Topic 19 - Rivers
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
what are fluvial processes?
this refers to all flowing water on Earths surface. ex: rivers, stream, floods, runoff
what is alluvium?
Rock material that has been deposited by moving water
what is base level?
the deepest level that a river can cut down to
what is temporary base level?
a smaller body of water such as a lake
what is the ultimate base level?
the ocean, sea level
what is downcutting?
making the river bigger and wider/eroding

what is a graded stream?
a river that is now down-cutting, it is at equilibrium. Now the river erodes side to side.
Rivers are great agents of …
erosion and movers of sediment
what is transportation?
carrying its load, material in transport
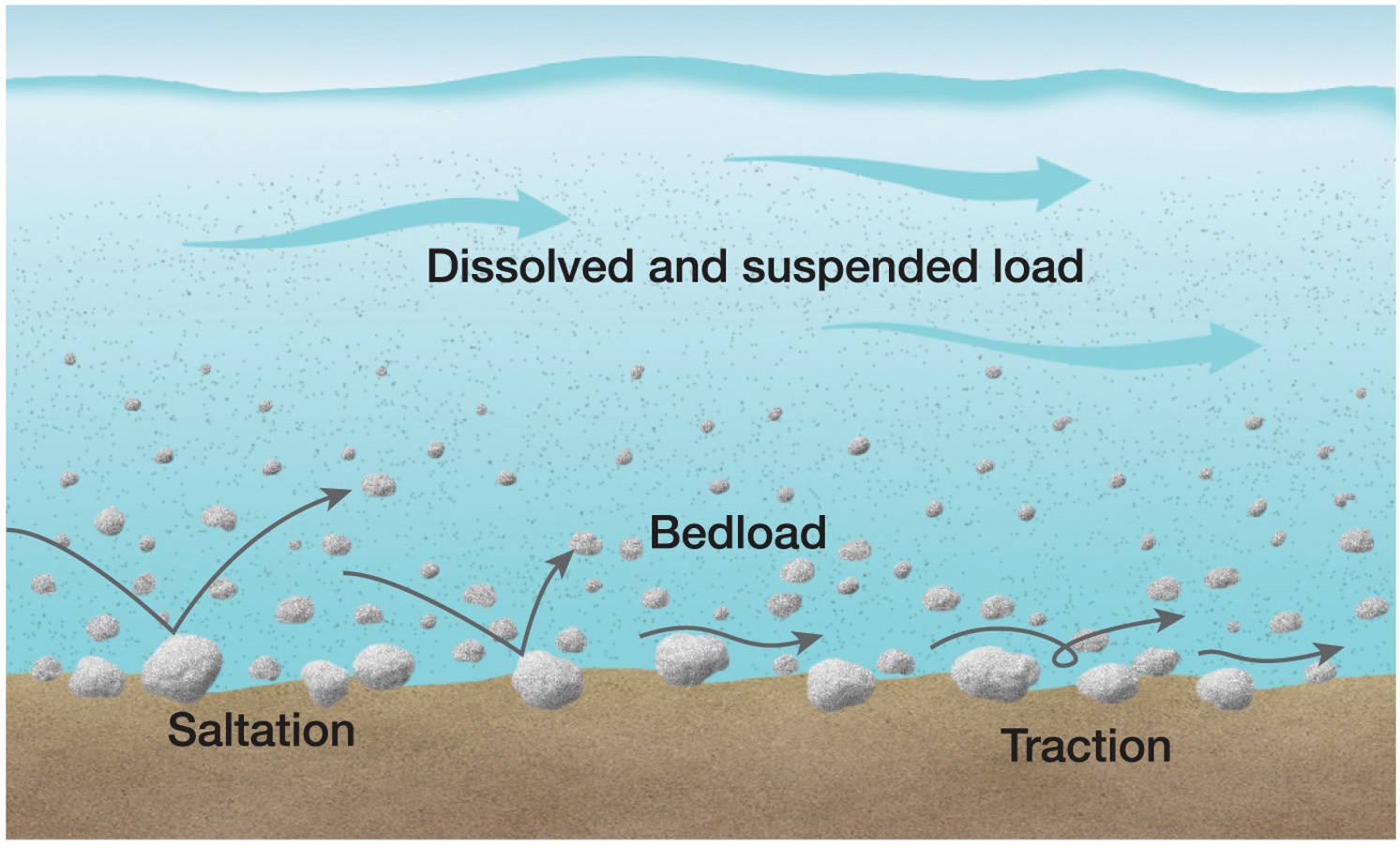
What are the three different ways that sediment transports?
suspended, dissolved and bedload
what is suspended transport?
the material is in the water column
what is dissolved transport?
the minerals are dissolved in the water
what is bedload transport?
moving along on the river floor, the big pieces that get pushed and shoved along
what is stream patterns?
the actual shape of the river channel
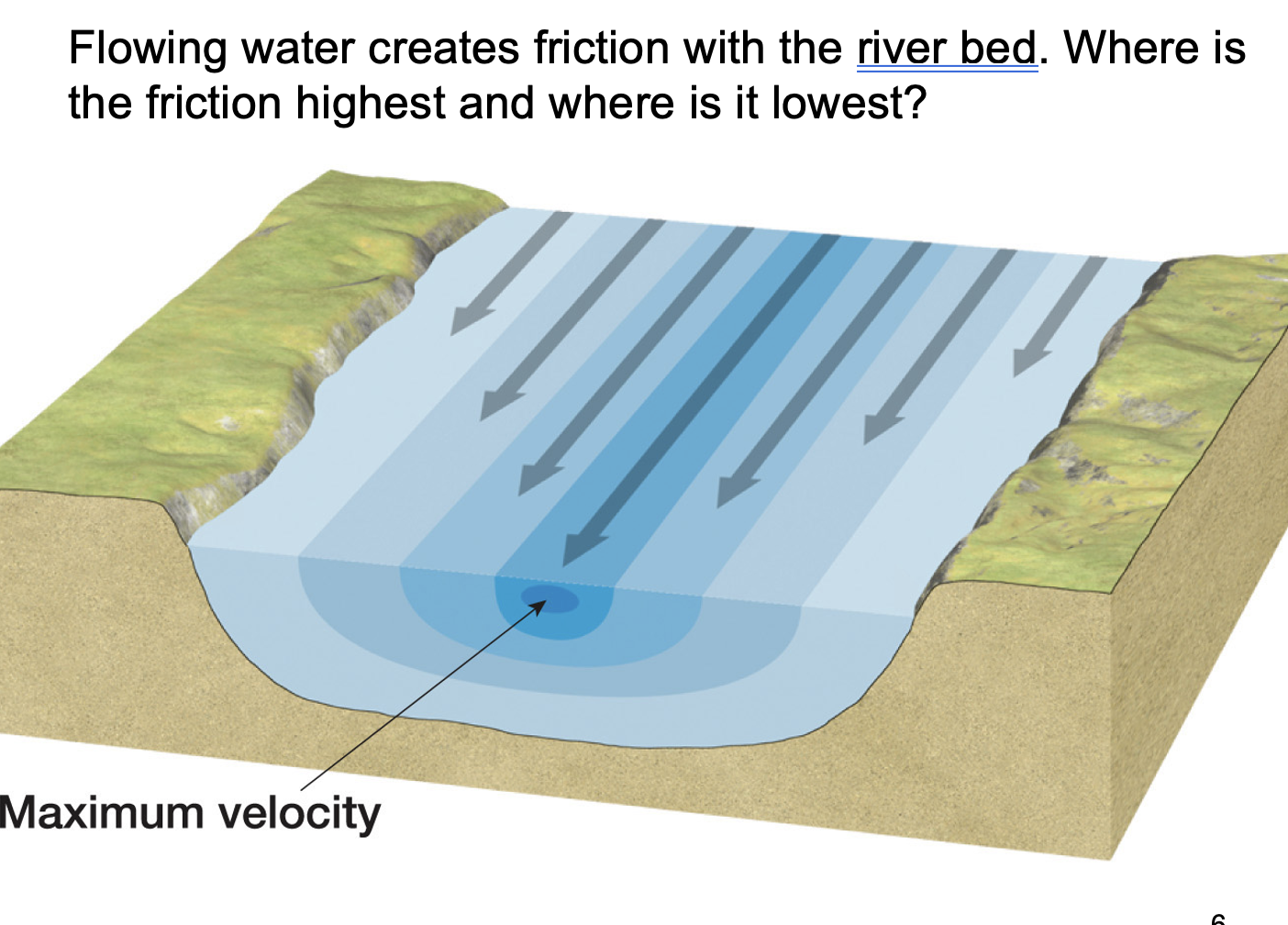
what is a straight stream pattern?
very rare, these don’t last, erosion takes over. Along the sides and the bottom the friction is higher
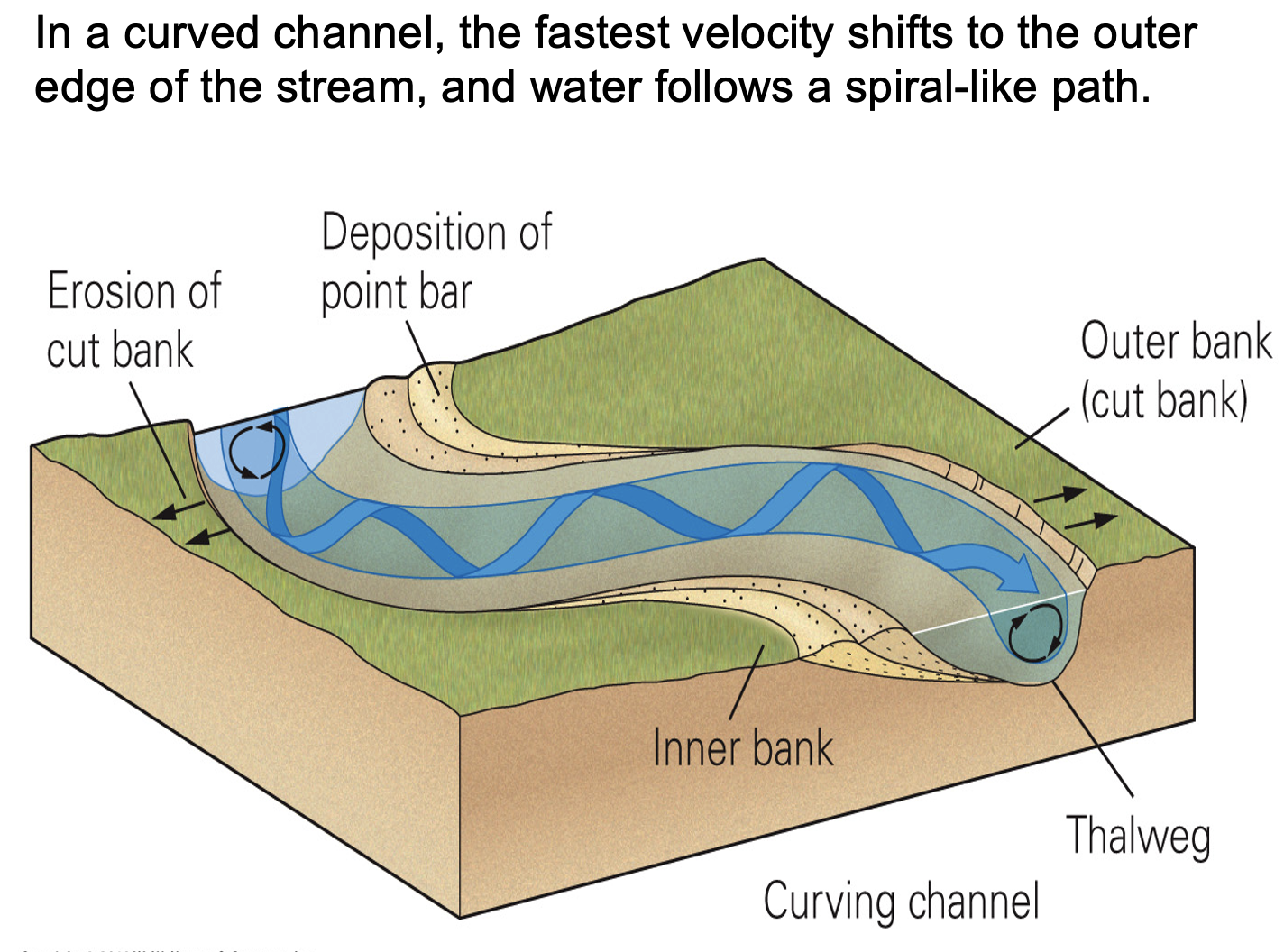
what is meandering?
Not stationary, shape migrates due to velocity changes and erosion
what is meander?
is an s-shaped bend in a river
where does erosion occur on a meandering curve?
Erosion occurs on the outside of the bend – makes wider
where does deposition occur on a meandering curve?
Deposition occurs on the inside of the bend – sediment gets deposited
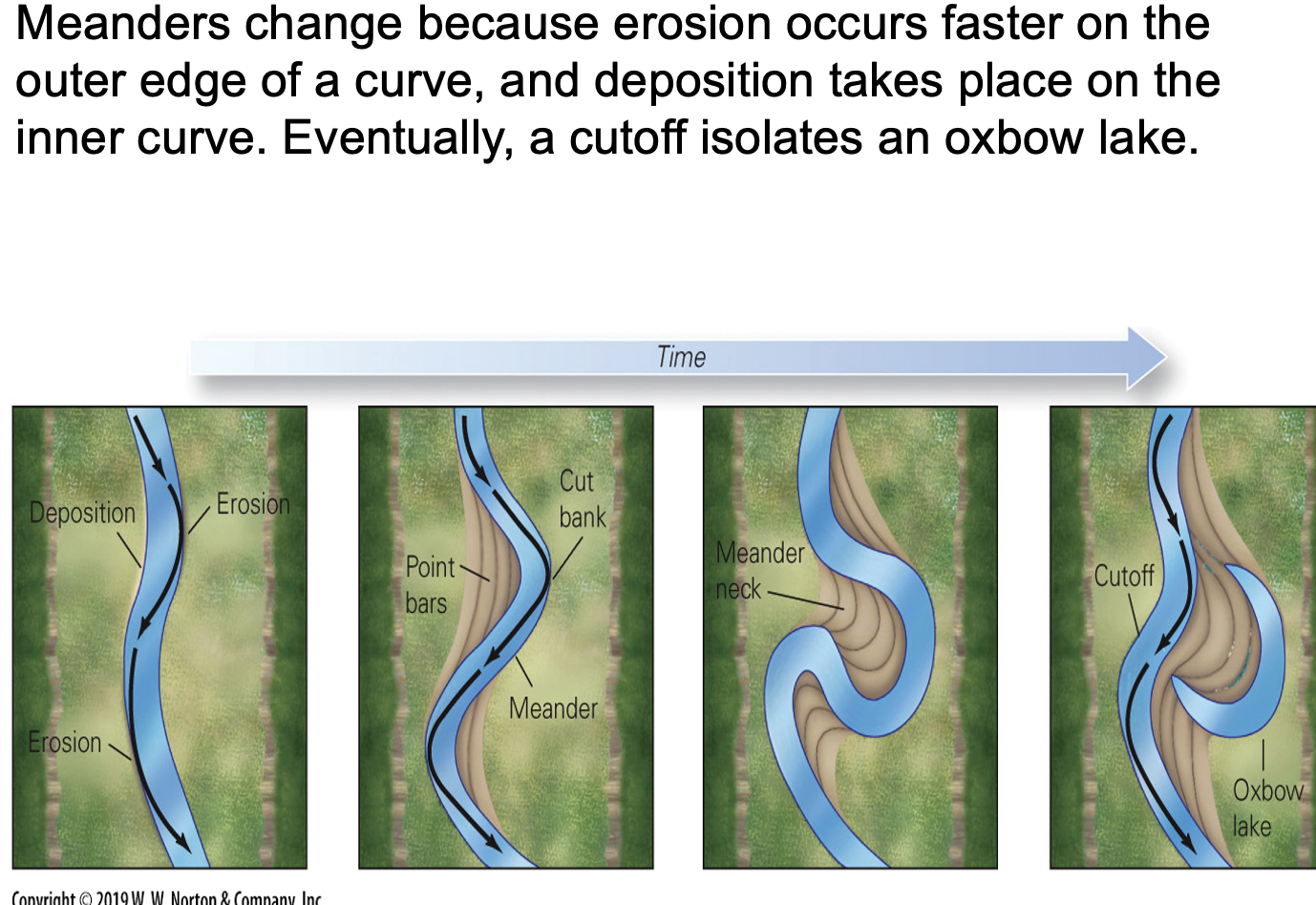
what are oxbow lakes?
Form when two meander bends meet and the bend gets cut off

what are point bar deposits?
form on the inside of the meander bend, deposits of sand and gravel

what is braided?
Forms when the sediment load is really high. The river is choked with sediment
where are braided rivers common?
Common in areas where glacial ice is melting – glaciers contain sediment/rocks
how does the discharge from braided streams vary?
discharge varies from v. low to v. high - such as during spring melt from glaciers and then winter when little to no water flows out
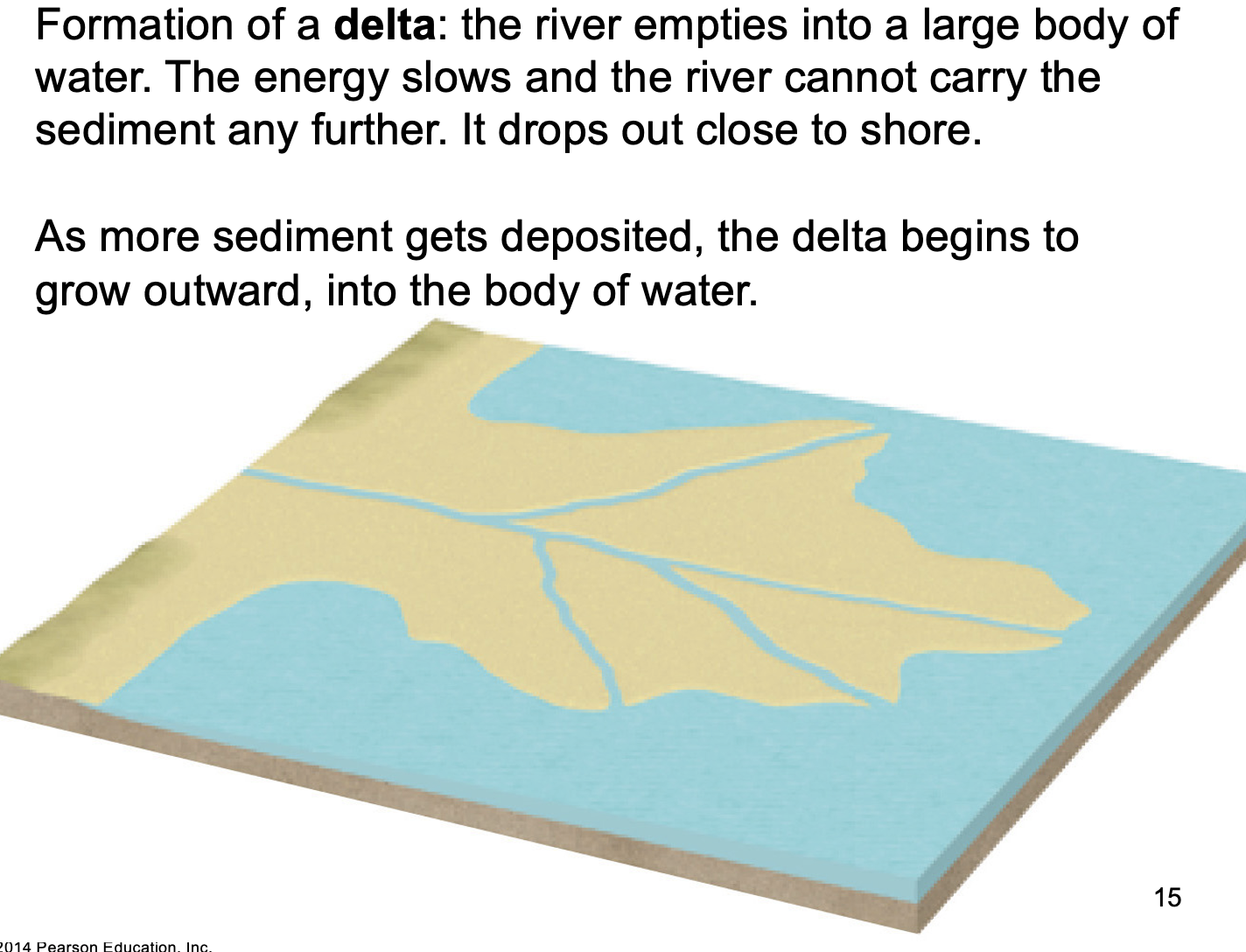
At the end of a river, if it flows into a body of water what forms?
a delta forms

If it flows out from a mountain stream onto the flat plain below, you get an?
alluvial fan
what is a basin?
the land area that contributes water to a stream - all water has a destination
what is a divide?
an imaginary line separating one basin from another

what is the continental divide?
on the west side; rivers empty into the Pacific Ocean. on the east side, they empty into the Gulf of Mexico
Ultimately rivers become organized into a…
pattern or net
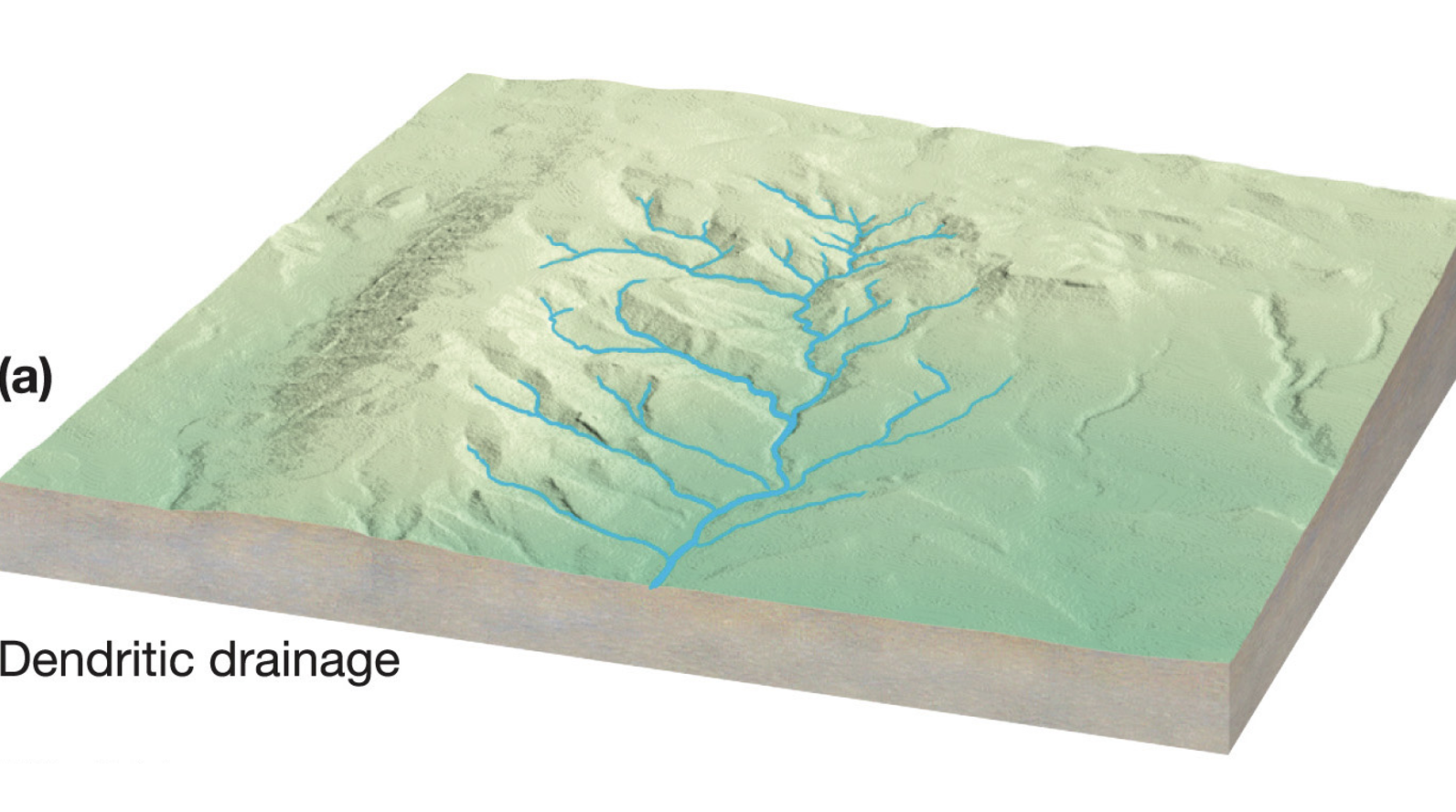
what is dendritic?
This rivers pattern forms when the geology is uniform, relatively flat-lying and looks like tree branches

what is rectangular?
this river pattern forms when the rock layers are cracked and jointed

what is radial?
this pattern is like spokes on a bicycle wheel, they spread out from a central point and forms around mountain peaks

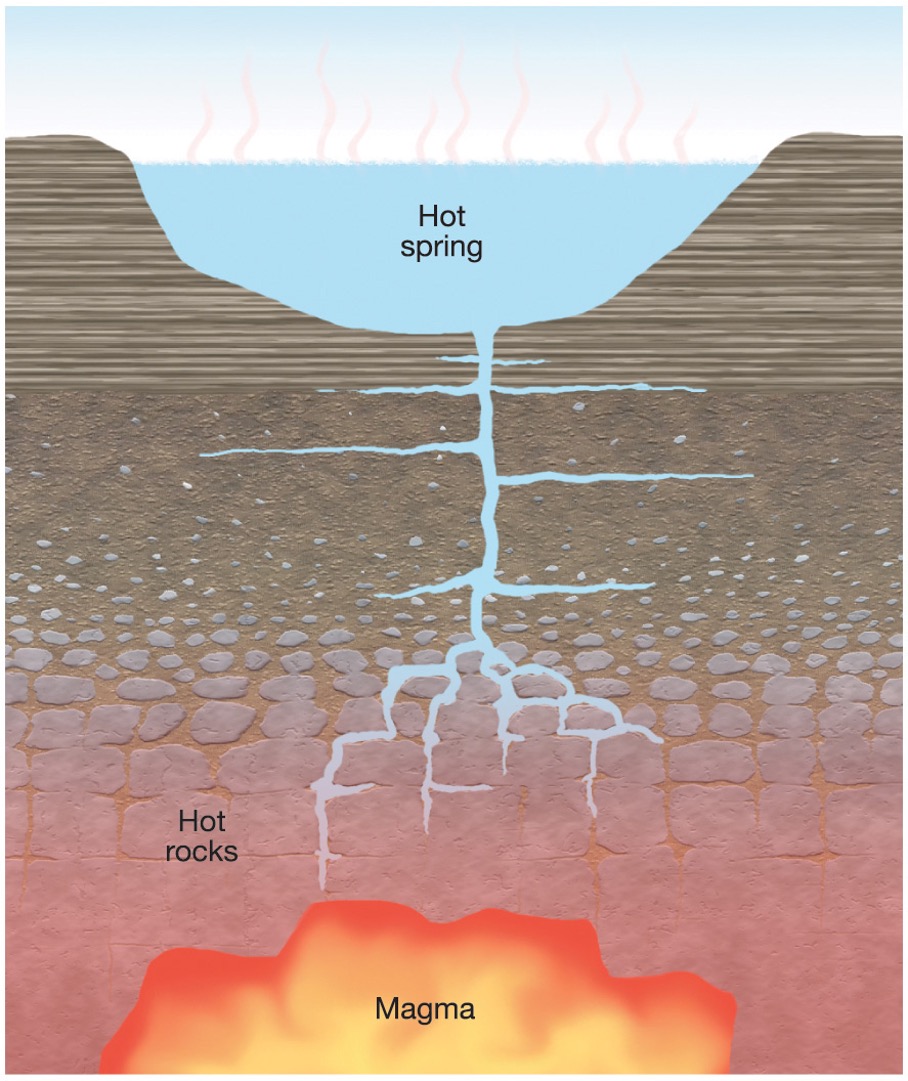
what are hot springs and geysers?
places where really hot water comes out of the ground
where are most hotsprings and geysers located?
concentrated in the western U.S. The Western U.S has most igneous activity, cooling igneous rock below the surface provides the heat
what is Yellowstone National Park?
is essentially above a hot spot. Large magma chamber beneath the surface. Providing thermal energy needed to heat the ground water.
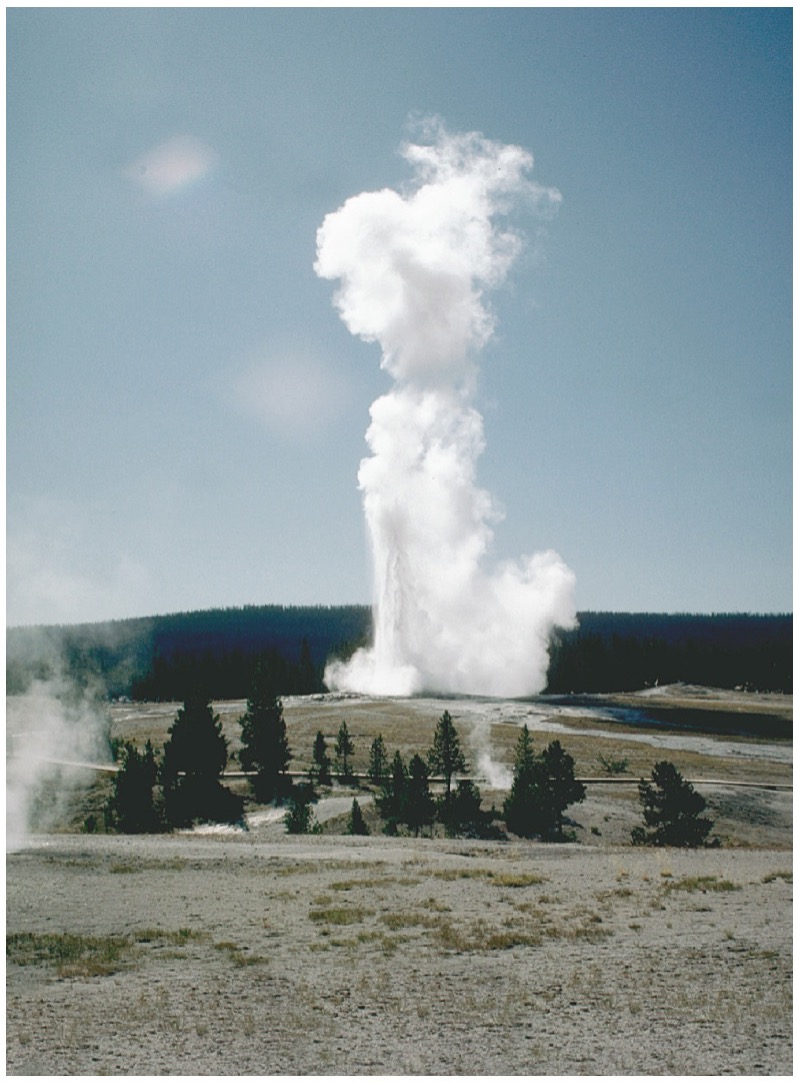

what is a geyser?
intermittent hot springs
how does a geyser erupt?
1)cool water comes in, 2)heated by surrounding rock, 3) overlying water creates great pressure - so the boiling point is greater than 2120 F. 4) the temperature increases. 5) water expands and some water flows out at the surface. 6) pressure then decreases, which in turn causes the boiling point to decrease. 7) some of the water turns to steam and 8) the geyser erupts
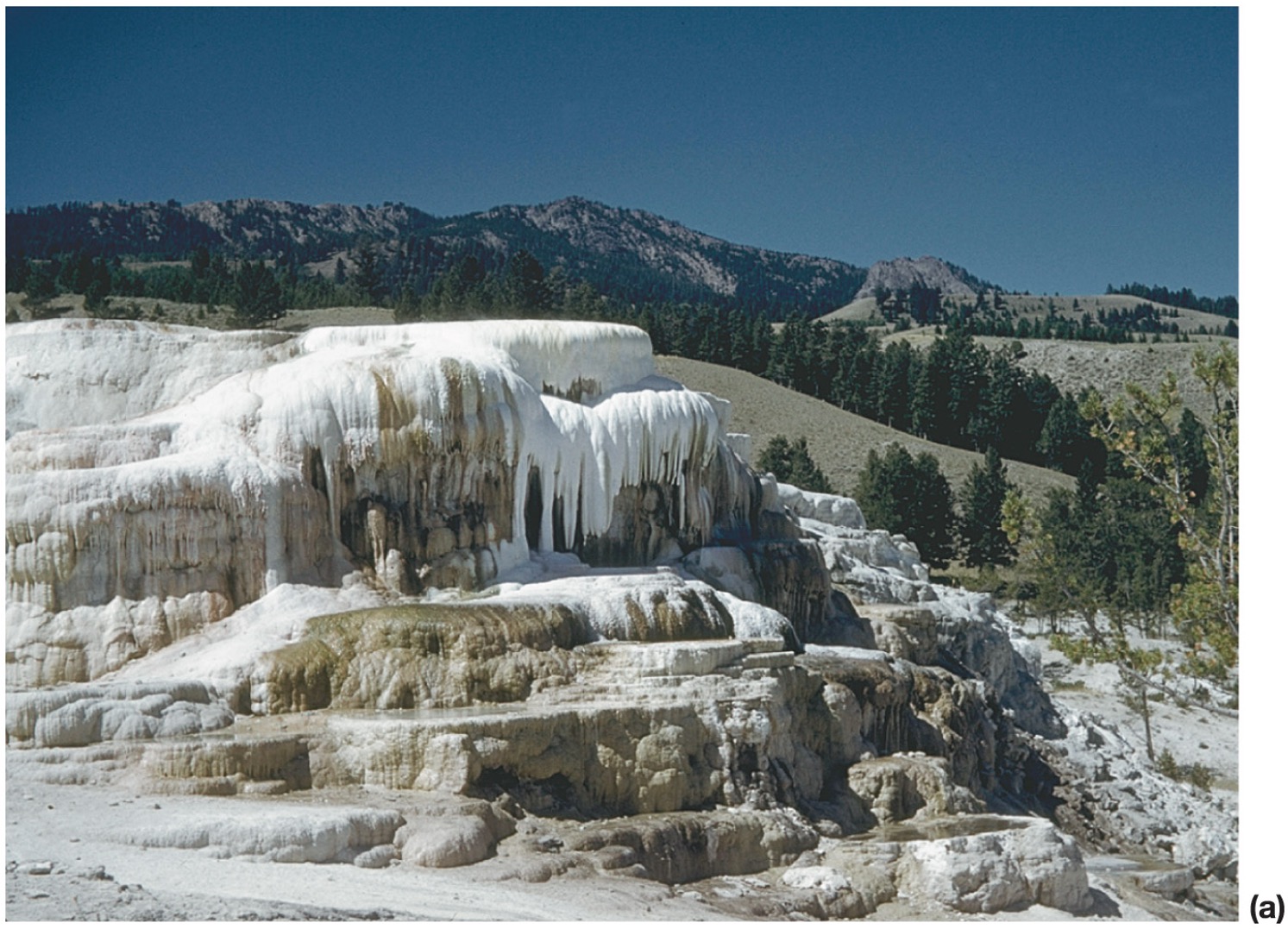

when water that is rich in dissolved minerals and evaporates what happens?
deposits of minerals accumulate

what is a fumarole?
a hot spring that has dried up. Just emits steam