CC-Lecture-Quality Control
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
is important to customers. It can be assessed and monitored. It can be improved
Quality
Three Phases of Testing Processes
Pre-Analytic, Analytic, Post-Analytic
The only phase of Testing Processes under Quality Control?
Analytic
Planned and systematic activities to provide adequate confidence that requirements for quality will be met
Quality Assurance
Who stated that Quality Assurance is the Measurement of the broader dimension of quality from the perspective of the end-user (client)
Bishop
What are the three (3) parts of the Quality Assurance Model.
Proficiency testing, Staff, Quality Control
Systematic monitoring of analytic processes to detect analytic errors that occur during analysis and to ultimately prevent the reporting of incorrect patient test results
Quality Control
A testing designed to assess the “HEALTH” of an analytical method
Quality control
QC results in lab are used to _________ (confirm) whether the instrument is operating within pre-defined specifications; concluding that patient test results are reliable.
VALIDATE
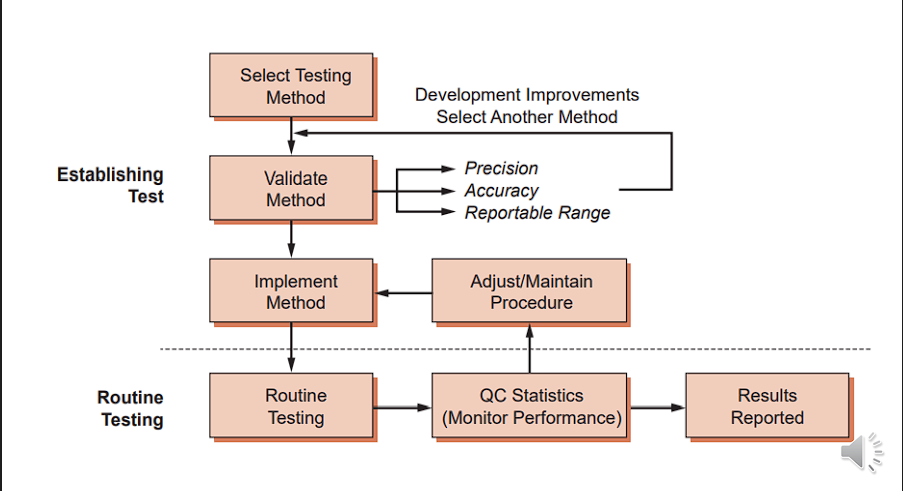
How Does Basic QC Work?
Run a control sample
Compare result with expected range of values
Check to see if the result is right:
✓YES → system is working → report good patient results
✓NO → system is not working → do not report any bad data
Under QC what can you do if there are errors on testing?
• Application of multirule systems (Westgard Rule)
• Plotting data (Levey-Jennings Chart)
• Statistical concepts (Central Tendency, Range, SD, CV)
• “SETTING” the analyzer to give correct results
• Uses calibrators (standards)
CALIBRATION
• “CHECKING”
• if the analyzer is producing correct results
• the instrument’s calibration and other analytical processes
QUALITY CONTROL
• Solution that contains a known amount of an analyte used to calibrate an assay method
CALIBRATION
• QC material or solutions used to monitor the performance (precision and accuracy) of an assay method once it has been calibrated
QUALITY CONTROL
• Run prior to QC manually by the laboratory analyst or automatically by the microprocessors controlling the instrument
CALIBRATION
• Run along-side patient samples and results are calculated from calibration data as the same manner that patient results are calculated.
QUALITY CONTROL
Refers to the substance or base from which the control material is prepared. All of the characteristics of a sample
MATRIX
Control Material that is dehydrated to powder.
LYOPHILIZED control material
• Target value predetermined
• Verify and use
• More expensive
Assayed
• Target values not predetermined
• Full assay to be established
• less expensive
Unassayed
• Pooled sera collected in the laboratory
• Full assay, validation needed
“Homemade” or “Inhouse”
True or False?
“If assayed materials are used, the values stated on the assay sheets should be used only as guides.”
True
True or False?
The Clinical Laboratory Standard Institute (CLSI) recommends that at least 15 measurements should be made everyday when the measurement system is known to be stable.
The Clinical Laboratory Standard Institute (CLSI) recommends that at least 20 measurements should be made on “separate” days when the measurement system is known to be stable.
Describes the closeness of a test value to the actual/ target/ true value.
ACCURACY
ACCURACY can be measured in three ways:
1. Recovery study
2. Interference Study
3. Comparison of Methods of Study
• The consistency of a series of test results
• The closeness of agreement between independent test results obtained under prescribed condition.
• The degree of replication of data
PRECISION
• Ability of an analytical method to give repeated results on the same sample that agree with one another
PRECISION
The capacity of a method to maintain both accuracy and precision
RELIABILITY
Capacity to produce the same results on one sample again and again when performed by the same individual using the same lot numbers on the same instruments
Repeatability/ Practicability
Capacity of the method to produce the same results on one sample again and again when performed by different individuals on different days using different sets of reagents
Reproducibility
• Ability of an analytical method to measure the smallest concentration of the analyte of interest
ANALYTICAL SENSITIVITY
• Ability of an analytical method to measure only the analyte of interest
ANALYTICAL SPECIFICITY
Ability of the test to detect the proportion of individuals with that disease who test positively with the test
DIAGNOSTIC SENSITIVITY
Ability of the test to detect the proportion of individual without the disease who test negatively for the disease
DIAGNOSTIC SPECIFICITY
Central organization sends out challenge specimens for testing
Proficiency Testing or External Quality Assessment from NRL’s
Can you Explain Method Evaluation?