Neoplasms - MedPath
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What does this refer to
Present at or before birth due to developmental anomalies
Etiologies: Genetic mutations, teratogenic exposures, in utero obstruction
May affect kidneys, ureters, bladder, or external genitalia
Detected through prenatal imaging or postnatal symptoms like UTIs, incontinence, or renal dysfunction
Overview of Congenital Conditions
What does this refer to
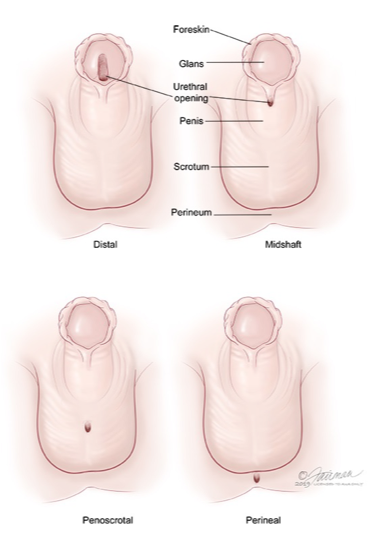
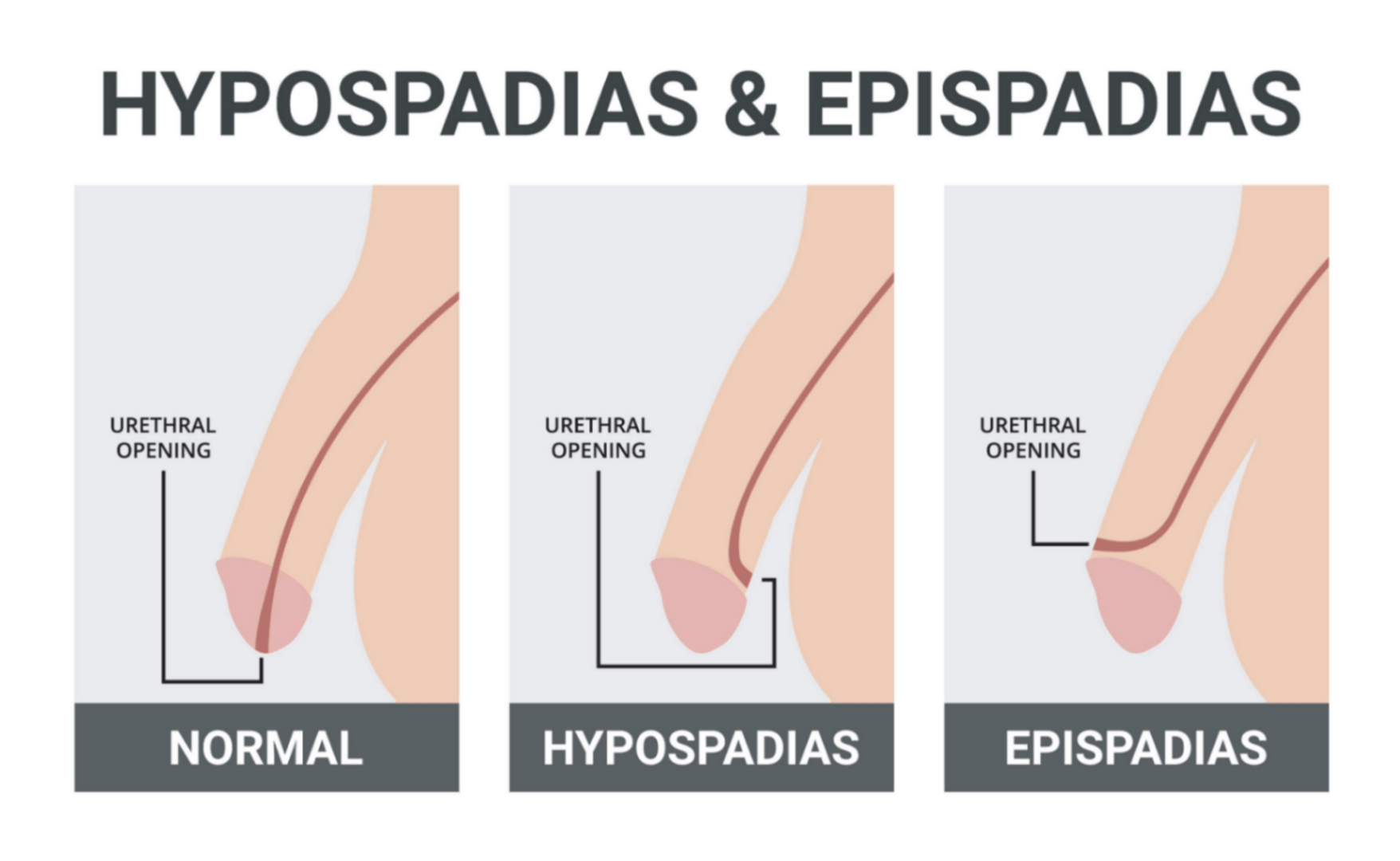
• Urethral meatus opens on the ventral side of the penis
• Pathophysiology: Failure of urethral folds to fuse during fetal development
• Clinical: Abnormal stream, chordee (curvature), cosmetic concerns
• Managed with surgical repair between 6–18 months of age
Hypospadias
What does this refer to
Urethral opening on the dorsal surface of penis or clitoris
Often associated with bladder exstrophy complex
Pathogenesis: Malposition of genital tubercle
Surgical reconstruction is required for continence and function
Epispadias
What does this refer to
One or both testes fail to descend into the scrotum
Pathogenesis: Hormonal or mechanical disruptions in testicular descent
Increased risk of infertility and testicular cancer
Managed by orchiopexy, ideally before 1 year of age
Cryptorchidism
What does this refer to
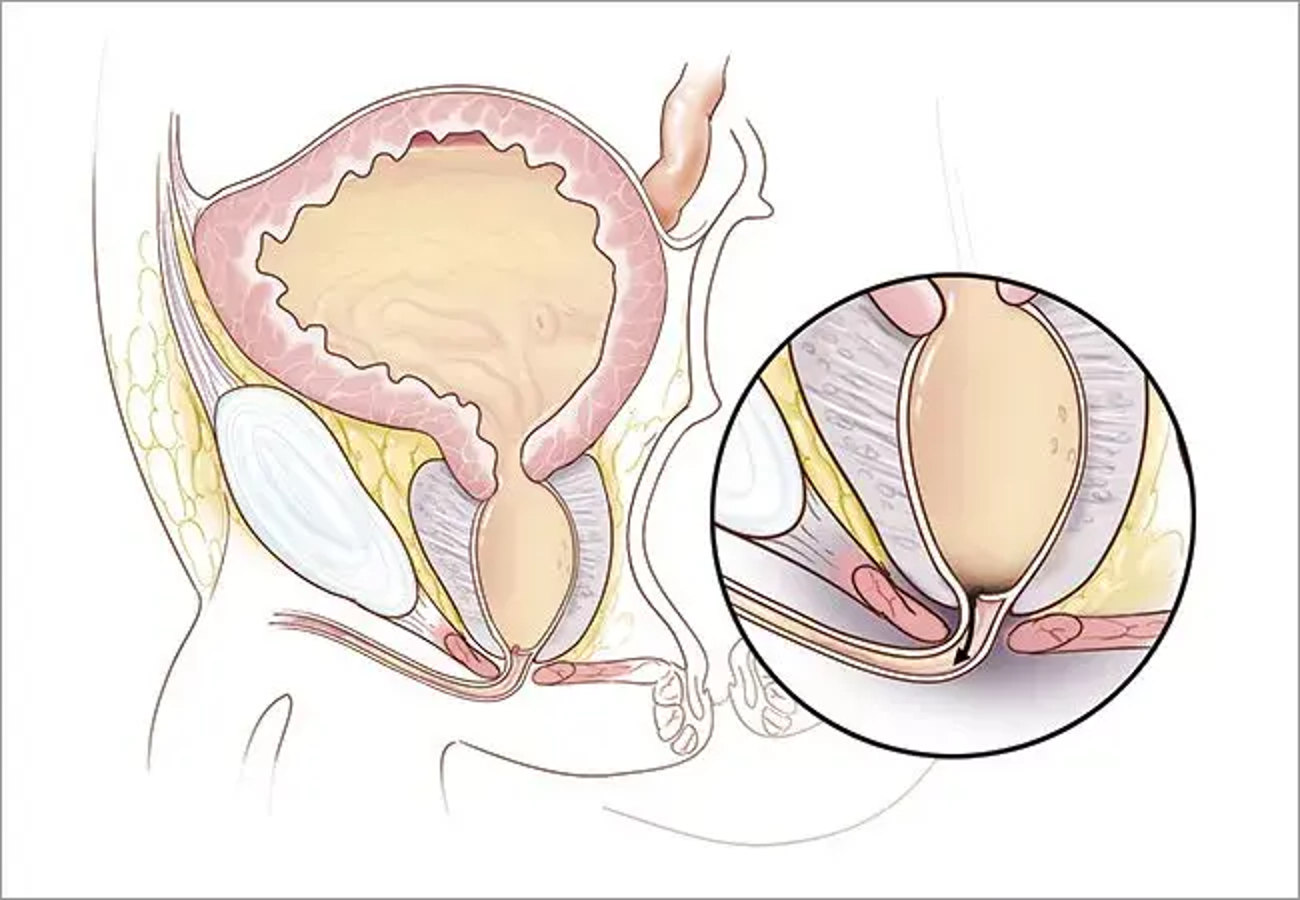
Congenital membranous obstruction in male posterior urethra
Leads to bladder outlet obstruction and progressive hydronephrosis
May cause oligohydramnios and Potter sequence deformities prenatally
Requires catheterization and surgical ablation
Posterior Urethral Valves
What does this refer to
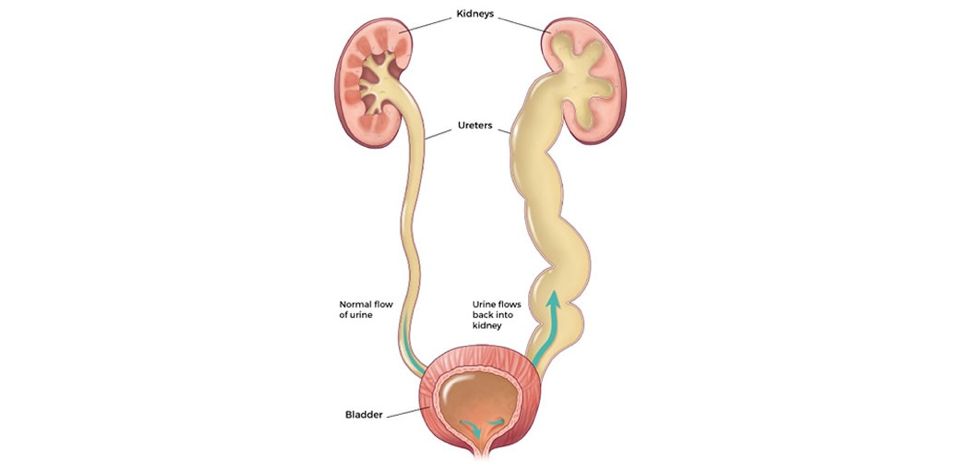
Retrograde flow of urine from bladder to ureters/kidneys
Due to congenital incompetence of vesicoureteral junction
May result in recurrent pyelonephritis and renal scarring
Diagnosed via voiding cystourethrogram (VCUG)
Vesicoureteral Reflux (VUR)
What does this refer to
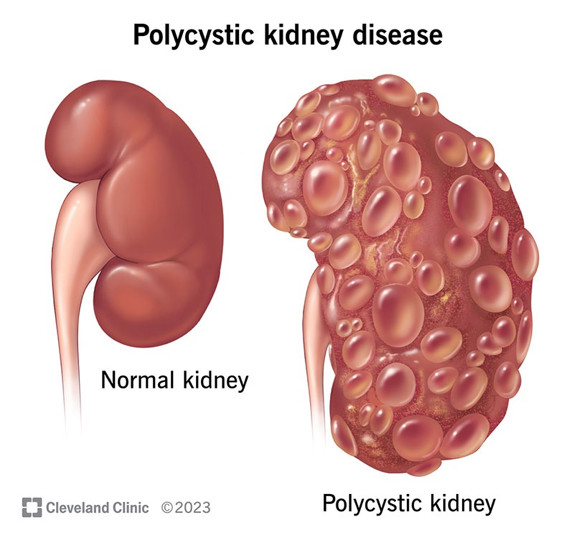
Genetic disorder causing multiple renal cysts
ADPKD: presents in adulthood; PKD1/PKD2 mutations
ARPKD: presents in infancy; associated with hepatic fibrosis
Leads to progressive renal failure, HTN, and cyst rupture
Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD)
What does this refer to
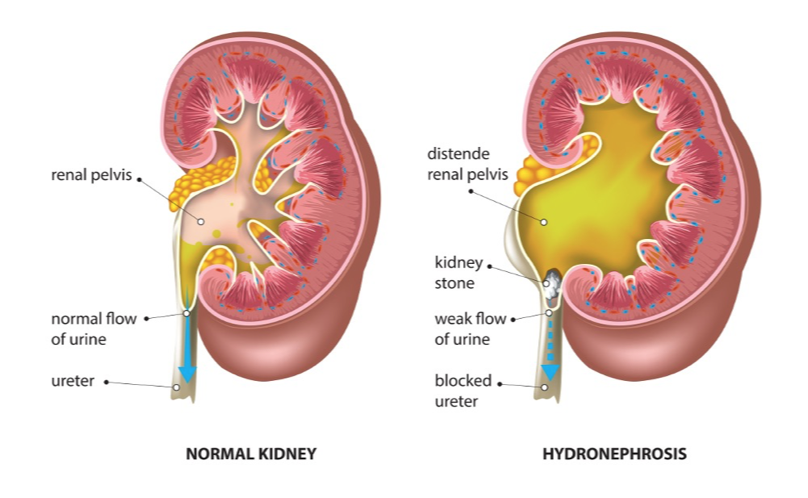
Dilation of renal pelvis/calyces due to outflow obstruction
Can be congenital or acquired
Chronic backpressure leads to ischemia and atrophy
Imaging: ultrasound shows fluid-filled renal pelvis
Hydronephrosis
What does this refer to
Seen in patients on long-term dialysis
Pathophysiology: hyperplasia of renal tubules with cyst formation
Increased risk of renal cell carcinoma
Regular imaging recommended for surveillance
Acquired Renal Cystic Disease
What does this refer to
Obstruction → Pressure buildup → Ischemia → Atrophy
Reflux → Infections → Inflammation → Scarring
Genetic mutations → Abnormal morphogenesis → Functional impairment
Pathophysiologic Themes
What does this refer to
Prenatal US: detects hydronephrosis, oligohydramnios
Postnatal US: structural evaluation
VCUG: reflux and urethral abnormalities
CT/MRI: stone, abscess, masses
Diagnosis and Imaging
What does this refer to
Surgical: hypospadias repair, valve ablation, orchiopexy
Medical: antibiotics, anticholinergics, dialysis
Long-term: monitor renal function, manage complications
Treatment Approaches
What does this refer to
Arise from diverse tissues: epithelium, muscle, germ cells
Include both benign (e.g., oncocytoma) and malignant types
High morbidity and mortality if not detected early
Risk factors: genetics, toxins, infections, hormones
GU Neoplasms
What does this refer to
Originates in renal tubular epithelial cells (usually proximal tubule)
Clear cell RCC: most common, VHL gene inactivation → ↑HIF → ↑VEGF
Papillary RCC: MET gene mutations
Symptoms: hematuria, flank pain, palpable mass (classic triad, but rare)
Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC)
What does this refer to
Pediatric malignancy of nephrogenic blastemal origin
WT1 gene (regulates kidney and gonad development) often mutated
Associated syndromes:
WAGR (Wilm’s tumor, aniridia, GU abnormalities, and developmental delays),
Beckwith-Wiedemann ( increased birth weight and height, macroglossia, and an increased risk of childhood cancers like Wilms tumor and hepatoblastoma )
Histology: triphasic pattern—blastemal, epithelial, stromal components
Wilms Tumor (Nephroblastoma)
What does this refer to
Most common in bladder but can arise in renal pelvis/ureters
Initiated by chronic exposure to carcinogens (e.g., tobacco, dyes)
Papillary (low grade) vs. Flat (high grade/CIS) pathways
Genetic alterations: TP53, FGFR3, RAS
High recurrence due to field cancerization
Urothelial Carcinoma
What does this refer to
90% are transitional cell carcinomas
Multifocal origin: entire urothelium at risk
Clinical signs: painless gross hematuria, irritative voiding symptoms
Pathophysiology: dysplasia → carcinoma in situ → invasive carcinoma
Muscle-invasive disease has worse prognosis
Bladder Cancer
What does this refer to
Adenocarcinoma from peripheral prostate glands
Hormone-driven (androgen receptor signaling)
TMPRSS2-ERG fusion gene in ~50%
Graded using Gleason score (pattern-based histologic grading)
Metastasizes to bone: osteoblastic lesions (elevated alkaline phosphatase)
Prostate Cancer
What does this refer to
Peak incidence: ages 15–35
Seminoma: radiosensitive, slow-growing, ↑placental ALP
Non-seminomas: aggressive, elevated AFP/β-hCG
Cryptorchidism is a major risk factor
Histology and serum markers guide diagnosis and treatment
Testicular Germ Cell Tumors
What does this refer to
Less than 5% of testicular tumors
Leydig cell tumors: androgen excess → virilization, precocious puberty
Sertoli cell tumors: rarely hormonally active
Usually benign but may rarely become malignant
Diagnosis based on hormonal profile and pathology
Testicular Sex Cord-Stromal Tumors
What does this refer to
Squamous cell carcinoma linked to high-risk HPV (16, 18)
Often preceded by penile intraepithelial neoplasia (PeIN)
Risk factors: poor hygiene, phimosis, smoking
Lymphatic spread to inguinal nodes is common
Treatment: surgery, chemo, and/or radiation based on stage
Penile Cancer
What does this refer to
Key Pathways:
renal cell carcinoma in
Von Hippel-Lindau disease-congenital disease of GU tumors
Hypoxia-inducible Factor-protein involved in bladder/kidney CAs
VEGF
Androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer
FGFR3 and TP53 mutations in bladder cancer
Epigenetic silencing (e.g., hypermethylation of tumor suppressor genes)
Immune evasion via PD-L1 (programmed death-ligand 1) overexpression in RCC and urothelial cancers
Molecular Mechanisms in GU Cancer
What does this refer to
• Grading: assesses differentiation
- RCC: Fuhrman nuclear grade
- Prostate: Gleason score (sum of 2 most common patterns)
• TNM Staging: guides prognosis and treatment
- T: local invasion
- N: nodal involvement
- M: distant metastasis
Tumor Grading and Staging
What does this refer to
RCC:
EPO → polycythemia
PTHrP → hypercalcemia
Renin → hypertension
Prostate:
Bone pain, high ALP due to osteoblastic metastases
Bladder:
Rare systemic symptoms like fever, weight loss
Paraneoplastic Syndromes
What does this refer to
Renal tumors: US → CT abdomen w/contrast
Bladder cancer: cystoscopy with biopsy
Testicular tumors: scrotal US → tumor markers (AFP, β-hCG, LDH)
Prostate: PSA + digital rectal exam → TRUS biopsy
MRI, PET for metastasis workup
Diagnosis and Imaging
What does this refer to
Prostate: PSA and DRE (individualized, start age 50 or 40 with risk factors)
Bladder: screening not routine unless high risk (e.g., chemical exposure)
Testicular: self-exam education in young men
Preventive measures: quit smoking, HPV vaccination, avoid toxins
Screening and Prevention
What does this refer to
RCC: partial or radical nephrectomy
Bladder: TURBT (early), cystectomy (muscle-invasive)
Prostate: prostatectomy, sometimes nerve-sparing
Testis: radical inguinal orchiectomy
Penile: partial or total penectomy, lymph node dissection
Surgical Treatment Options
What does this refer to
RCC: resistant to chemo → use immunotherapy or TKIs
Testicular: platinum-based chemotherapy (cisplatin)
Bladder: BCG intravesical therapy for CIS
Prostate: external beam radiation or brachytherapy + ADT
Penile: chemoradiation in advanced cases
Medical & Radiation Therapies
What does this refer to
RCC: TKIs (sunitinib, pazopanib), mTOR inhibitors, checkpoint inhibitors
Prostate: PARP inhibitors (BRCA mutations), androgen receptor blockers (enzalutamide)
Bladder: anti-PD-1/PD-L1 agents for advanced/metastatic disease
Precision oncology is evolving in all GU cancers
Targeted and Immunotherapies