4. Batteries and Water Systems
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is the memory effect?
When batteries are repeatedly recharged they begin to lose their original capacity and power. This becomes an issue with some types of cell particularly if they are recharged before half the power has been discharged
It is said to ‘forget’ its original power capacity
What are electrolytes?
Ionic salts in solution
How is the conductivity of a solution determined?
by measuring its electrical resistance
The usual methos is to incorporate a conductivity cell into one arm of a Wheatstone bridge and to search for the balance point (point there is zero current)
cations will migrate towards the negatively charged electrode and anions towards the positively charged electrode
Ions of different valency will transport different amounts of electricity e.g. NaCl, each ion carries one unit of charge, CuSO4, each ion transports 2 units of charge
What is the equation for molar conductivity?

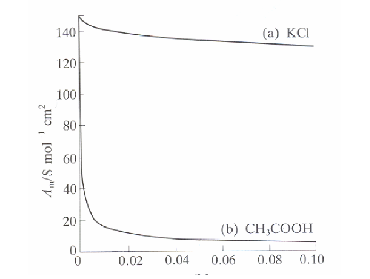
What are the two classes of electrolyte and how does the measure3ment of concentration dependence of molar conductivities show this?
Strong electrolytes like KCl, they show only slight concentration dependence
Weak electrolytes like CH3COOH, these show that the conductivity drops sharply when the conc is increased.
Strong electrolytes will fully ionise in solution - ionic solids and strong acids
Weak electrolytes will not fully ionise (more likely to be carboxylic acids)
What did Kohlrausch state about molar conductivity?
Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions
Each ion contributes to the molar conductivity in a purely additive manner and its contribution is proportional to its concentration
And therefore lambda must be the sum of the limiting molar ion conductivities of the cation and anion.
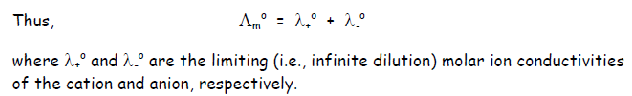
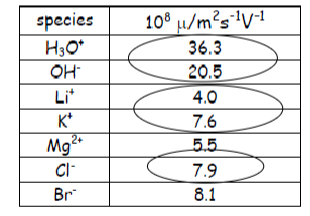
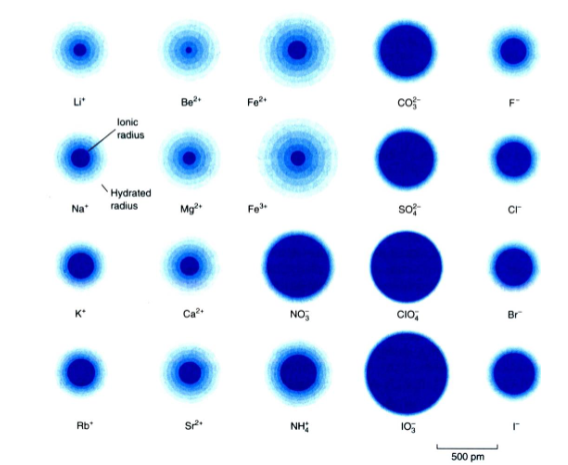
How does conductivity relate to the radii of an ion? For example why is sodium’s conductivity lower than potassium’s?
Sodium is a small highly polar ion that attracts hydration shell and the hydrodynamic radii of ions are not directly proportional to the ionic radii
What are ionic mobilities?
when ions in solutions are subjected to a uniform electric field they quickly attain a steady speed
The quotient speed/electric field strength is called the mobility of the ion and have the symbol μ
What are the molecular aspects of water?
Uniquely hydrogen bonded structure
Bonds form and break dynamically
Only about 15% of hydrogen bonds break on melting
Affinity of water for itself is unusually high
Has a high specific heat capacity
What are the affects of hydrogen bonding in water?
holds water molecules together in a unique way
Each water molecule can form a max of 4 hydrogen bonds
Hydrogen bonds between water molecules are eak (1/20th as strong as a covalent bond) so they form and break with great frequency
Results in high surface tension, higher boiling point, high heat vaporisation and molecule expansion on colling
Why does ice have a lower density than water?
when water hits zero degrees the water becomes locked in a crystalline lattice with each molecule bonded to the max of four partners
As ice starts to melt, some H-bonds break and some water molecules pack closer together than they could int eh ice state
due to the spaces in between molecules when they freeze to ice it cases it to be around 10% less dense than water around 4 degrees C.
Molecules are less packed together and actually have 4 H-bonds, liquid water has an average of 3.4 H-bonds
This also explains why ice expands when frozen and why less dense ice floats in water.
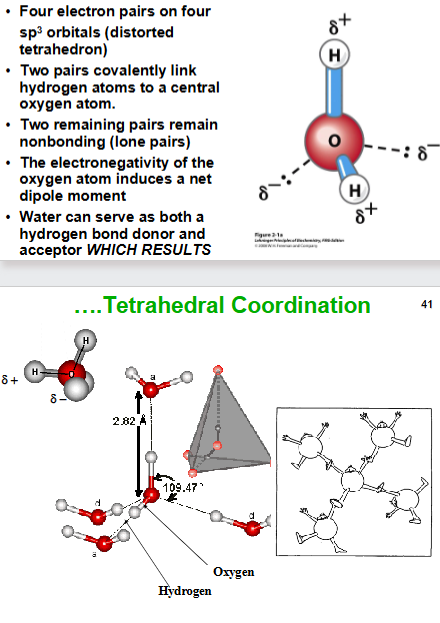
What is the structure of a water molecule?
four electron pairs on four sp3 orbitals
Distorted tetrahedron structure
Two pairs are covalently linked hydrogens to the central oxygen and two are lone pairs
Electronegativity of the oxygen atom induces a net dipole movement
Water can be a hydrogen bond donor and acceptor which causes tetrahedral coordination.
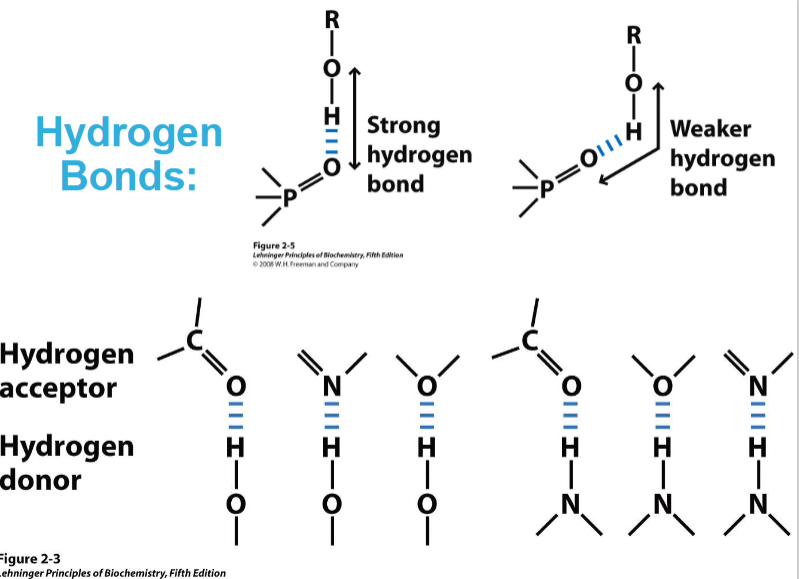
What is the nature of Hydrogen bonds?
strong dipole-dipole or charge-sipole interaction that arises between and acid (proton donor) and a base (proton acceptor)
Hydrogen bonds are strongest when bonded molecules are oriented to maximise electrostatic interaction - ideally three atoms involved are in a line E.g. O-H - - - O= would be in a straight line and make a stronger H-bond than if it was at an angle.
O and N are hydrogen acceptors that can form hydrogen bonds
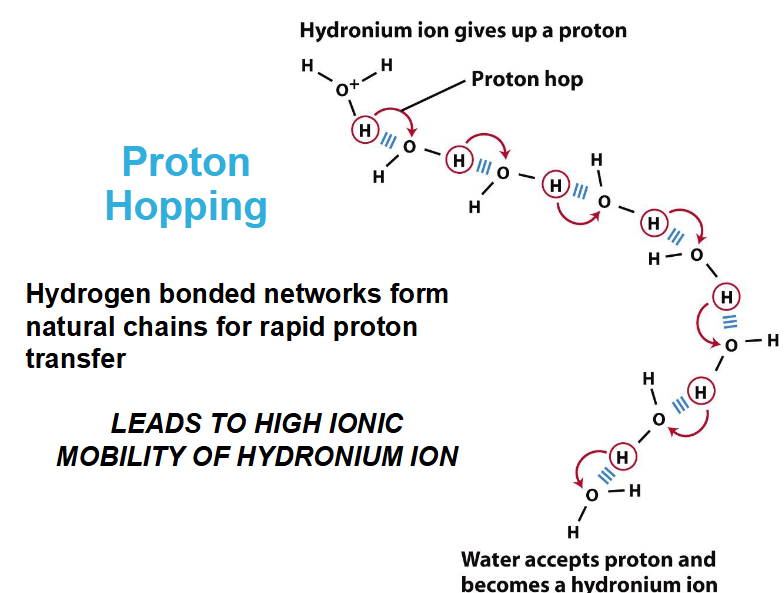
What is proton Hydration?
protons don’t exist freely in solution
They are hydrated to form hydronium (oxonium) ions (H3O+)
hydronium ions are solvated by nearby water molecules
Covalent and hydrogen bonds are interchangeable which allows for fast mobility of protons in water via proton hopping
Proton hopping leads to high ionic mobility for hydronium ion
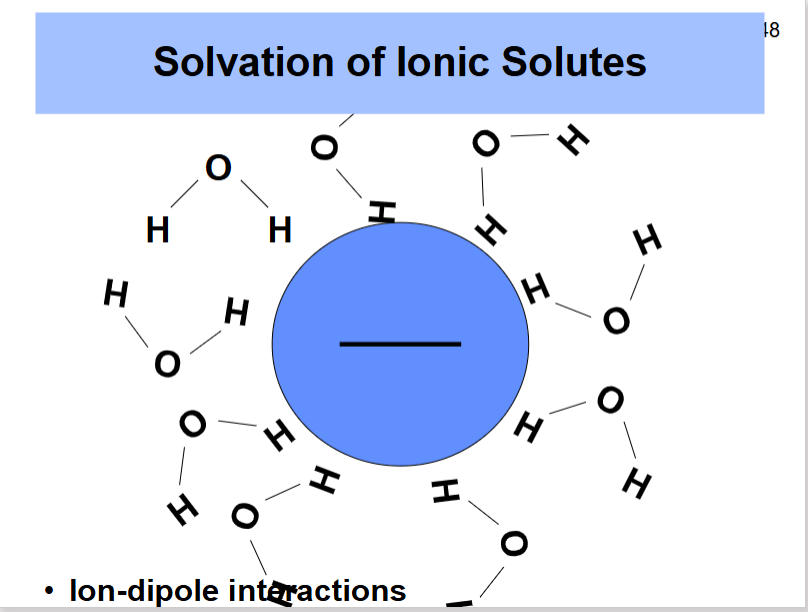
What does the solvation of anionic solutes look like?
ion-dipole interactions, one of the hydrogens in the water are surrounding the anionic charge
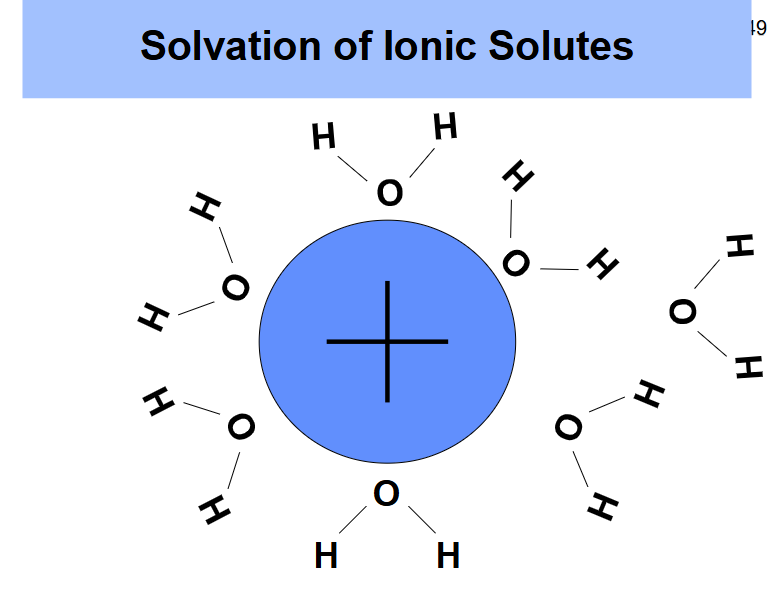
What does the solvation of cationic solutes look like?
Ion-dipole interactions where the oxygen is facing the positive charge and and the hydrogens are facing out
How does the size of the hydration shell change?
Size and charge of ion determines the number of bound water molecules
smaller, more highly charged ions bind more water molecules
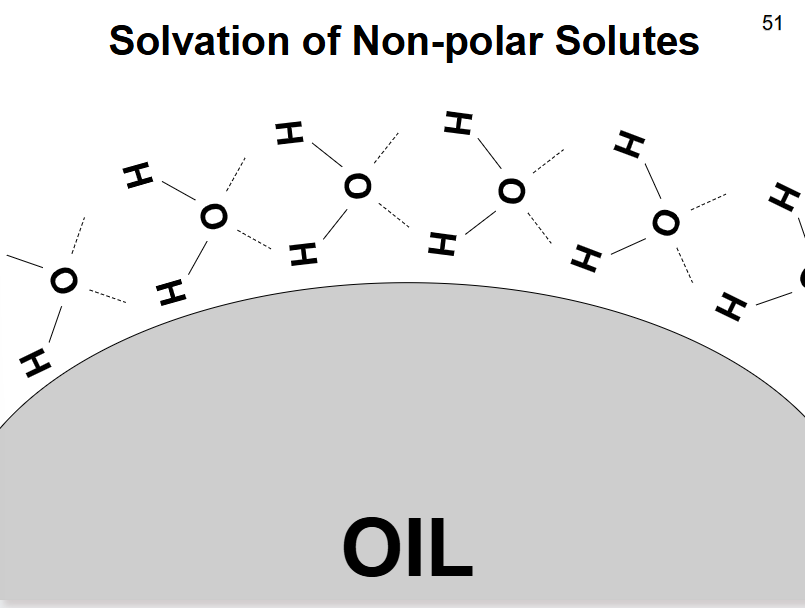
What does the solvation of non-polar solutes (oils) look like?
hydrogen bonds between water molecules surrounding the oil
What is the hydrophobic effect?
the association or folding of non-polar molecules in aqueous solution
Main factor behind protein folding, protein-protein association, formation of lipid micelles, binding of steroid hormones to their receptors
What are the 4 Battery types and their characteristics?
Lead-acid - used in cars - rechargeable and have no memory effect
Alkaline - common Duracell battery - non-rechargeable
Nickel-cadmium - phones - rechargeable, has memory effect
Lithium-ion - laptops, phones - rechargeable, no memory effect