Energy and Nutrient Cycling II
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is the role of detritivores?
- Detritivores are decomposers that break down dead matter (like animals and plants)
- They play a major role in the cycling of nutrients (as they make molecules from high level consumers available for plants (primary producers)
What are the major factors of decomposition?
- Temperture (more = faster rate)
- Moisture (more = faster rate)
- Nutrient availability (more=faster rate)
How is decompistions effected in different biomes?
Tropical biomes
(warm & high moisture lvls)
- Decompistion occurs at a rapid rate
- This means there is less nutrients in the soil because they get washed away in a faster rate
- More exposed bedrock
Colder biomes
(cold and lower mostiture lvls)
- Decompisition happens slower due to microbes working slower (decompisition stops at -14˚c)
- More nutrients in soil as there is more time for the pummus to build up
Why are nutreint cycles called biogeochemical cycles?
Bio=apart of biological systems (eg cell function)
Geo=occurs over a geographic timescale (eg rocks weathering)
Chemcial=nutrients are chemical compounds that cycle round
Cycle=it is a cycle
What are the two characteristics that define the main reservoirs of elements?
- Whether they contain organic or inorganic matter (organic vs inorganic)
- Whether these materails are directly available for use by organisms ( available vs unavailable)
Organic molecules occur when other molecules bond to carbon
What are the 4 resourviours of resources?
Organic, available
- Living organisms (eg animals & plants)
- Detritus
Organic, unavailable
- Peat, coal, oil
Inorganic, available
- Atmosphere (eg. CO2, N)
- Water
- Soil
Inorganic, unavailable
- Minerals in rocks
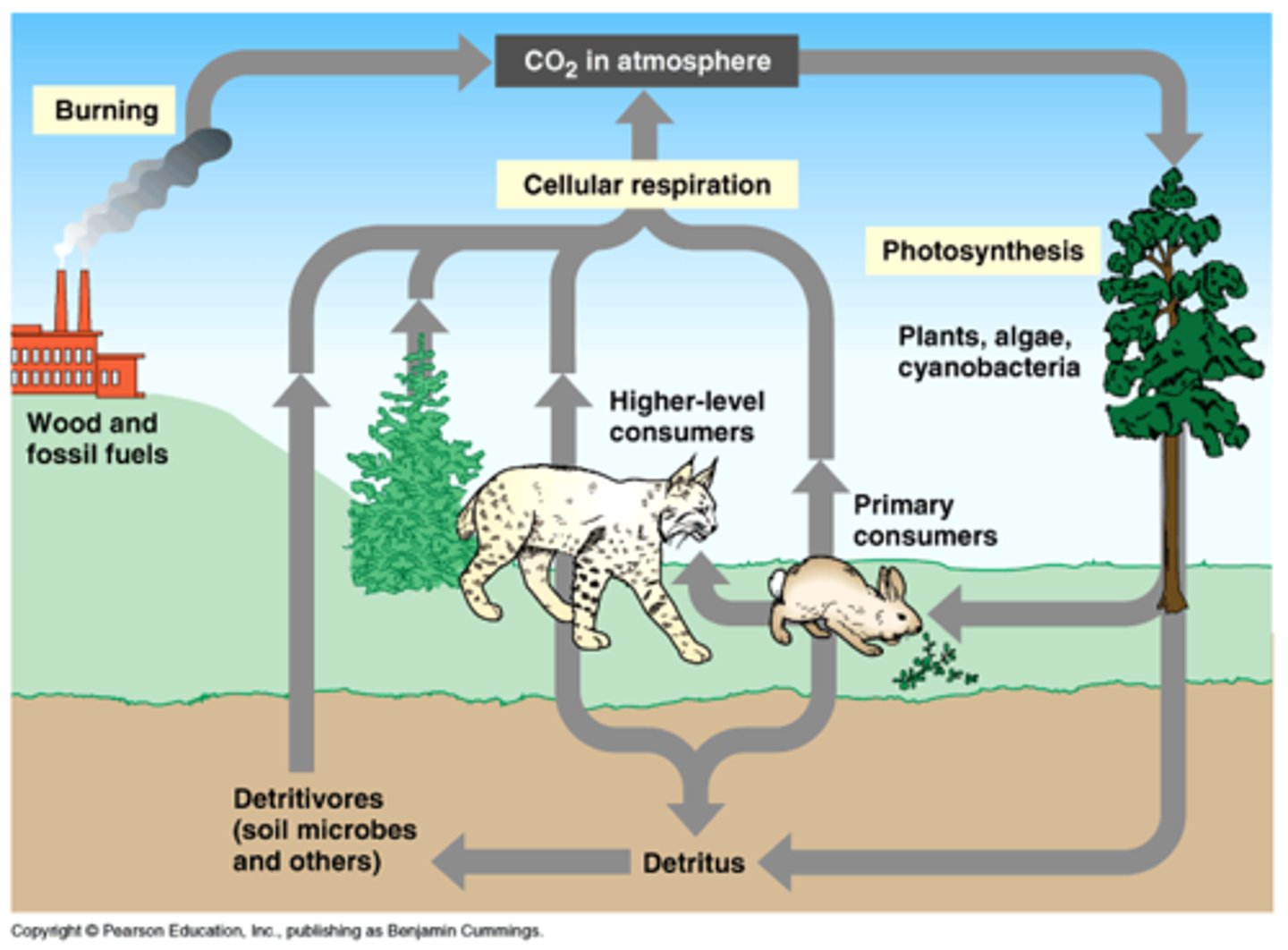
What are the four major factors to consider in the cycling of water, carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus?
- Each chemical's biological importance
- Forms in which each chemical is available for use
- Major resorvures for each chemical
- Key processes driving movement of each chemical throughout it's cycle
Describe the water cycle
- Essentail for all organisms
- Needed for cellular function
- Movement of water happens via evaporation, condensation (clouds), precipitation (rain) and percolation (water movement through soil)
Describe the carbon cycle
- Nearly all life forms are made out of carbon organic molecules
- Plants convert CO2 into organic molecules that are made avaiable to consumers
- Carbon only available from primary producers
- Carbon is released when organisms breath
- Carbon resourviours are made out of fossil fuels, forests etc.
^ carbon resourviours are needed to sustain carbon equilibrium, if they are damaged/taken away then there is more carbon in the atmosphere which changes the enviroment of the atmosphere
Describe the nitrogen cycle
- Nitrogen is available for plants as NH4 (ammonia) and NO3 (nitrate) (nitrate is main one tho)
- Enters the plants via nitrogen fixing bacteria
- Ammonification makes NH4 molecules from NH2
- Nitrofication is when NH4 is broken down into nitrate
- The air is made up of around 70% nitrogen
- All organisms need nitrogen to survive
Describe the phospherous cycle
- Phospherous makes up phospholipids and ATP
- Mainly found in rocks of marine origin
- Has a cycle that is a long geographical time span
^ sedimentation, takes a long time (20, 000-100, 000 years)
How has human activity determentally impacted the enviroment of the earth?
- Higher levels of carbon due to burning fossil fuels, leads to increase in temp. due to carbon particles letting a lot of sunlight through
- More nitrogen in the biosphere and terrisitrially
^ terisitrally leads to eutrophication
- Deforestation leads to water lose and a loss of clouds due to transpiration (important for inland terristiral ecosystems)
- Deforested areas have more nitrogen run off due to lack of roots
- Water scarcity