skeletal muscle
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
muscle cells can be classified as [ ] or [ ]
striated, non-striated
skeletal muscle is [ ] and has [ ] on the periphery of the cell
striated, nuclei
skeletal muscle has a [ ] mode of contraction
voluntary
skeletal muscle is made of [ ], [ ] and [ ] connective tissues
endomysium, perimysium, and epimysium
the four types of tissue are [ ], [ ], [ ], and [ ]
connective tissue
muscular tissue
epithelial tissue
nervous tissue
skeletal muscle is widely distributed throughout the body, it is [ ] to the skin and hypodermis
deep
skeletal muscles are attached mainly to bone except for [ ] and [ ]
muscles of facial expression
intrinsic tongue muscles
the hierarchy of the structures in skeletal muscle is?
epimysium » perimysium » endomysium » sarcolemma » nucleus » sarcoplasm » myofibril
the connective tissue around muscle is known as [ ]
epimysium
connective tissue that surrounds fasicles (group of muscle cells)
perimysium
the connective tissue that is around a muscle cell / myofiber is [ ]
endomysium
the muscle cell plasma membrane is the [ ]
sarcolemma
the muscle cell cytoplasm is known as [ ]
sarcoplasm
sarco-, myo-, and -mysium mean muscle
[ ] are cord-like where [ ] is more of a sheet
tendons, aponeurosis
tendons/aponeurosis are fibrous and [ ]
non-contractile and inflexible
[ ] inform the CNS about changes muscle stretch and tension
Proprioceptive sensory organs
[ ] detect stretch while [ ] detect tension
muscle spindles, golgi tendons
the golgi tendon organ detecting tension is a [ ]
protective feedback mechanism
a [ ] is a bundle of skeletal muscle fibers
fascicle
fascicles are surrounded by perimysium and contain [ ] and [ ]
collagen and elastin
the [ ] is composed of reticular fibers and contain capillaries, nerve fibers, and stem cells for repair
endomysium
the [ ] and [ ] are composed of dense irregular connective tissue
epimysium and perimysium
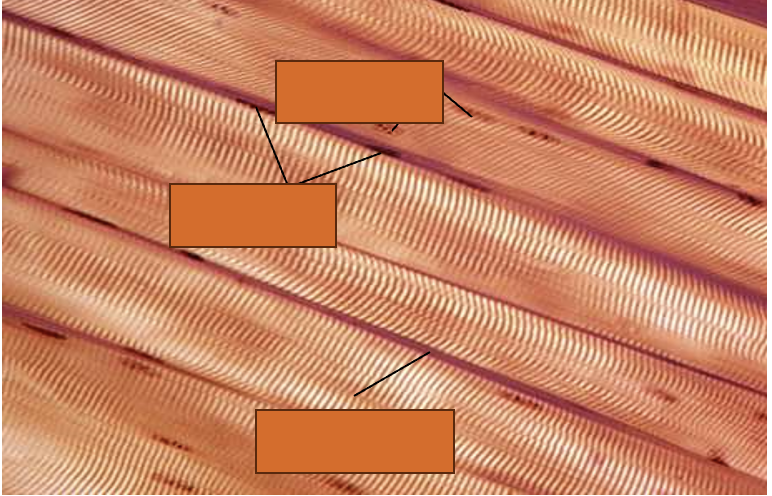
from top to bottom, the arrows are pointing at ?
1) muscle cell nuclei
2) fibroblast nuclei
3) endomysium
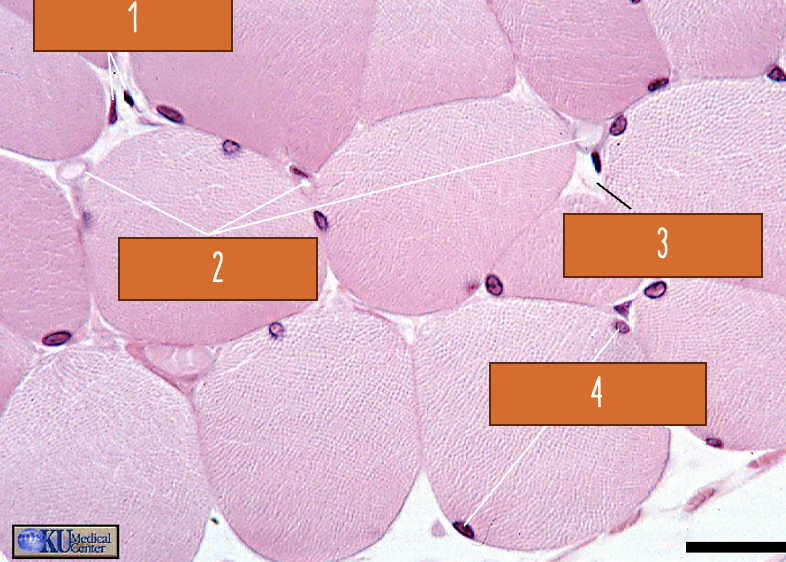
the arrows are pointing to?
1) fibroblast nuclei
2) capillaries
3) endomysium
4) muscle cell nuclei
[ ] synthesize proteins to make up myofilaments
myotubes
a portion of the myoblast population does not fuse but instead differentiate into [ ]
satellite stem cells
[ ] are organized bundles of sarcomeres that are surrounded by sarcoplasmic reticulum with an abundance of mitochondria distirbuted around myofibrils
myofibrils
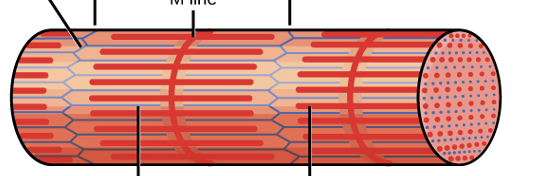
the parts of this myofibril include?
Z line
M line
Thin filament
Thick filament
the [ ] is the basic contractile subunit of skeletal muscle
sarcomere
the [ ] is the dark band that contains thick and thin filaments
A band / Anisotropic band
the [ ] is the light band containing only thin filaments
I band / Isotropic band
the area between the M line and Z disc is known as the [ ] containing only thick filaments
H zone
the attachment site for thick filaments is the [ ]
M line
the area where two thin filaments connect and transverse I bands is called [ ]
Z disc
the [ ] is held constant while the [ ] and [ ] bands narrow
A-band
I-band / H-band
striations are produced by the arrangement of the [ ], [ ], and [ ]
myofibrils, sarcomeres, myofilaments
the three major proteins in skeletal muscle include [ ], [ ], and [ ]
G-actin
Tropomyosin
Troponin
[ ] is the filamentous protein that binds to actin and covers myosin binding site
Tropomyosin
the function of Troponin T (Tnt) is to ?
anchor troponin complex to tropomyosin
the function of Troponin I (Tni) is to ?
inhibit filament interaction
it covers myosin binding site with tropomyosin
the function of Troponin C (Tnc) is to?
bind calcium for initiation of contraction
Myosin is composed of 6 polypeptide chains, 2 of which are [ ] and 4 that are [ ]
heavy
light
the heavy chains have a [ ] structure and form the “tail” of myosin
alpha helical
the light chains of myosin [ ] and contain a [ ]
bind to actin, ATPase site
[ ] prevent treadmilling or “cap them”
accessor sarcomere proteins
[ ] connects the cytoskeleton of a muscle fiber to the surrounding extracellular matrix through the cell membrane
Dystrophin
[ ] caps the plus end of actin filaments where [ ] caps the minus end
CapZ
Tropomodulin
[ ] regulates thick filament length where [ ] regulates thin filament length
Titin
Nebulin
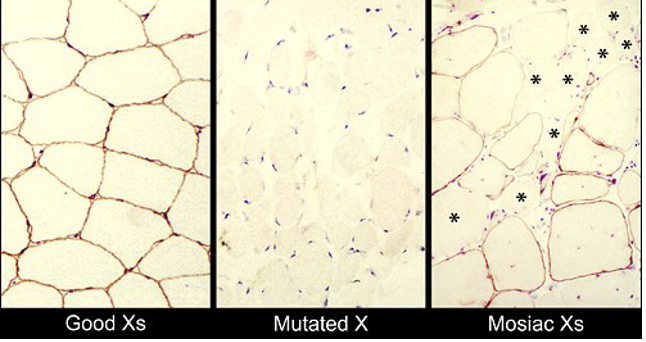
the picture is showing?
A Normal Person
Someone with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
A carrier of DMD
the transverse tubule system contains [ ], [ ], [ ], and [ ]
Sarcolemma
T-Tubule
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
Terminal Cisternae
skeletal muscle contraction is initiated by direct contact at [ ]
somatic-motor- neuron axon terminals
[ ] in the synaptic cleft degrades ACh ending the stimulus and allowing the sarcolemma to repolarize
Acetylcholinesterase
[ ] and [ ] are caused by neurotoxins
Botulism and Tetanus
botulism is characterized by [ ] whereas tetanus is characterized by [ ]
flaccid paralysis
spastic paralysis
[ ] is a chronic autoimmune neuromuscular disease where antibodies are directed against acetylcholine receptors
Myasthenia Gravis