OCR B Geography GCSE Urban Futures
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
urban
refers to areas that have been built by people; towns and cities
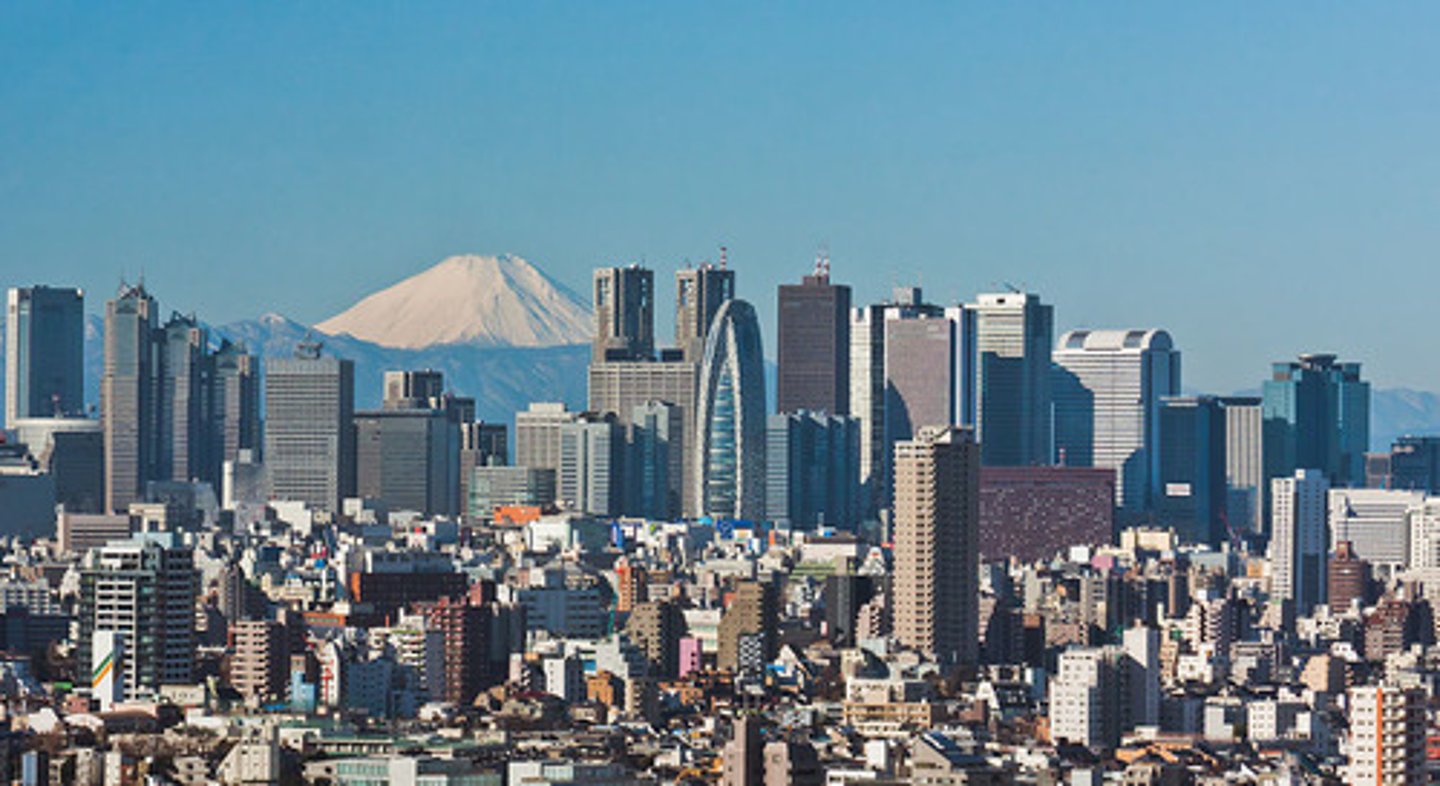

urbanisation
the process of towns and cities developing and becoming bigger as their population increases
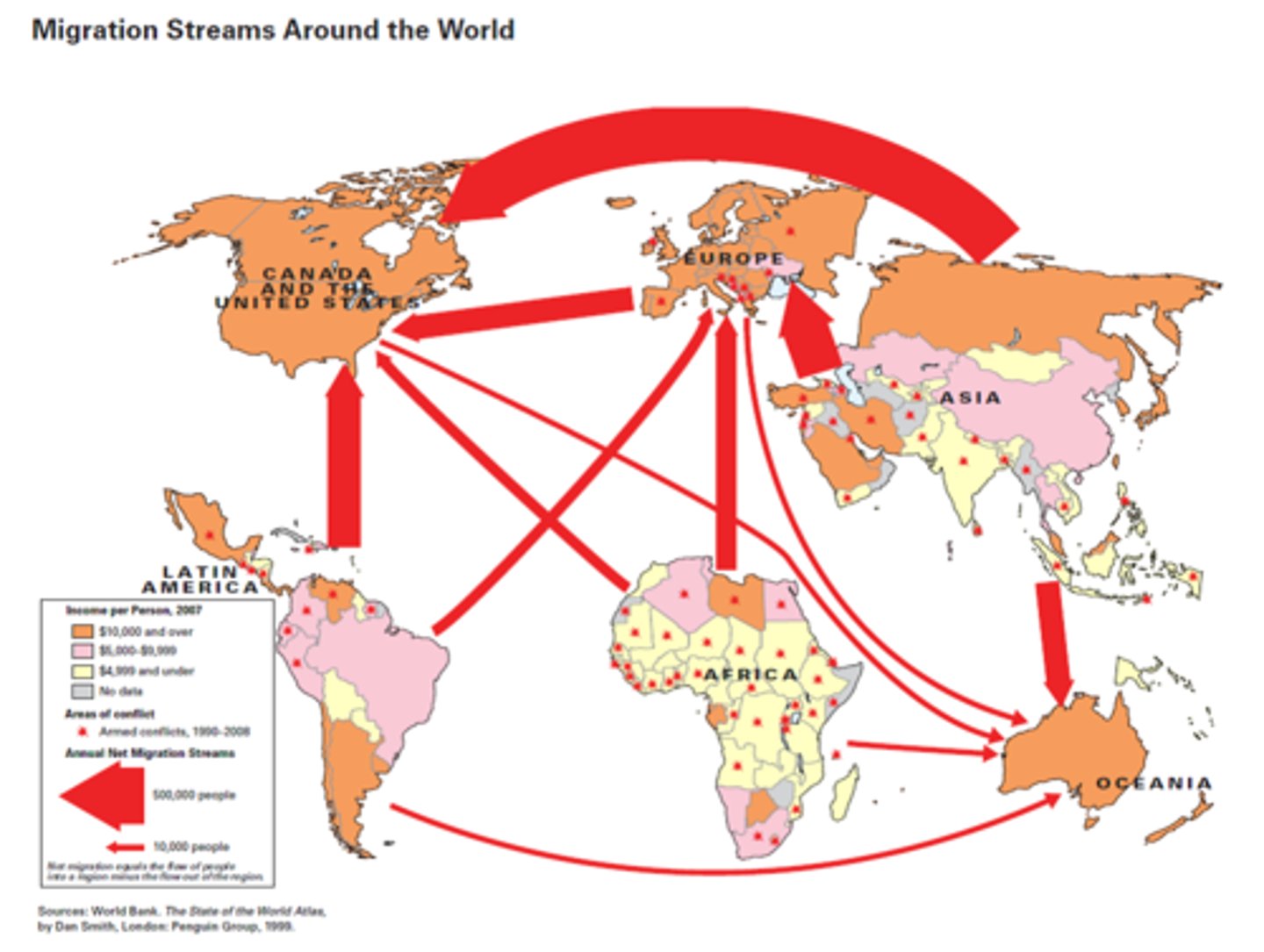
migration
the movement of people from one place to another; may be voluntary or forced, permanent or temporary, domestic or international
internal growth
growth within a city that results from births among the resident population rather than people moving into the city
function
a role performed by something; in the case of a city, this may be administrative or related to a sphere of activity
urban belt
an area of land which has become more urban in character
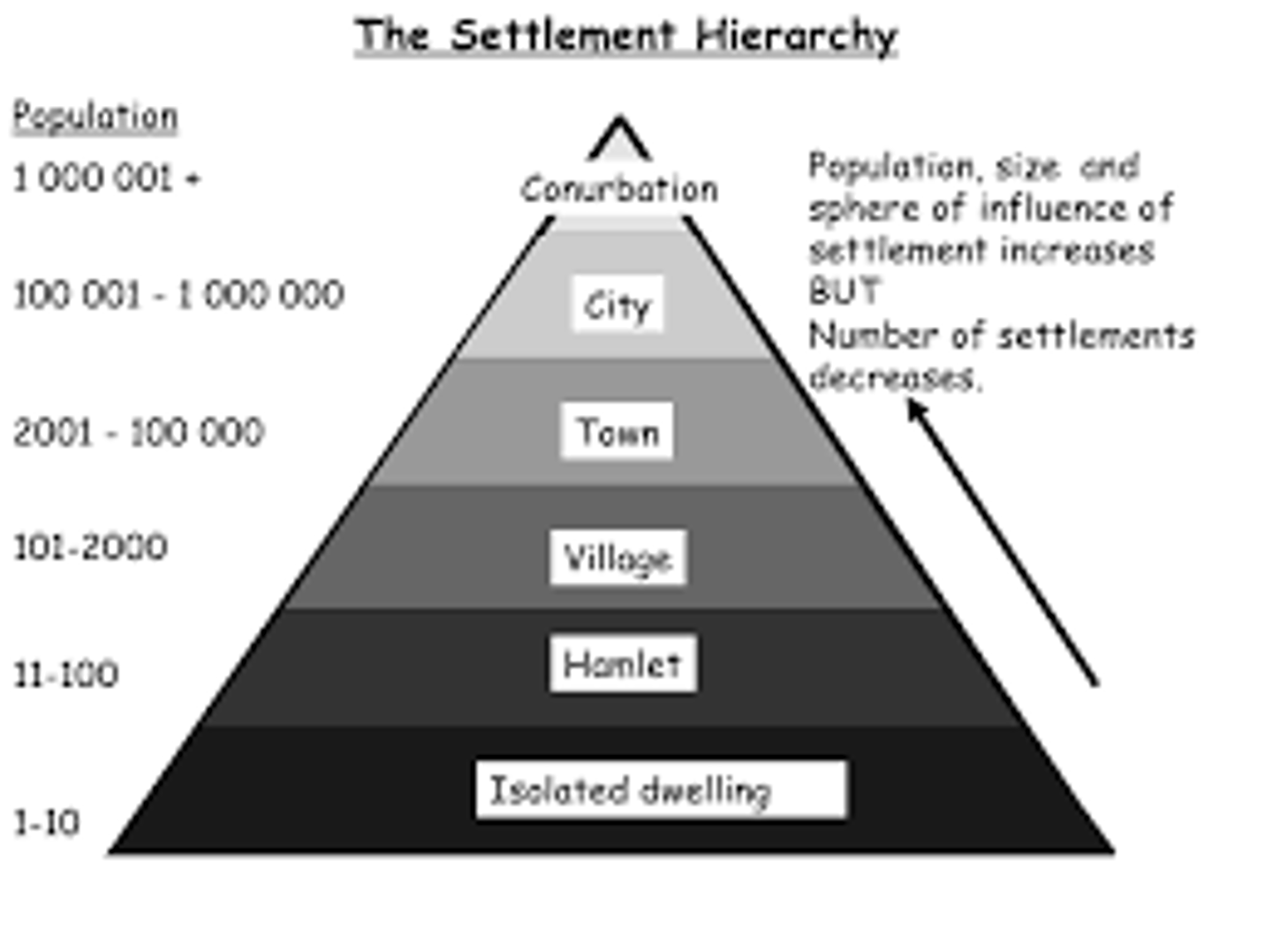
isolated dwelling
the smallest form of settlement
farm
an isolated dwelling involved in agriculture
hamlet
a small collection of dwellings
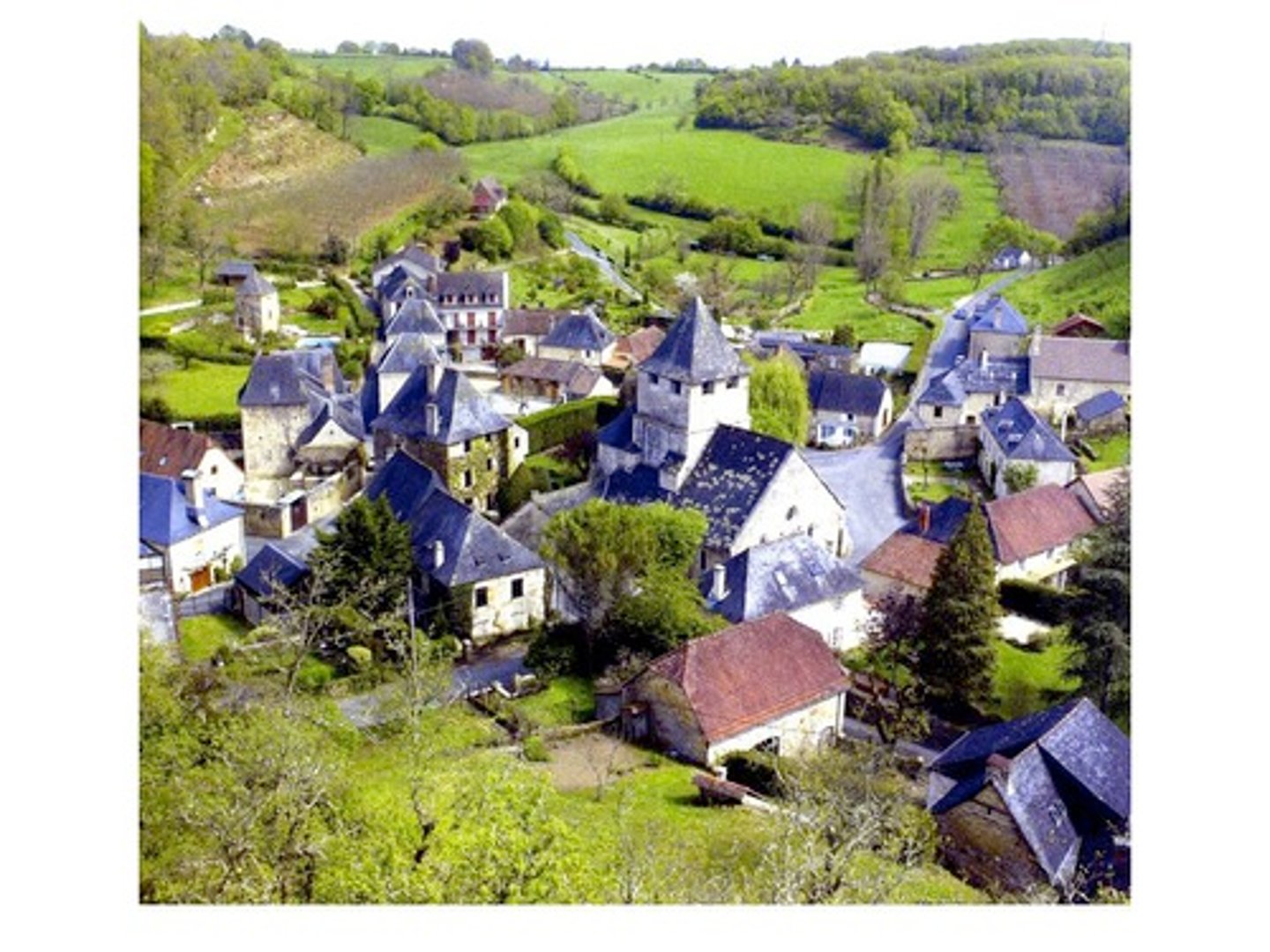

village
a small community, bigger than a hamlet but smaller than a town
town
a settlement which is bigger than a village but smaller than a city
city
a large settlement which a full range of residential, industrial and service functions
conurbation
an extended urban area, typically consisting of several towns merging with the suburbs of one or more cities.
settlement hierarchy
the scale of settlements ranging from isolated dwelling to conurbation
advanced countries
countries that share a number of important economic development characteristics including well developed financial markets, high degrees of financial intermediation and diversified economic structures with rapidly growing service sectors; classified by the IMF
emerging and developing countries
countries which neither share all the economic development characteristics required to be advanced or are eligable for the Poverty Reduction and Growth Trust; classified by the IMF
low-income developing countries
Countries which are eligable for the Poverty Reduction and Growth Trust from the IMF; classified by the IMF
rural-urban migration
movement of people from rural areas to urban areas
megacity
usually defined as a city that has a population of over 10 million, although the exact number varies

world city
a city considered to be an important node in the global economic system, and one which has iconic status and buildings, e.g. London or New York
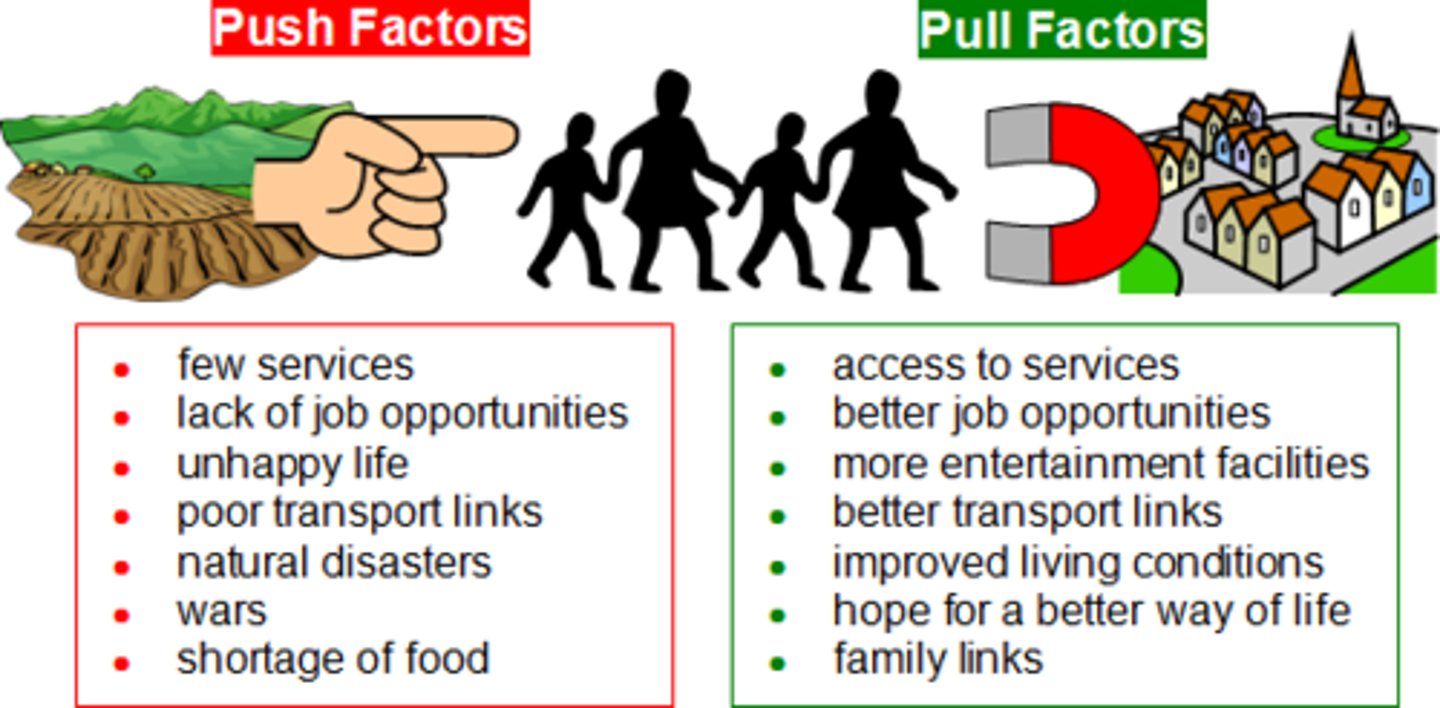
pull factors
a positive factor that attracts people to an area
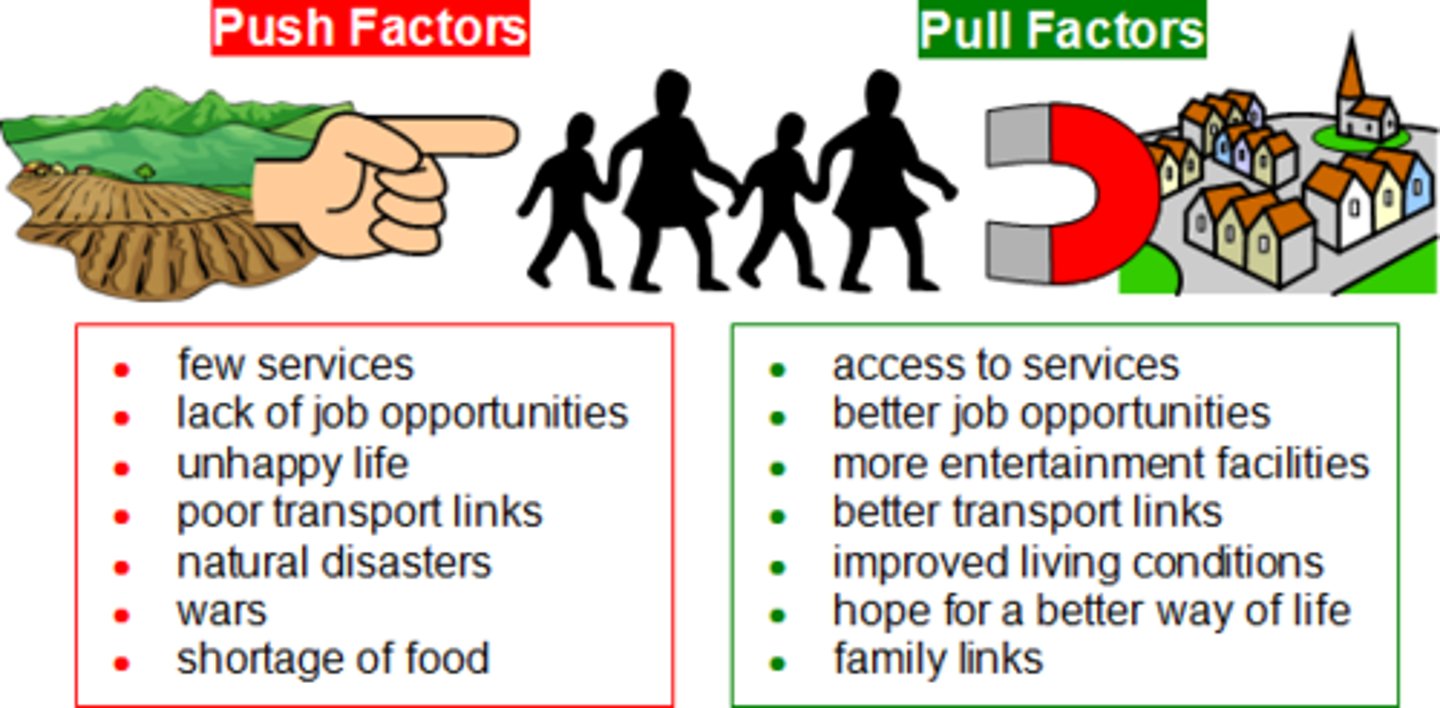
push factors
a negative factor which results in the movement of people away from an area
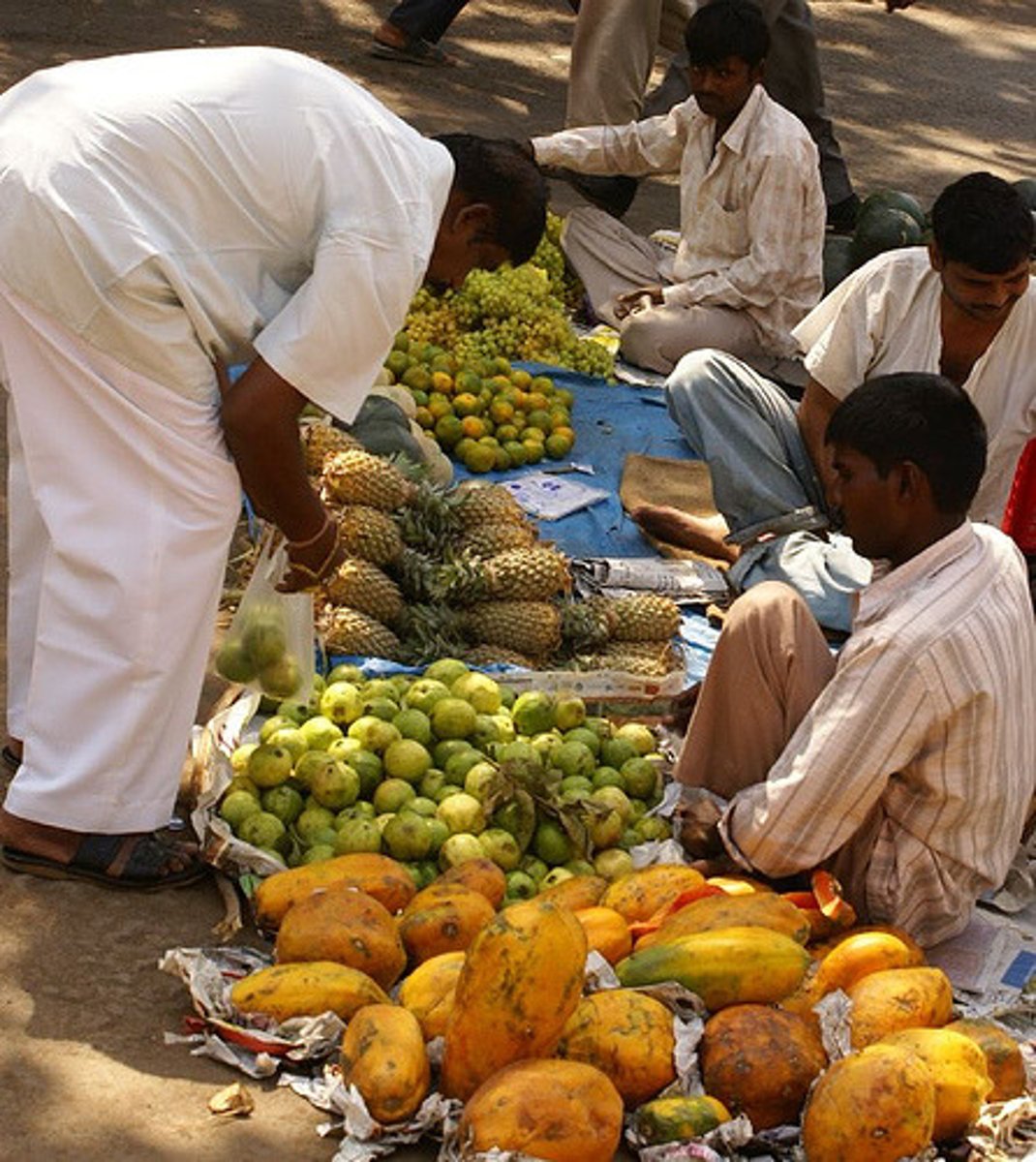
informal sector
refers to jobs that don't offer regular contracted hours, salary, pensions or other features of more formal employment; may refer to illegal or unlicensed activity.

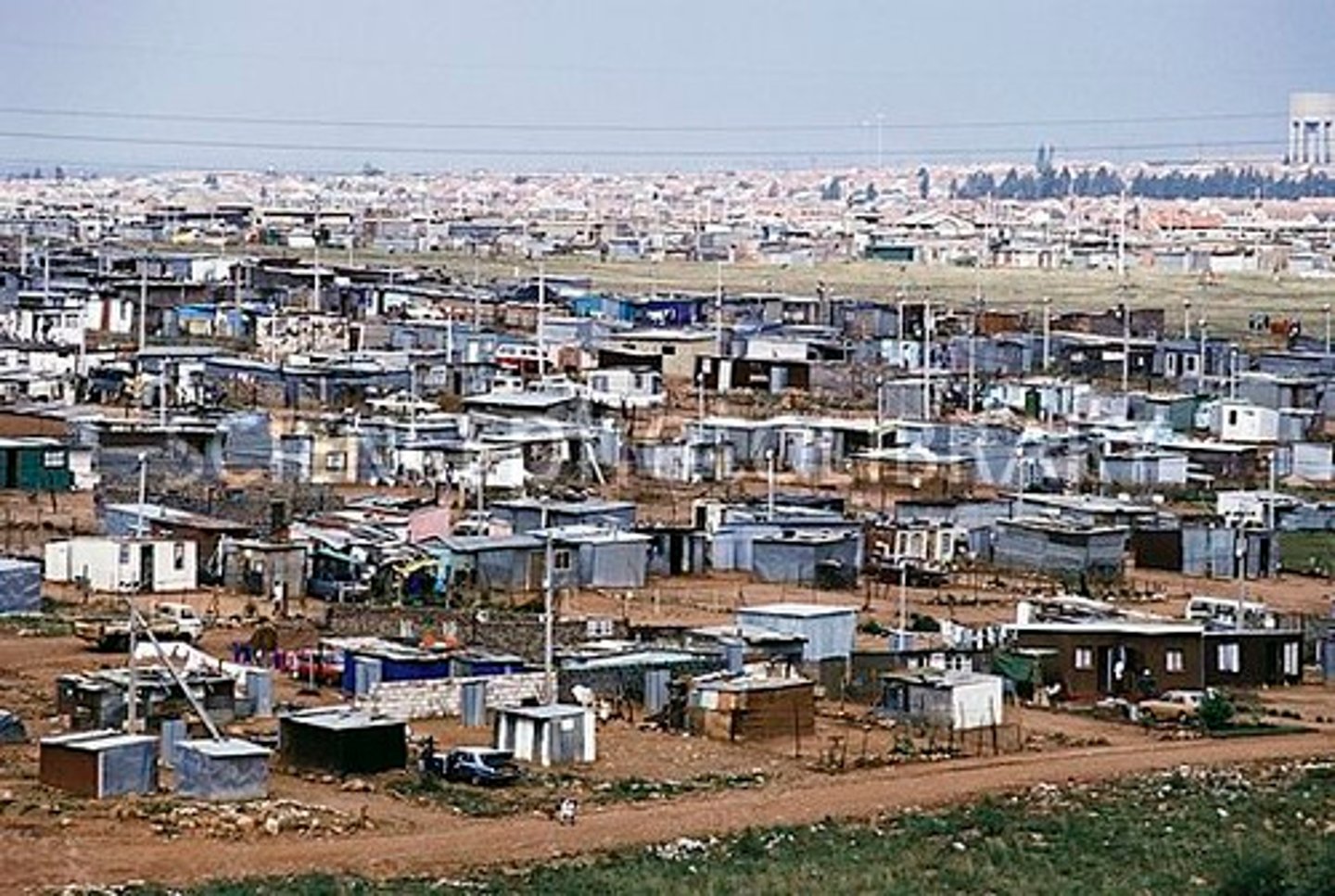
informal housing
housing built on land not owned, including slum and shanty town settlements.

suburbanisation
a change in the nature of rural areas surrounding urban areas such that they start to resemble the suburbs
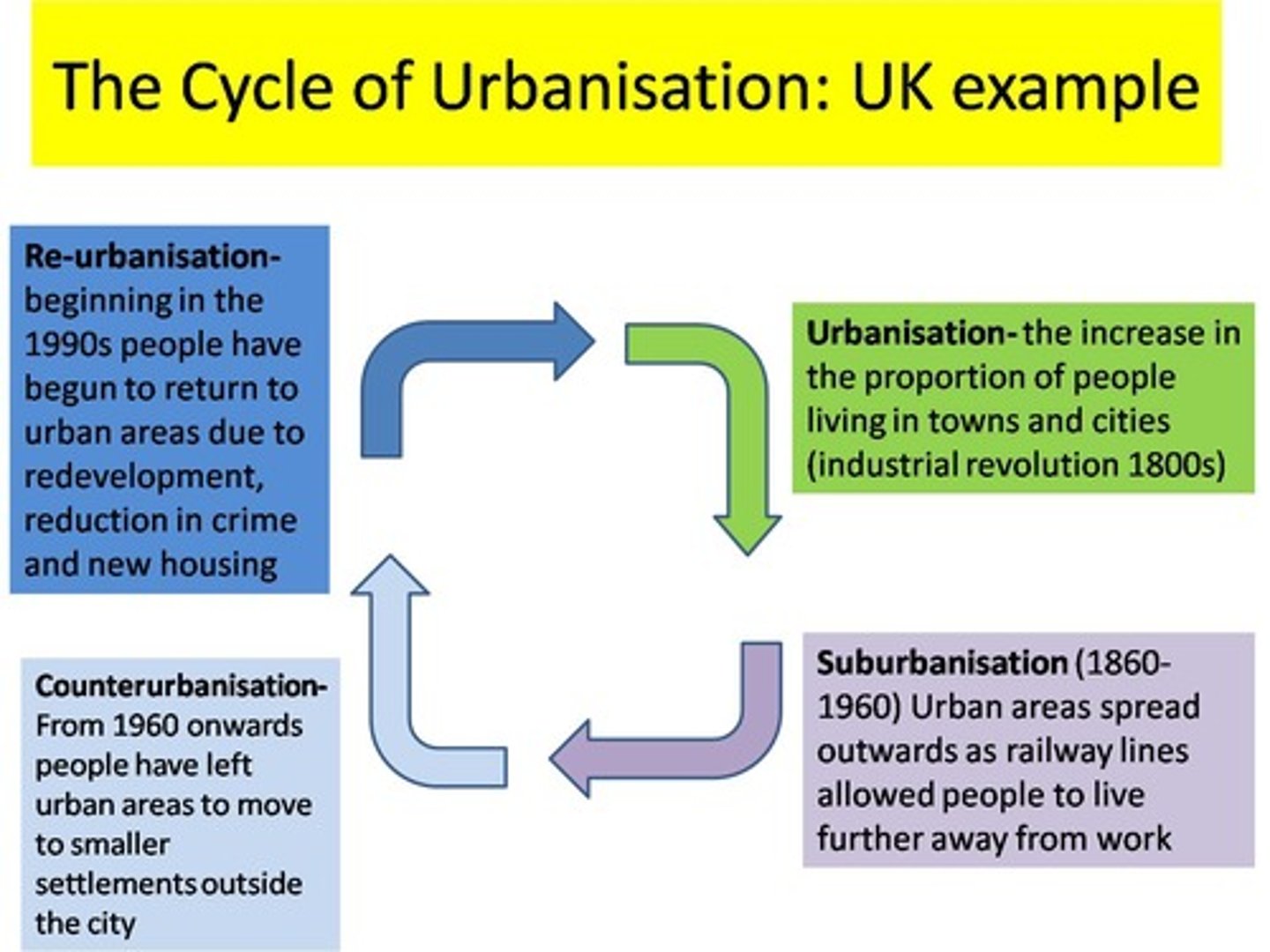
counter-urbanisation
the movement of people from urban areas into rural areas; these may be people who originally made the move into a city

suburb
A residential district located on the outskirts of a city.

green belt
an area of land around several major urban areas, given protection under the Town and Country Planning Act of 1947, to prevent urban sprawl
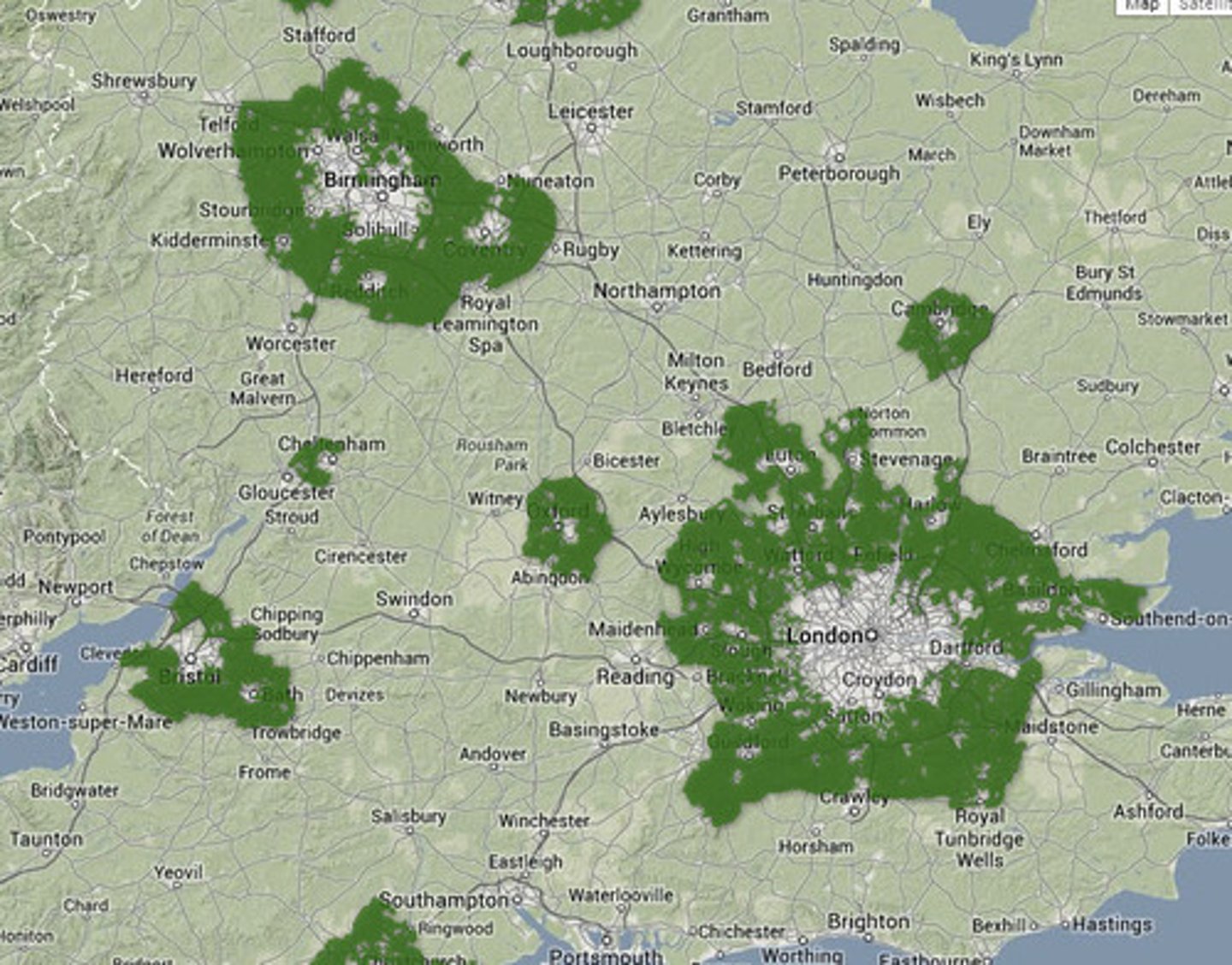
urban sprawl
The process of urban areas expanding outwards, usually in the form of suburbs, and developing over fertile agricultural land.

re-urbanisation
the use of initiatives to counter problems of inner city decline, often this involves redevelopment of brownfield sites

social inequality
the extent to which people have unequal opportunities and rewards as a result of the position they occupy within the society; different groups characterised by age, gender, 'class' and ethnicity, may have different levels of access to employment, education and healthcare.
fuel poverty
a situation that occurs when people's income means that spending money to heat their home would take them below the official poverty line
child poverty
living in a household with an income below 60% of the national average.