Foundations of Physics Chapter 2: Motion Concept questions
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
A ball is thrown straight upward with some initial speed. When it reaches the top of its flight (at a height h), a second ball is thrown straight upward with the same initial speed. Where will the balls cross paths?
above height h/2
Alice and Bill are at the top of a building. Alice throws her ball downward. Bill simply drops his ball. Which ball has the greater acceleration just after release?
neither-- they both have the same acceleration.
You drop a very bouncy rubber ball. It falls, and then it hits the floor and bounces right back up to you. Which of the following represents the v vs. t graph for this motion?
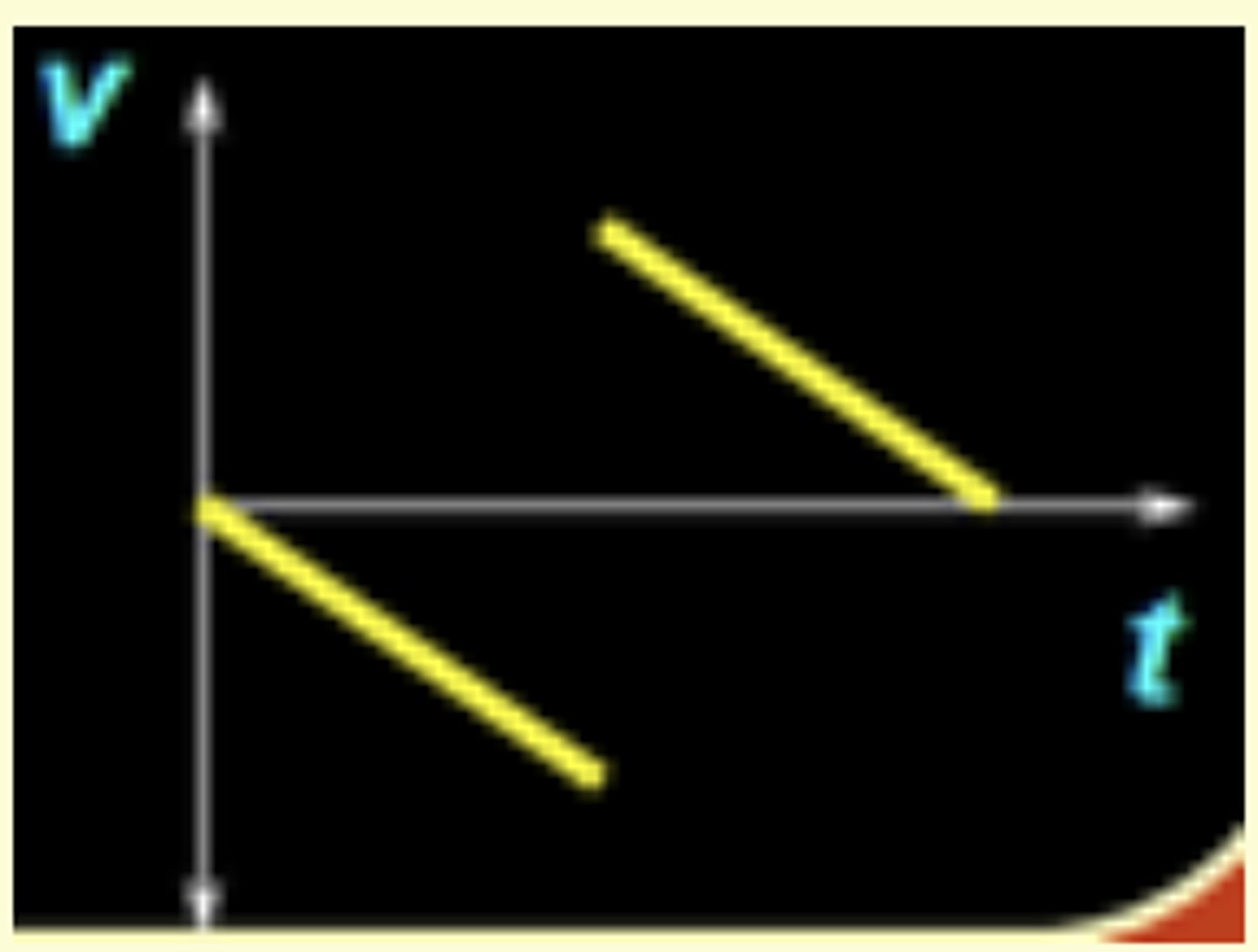
If the position of a car is zero, does its speed have to be zero?
no
Does the odometer in a car measure distance or displacement?
distance
You drop a rock off a bridge. When the rock has fallen 4 m, you drop a second rock. As the two rocks continue to fall, what happens to their velocities?
both increase at the same rate
When an object is released from rest and falls in the absence of friction, which of the following is true concerning its motion?
its acceleration is the same
You drop a rock off a bridge. When the rock has fallen 4 m, you drop a second rock. As the two rocks continue to fall, what happens to their separation?
the separation increases as they fall
Does the speedometer in a car measure speed or velocity?
speed
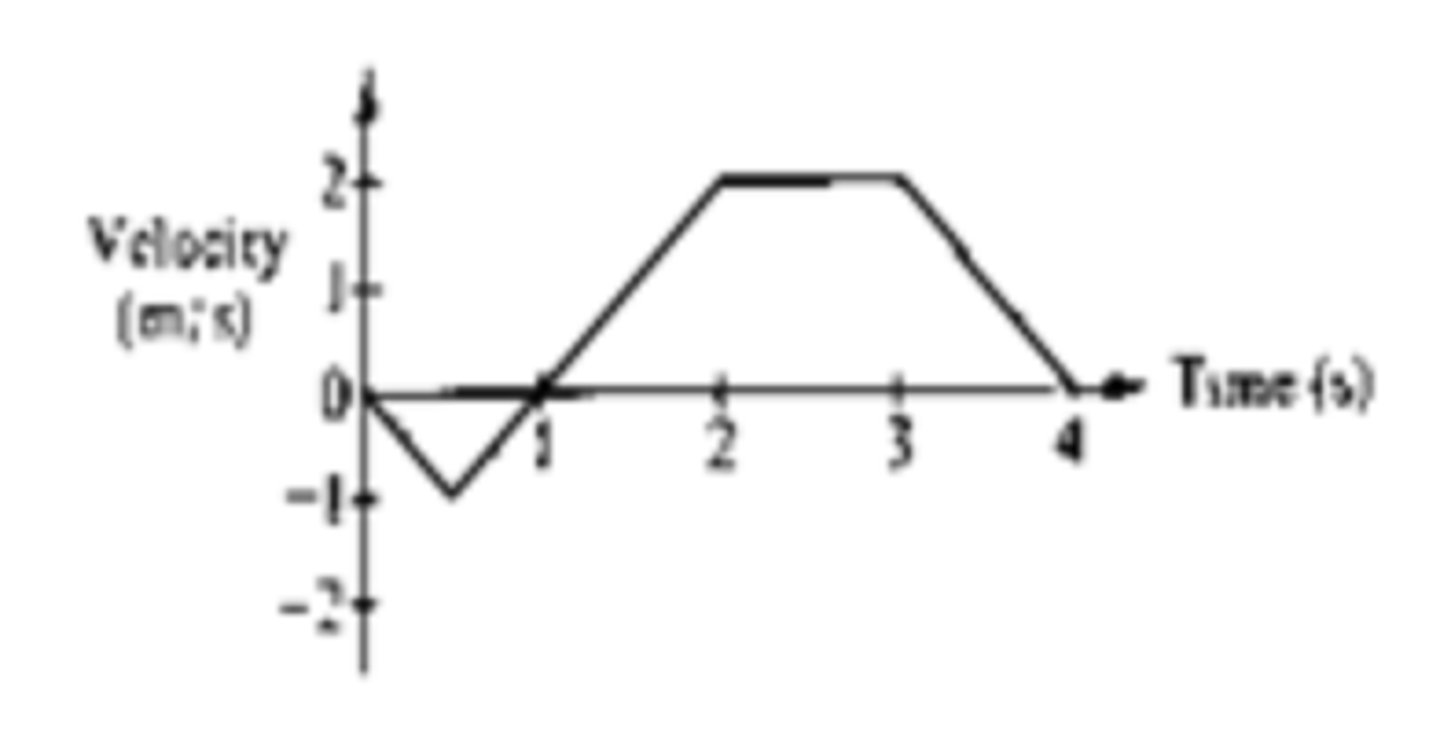
between 1 and 2s
The graph above shows the velocity versus time for an object moving in a straight line. At what time after time = 0 does the object again pass through its initial position?
You drop a rubber ball. Right after it leaves your hand and before it hits the floor, which of the below plots represents the v vs. t graph for this motion? (Assume your y-axis is pointing up.)
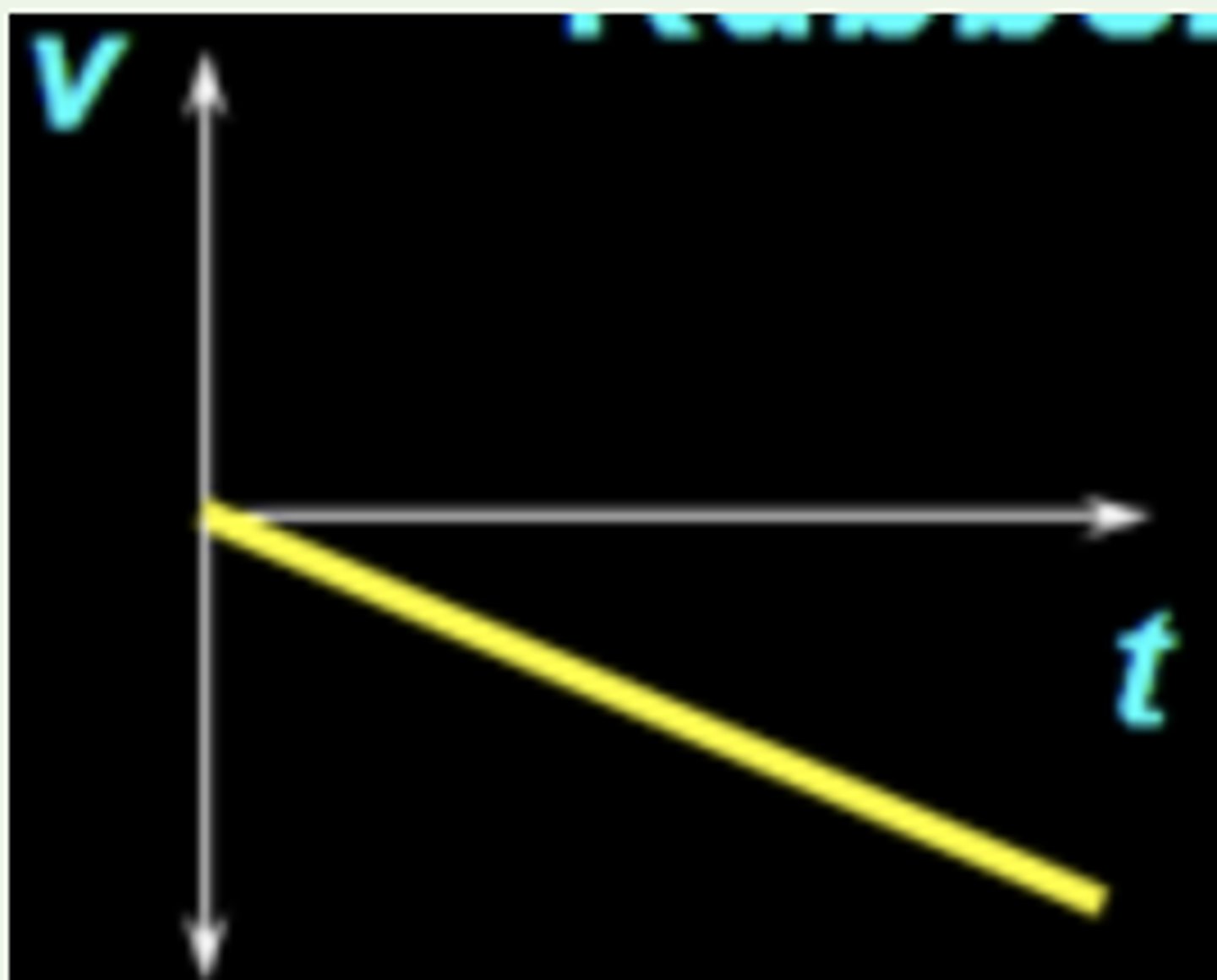
If the velocity of a car is non-zero, can the acceleration of the car be zero?
yes
You drive 4 miles at 30 mi/hr and then another 4 miles at 50 mi/hr. What is your average speed for the whole 8-mile trip?
less than 40 mi/hr
Down arrow
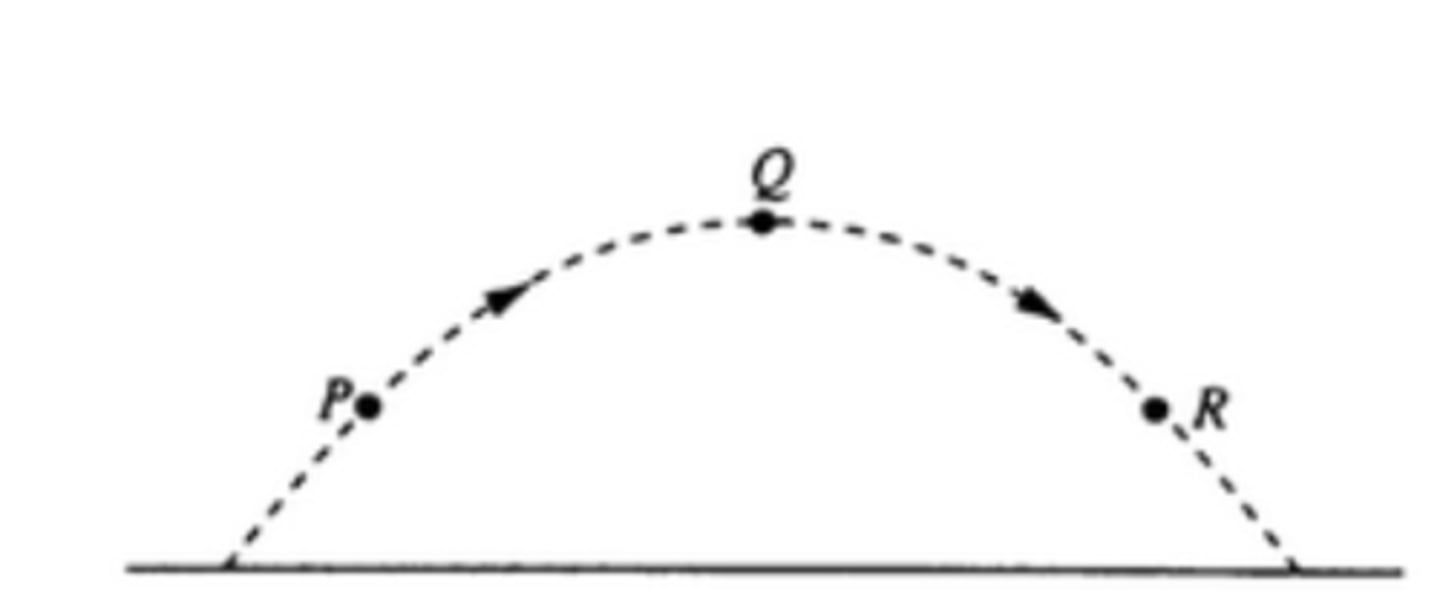
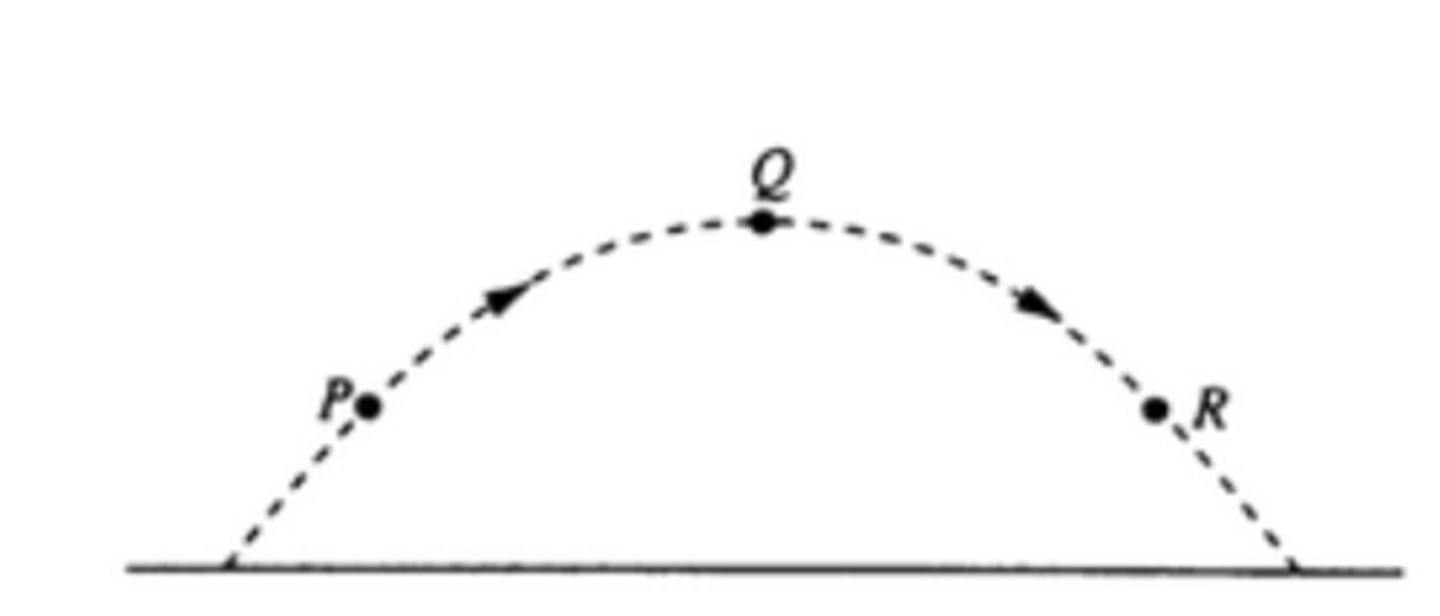
A ball is thrown and follows the parabolic path shown above. Air friction is negligible. Point Q is the path. Points P and R are the same height above the ground. Which of the following diagrams best shows the direction of the acceleration of the ball at point P?
it slows down all the time
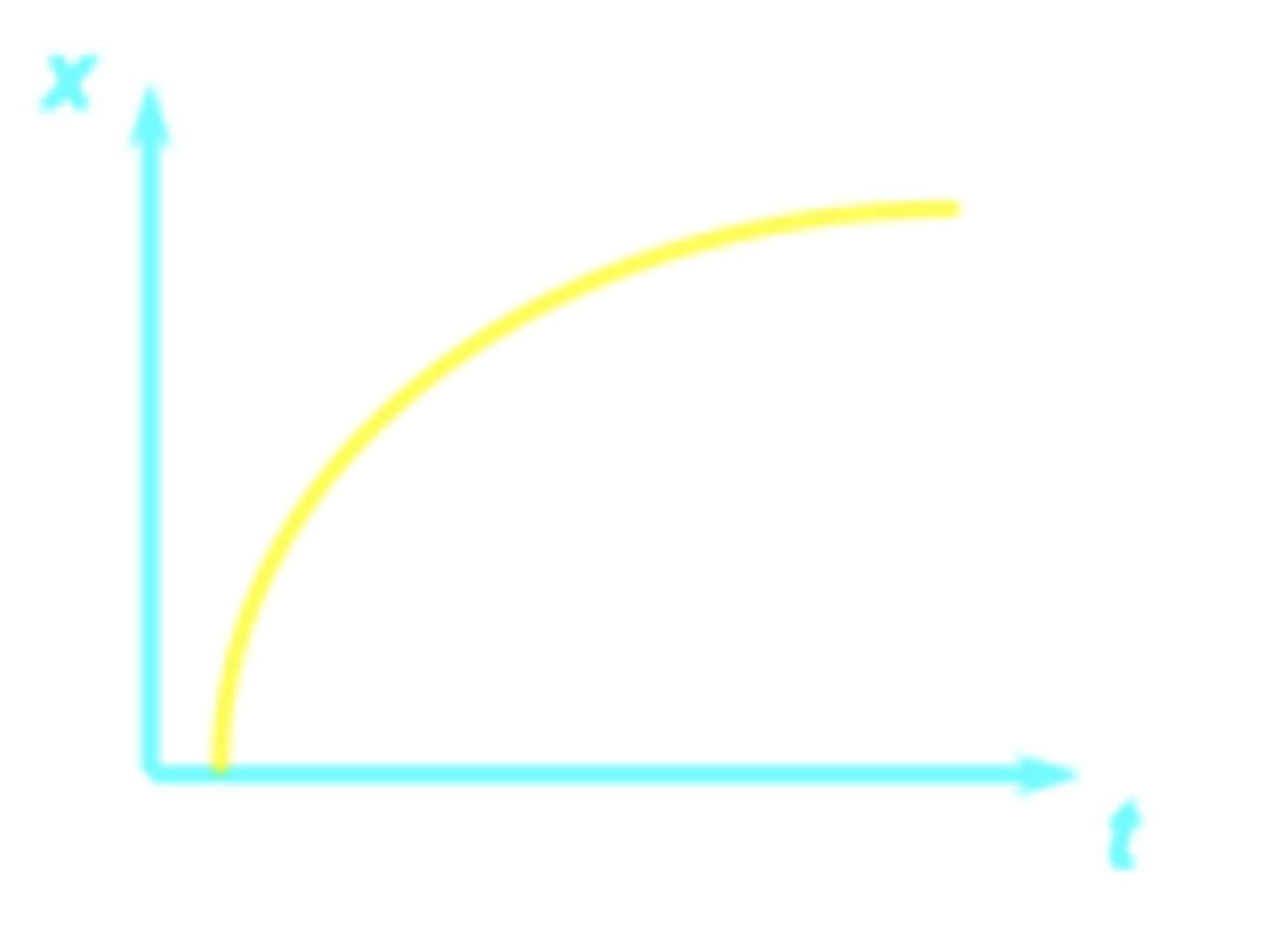
The graph of position vs. time for a car is given. What can you say about the velocity of the car over time?
You throw a ball straight up into the air. After it leaves your hand, at what point in its flight does it have the maximum value of acceleration?
its acceleration is constant everywhere.
The area under a curve in an acceleration versus time graphs gives you?
velocity
You throw a ball upward with an initial speed of 10 m/s. Assuming that there is no air resistance, what is its speed when it returns to you?
10 m/s
When throwing a ball straight up, which of the following is true about its velocity v and its acceleration a at the highest point in its path?
v = 0, but a not 0
Does the displacement of an object depend on the specific location of the origin of the coordinate system?
no
it moves at constant velocity
The graph of position versus time for a car is given. What can you say about the velocity of the car over time?
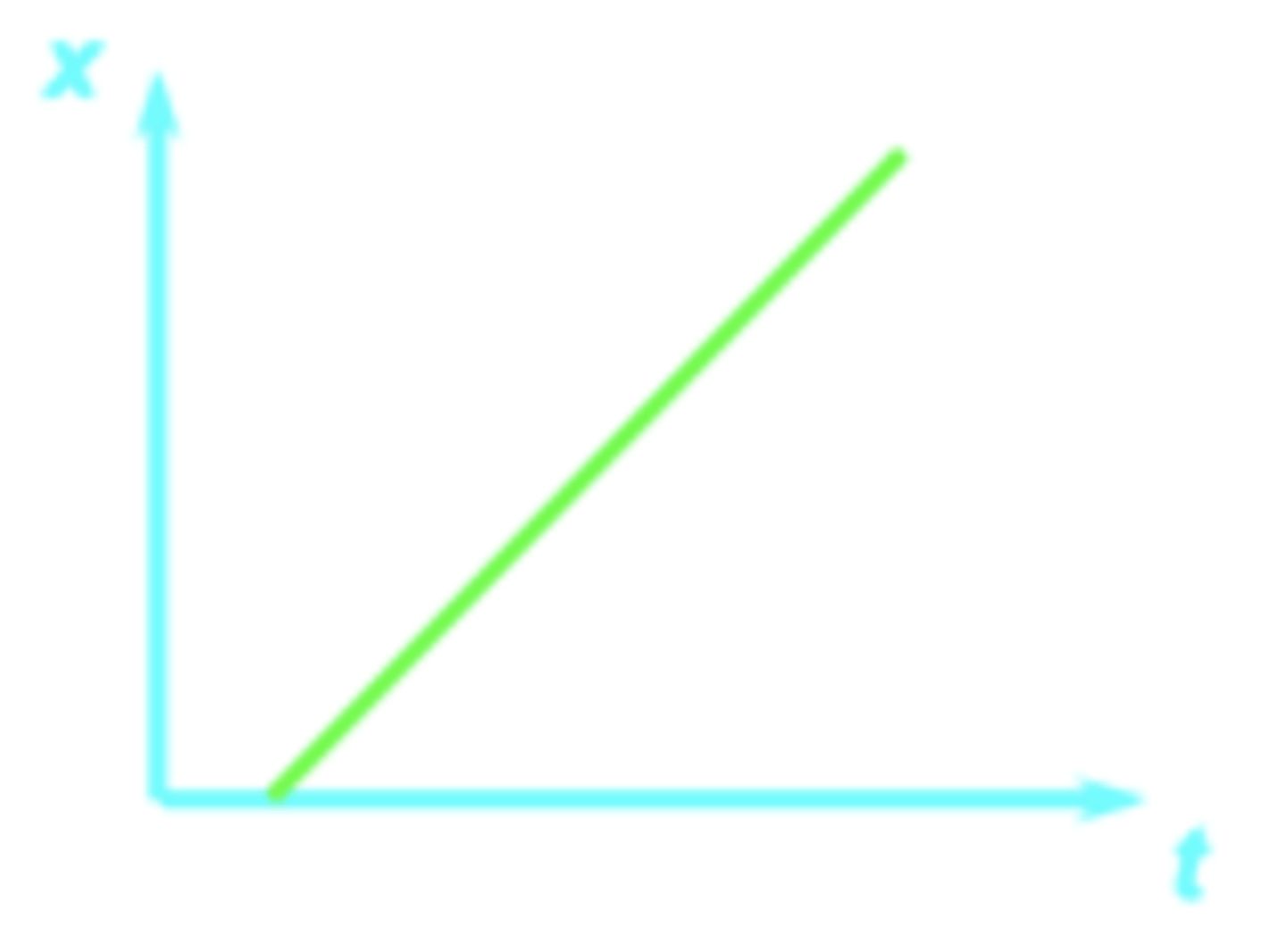
increases
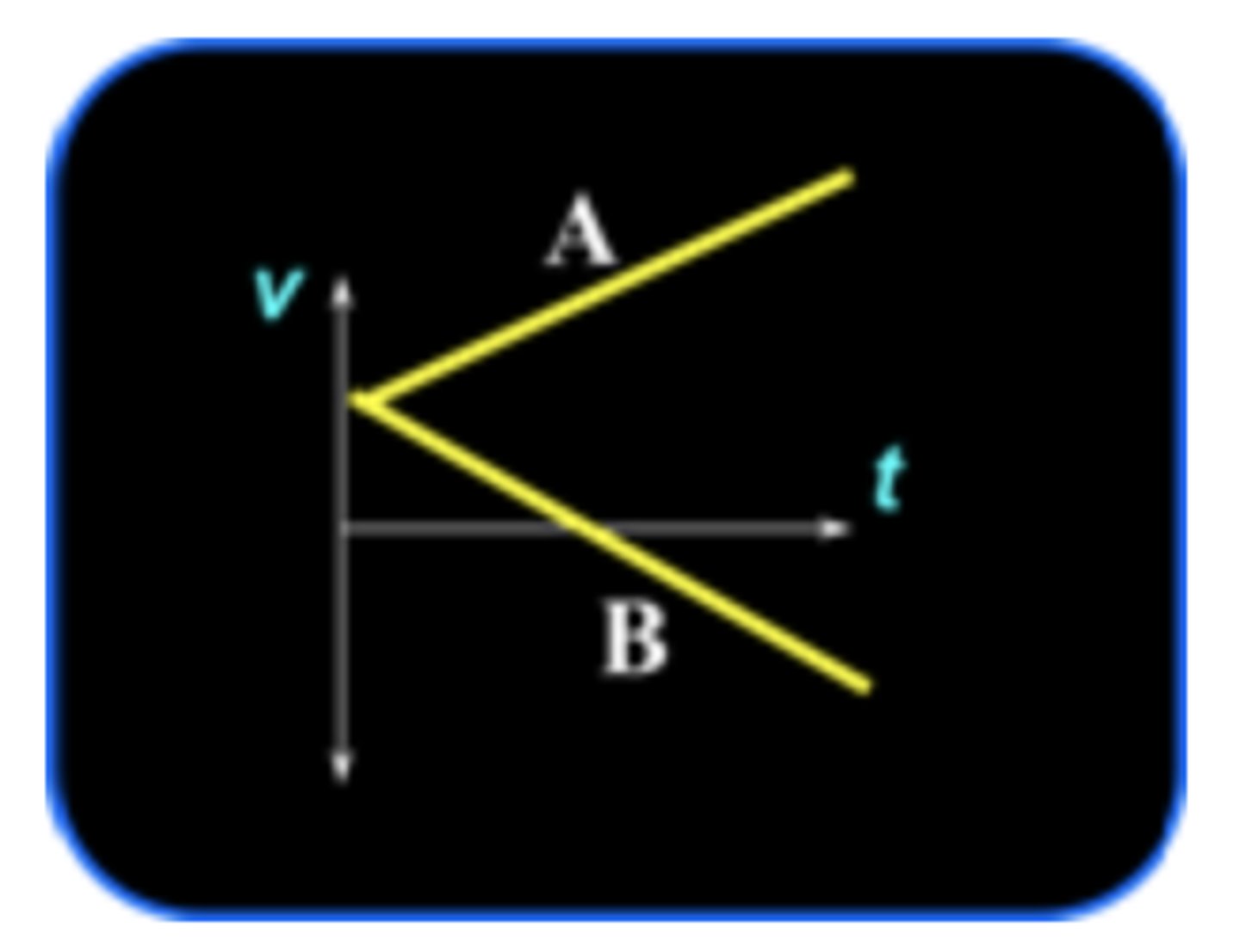
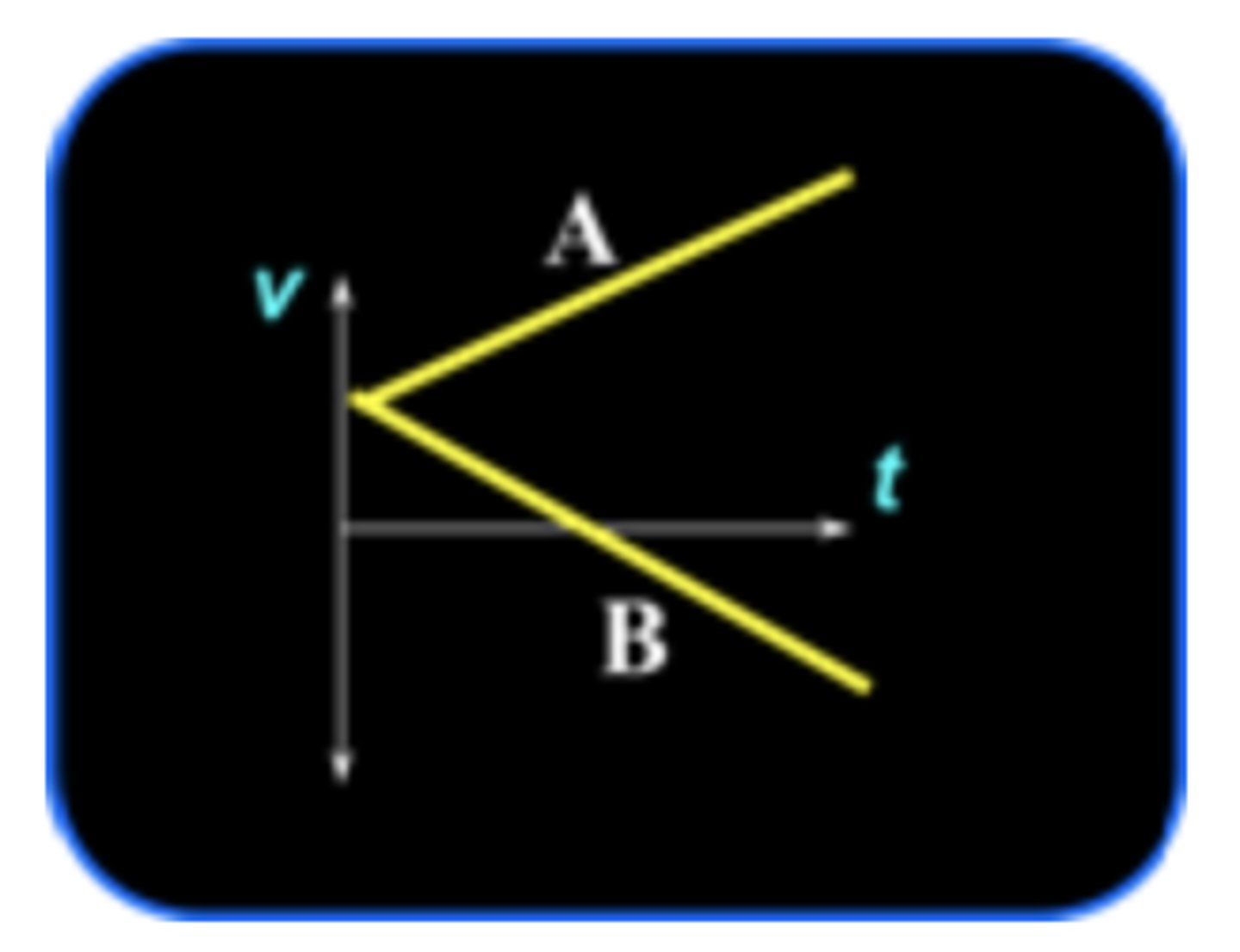
Consider the line labeled A in the v versus t plot below. How does the speed change with time for line A?
square root (2h/g)
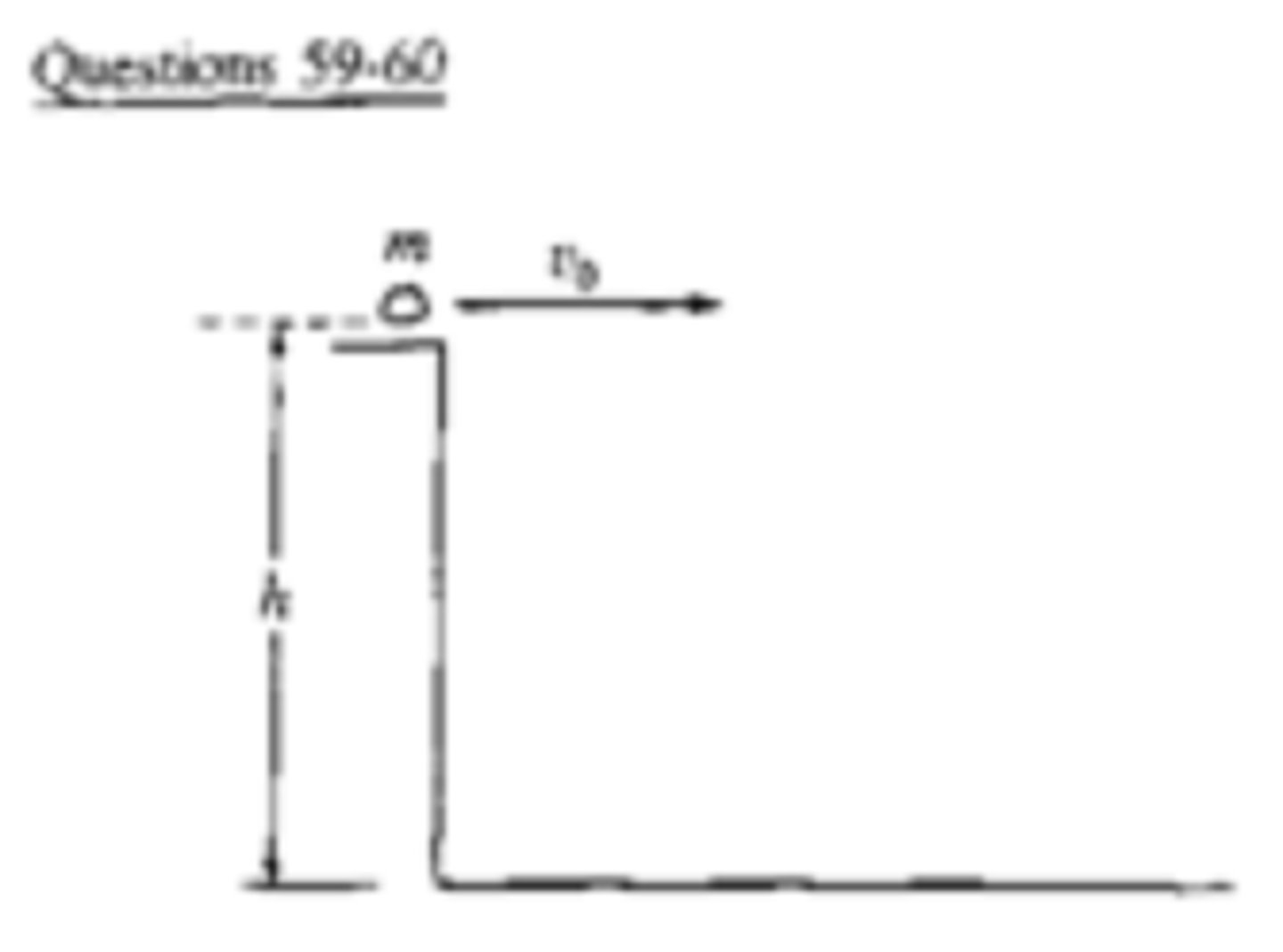
A rock of mass m is thrown horizontally off a building from a height h, as shown above. The speed of the rock as it leaves the thrower's hand at the edge of the building is v0.
How much time does it take the rock to travel from the edge of the building to the ground?
You and your dog go for a walk to the park. On the way, your dog takes many side trips to chase squirrels or examine fire hydrants. When you arrive at the park, do you and your dog have the same displacement?
yes
In which of the following situations would an object be accelerated?
I. It moves in a straight line at constant speed.
II. It moves with uniform circular motion.
III. It travels as a projectile in a gravitational field with negligible air resistance.
II and III only
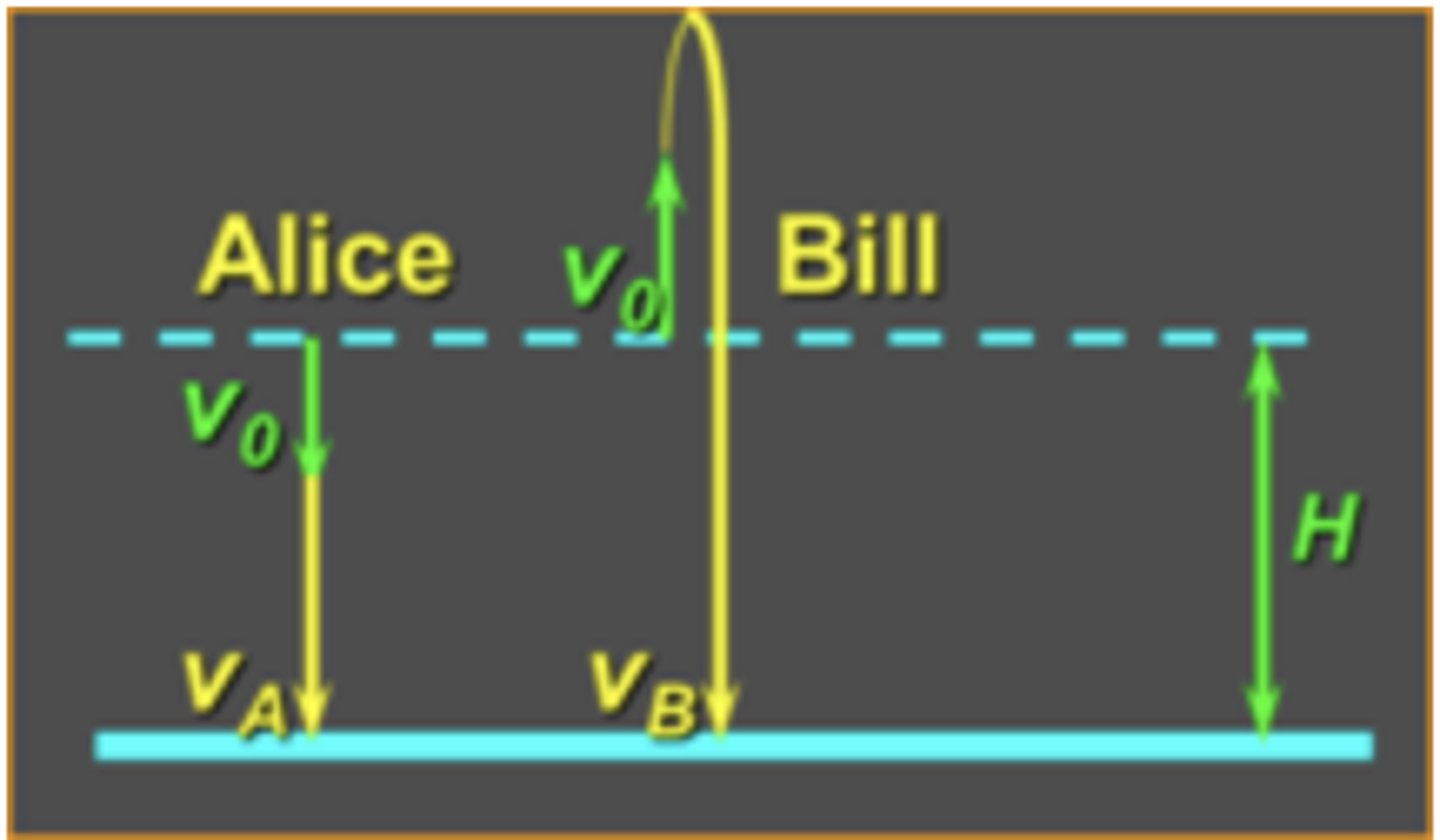
vA = vB
Alice and Bill are at the top of a cliff of height H as shown below. Both throw a ball with initial speed v0, Alice straight down and Bill straight up. The speeds of the balls when they hit the ground are vA and vB. If there is no air resistance, which is true?
decreases, then increases
Consider the line labeled B in the v versus t plot. How does the speed change with time for line B?
If the average velocity is non-zero over some time interval, does this mean that the instantaneous velocity is never zero during the same interval?
no
A ball falls straight down through the air under the influence of gravity. The magnitude of the acceleration a of the ball at any time is equal to 9.8m/s2 that means (assuming down is positive):
the velocity of the body increases by 9.8 m/s during each second
An object is released from rest on a planet that has no atmosphere. The object falls freely for 3.0 meters in the first second. What is the magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity on the planet?
6.0 m/s2
vQ < vP = vR
A ball is thrown and follows the parabolic path shown above. Air friction is negligible. Point Q is the path. Points P and R are the same height above the ground. How do the speeds of the ball at the three points compare?
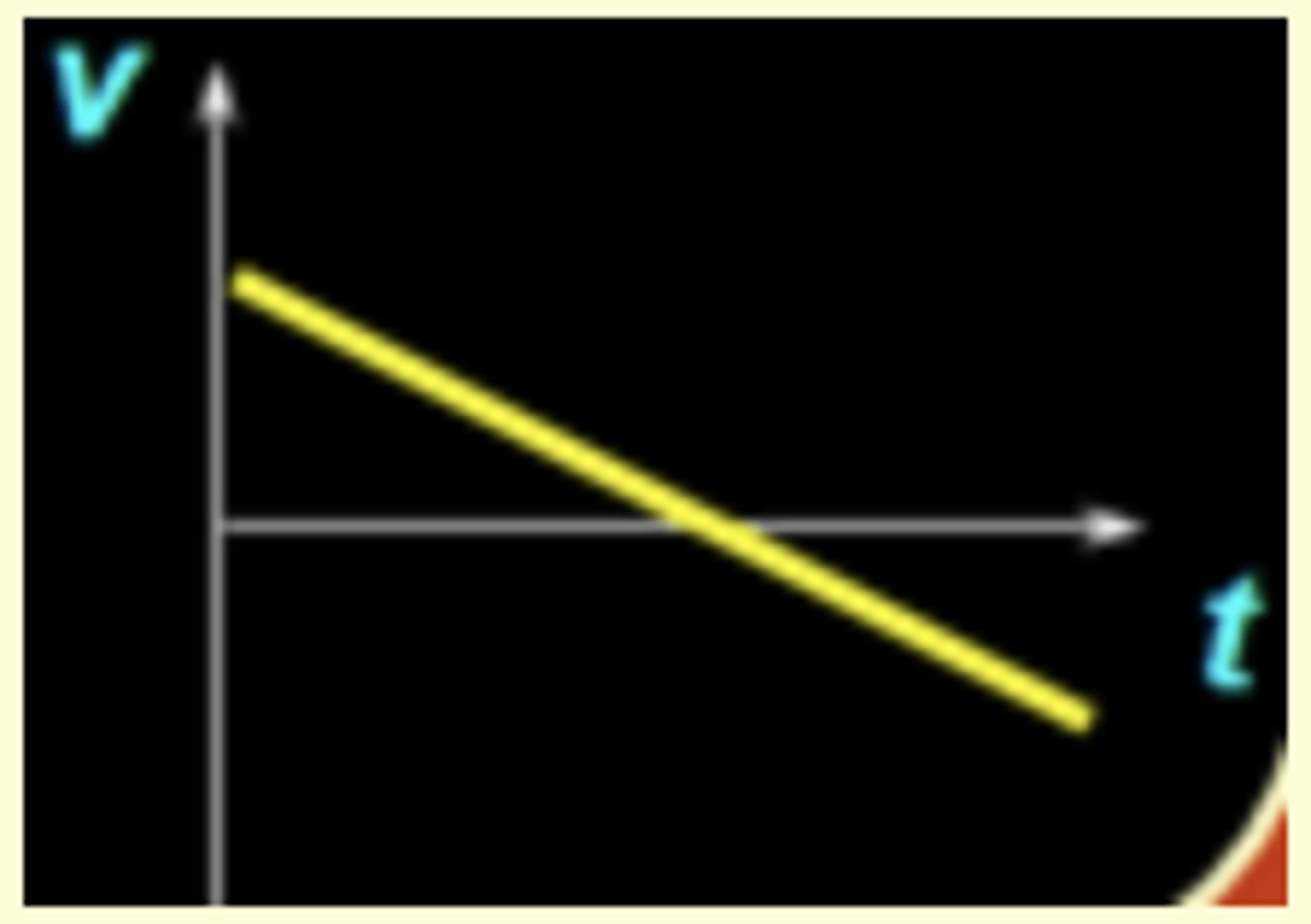
You toss a ball straight up in the air and catch it again. Right after it leaves your hand and before you catch it, which of the below plots represents the v vs. t graph for this motion? (Assume your y-axis is pointing up.)
A block rests at the edge of a platform that is 10 meters above level ground. Air resistance is negligible. The time it will take for the block to reach the ground is most nearly
1.4 s
You drive for 30 minutes at 30 mi/hr and then for another 30 minutes at 50 mi/hr. What is your average speed for the whole trip?
equal to 40 mi/hr
The slope of a position versus time graph gives
velocity