Heat Transfer Mechanisms
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
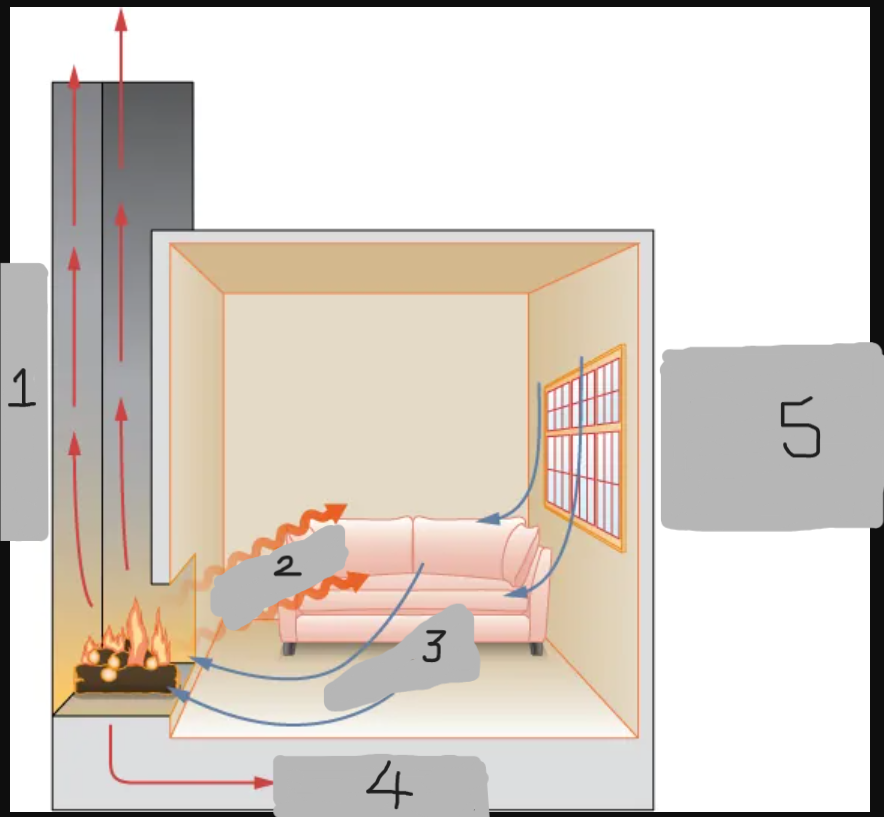
Convection (Hot Air)
(1)
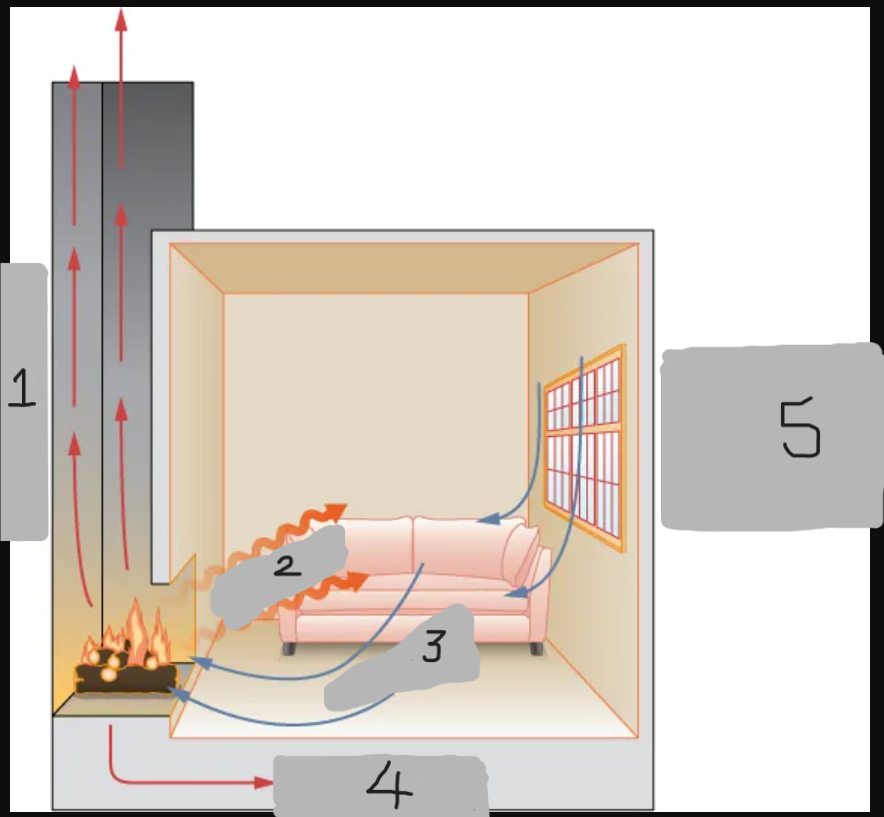
Radiation
(2)
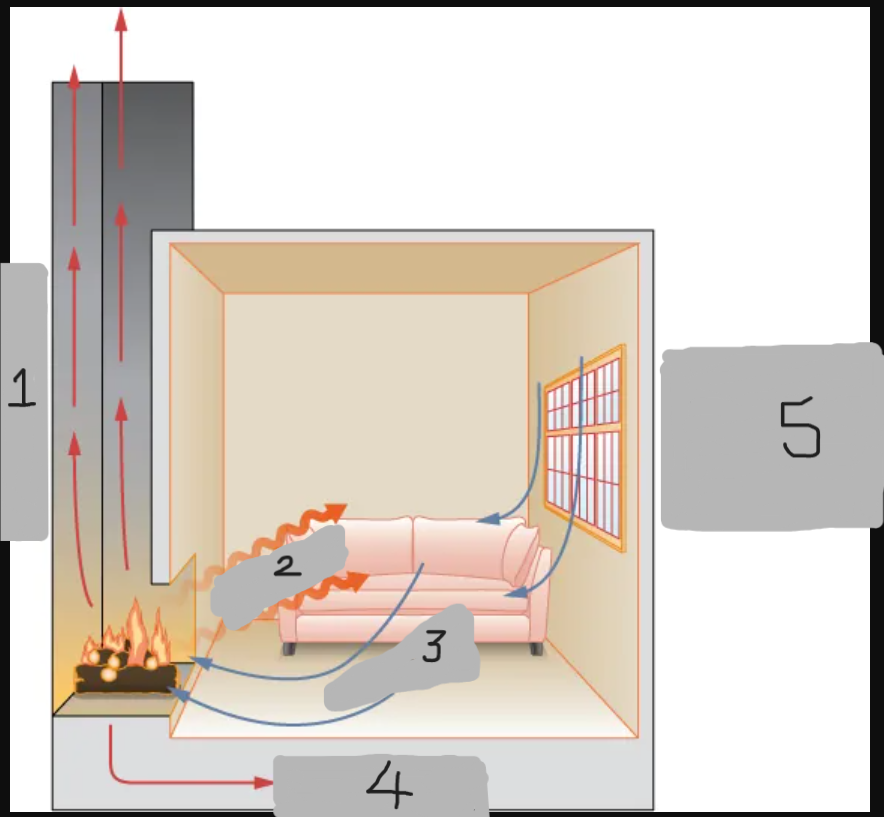
Convection
(3)
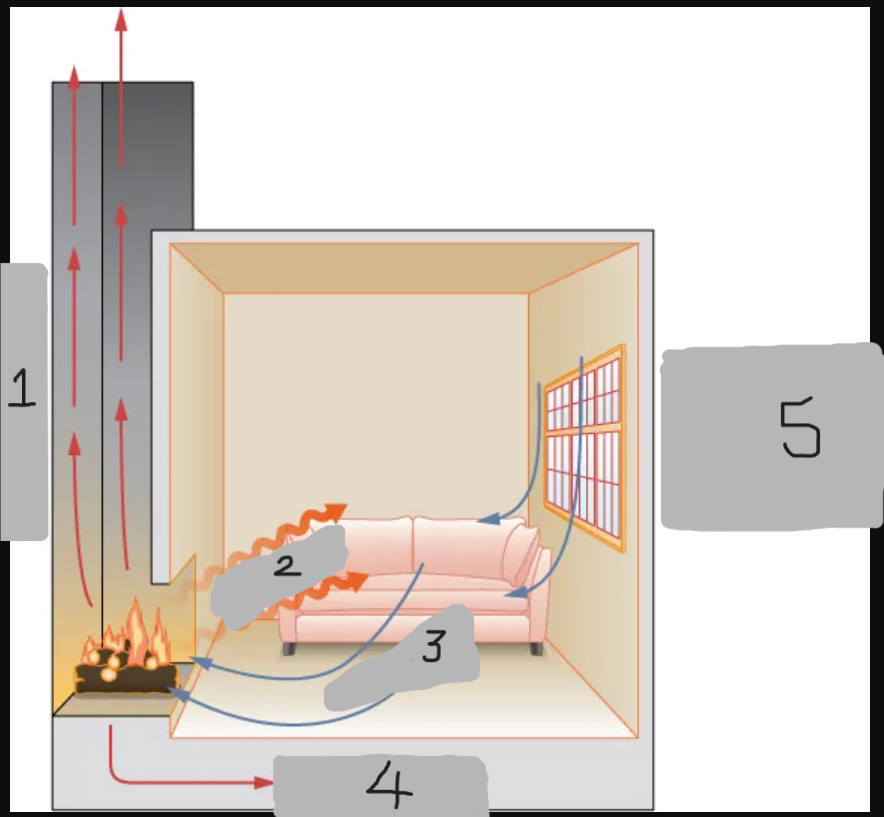
Conduction
(4)
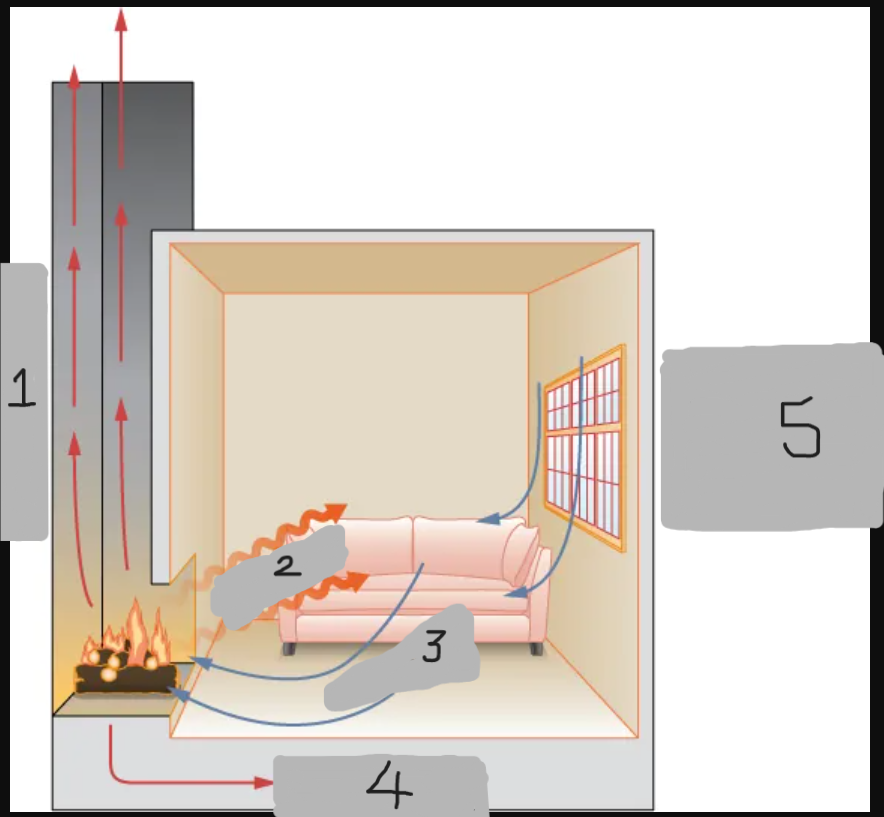
Convection around windows and doors (cold air)
(5)
Conduction
Heat transfer through stationary material by microscopic collisions of atoms, molecules, and (in metals) free electrons across a temperature gradient.
Thermal Conductor
A material that transfers heat quickly by conduction
High thermal conductivity k
Examples: Copper, Aluminium, silver
Thermal Insulator
A material that transfer heat slowly
By conduction (low k)
Often contains many trapped air pockets
Like polystyrene foam, fiberglass, fur, or wool
Q
(i)
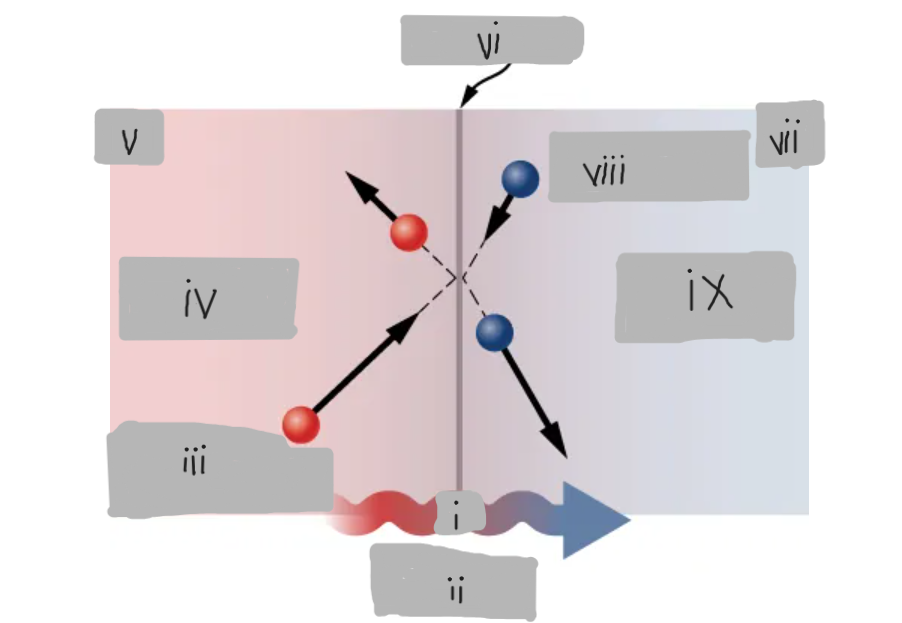
Heat Conduction
(ii)
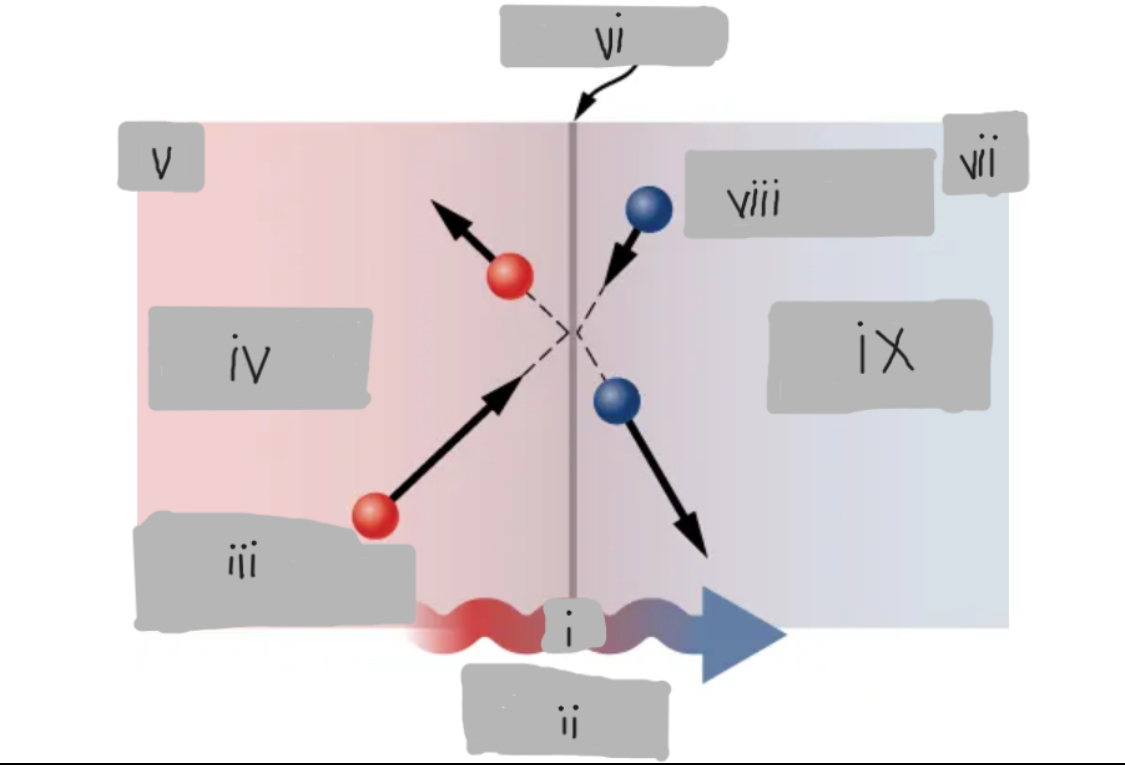
High energy before collision
(iii)
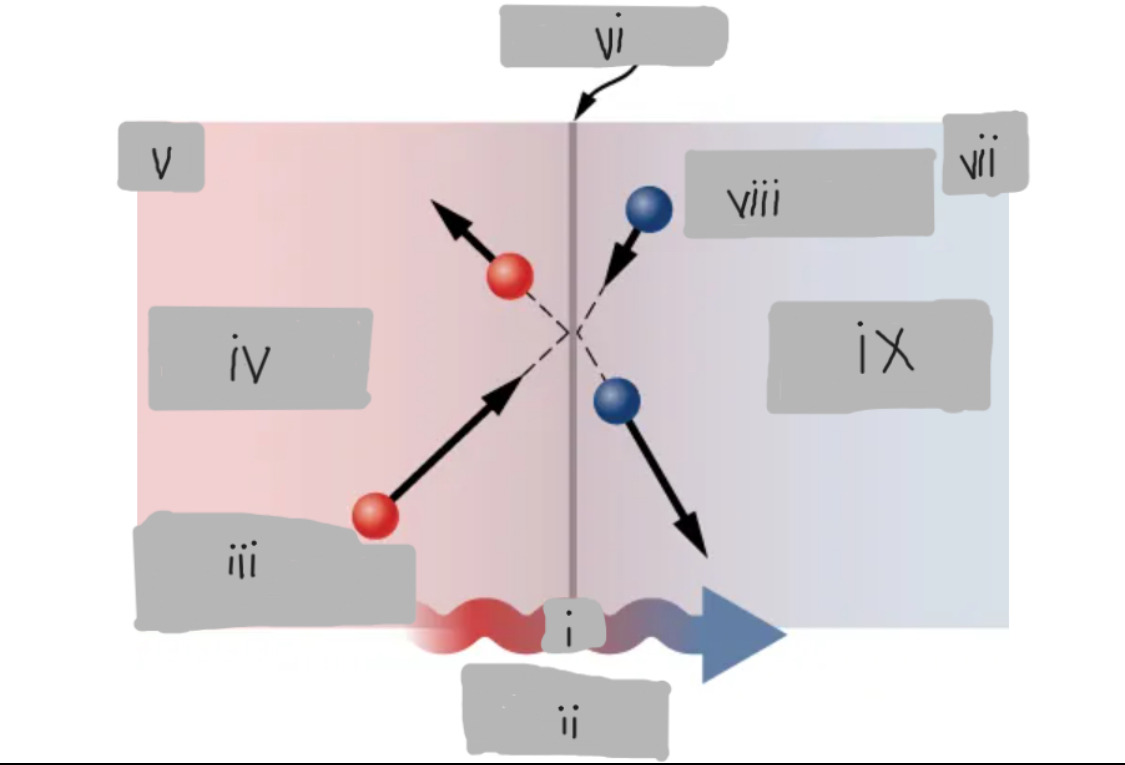
Higher temperature
(iv)
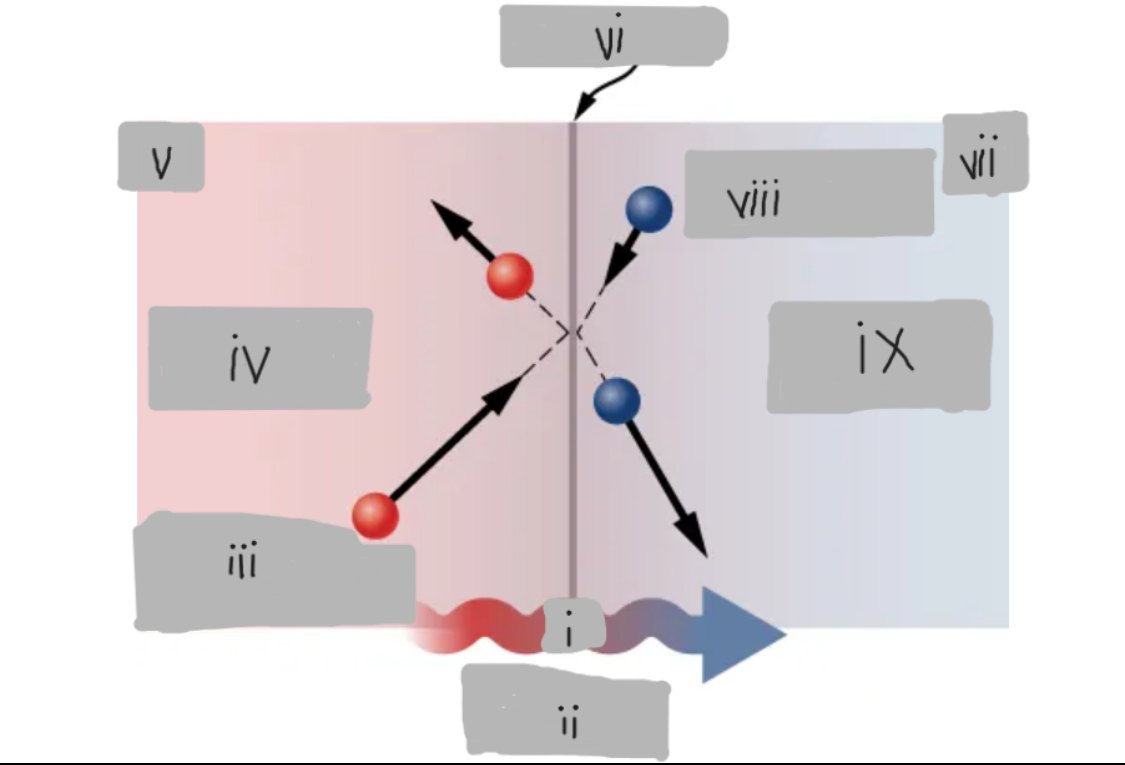
Th
(v)
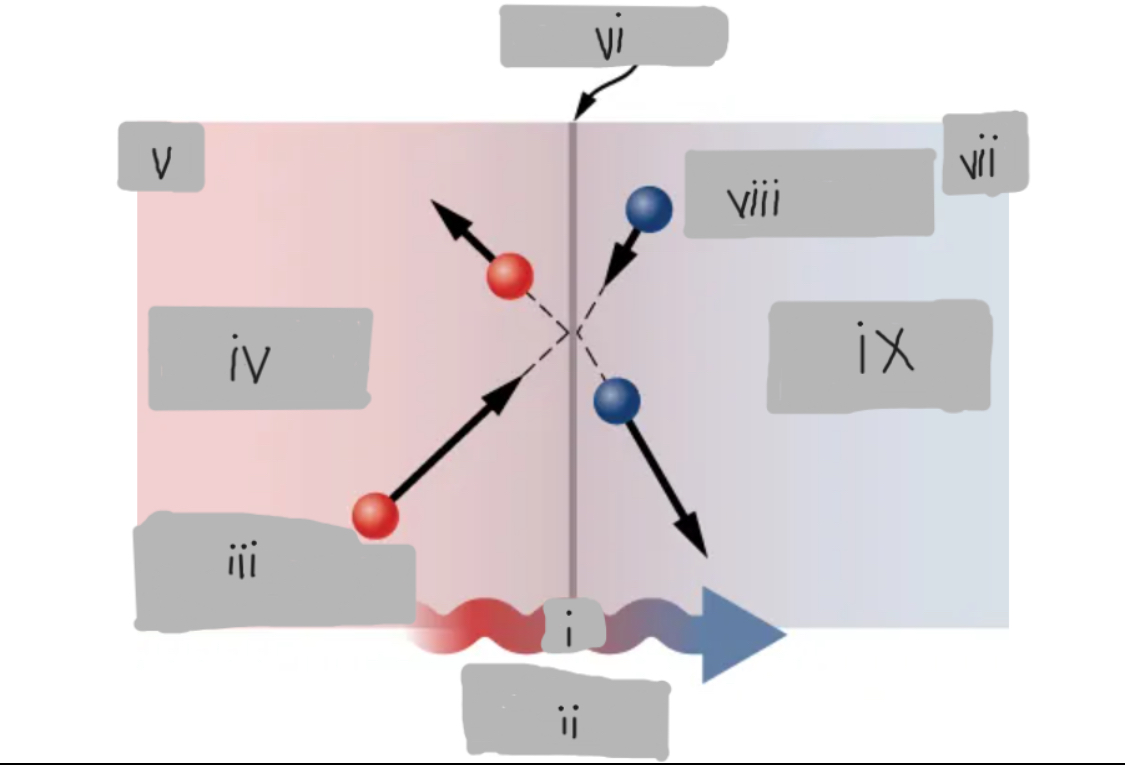
Surface
(vi)
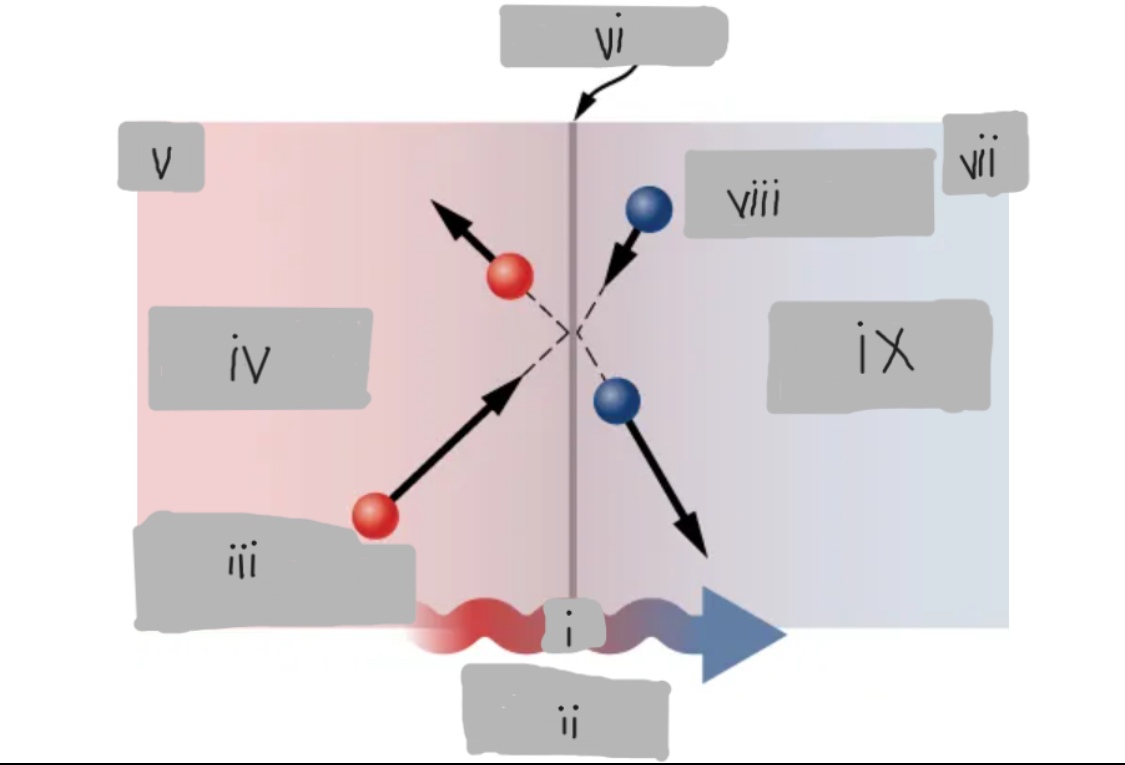
Tc
(vii)
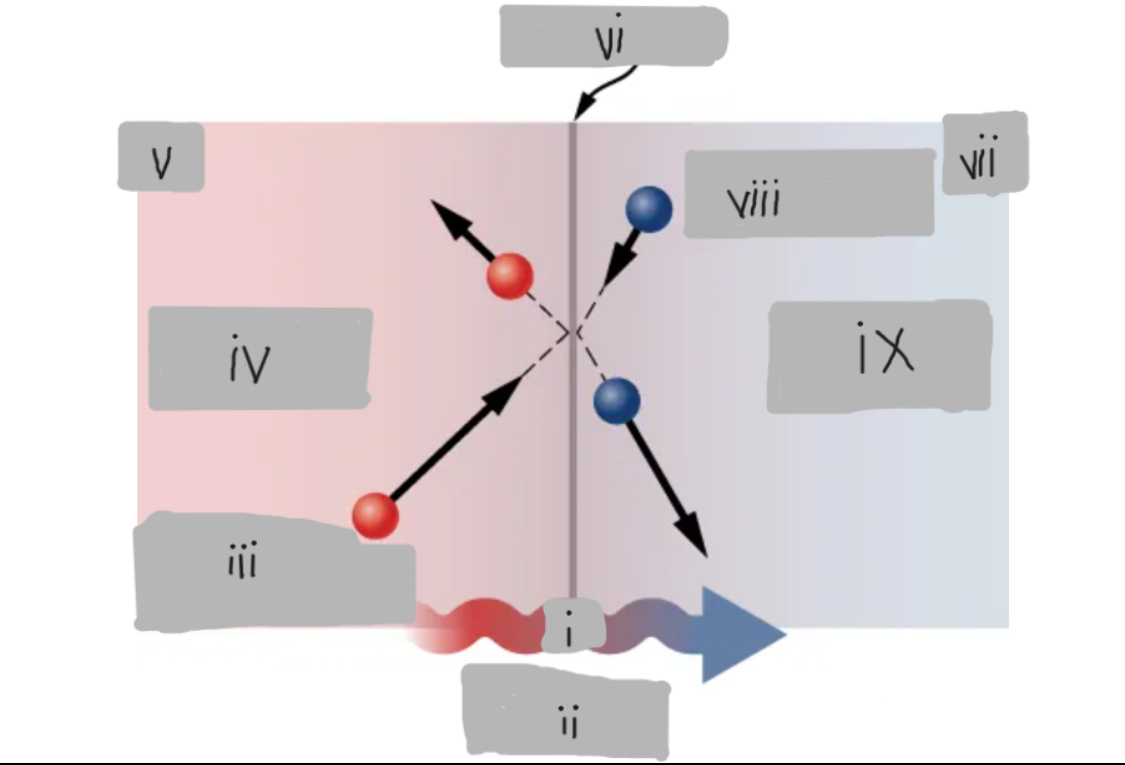
Low energy before collision
(viii)
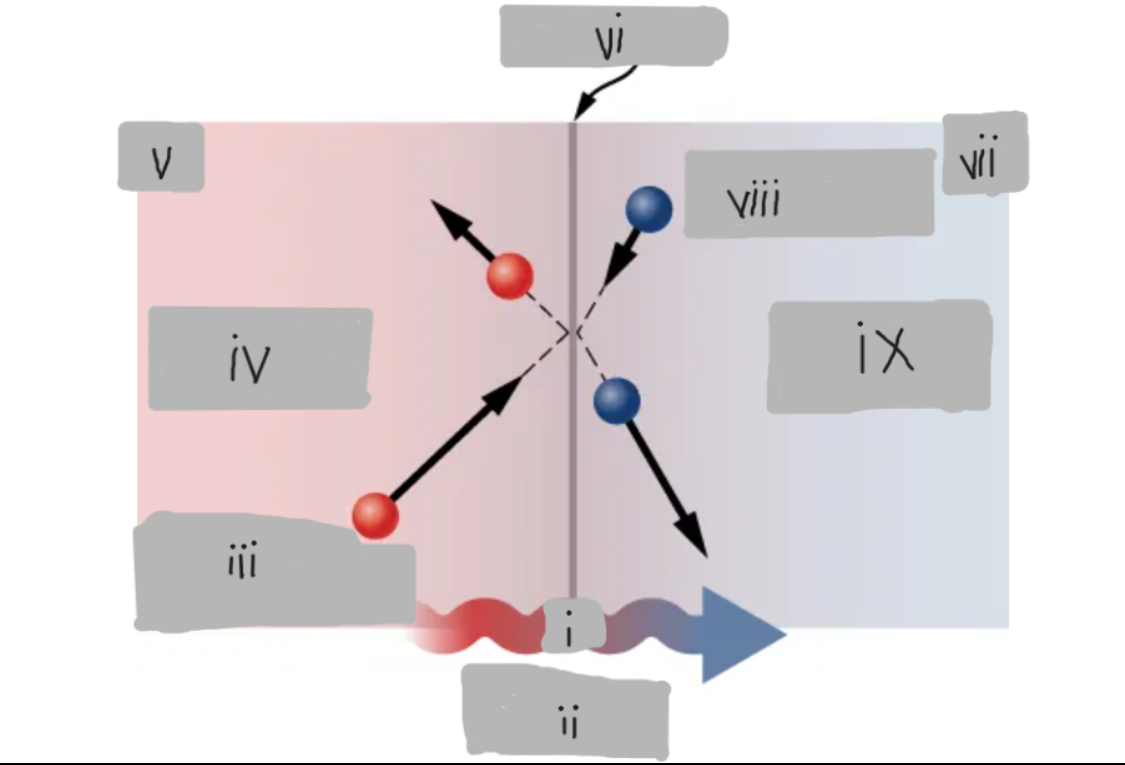
Lower temperature
(ix)

d
(१)
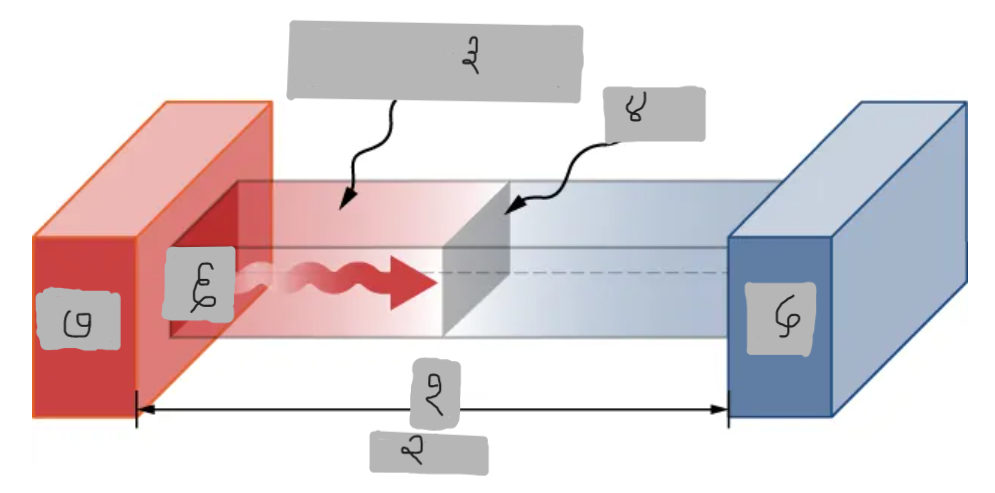
Th > Tc
(२)
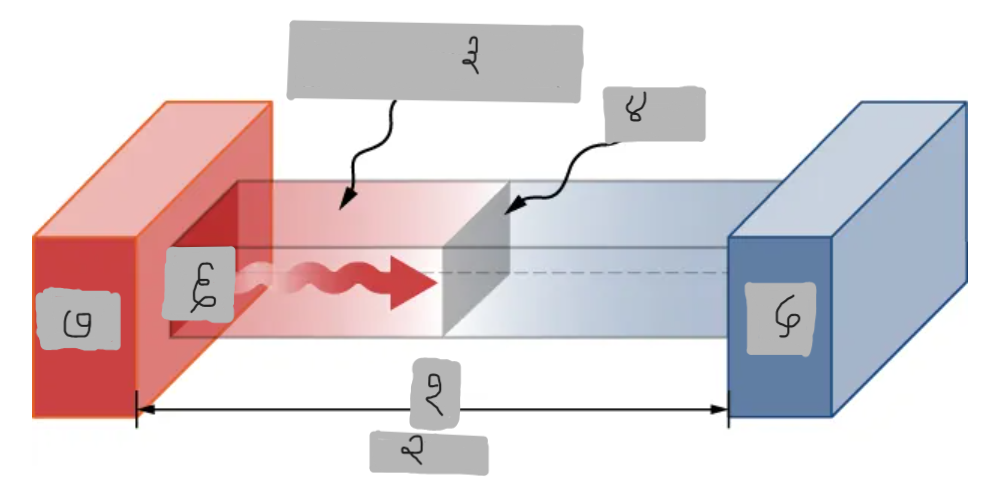
Material having thermal conductivity k
(३)
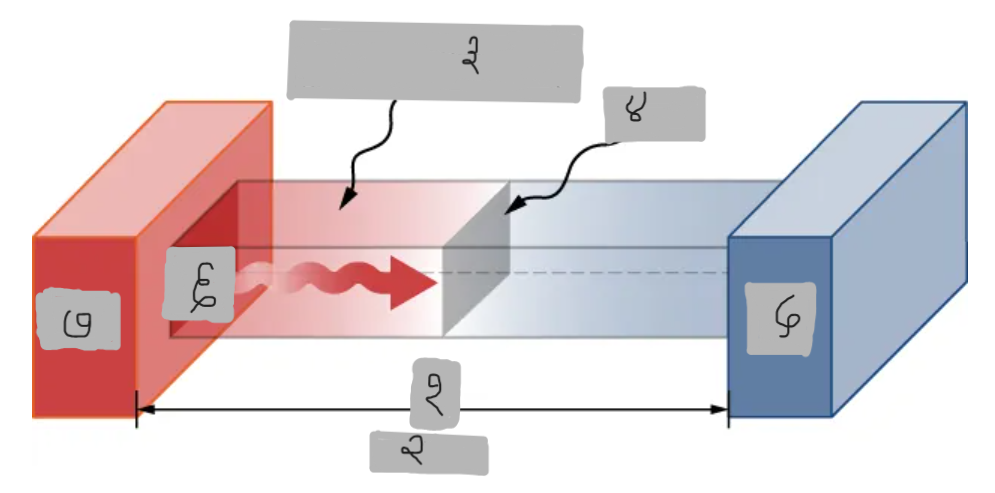
Area A
(४)
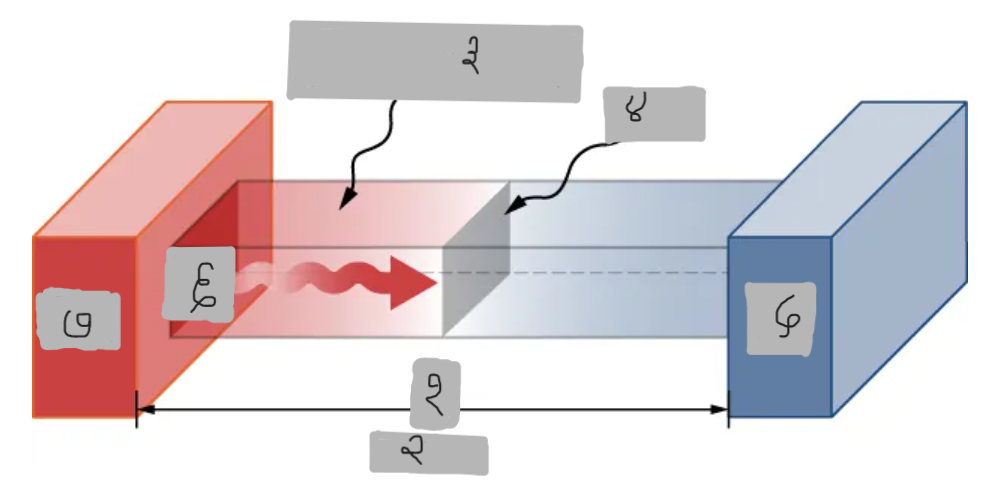
Tc
(५)

Q
(६)
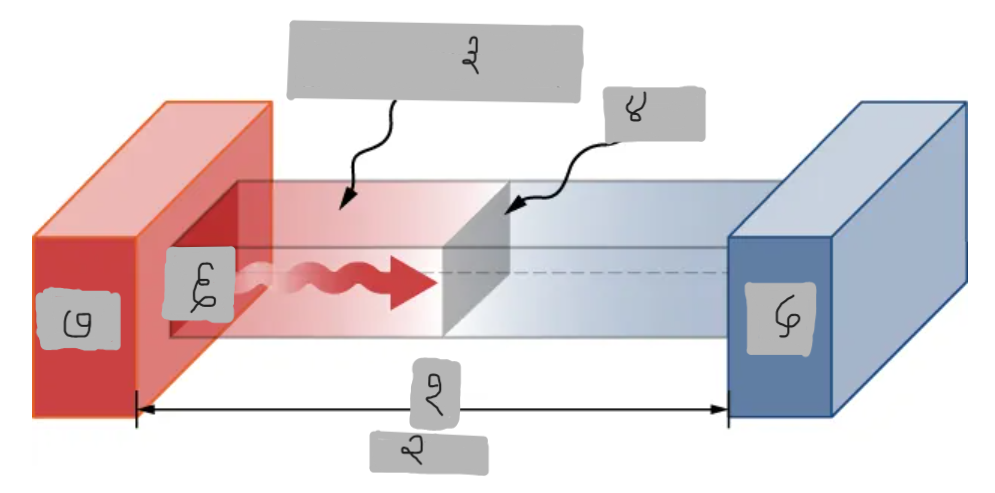
Th
(७)
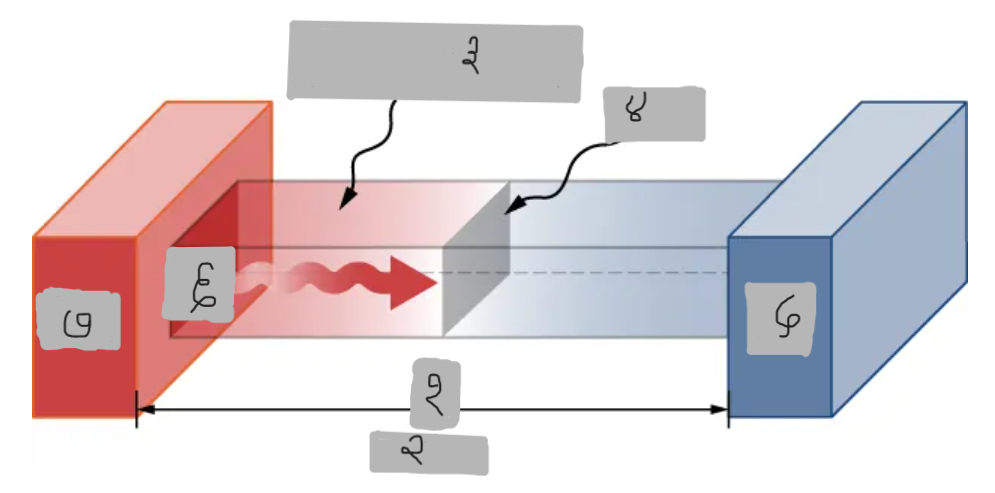
Hot
___ side has molecules with higher average kinetic energy
Collisions
__________ at the interface transfer energy from fast (hot) molecules to slower (cold) ones, creating a net energy flow from hot to cold.
Factors Affecting Conductive Heat Transfer
Larger temperature difference ΔT,
Larger cross-sectional area A,
Higher thermal conductivity k,
Larger thickness d of material (for decrease)
Thermal Conductivity (k)
A material property that measures how well a substance conducts heat.
Having this in higher quantity means it is a better conductor
Having this in lower quantity means it is a better insulator
ΔT = Th - Tc
Equation for the temperature difference
d
Symbol that represents thicknesses
A
Symbol that represents Area
k
Symbol that represents Thermal Conductivity
P
Symbol that represents The rate of heat transfer
P = dQ/dt = (kA(Th - Tc))/d
Provide the Conduction Power Formula
dT/dx
Representation of the temperature gradient along the direction of heat flow
P = -kA(dT/dx)
General Conduction Formula (1D)
That heat flows from higher to lower temperature.
What does the negative sign indicates inside General Conduction Formula (1D)
R Factor (Thermal Resistance)
A measure of how well a material resists heat flow by conduction
R ∝ d/k
Mathematical representation of the R-Factor
better insulation, smaller conduction rate
Larger d/k → _______________ → ____________________
Convection
Heat transfer by bulk motion of fluid (liquid or gas). Warmer, less dense fluid rises, denser fluid sinks.
Forced Convection
Convection where fluid motion is driven by external devices like fans or pumps (e.g., car radiator, fan blowing air over skin)
Natural (free) Convection
Convection driven by buoyancy.
Heat fluid expands, density decreases, it rises,
Cooler fluid sinks, forming convection currents.
Examples: warm air rising in a room, ocean, and atmospheric circulation
poor conductor
Air is a ______________, so heat transfer through air is dominated by convection.
trapping
Insulation often works by ________ air in small pockets to prevent large convection loops
latent heat, skin, convection, cooling
Evaporation of sweat requires _________ from the ___; ________ moves away humid air, allowing continued evaporation and _______ of the body.
Radiation
Heat transfer via electromagnetic waves (infrared, visible, etc.) emitted by all objects with temperature above absolute zero. No material medium is required.
Hotter, wavelengths, shorter wavelengths
______ objects radiate more energy at all ___________ and peak at ___________________.
red, yellow, white, blue
As temperature increases, color shifts from ___ → ______ → _____ → ____
Emissivity (e)
A number between 0 and 1 that measures how effectively a surface emits and absorbs thermal radiation.