Orgo 2 Test 2
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Naming oxygen sandwiched between two groups
R1 R2 Ether
Naming ether with other functional groups
use ____ oxy as functional group
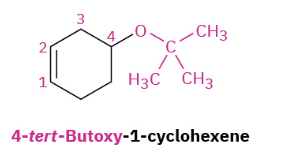
Williamson Ether Synthesis

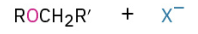
Sn2 rxn
Alkoxymeryuration/demercuration
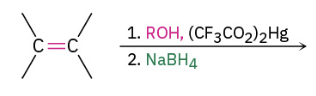
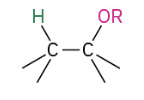
The OR group ends up on the more substituted side.
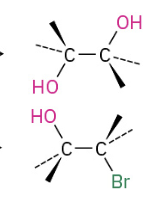
Cleavage by HBR or HI
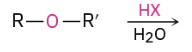
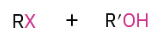
O grabs H and creates great leaving group. X then attacks less hindered side
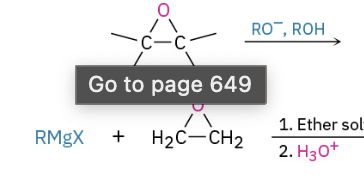
Base Catalyzed Epoxide Opening (attacks less substituted side)
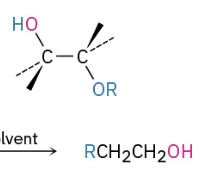
Acid Catalyzed Opening (attacks more substituted side)
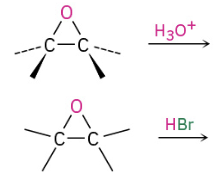
Sn2 Backside attack when 1 or 2 (if 1 and 2 will attack less substituted)
If tertiary present will attack the tertiary
Synthesis of Thiols using thiourea
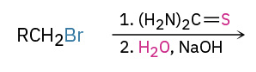
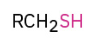
Sn2 displacement where S attacks
Oxidation of Thiols
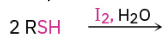

Can also work with H2O2 or other mild oxidizers
Reversible using Zn and H+, or FADH2
Synthesis of sulfides
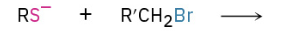
S- can be stablized with Na+
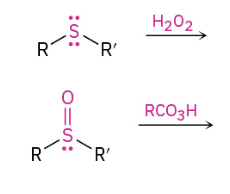
Oxidation of sulfides
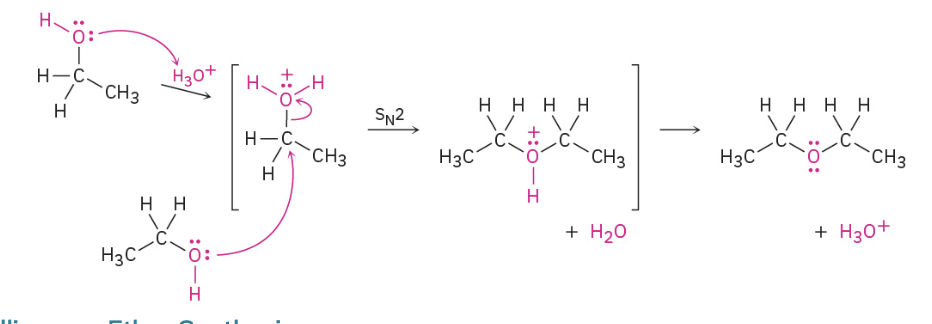
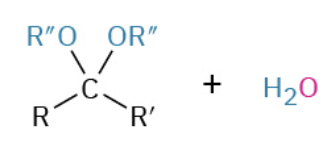
Preperation of ethers from alchohol
ROH + R’OH with acid-catalyzed rxn. Kicks off one OH and uses Sn2 Method to join
Prep of epoxide from alkene using Oxygen
O2
—>
Ag2O
300˚C
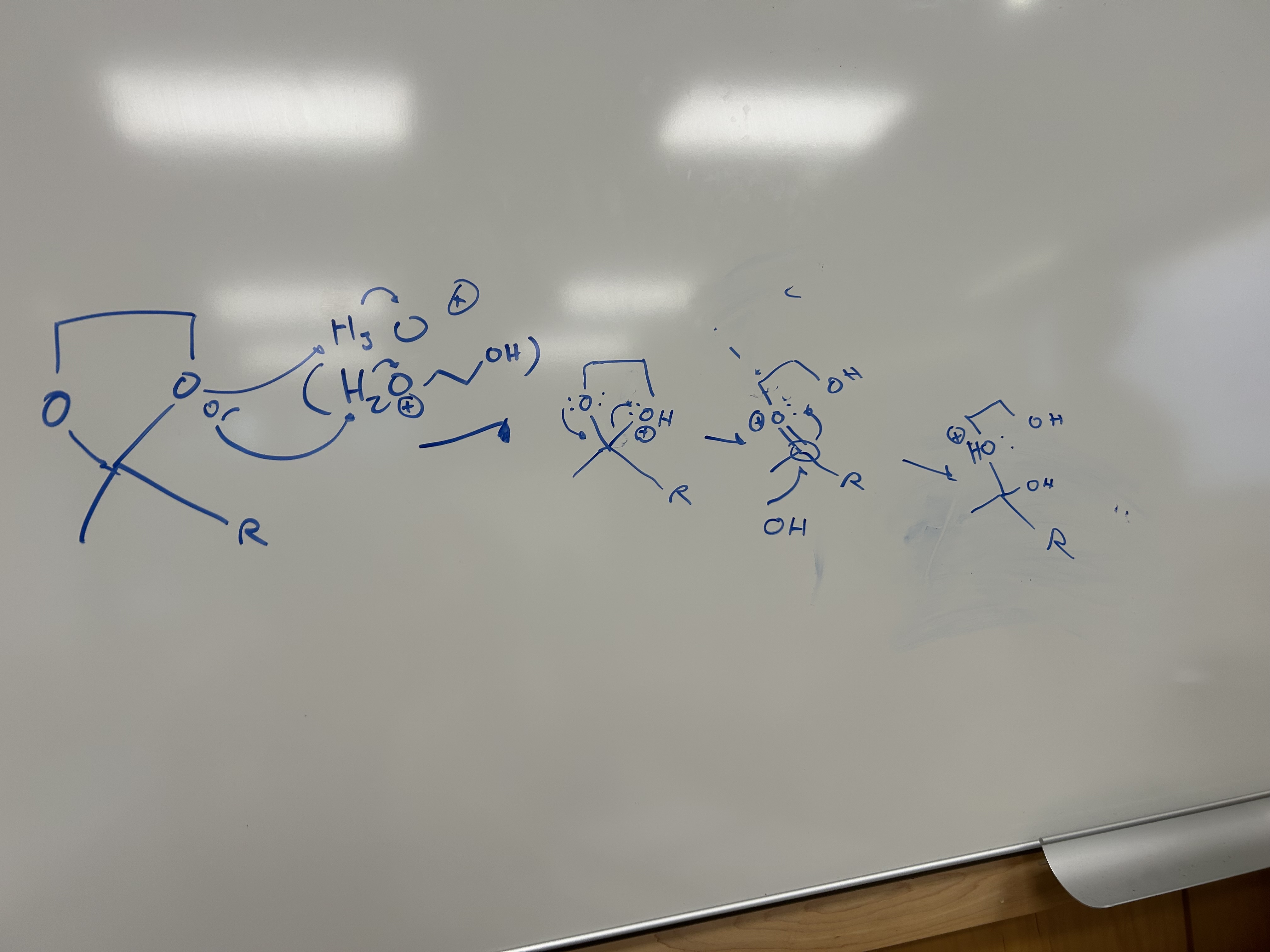
Prep of epoxide from alkene using peroxyacid
RCO3H
—>
CH2Cl2
Naming if have SH group (mercaptan)
thiol if primary substituant, n-meracpto… if part of multiple group molecule
Acetal mechanism (two OR groups)
Acid H attacks OR group, creating good leaving group
OR group leaves and other becomes double bond
Conj base (H2O) attack O=C (electrophilic carbon)
Repeat acid protinaton and group leaves forming ketone
MCPBA with Alkene
Epoxide

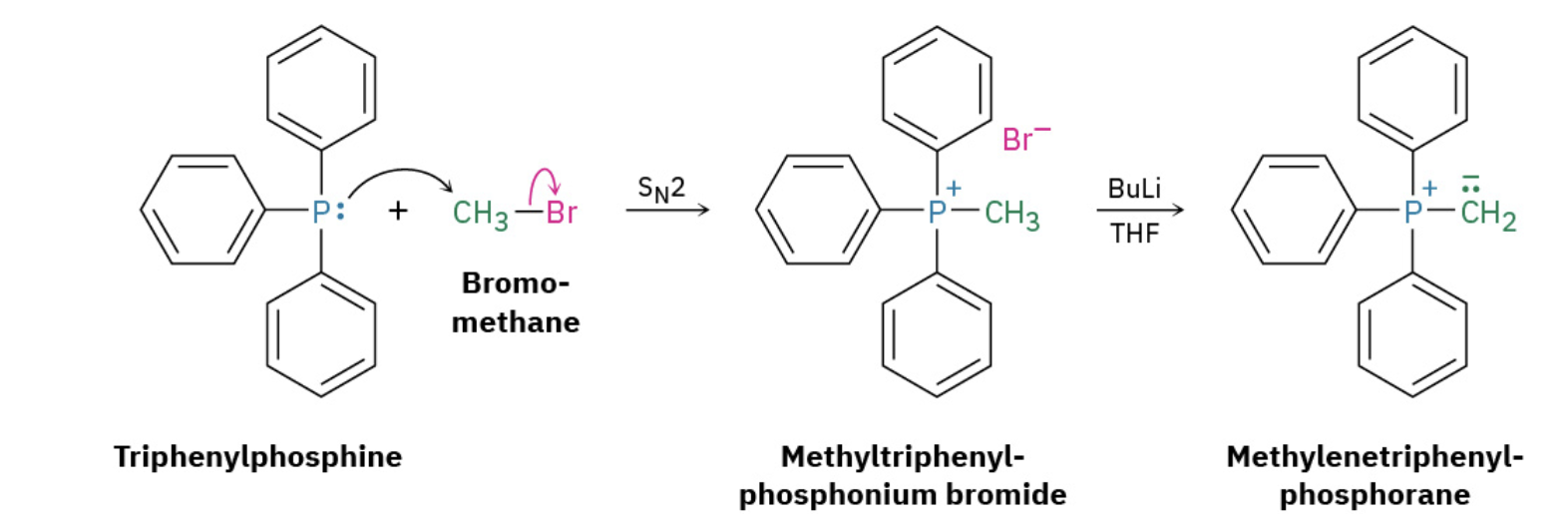
Formation of R-PPh3 (2 step)
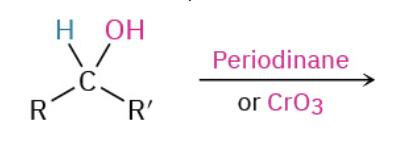
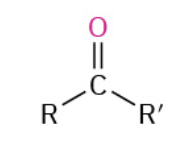
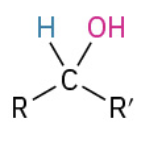
Oxydation Primary Alc
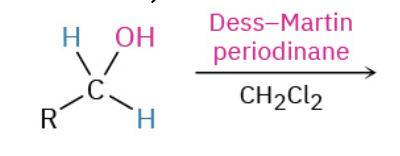
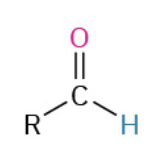
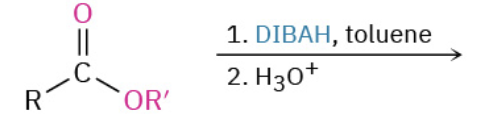
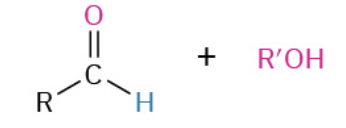
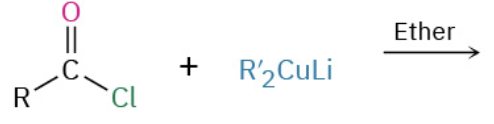
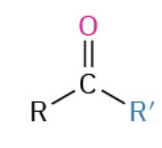
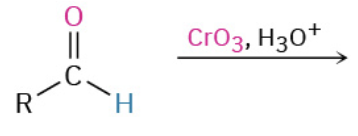
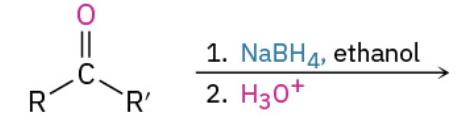
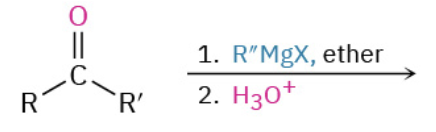
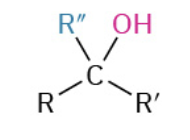
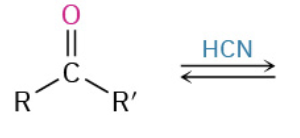
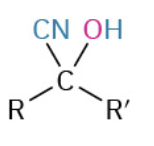
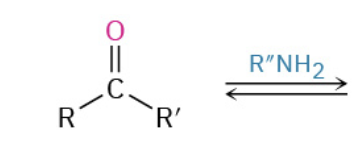
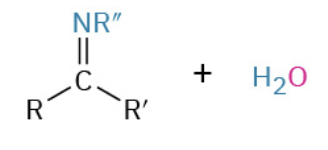
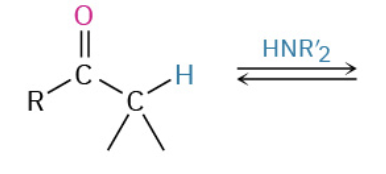
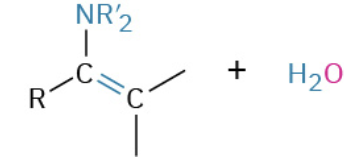
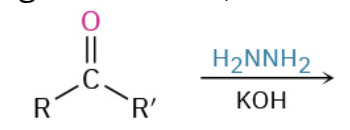
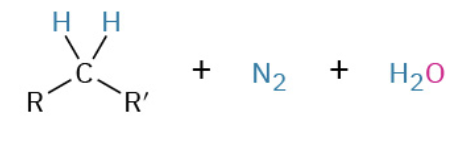
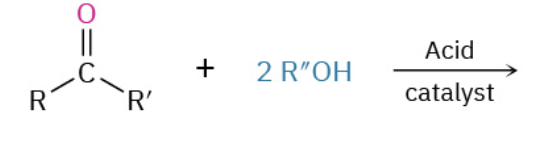
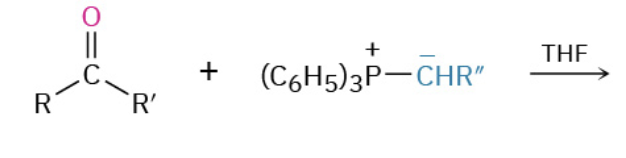
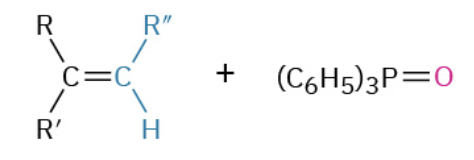
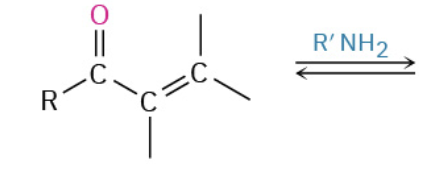
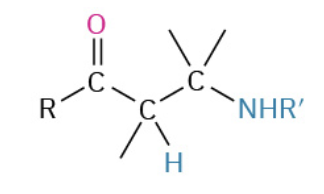
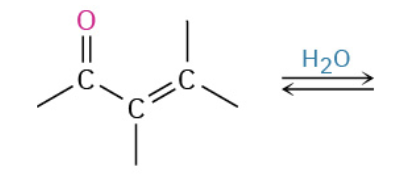
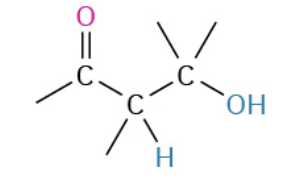
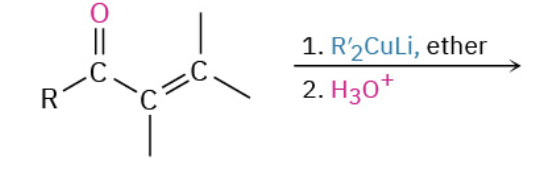
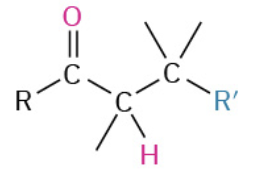
Nucleophiles that participate in 1,4
Amines (NH2)
CN-
RS-
Enolates (- charge O + C that resonate)
Orgaocuperates
enamines (—NH—)
Alkene
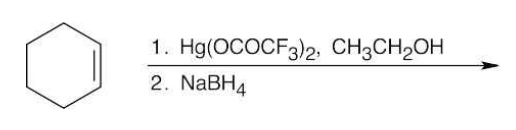
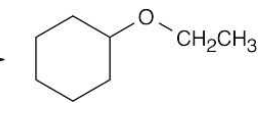
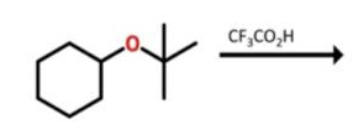
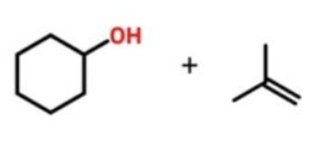
Naming of
carbox Acid
Dioic Acid
Nitriles (CN)
e replaced with oic acid (propanoic acid)
add diol acid (propanediol acid)
Add nitrile to hydrocarbon (ethane nitrile) replace ic or oic acid *acetonitrile),
Also cyano substituent (2-cyanopropanoic acid)
Pka
ethanol
Phenol
Acetic Acid
16
10
5
Factors that influence acidity ranked
Bond strength (HF stronger than HI)
Electronegativity (more EN means more stable conj base)
Resonance (more resonance spreads charge)
Hybridization (More S character means stability as closer to nucleus)
Inductive and Field Effects (having a carbon bonded to 3 carbon makes more acidic)
Henderson-Hasselbalch eq (Pka as it relates to carbox acid)
Carbox acids mostly exist in deprot form
Oxidation to Alchohol to carbox acid
Strong Oxidizer KMNO4 or H2CrO4
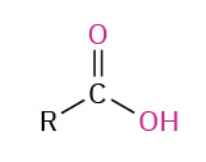
Oxidation Aldehyde
Na2Cr2O7/H2SO4, KMnO4, CrO4, Tollens’ (Ag), Benedict Reagent (Cu) specifically for aldehyde to carboxylic acid
Oxidation benzylic CH containing group + KMNO4
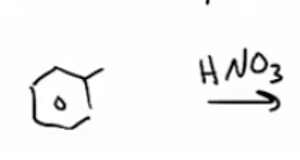
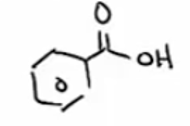
KMnO4 with HNO3 will cleave any R group
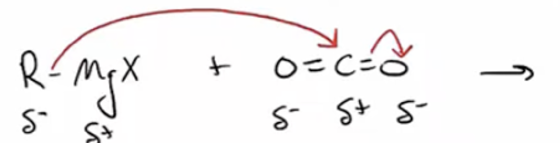
Grinard, Organolithium, or organosodium reagents with CO2
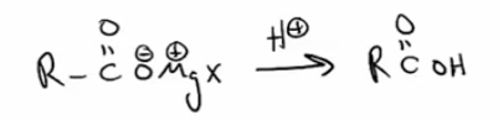
Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of nitrile
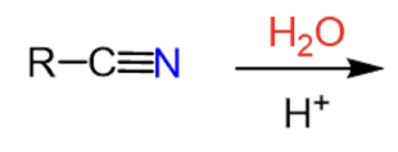
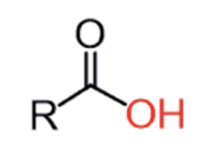
Ozonation of alkene followed by oxadative workup or H2O2
Carbox Acid
Ozonation of alkene followed by Reductive workup (DMS or Zinc)
Ketone or Aldehyde
Hydrolysis under acidic conditions
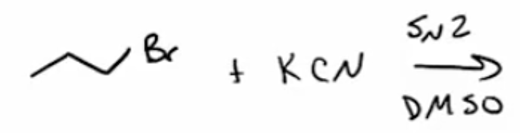
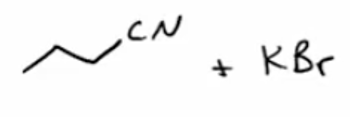
Dehydration of amides to nitriles
RCONH2 —>
Use SOCl2, P4O10, or POCL3
RCN