Organic Chemistry III - topic 18
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What is the most common type of reaction of benzene?
substitution (of a H for a different functional group)
What happens to the 4th electron in the p orbital of each C atom in benzene?
It delocalises to form delocalised pi system above and below the hexagon, forming rings of delocalised electron density above and below the hexagon plane.
Describe how the orbitals from carbon atoms interact to form the bonds in a benzene ring
head on overlap between orbitals to form a sigma bond
side on overlap between p orbitals to form pi bond
electrons are delocalised around the ring
what was different than expected about Kekule’s idea of benzene?
All the bonds are at the same length - proved by X ray diffraction data
the enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene is less exothermic than expected, much more stable than expected - proved by thermochemical data, which provide evidence for benzene’s structure and stability
1 proton environment, proved by magnetic resonance spectroscopy, kekule would give 2 environments
infrared data provide evidence for benzene’s structure
Why is benzene stable?
The electrons in the p orbital of C are delocalised to form an electron cloud in the delocalised pi electron system above and below the plane.
why is benzene attacked by electrophiles?
it has high electron density above and below the ring due to delocalised electrons
what is seen when benzene is combusted? Why?
smoky flames due to soot from unburnt carbon because of the high Carbon:Hydrogen ratio
General electrophilic substitution of benzene
with bromine, FeBr3 as catalyst, forms bromobenzene + HBr
with chlorine, FeCl3 as catalyst, form chlorobenzene + HCl
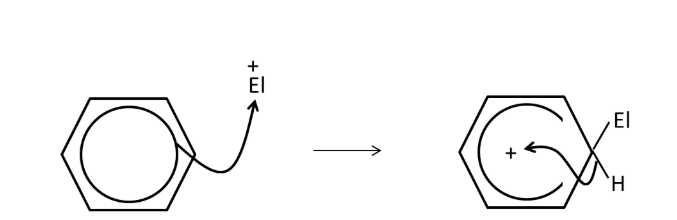
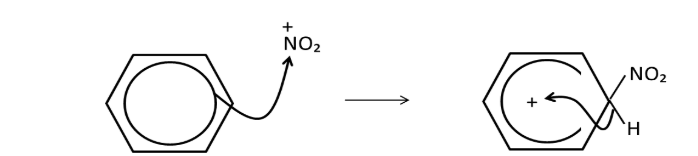
which ion is used to nitrate benzene? How is it generated? (how to turn benzene to nitrobenzene)
what is the catalyst, how is it regenerated?
Nitration reaction: electrophilic substitution where a hydrogen atom is replaced by a nitro group
NO2 +
H2SO4 + HNO3 → H2NO3+ + HSO4-
H2NO3+ → H2O +NO2+
H2SO4 + HNO3 → HSO4 - + NO2++H2O
catalyst: conc.H2SO4, 55 degree temperature - CANNOT be hotter to prevent further substitution reactions
HSO4- + H+→ H2SO4, H+ from the benzene ring
How do substituents with alkyl groups affect further substitution?
Alkyl group has inductive effect, they release electrons into the delocalised electron ring, increasing electron density and making further substitution reactions more likely
Direct substituents to 2,4,6 positions
How do substituents with NH2 affect further substitution?
NH2 has negative inductive effect. Remove electrons from the delocalised electron ring, decreasing the electron density and making further substitution reactions less likely
Direct substituents to 3,5 positions
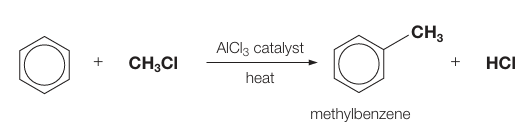
What type of catalyst is used for a Friedel-Crafts reaction? Alkylation?
A halogen carrier, e.g. AlCl3
Write an equation to form an electrophile to be used to acylate benzene with AlCl3 and RCOCl, How is the catalyst reformed?
Acylation:
AlCl3 + RCOCl → AlCl4- + RCO+, which can attack benzene
AlCl4- + H+ → AlCl3 + HCl
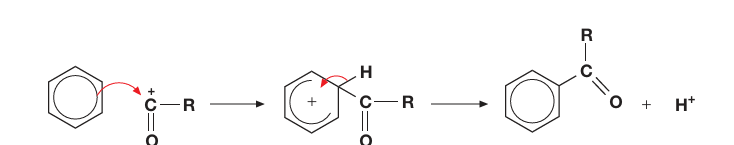
Draw the mechanism for the acylation of benzene from RCO+
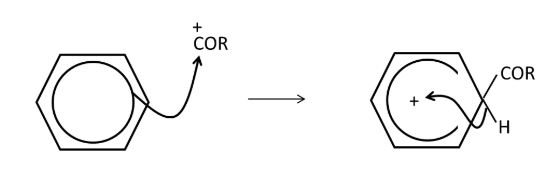
how to form cyclohexane from benzene?
add hydrogen in the presence of a nickel catalyst
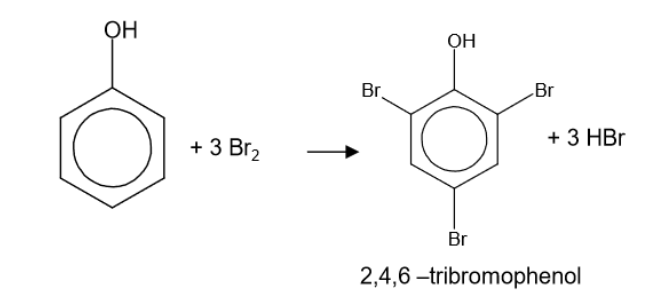
write an equation between phenol and bromine water
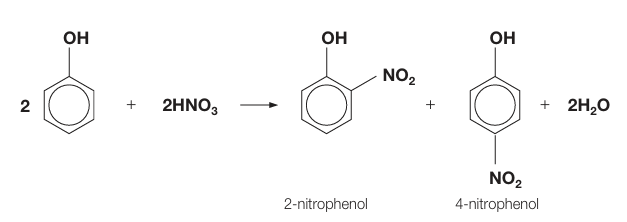
draw the mechanism of reaction between phenol and nitric acid
forms two nitrophenol and water, basically plus onto phenol but loses hydrogen (at 2,4 )
why is phenol more reactive than benzene?
the lone pair of electrons on the -OH group becomes delocalised with the delocalised pi electron system, increasing electron density in the ring. This makes phenol more nucleophilic, makes the ring more susceptible to electrophilic attack
why is the reaction of phenol and bromine more reactive than benzene with bromine?
in a phenol the lone pair of electrons on the p orbital on the oxygen is delocalised into the delocalised pi electron system. This increases electron density and increases the attractiveness to the electrophiles.
why can phenols react with sodium hydroxide but not sodium carbonate?
phenols are very weakly acidic even weaker acids than carboxylic acids, Only carboxylic acids will react with sodium carbonate as phenol is not strong enough to react.
why are amines so reactive?
The lone pair of electrons on the Nitrogen due to the polar N-H bond
Solubility of phenylamine? Why?
Not very soluble, due to the non-polarity of the benzene ring C6H5 cannot form hydrogen bonds
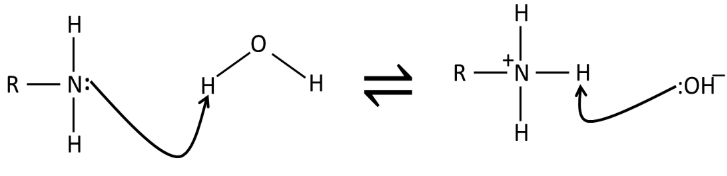
Draw a mechanism for the basic action of an amine with water
product formed: ammonium ion
write the equation for the acidic action of an amine with HCl
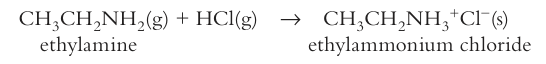
primary amine, ammonia, aromatic amines, which is the strongest base
primary aliphatic amines are the strongest base as the alkyl groups have inductive effect and push electrons towards the nitrogen atom, increases electron density making electrons more available for the proton, so accept a proton more easily
Draw a mechanism for nucleophilic substitution of NH3 with RCH2Br to form primary amines. What might then happen?
multiple substitutions, then secondary, tertiary ammonium ions might form, hence produces a low yield of primary amine, use excess ammonia to maximise the yield
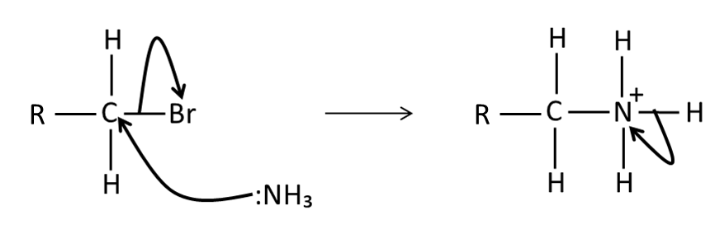
how to make primary amine from halogenoalkanes?
halogenoalkanes and conc. NH3 in ethanol, heat in a sealed tube, lead to further substitution
how to get from nitrile to primary amine? why is this better than using halogenoalkanes?
reduction using nickel catalyst, only primary amine forms
reduction using LiAlH4, in dry ether
does not lead to further substitutions
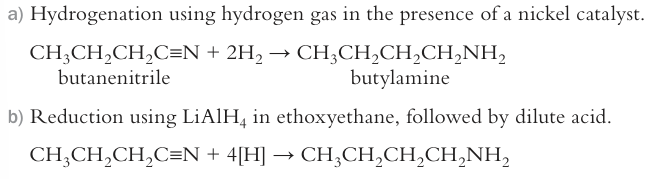
how to form an phentlamine salt from nitrobenzene?
reduction using Tin and conc. HCl
Room temperature
Equation for the reaction of nitrobenzene to phenylamine
C6H5NO2 + 6[H] → C6H5NH2 + 2H2O
what mechanism is used for forming amides from acyl chlorides and amines?
nucleophilic addition elimination
draw mechanism showing reaction between ethanoyl chloride and amine
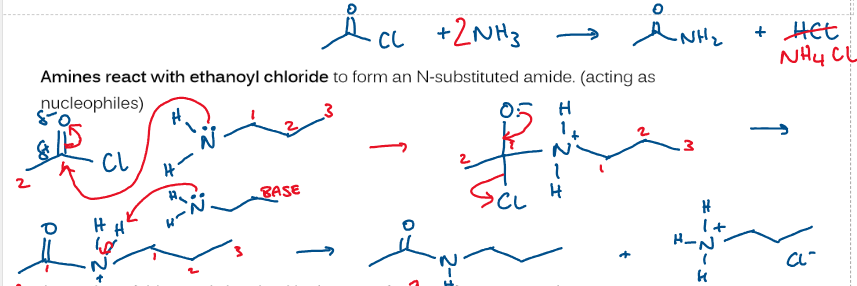
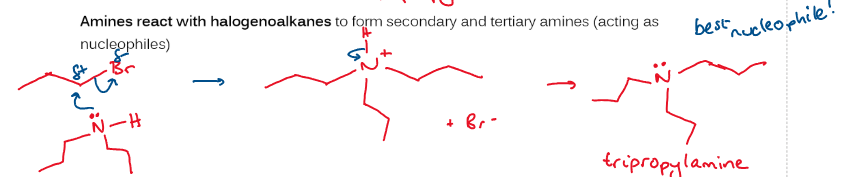
draw mechanism showing reaction between halogenoalkanes and amine
recrystallisation practical to purify a solid
choose a solvent
the solid should be soluble when in hot solvent and insoluble in cold solvent
record the mass of solid, pour in a beaker with minimum amount of hot solvent
filter out the insoluble impurities
add minimum amount of hot solvent to dissolve the residue on the side of conical flask
put the rest of solution in ice cold water bath, leave to crystallise
filter using a vacuum to filter out the pure solids, the liquid left is the soluble impurities
rinse the crystals with minimum volume of ice-cold solvent to wash away any solution containing impurities
allow solvent to evaporate
what is a zwitterion
a molecule/ion in neutral condiiton having separate positive and negative ions
when ph low, tend to form positive ions and ph high, negative
when amino acid add to water, zwitterion is formed
are amino acids, apart from glycine, chiral?
yes, amino acids have a chiral C atom and exist as two enantiomers
though in nature, only one of these enantiomers is present
these enantiomers are able to rotate the plane of plan-polarised light in the opposite directions
these amino acids are usually called the 2-aminoacids by their IUPAC names
Explain why recrystallisation would separate pure solids from impurities
the pure solid is less soluble in cold solvent than hot
when cooled, pure solids comes out of solution, leaves the impurities behind
What happens when phenol reacts with sodium carbonate
Nothing because phenol is not acidic enough, phenol is a weak acid
Recrystallisation
dissolve in minimum quantity of hot solvent
filter to remove insoluble impurities
allow to cool and crystallise
filter crystals to remove soluble impurities under vacuum
allow crystals to dry and determine melting temperature
compare to known values in a database
Steam distillation
separate an immiscible organic liquid from an aqueous mixture
the organic compound needs to have a higher boiling point than water
the organic compound is distilled with water at a lower temperature and prevents decomposition