act
<0 should not do the act
Ex. Prairie dogs give out call to warn others of predators but puts them self at risk so they usually do this when they are in a population where they have more kin
Green beard alleles
Identifying kin
an allele that simultaneously produces a phenotype (a green beard), allows recognition of the phenotype in others, and initiates altruistic behavior towards them
All three requirements met means high beneficial so should be selfish
Selfish genes
enhance their transmission at expense of other genes
• Meiotic drive, segregation distorters, MITOCHONDRIA!!!, etc.
Selfish mitochondria
Decreased energy
• Replicated faster/more often
• “moral hazard” hypothesis: passed on more but might not produce most energy for cell
• “Mother’s curse”: maternal inheritance so select for having high fitness in daughters but low fitness in sons so it’s beneficial
Eusociality
Ultimate form of altruism
• “Castes” of nonreproductive that help raise young
Evolve by kin selection and haplodiploidy hypothesis
Haplodiploidy hypothesis
• Sisters are more closely related than they would be to offspring
• Higher fitness for helping raise sisters than making your own offspring
• Largely refuted because eusocial species don’t have haploid diploid sex determination
Monogamy hypothesis
• If you know your sibs are full sibs, they are as closely related to you as your own
offspring
• Similar problems as haplodiploidy
Ecology and life history hypothesis
Best one
• All eusocials have “fortress” nests and larvae that require lots of care
• Hard to go it alone
• Vespid wasps and gradations of eusociality
Reciprocity
• Non-kin selection
• Social networks
• Punishment is important punishment selfish moochers
Do something good for me and I’ll do something good for you
Can Hamilton’s rule explain spite?
• B is negative
• Yes, if r is negative too
B and r negative makes positive and offset costs
• Better for the average to reproduce than the recipient
Hamilton and controversy
• Eugenics
• Lack of natural selection in modern humans