BBE 4001 MASTER LIST
1/436
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
437 Terms
Proteins in plant materials
natural polymer, contains carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur for growth and development. They serve as structural components, enzymes, and play a role in metabolic processes.
amino acids
the building blocks of proteins, consisting of a central carbon atom, an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a unique side chain. They link together via peptide bonds to form proteins.
what does the “L” mean in l-amino acid?
Indicates that the amino group is on the left side of the fischer projection.
what does the “alpha” mean in alpha-L-amino acid?
indicates that the amino acid is on the alpha carbon.
amphoteric/zwitterion
a molecule that can donate a positive and/or a negative charge (amino acids are these)
Different R groups in amino acids
Contains Sulfur
Contains a Carboxyl group
Contains a basic amino group
Neutral
Contains an -OH group
polypeptides
amino acids linked by polypeptide bonds. Point of bond rotation limited due to resonance structure containing a double bond
peptide bond
covalent bond between amino acids, connects amino group to the carboxyl group
primary structure
amino acid sequence
secondary structure
arrangement of primary structure; alpha-helix or beta folded sheet
tertiary structure
arrangement of secondary structure in space, ex. coiled up helix
quaternary structure
arrangements of several proteins in one structure
how do protein structures stay together?
hydrogen bonds
ionic bonds
hydrophobic/philic interactions
electrostatic forces
covalent bonds (eg. sulfur bonds)
side group (R) size
denatured protein
happens after a protein is exposed to high heat (65-90C) or low pH; non-reversable unfolding of their structure, loss of functionality
what is corn protein/zein used for?
coating and plastics
isoelectric point
where the concentration of the dipolar ion is at maximum
enzyme
a catalyst that changes the rate of reaction without being consumed in the process by lowering the activation energy— reaction rate 10^6 to 10^12 higher
how are enzymes effective?
structure provides active site
substrate specific and based on active site
will only react with their substrate—one reaction with one substrate but done very efficiently
how do enzymes catalyze reactions
active site provides a template for two or more reactants to come together in the right orientation
can stretch or distort the substrate molecule to make bonds that need to be broken weaker
active sites with amino acids that contain acid groups can provide a pocket of low pH
enzymatic reaction rate depends on…
substrate concentratiom
increase in temperature, optimal temperatures between 30 and 50C
increase in pH, optimal pH between 6-8
binding affinity; how fast the substrate could get to the active site and how fast the product can leave
cofactors
often inorganics like metal
assists enzyme by binding to the enzyme
metals often found in redox reactions
platform chemical
starting material that can be converted to useful materials for other applications
what is used for cellulose/hemicellulose hydrolysis to produce sugars?
acids or enzymes
is hemicellulose or cellulose easier to convert?
hemicellulose is easier to convert than cellulose since it can dissolve
why are stronger acids needed for cellulose?
to ensure crystalline areas are attacked
problems with hemicellulose/cellulose hydrolysis
hard to isolate the cellulose
acid and enzymes are hindered by lignin
biomass needs pretreatment to open up cells
pretreatment methods need to…
reduce size of particles
reduce crystalline areas, potentially with ball milling
produce a homogeneous mixture
mechanical method
milling/grinding
creates a higher surface area
homogeneous mixture
breaks up some crystalline areas
considered a necessity
steam explosion (hydrothermal)
steam in pressurized vessels (180-280C)
short retention time, quick release of pressure
explodes cells
natural acids (acetic acid) start to break down polysaccharides
breaks some LCCs
hot water treatment
presteaming/hot water extraction
20 minute retention time
natural acids released
large part of hemicelluloses removed
little lignin removed
cells open
thermochemical treatment, Acid
uses sulfuric, HCl, SO2, or nitric acid (diluted)
causes random chain cleavage
thermochemical treatment, alkaline
Uses NaOH or Ca(OH)2
causes peeling reactions + dissolving
takes out hemicellulose and lets enzymes react with cellulose
thermochemical treatment, AFEX
Ammonia Fiber Expansion
water/conc. ammonia, 60-140C, 5-45 min
explosive release
ammonia can be recovered and used as N source, like fertilizer
Removes acetyl groups and LCC bonds to open cell wall, may dissolve some lignin
chemical treatment
most often used for removing lignin
oxygen
ozone
peracetic acid, etc.
biological treatment, fungi
uses white rot which can eat lignin (with a bit of carbs), but can take a long time
how does lignin hinder enzymes?
Lignin can get in the way physically, and cellulase enzymes sometimes attaches to lignin instead and inhibit themselves
biological treatment, esterases
breaks ester bonds in LCC, takes a day or two
biological treatment, laccases
oxidative and can remove lignin, takes a day or two
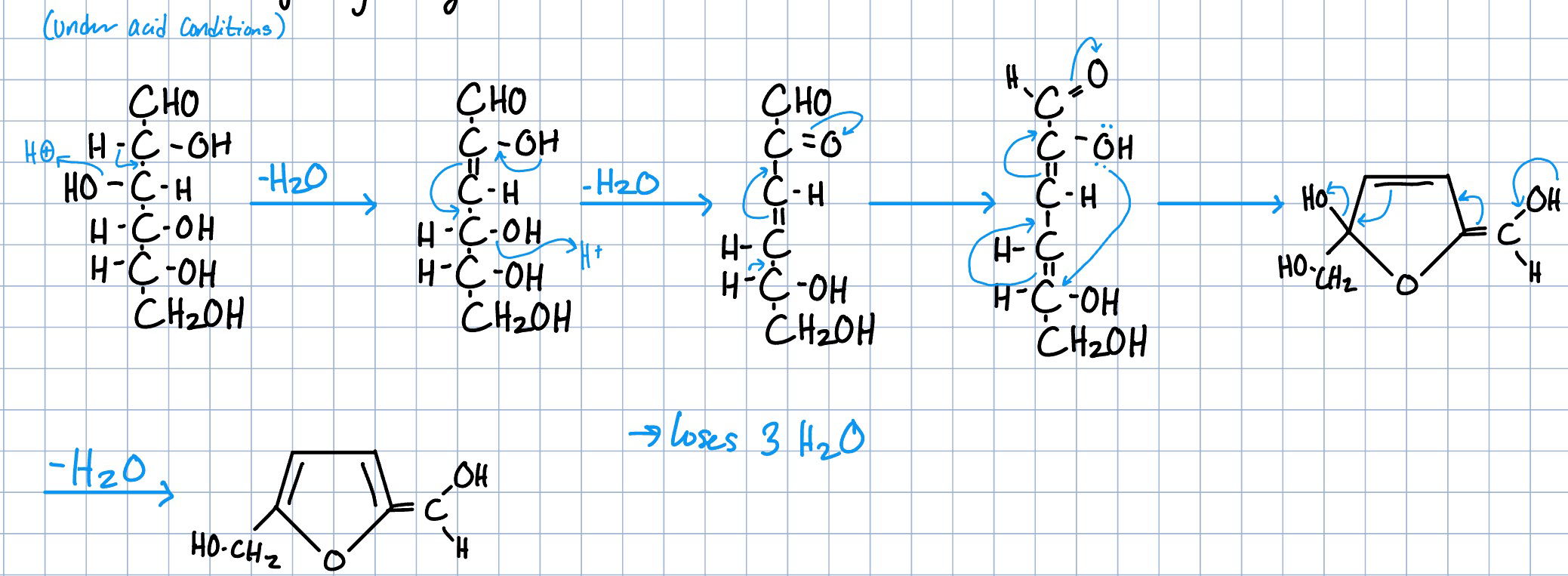
furfural reaction
strong acids and high temperatures applied to pentoses
glucose to hydromethylfurfural
(under acid conditions)
acid conditions cause OH group on C3 to leave as water, H on C2 moves down to form double bond
OH group on C4 gets protonated, double bonds shift
H on C5 forms double bond, C3-C4 double bond moves up, C2 double bond moves electrons back to O
C2 OH electrons go to C2, forming a ring. double bonds shift accordingly
OH on C1 becomes double bond, bonds shift accordingly
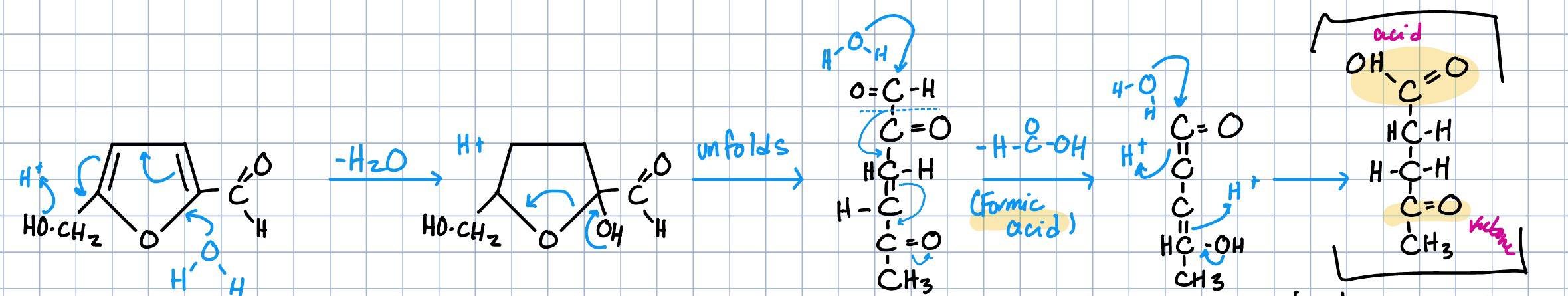
HMF to levulinic acid
succinic acid
biomass → pretreatment → fermentable sugars (enzyme/acid) → microorganisms + CO2 → product
Reaction consumes CO2
platform chemical
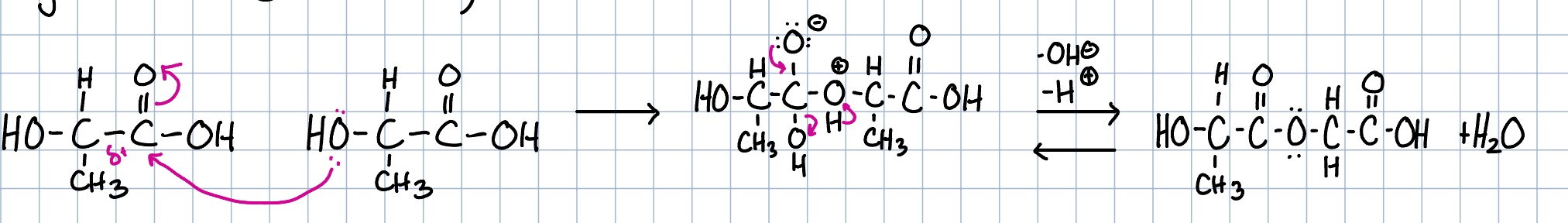
lactic acid monomer reaction
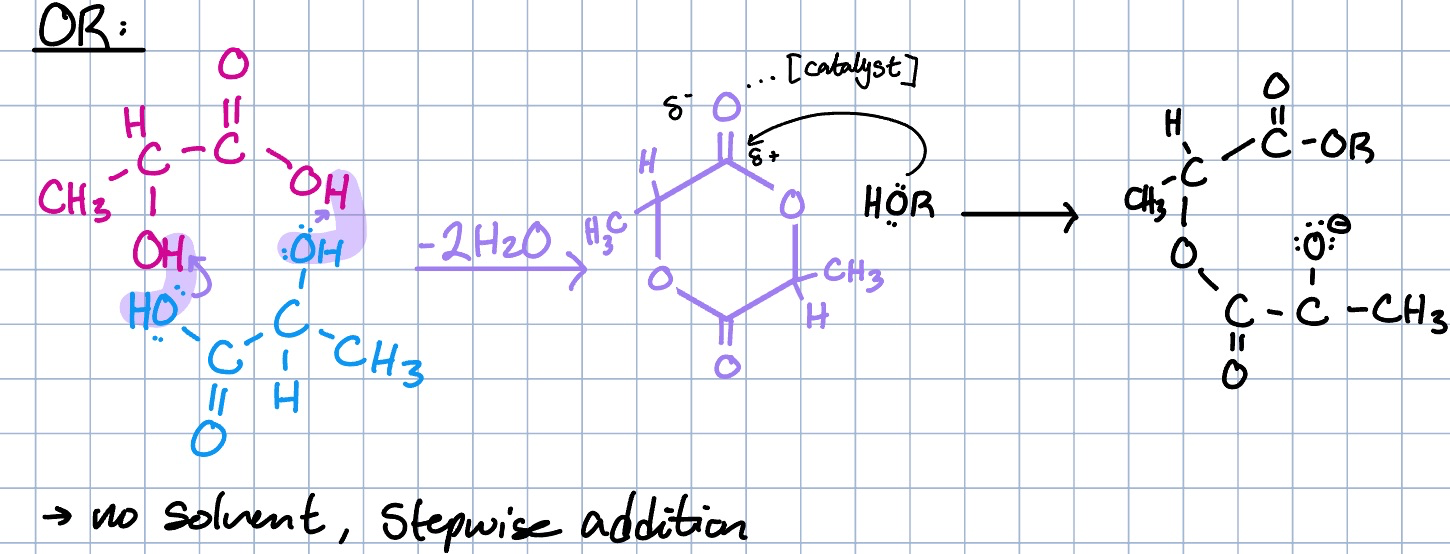
lactic acid dimer reaction
Bio-isobutanol to paraxylene reaction
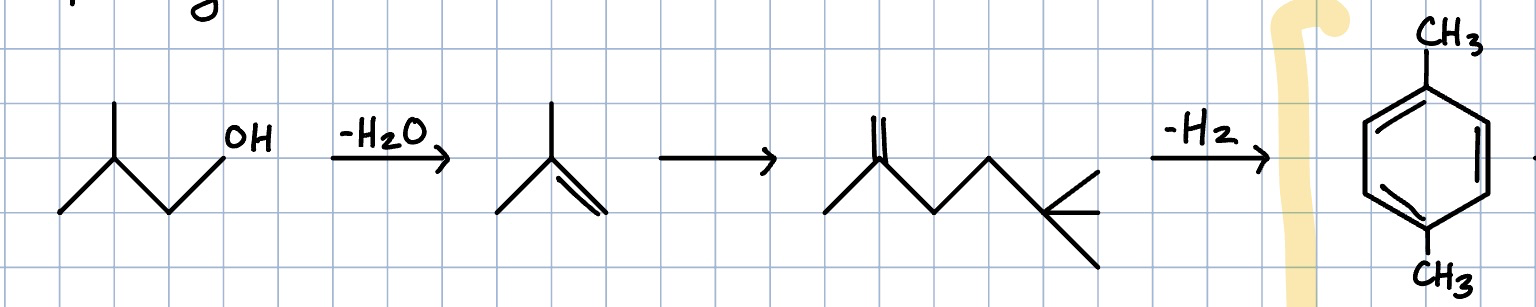
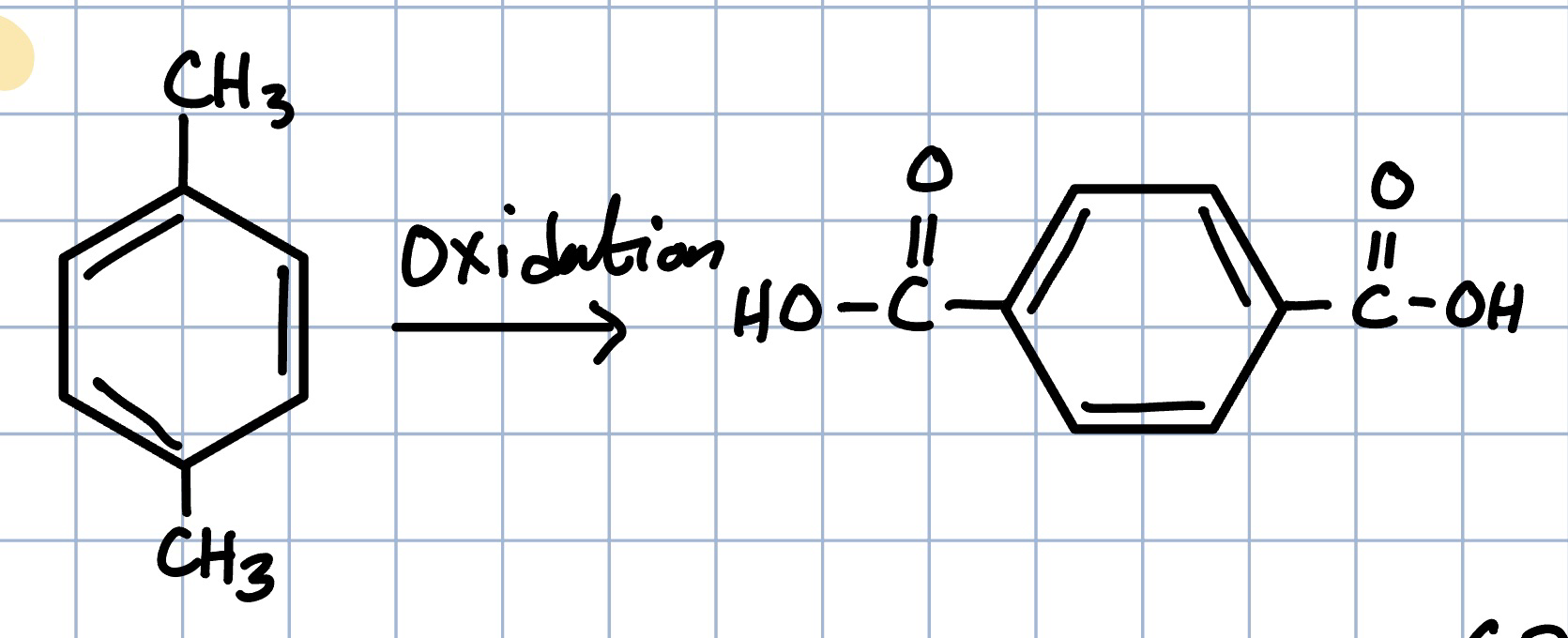
Paraxylene to tereptalic acid
why is the lactic acid dimer reaction preferred over the monomer reaction?
since the monomer reaction is reversible, the acid would get taken apart as you are making it
the dimer reaction creates a cyclic structure that allows for a more efficient and stable polymerization process
enzymatic hydrolysis
uses a mixture of cellulase to break down cellulose including:
endocellulase
exocellulase
beta-glycosidase
endocellulase
breaks down crystalline areas
exocellulase
breaks down glucose into small subunits
beta-glucosidase
breaks down 2-4 subunits to glucose
ABE process
process that produces acetone, butanol, and ethanol using solventogenic clostridia and fermentation
can use easily digestible sugars, cannot directly digest cellulose (needs to be pretreate)
paraxylene
feedstock for terephthalic acid (PTA), can be made from bio-isobutanol
terephthalic acid (PTA)
monomer used in the production of polythylene terephthalic (PET)
polylactic acid (PLA)
made from plant starch, compostable; needs heat and water to break down
polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA)
biodegradable polymers (polyester) produced by bacteria— can be degraded by other organisms right away
similar to petroleum based polymers
PHB
produced by genetically engineered soil bacteria as energy storage, biodegradeable
plant bottle
30% renewable material and 100% recyclable—made with ethylene glycol and terephtalic acid
only 30% because terephtalic acid does not have viable pathways for renewable production
xylitol
also called wood/birch sugar, sugar alcohol from hydrogenating (reacting with H2) xylose. used as a low calorie sugar substitute
sorbitol
also called glucitol, sugar alcohol of glucose. low calorie sweetener
maltitol
sugar alcohol of maltose
sucralose
600 times sweeter than table sugar but contains chlorine in its chemical structure
turpentine
solvent for varnishes and paints, produced using polymerization to polyterpenes (pressure sensitive or hot melt adhesives)— used in fragrances and insecticides as well
plasticizer
material mixed with polymers to make more flexible (ex. PVC)
used to be made with phtalates but creates health issues
soft and safe
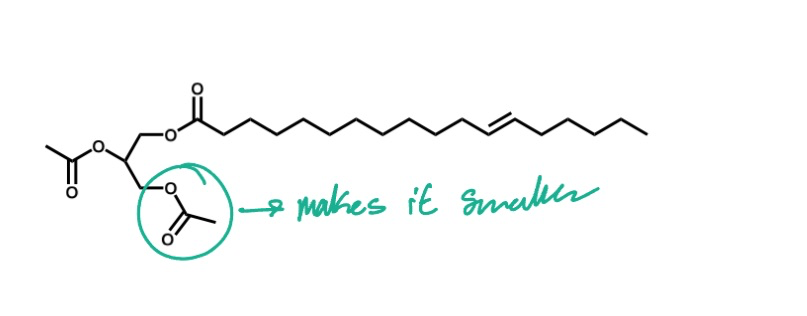
plasticizer — acetylated monoglyceride of castor oil, replaces fatty acid in triglyceride with acetyl group
most common use of lignin
burning for energy
lignin based products
vanillin
DMS and DMSO
phenol formaldehyde resins
dispersant, emulsifier
tanning agent
where would you get lignin from?
pulping liquors, organosolve (needs high temperatures and pressure, also hard to recycle solvent)
vanillin
flavoring agent, produced from softwood lignin (G-lignin) and fermentation
2-12 hours at 100-165C with NaOH
typical yield ~10% due to the production of other compounds (which get burned)
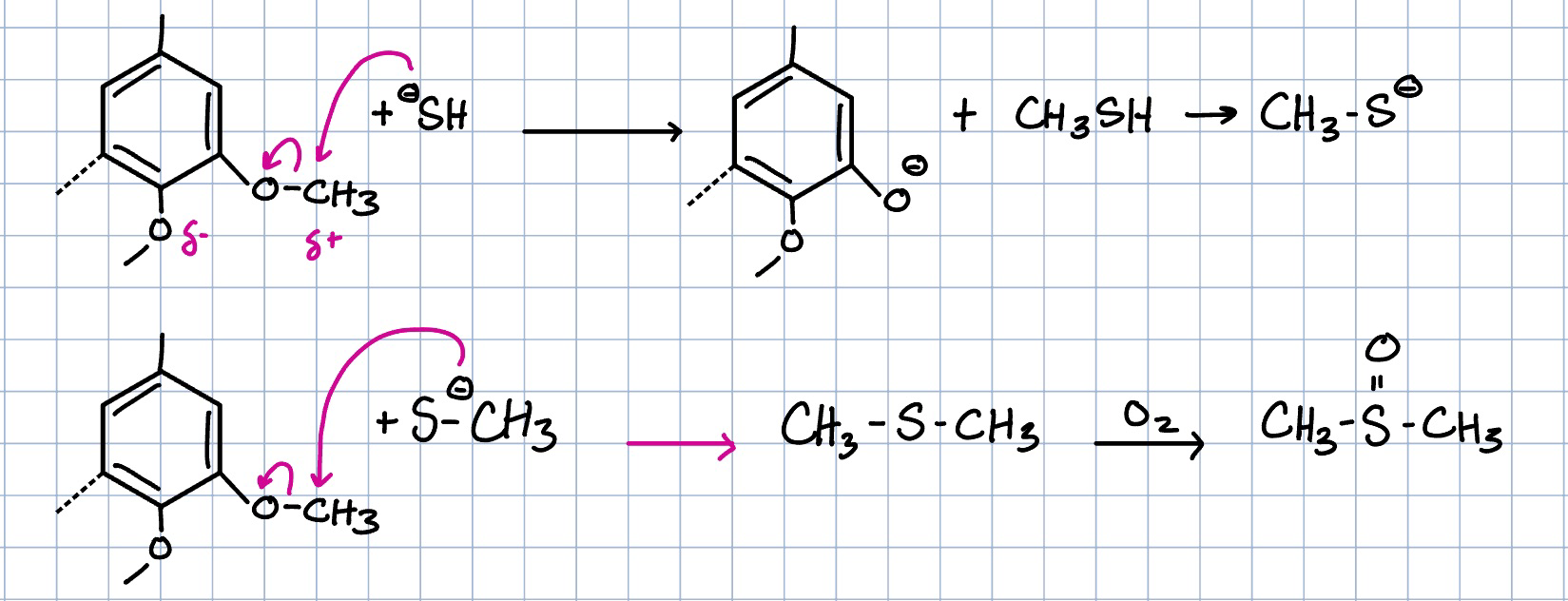
DMS and DMSO
produced from demethylation reactions with craft liquor and the addition of sulfur—used as a solvent
dissolving pulp
cellulose extraction, removal of hemicellulose, acid pre-hydrolysis, or alkaline pulping (low yield due to peeling)
alkali cellulose
also known as ripening; swelling of cellulose to different degress depending on metal
if exposed to oxygen, can decrease degree of polymerization, but in this process you want shorter chains
disassociates OH groups
cellulose reaction with acid
(esters)
NO2 reactive species, produces cellulose nitrate/guncotton
cellulose reaction with acid mechanism
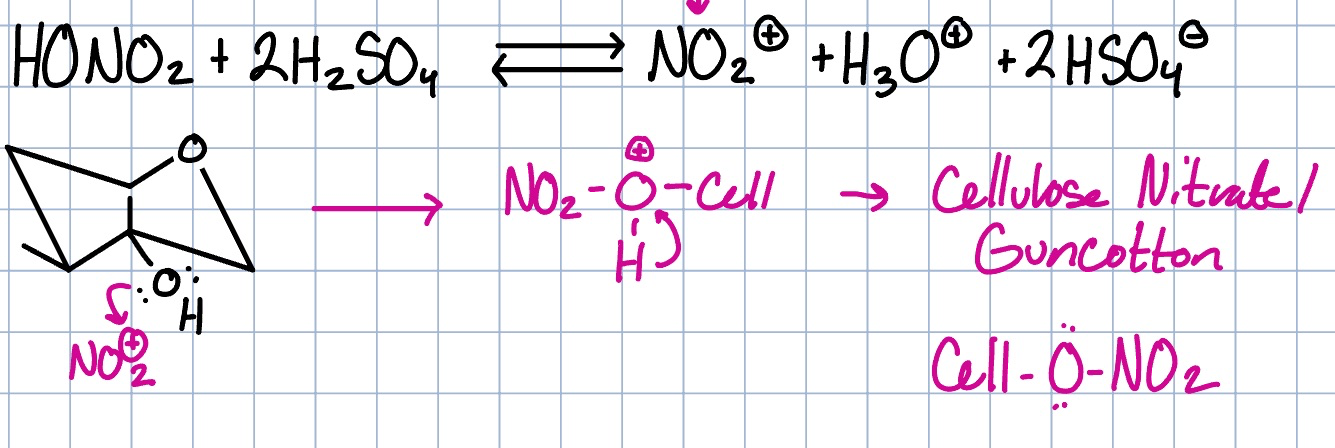
degree of subsitution
number of free OH in cellulose that can be reacted with. Determines properties. (higher number means more explosive)
C3, has 2 more H-bonds and is more hindered
in DS, which carbon reacts the slowest and why?
cellulose sulfate
used as a viscosity modifier and has been trialed a a microbicide
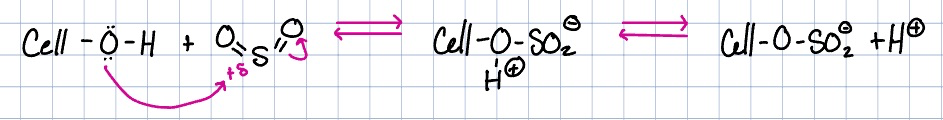
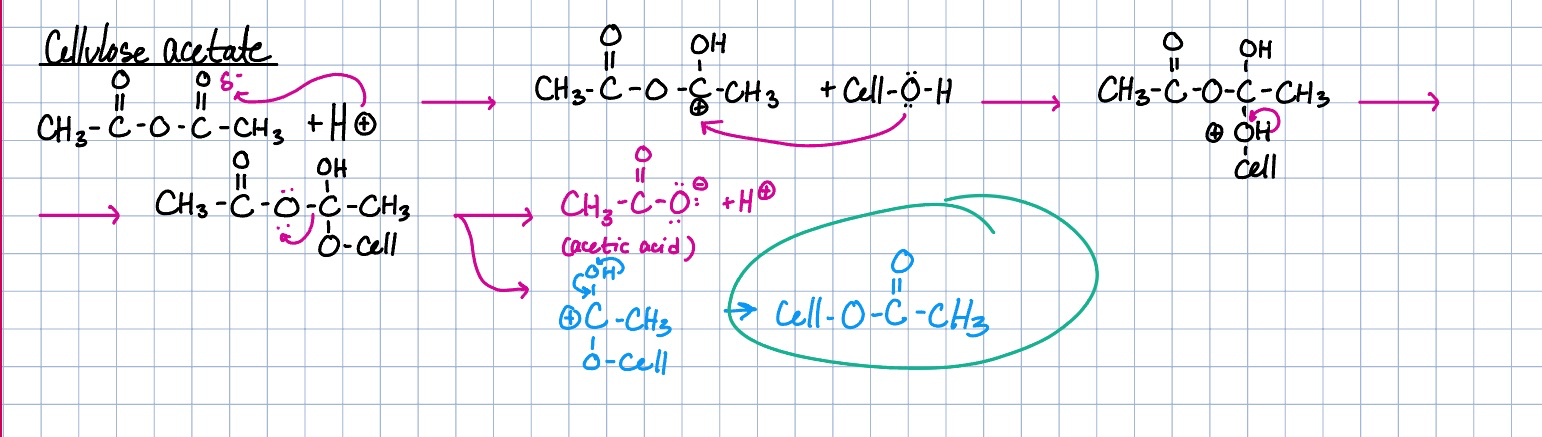
cellulose acetate
bioplastic with many uses (plastic, films, fibers, coatings for glasses, etc)
cellulose acetate reaction
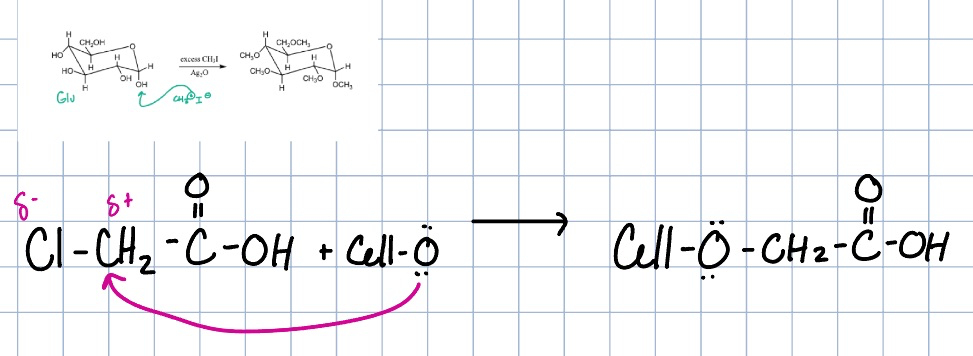
cellulose ethers
methyl and ethyl cellulose, used in thickening and dispersion agents (pseudoplastic)
cellulose ether reaction
carboxylmethylcellulose
most common water soluble cellulose, prepared from alkali cellulose and chloroacetate
used in detergents, food, and paper coatings for its water binding capability
cellulose xanthate
also known as rayon.
xanthate dissolved in caustic → viscose
spun into acid → rayon → regenerated cellulose
cellulose xanthate reaction
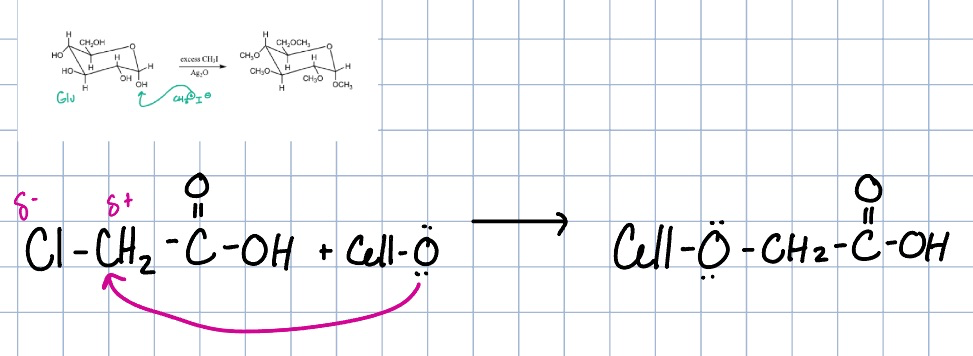
lyocell
newer process developed to address environmental concerns with rayon—cellulose directly dissolved in N-methylmorpholine N-oxide
spun into water bath with dilute amine oxide to regenerate cellulose
cellulose grafting
co-polymer system comprised of a backbone material (cellulose) where a second polymer is attached at intervals along the chain—done to improve compatibility/composite materials
viscose
xanthate + NaOH
rayon
also known as artificial silk…
regenerated cellulose
viscose + acid
water soluble
if a material has a low DS, it means…
What groups are included in the term "phenolic extractives"
-Lignans
-Tannins
-Flavonoids
Structure of Rubber vs guts percha
Rubber: 1-4-cis polymer
Guta Percha: 1-4 trans polymer
What do heartwood and bark often contain large varieties of?
Aromatic extractives
Phenolic extractives can be a problem in acid processes because they result in...
-burned chips
-condensation reactions
Does extractive content of wood increase or decrease during storage?
Decrease
What extractive group is lost first during storage?
Terpenes
What do all natural fatty acids have?
Even number of carbons
What is the immediate precursor of fatty acids?
Acetyl-CoA
What does the biosynthesis of fatty acids start with?
Glucose