Lecture 6: The Stem Cell Niche
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
In adults, what are the distinct populations of stem cells with restricted potency?
Mesenchymal stem cells: bone cells (osteoblasts), cartilage cells (chrondrocytes) + fat cells (adipocytes).
Blood stem cells: RBC, platelets + WBC.
Satellite stem cells: muscle.
Germ cells: oocytes + sperm.
What happens to each of the 2 daughter cells produced when stem cells divide?
One goes down route of differentiation (classic stem cell division).
Define transit amplifying cells
Undifferentiated population in transition between stem cells + differentiated cells.
Define populational asymmetry
In a stem cell population certain cell division may produce 2 stem cells, others make 2 cells that will differentiate + other may have one of each.
Why must division rates be balanced?
To keep stem cell population constant.
Describe the structure of the skin
Has 3 main layers: epidermis, dermis + subcutis. Has hair follicles, sebaceous glands + sweat glands.
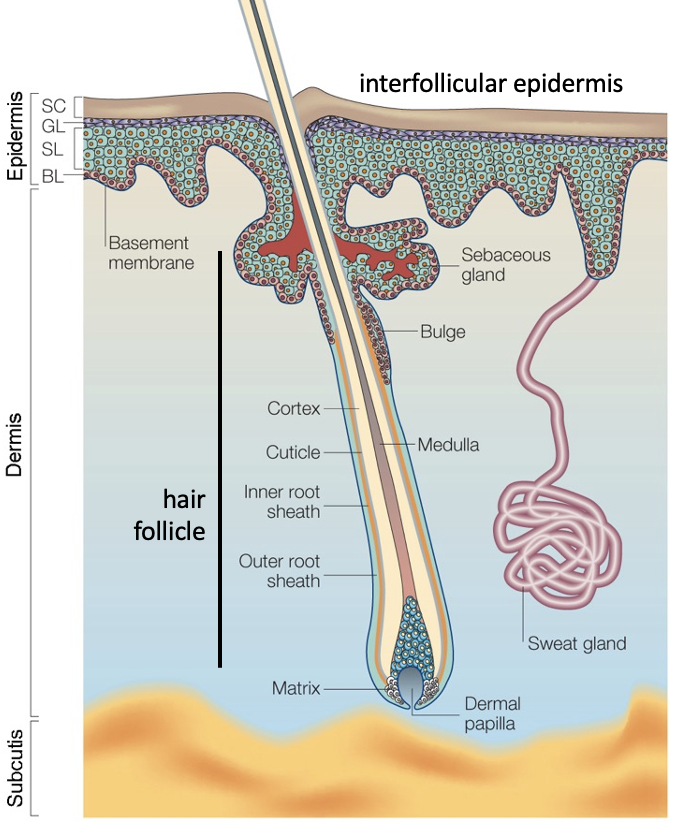
What is the epidermis made up of?
Keratinocytes.
What does the dermis contain?
Fibroblasts + BVs.
Define basal keratinocytes
Stem cells. Divide to make daughter cells which then move up into regions above, then die at a certain point by programmed cell death as contains keratin = gives outer layer of skin.
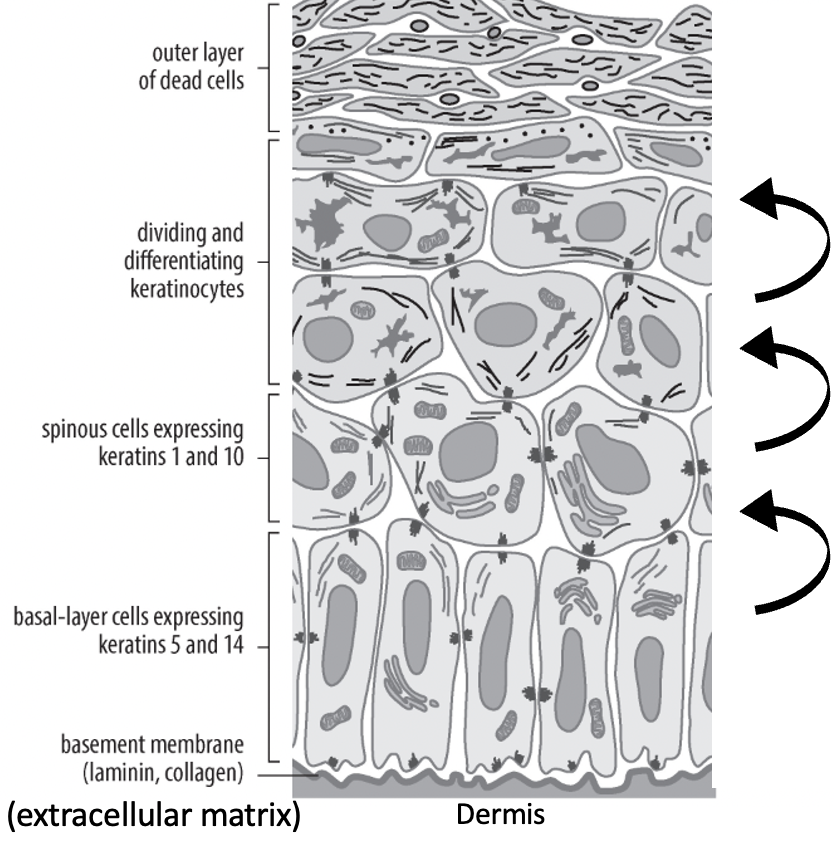
Why is the fact that keratinocytes express different keratins as they move up regions important?
Can be used as markers to indicate which level keratinocytes are at.
What do Wnt signals do + where are they released from?
Inhibit differentiation. Come from the dermis.
What do integrins do?
Hold cells to the basement membrane (maintains stem cell population. Expressed on outside of cells + can stick to the extracellular molecules.
What do Notch signals in maturing keratinocytes do?
Inhibits integrin gene expression.
What does ECF do?
Inhibits Notch activity.
What does the stem cell niche bulge do + where are they located?
Provide additional source of stem cells. Located in the hair follicle. Provide the cells that form the follicle. If the skin is badly damaged, bulge cells can also contribute to the epidermis + sebaceous glands.
Describe the disease junctional epidermolysis bullosa (JEB) + potential treatment method
Adhesion between dermis + epidermis is impaired. Patients have mutations in adhesion genes such as LAMB3. Can culture cells from JEB patients, replace the damaged gene in cell culture (done using virus to inject correct form of LAMB3), then grow it to replace the skin in the patient.
Why is the gut lining continuously replenished?
The contents of the gut create a very harsh environment where cells need to be continuously replenished.
What are the cells of the small intestine?
Enterocyte (absorption).
Goblet cells (secrete mucus).
Enteroendocrine cells (secrete peptide hormones).
Paneth cells (secrete anti-microbial peptides).
Stem cells.
Submucosa cells (help to maintain the stem cells).
What are the genes which are markers for stem cells in the small intestine?
Small dividing stem cells express Bim1. Fast dividing stem cells express Lgr5.
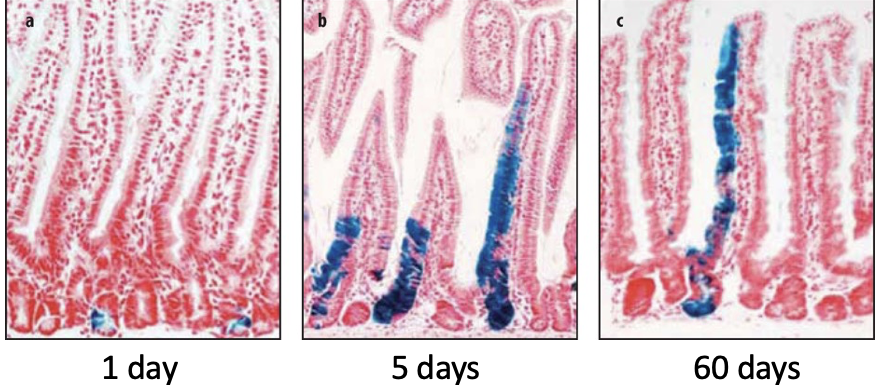
How do we know that Lgr5 positive cells are stem cells?
Lineage tracing means we can determine cell fate. Transgene made that is controlled by the promoter for Lgr5, causes single cells to express a marker. The marker is a bacterial gene (beta galactosidase) which turns cells blue, is expressed in the cell + all of its off spring permanently.
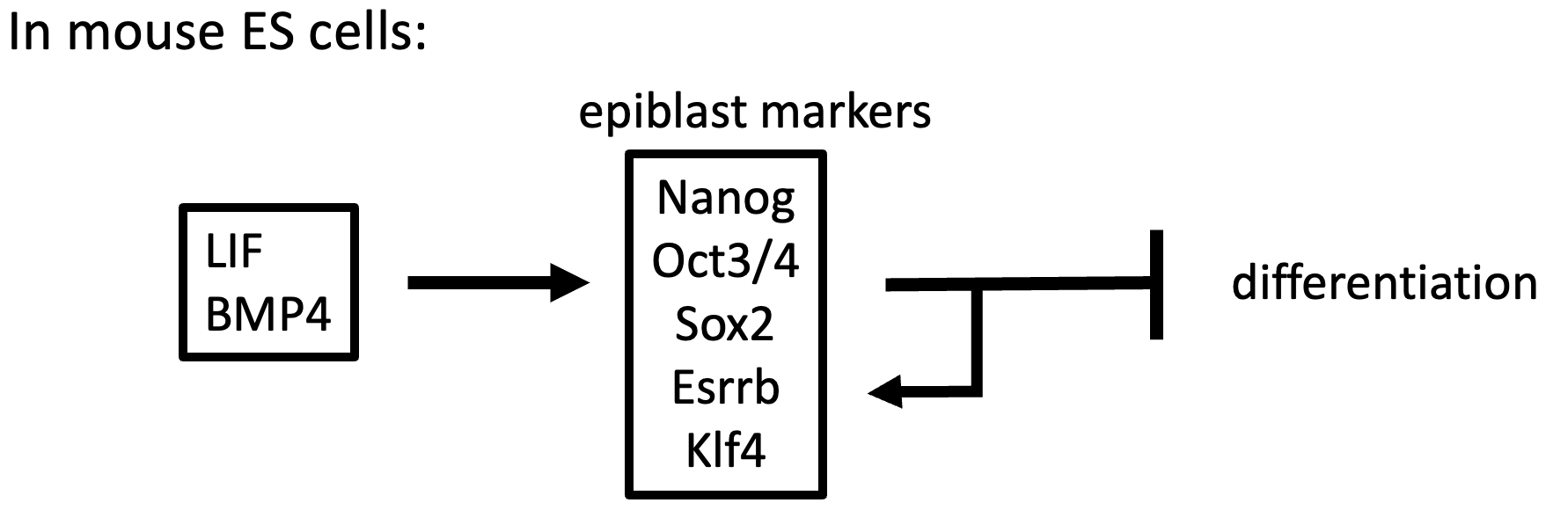
What happens if BMP/LIF (pluripotent state) is removed from cells? (in mice)
Causes them to differentiate into different cell types. Each cell needs a specific set of conditions.
When replicating the stem cell niche (in mice), what does specifically defined conditions do?
Maintains the embryonic stem cells in the pluripotent state (BMP + LIF) which replaces the stem cell niche found in vivo.
Define chimera
Animal with mixed genetic identity. Made the you mix ES cells with normal embryo + the ES cells contribute to different tissues in the adult.
Define teratomas
Benign tumours that contain differentiated tissues.
What is a difference between mouse and human ES cells?
Human ES cells need different treatment than mouse ES cells as they need FGF + actin. Human ES cells appear to be pluripotent.
What do LIF and BMP4 do?
Maintain epiblast markers (so all Tfs are inside the cell) which maintains ES identity as blocks differentiation.
What happens if we activate epiblasts marker expression in differentiated cells?
The cells dedifferentiate and become stem cells. Is because these Tfs were inserted into a differentiated cell using a viral vector: Oct3/4, Sox2, KIf4, c-Myc.
Why is it better to make stem cells by taking differentiated cells and turn them into iPS cells?
Don’t have to obtain ES cells which is difficult + has many ethical issues.