Petrology, Volcanology, & Igneous Rocks
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
The difference between magma and lava is…
that magma is found below the surface, whereas lava is found above the surface
Which of the following rock types is the MOST viscous?
felsic
intermediate
ultramafic
mafic
felsic
The following are all intrusive igneous structures EXCEPT…
Batholith
sill
dike
lava tube
lava tube
Tuff is produced in an ___________________ igneous setting under conditions of _________________ viscosity.
intrusive; high
extrusive; high
extrusive; low
intrusive; low
extrusive; high
Enormous areas of extrusive igneous rocks which were erupted with low viscosity (flowed readily across the surface) are known as…
gabbros
sills
baccoliths
flood basalts
flood basalts
A rock that is phaneritic and felsic is called…
gabbro
granite
basalt
komaiiite
granite
A rock is aphanitic and mafic is called…
granite
rhyolite
andesite
basalt
basalt

Identify the following extrusive igneous texture.
phanaretic
glassy
porphyritic
fragmented
fragmented

Identify the following intrusive igneous texture.
glassy
aphanitic
porphyritic
phaneritic
phaneritic

Identify the following intrusive igneous texture.
aphanitic
fragmented
porphyritic
phaneritic
porphyritic
When magma crystalizes underground, _______________________ are formed.
intrusive igneous rocks
extrusive igneous rocks
volatiles
pyroclastic debris
intrusive igneous rocks
As compared to coarse-grained igneous rocks, all fine-grained igneous rocks…
cool and solidify more quickly
cool and solidify more slowly
solidify at higher temps
solidify at lower temps
cool and solidify more quickly
Coarse grained granite is most close in mineral composition to fine-grained ___________________.
andesite
basalt
gabbro
rhyolite
rhyolite
Basaltic lava that continues to flow after the surface has frozen, resulting in fragmentation of the solidified rock into sharp, angular fragments is known as _____________________________.
pahoehoe
andesitic lava
a’a
rhyolite
a’a

What volcanic feature is shown in the picture?
pahoehoe
rhyolite dome
lahar
fissure
rhyolite dome
When andesitic pyroclastics have been lithified (turned into solid rock) it is known as _______________
tephra
tuff
ash
tuff
All of the following are Cascades Range USA volcanoes EXCEPT _________________.
Mt. Hood
Mt. St. Helens
Mt. Tammany
Mt. Rainier
Mt. Tammany

What is the volcanic feature pictured here?
fissure
crater
conduit
caldera
caldera

What is the volcanic feature pictured here?
fissure
crater
caldera
conduit
conduit

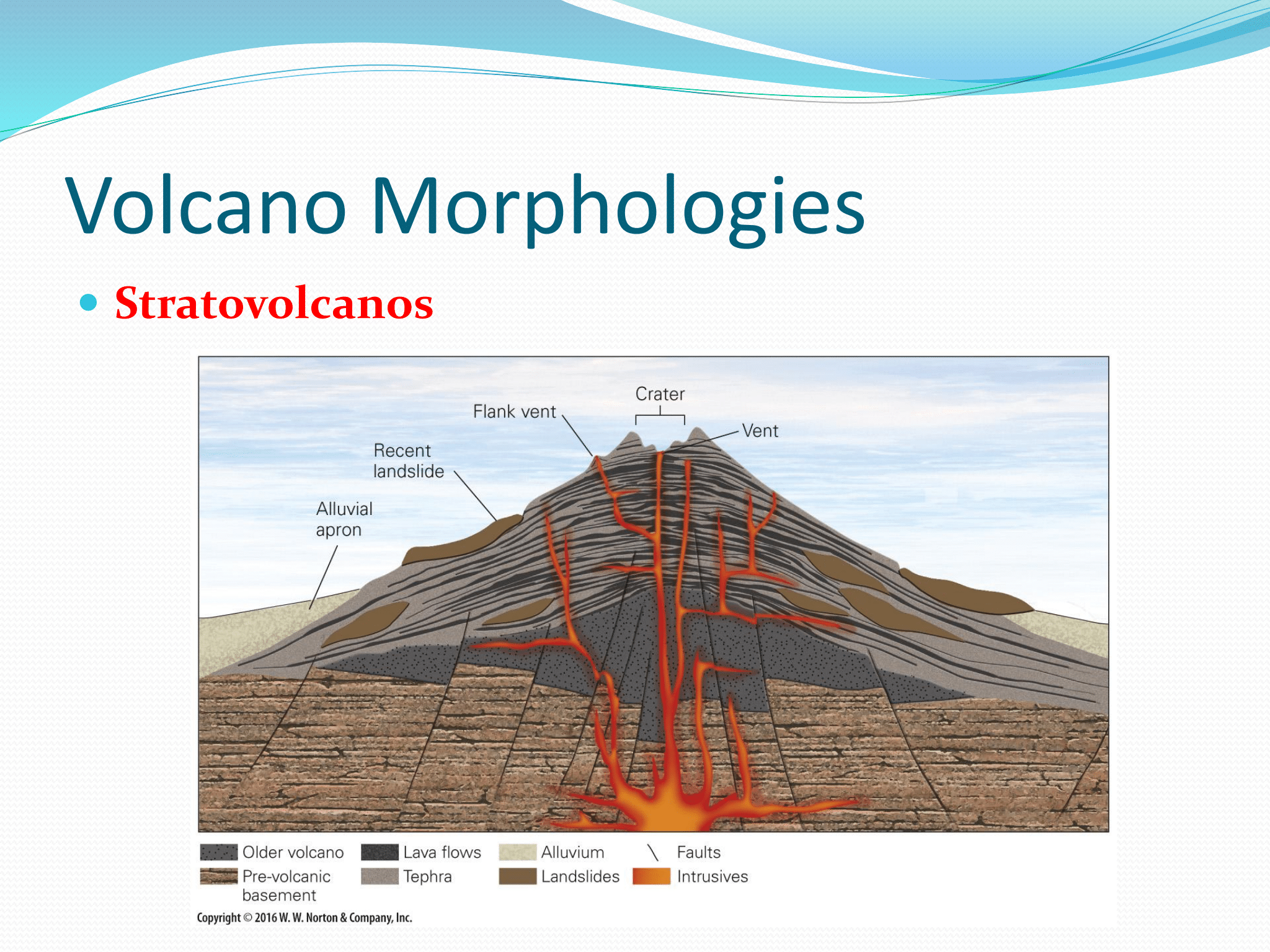
Which type of volcano is pictured here?
stratovolcano
cindercone volcano
shield volcano
duncecap volcano
stratovolcano
Which of the following is the largest eruption?
Krakatoa
Pinatubo
Tambora
Yellowstone
Yellowstone
The hot spot track of the Emperor Seamounts and Hawaiian Islands tells us that _______________________.
the Pacific plate has been moving southeastward for the past 30 million years, and was stationary before that time
The Pacific plate has been moving northwestward for the past 30 million years, but moved northward before that time.
The Pacific plate has been moving northwestward for the past 30 million years, but was stationary before that time.
The Pacific plate has been moving southeastward for the past 30 million years, but was moving southward before that time.
The Pacific plate has been moving northwestward for the past 30 million years, but moved northward before that time.
The Colombia Basin igneous deposits are what kind of volcanic product?
flood basalts
pyroclastic flow
andesitic lava flows
ashfall
flood basalt
Which volcanic gas product was responsible for the deaths at Lake Nyos in 1986?
hydrogen sulfide
sulfur dioxide
methane
carbon dioxide
carbon dioxide
Which of the following volcanic hazards is the most dangerous to humans in the vicinity of the eruption?
basaltic lava flows
pyroclastic flows
ashfall
tsunamis
pyroclastic flows
All of the following are indications that an eruption MIGHT be imminent EXCEPT ___________________.
basaltic lava flows
pyroclastic flows
ashfall
tsunamis
pyroclastic flows
The Mt. St. Helens eruption in 1980 was which type of eruptive style?
explosive
effusive
offensive
explosive
Tuff and tephra differ in what way?
tephra is made in ash falls, while tuff is made in pyroclastic flows
tephra is silica-rich, while tuff is mafic
tephra is unconsolidated material, while tuff has been lithified
tephra is weak, while tuff will beat you up
tephra is unconsolidated material, while tuff has been lithified
Minerals that can display multiple habits are called…
multifaceted
polycrystalline
polymorphic
pseudomorphic
polymorphic
Which of the following is NOT a part of the definition of a “mineral?”
solid
faceted
homogenous
Naturally occurring
faceted
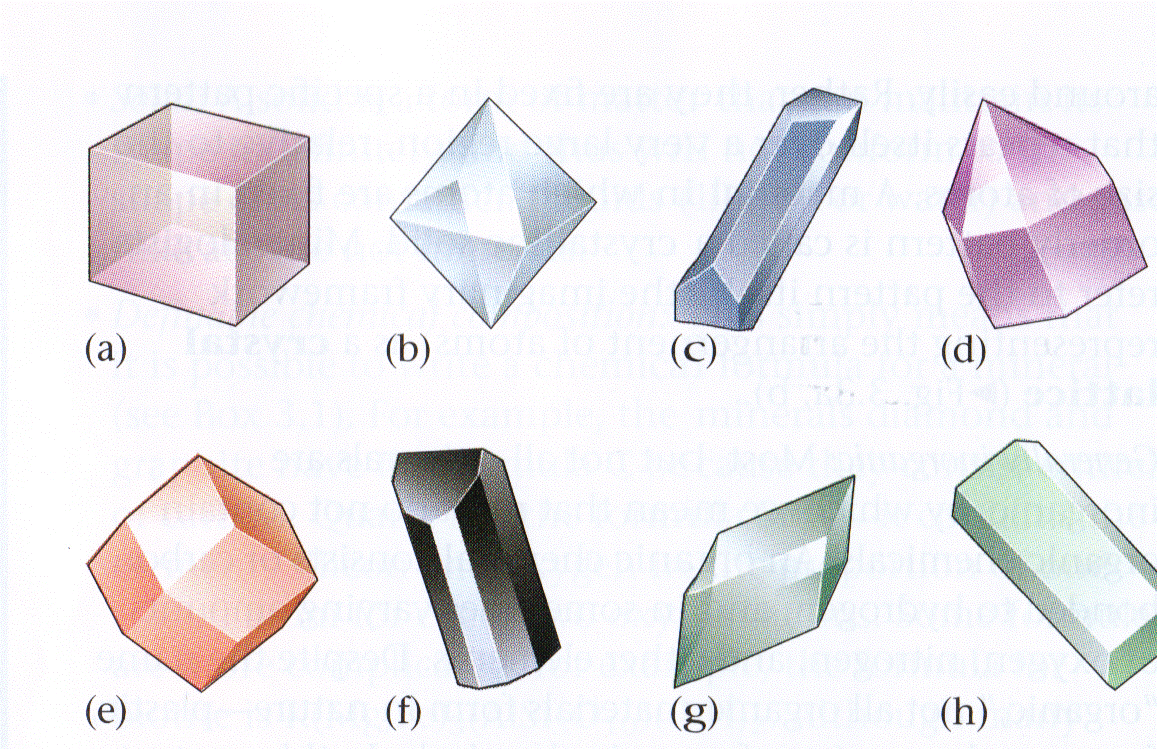
How many 4x symmetry axes does crystal A have?
1
2
3
4
3
Which of the following is NOT an example of luster?
Sticky
Metallic
Silky
Resinous
sticky
Gemstones do not display faces, instead they have…
facades
cleavage planes
facets
sides
facets
Which of the following exhibits conchoidal fracture?
calcite
muscovite
feldspar
quartz
quartz

The mineral pictured is scratched BY corundum but CAN scratch apatite and flourite. What is it likely to be?
Topaz
Garnet
Feldspar
Quartz
Garnet

The pictured mineral can be scratched with a penny. What is it likely to be?
Calcite
Feldspar
Quartz
Kyanite
Calcite

The following mineral is an example of what kind of silicate?
double-chain
sheet
independent
framework
sheet
Galena is an example of what type of mineral?
Halide
Carbonate
Sulfide
Native Metal
Sulfide
What simple field test could you perform to definitely identify calcite?
smash it into pieces with your rock hammer and examine the cleavages
taste it
hold it up to a magnet
Drip diluted HCl on it and observe fizzing
Drip diluted HCl on it and observe fizzing
The silicate tetrahedron that forms the backbone of all silicate minerals is composed of silicon and what other element?
Magnesium
Oxygen
Iron
Carbon
Oxygen
The Single property that can be used to identify any mineral is ________.
color
luster
cleavage
hardness
none of the above, multiple properties must be considered
none of the above, multiple properties must be considered
Cleavage in minerals refers to …
a tendency to break in an irregular pattern
a tendency to break along planes of weakness
the sharpness of edges between crystal faces
the development of distinct crystal faces
a tendency to break along planes of weakness
The New Age practice of surrounding one’s self with crystals has a strong positive effect on…
mental health
the immune system’s response to illness
the prospects for world peace
the bank accounts of rock shop owners
the bank accounts of rock shop owners
Name 6 characteristics of minerals?
homogenous
naturally occurring
solid
definable chemical composition
orderly internal structure
inorganic (generally)
Euhedral
Anhedral
WELL developed faces on crystals
POORLY developed faces on crystals
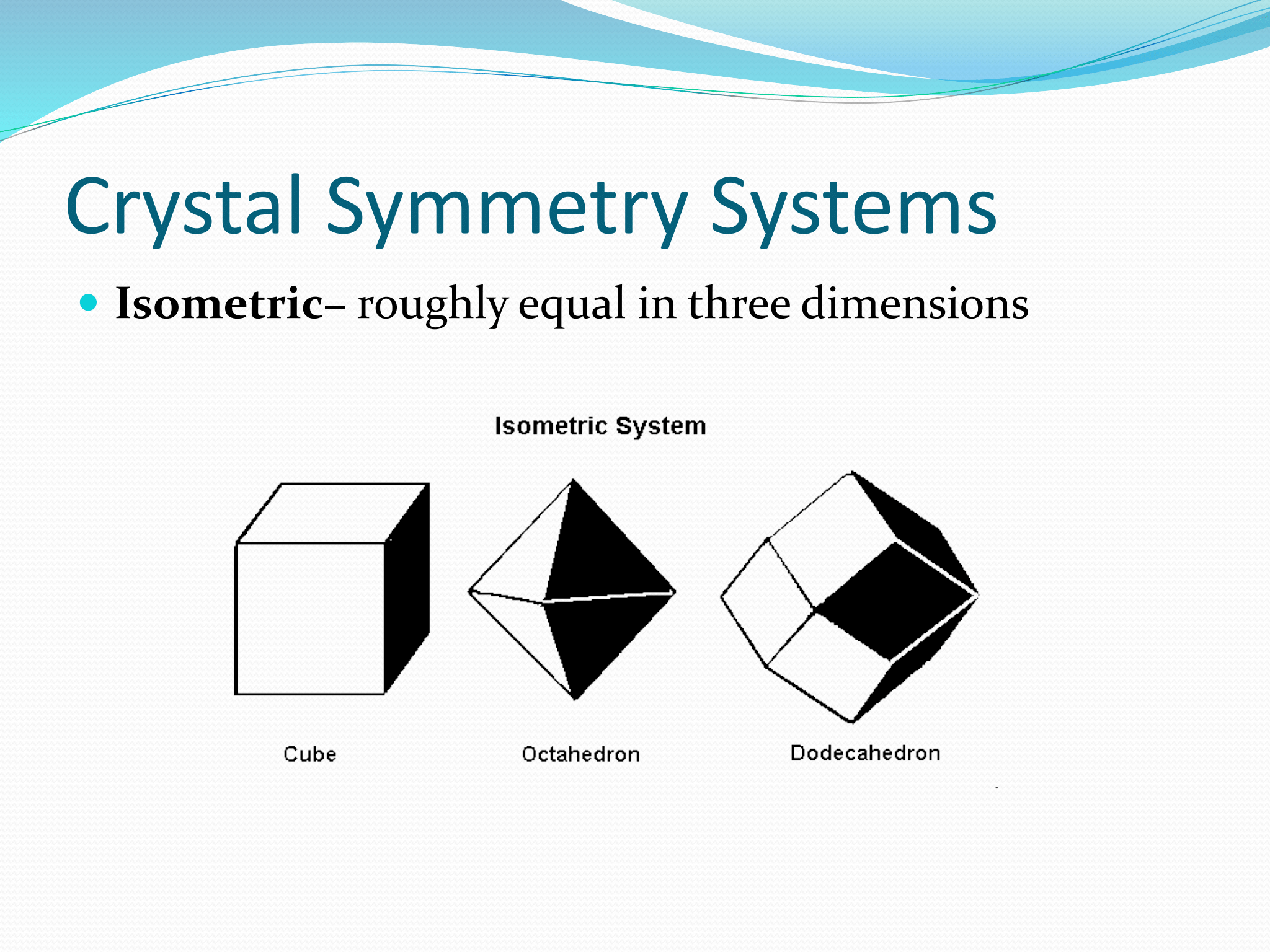
Isometric Symmetry
Roughly equal in three dimensions
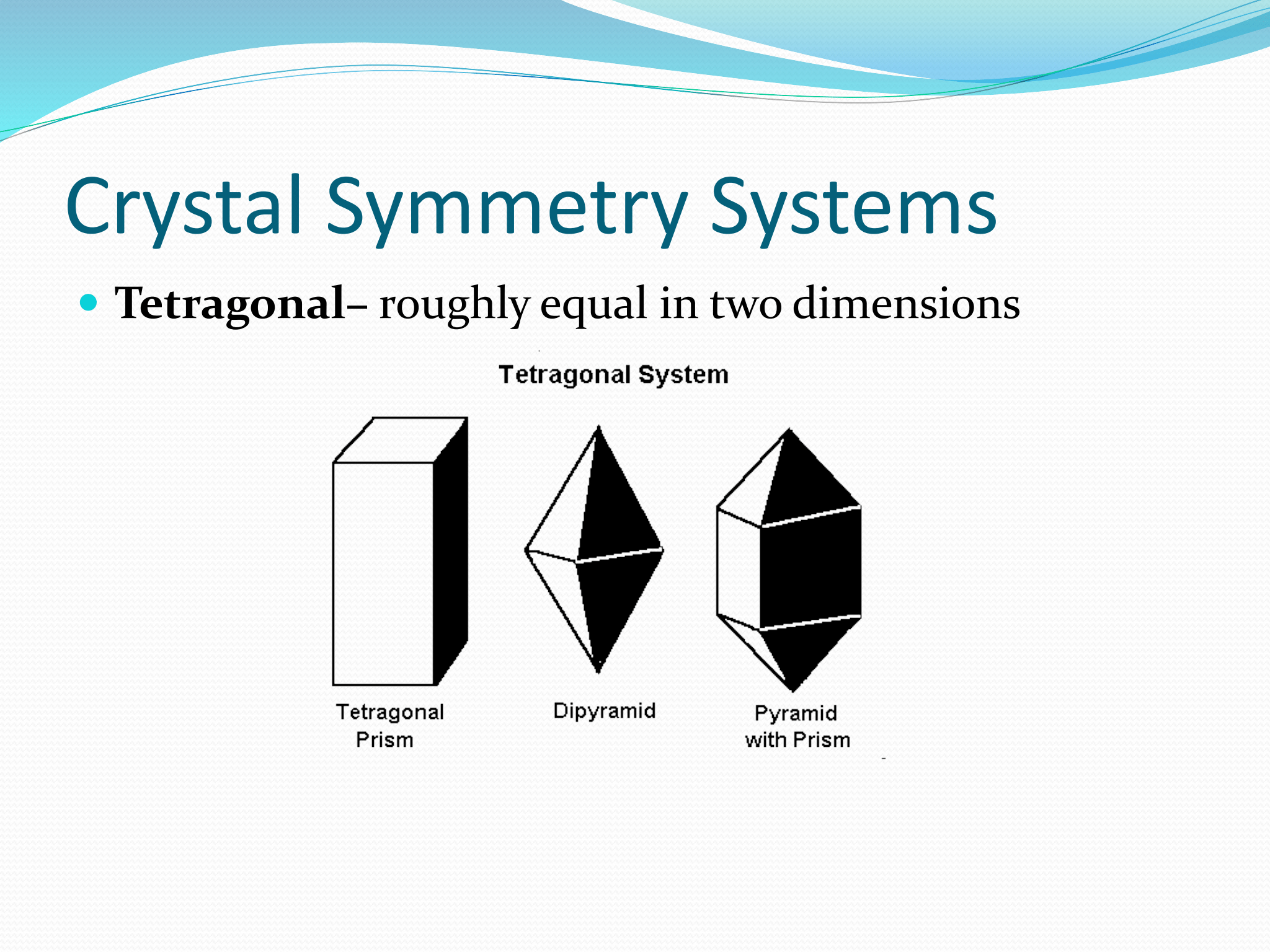
Tetragonal Symmetry
roughly equal in two dimensions
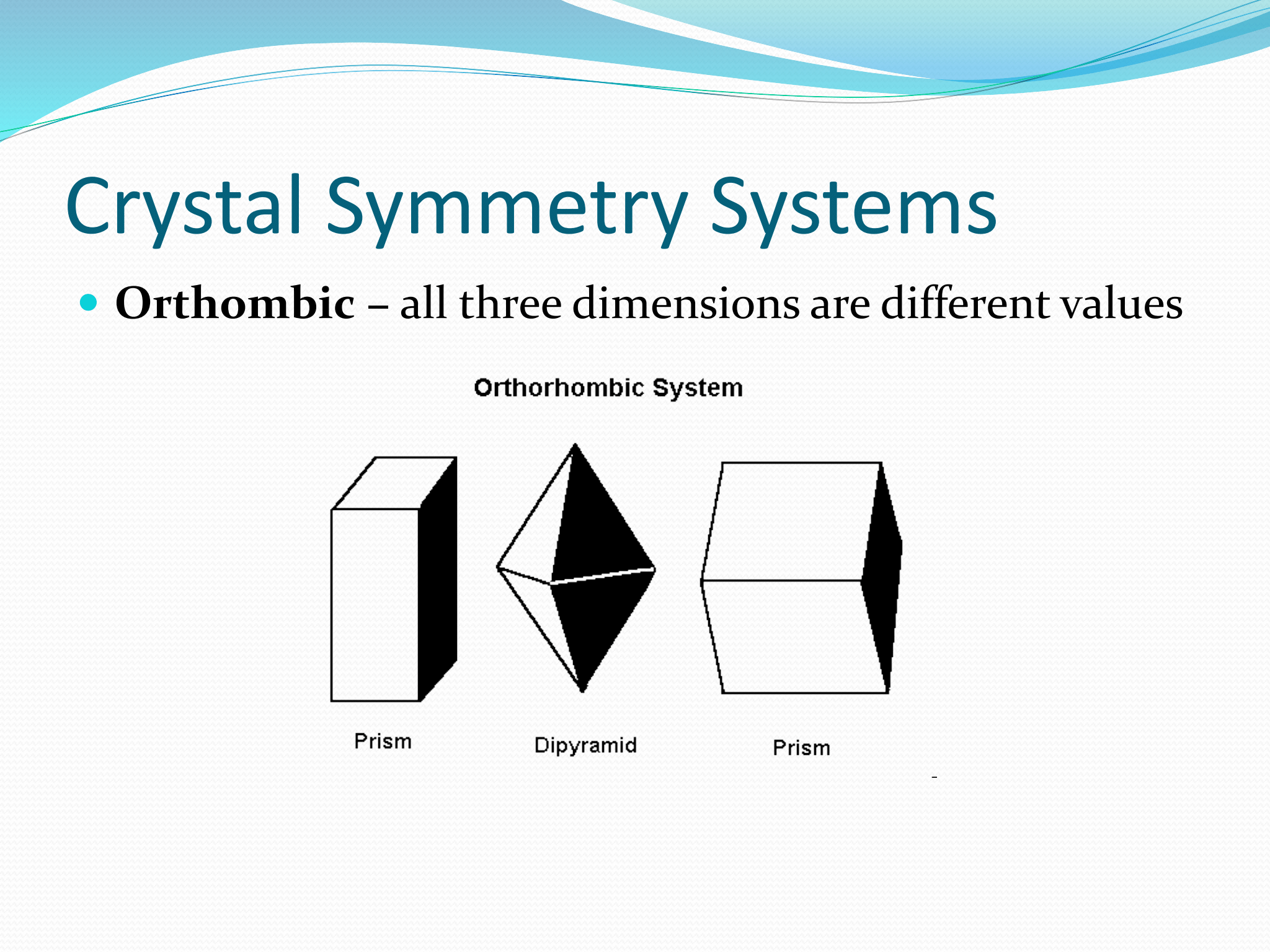
Orthombic Symmetry
all three dimensions are different values
Monoclinic Symmetry
orthombic, but “bent” in one plane
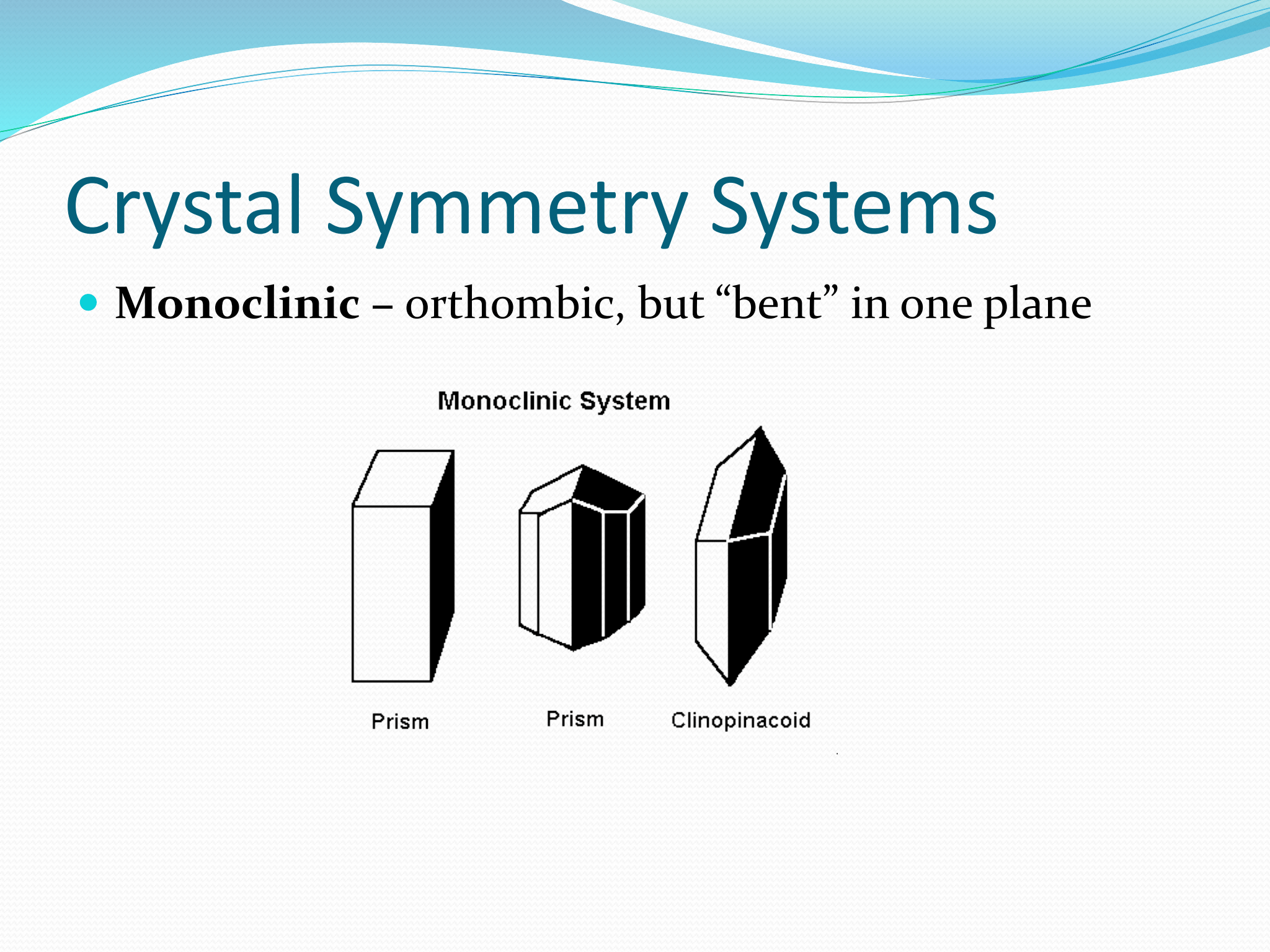
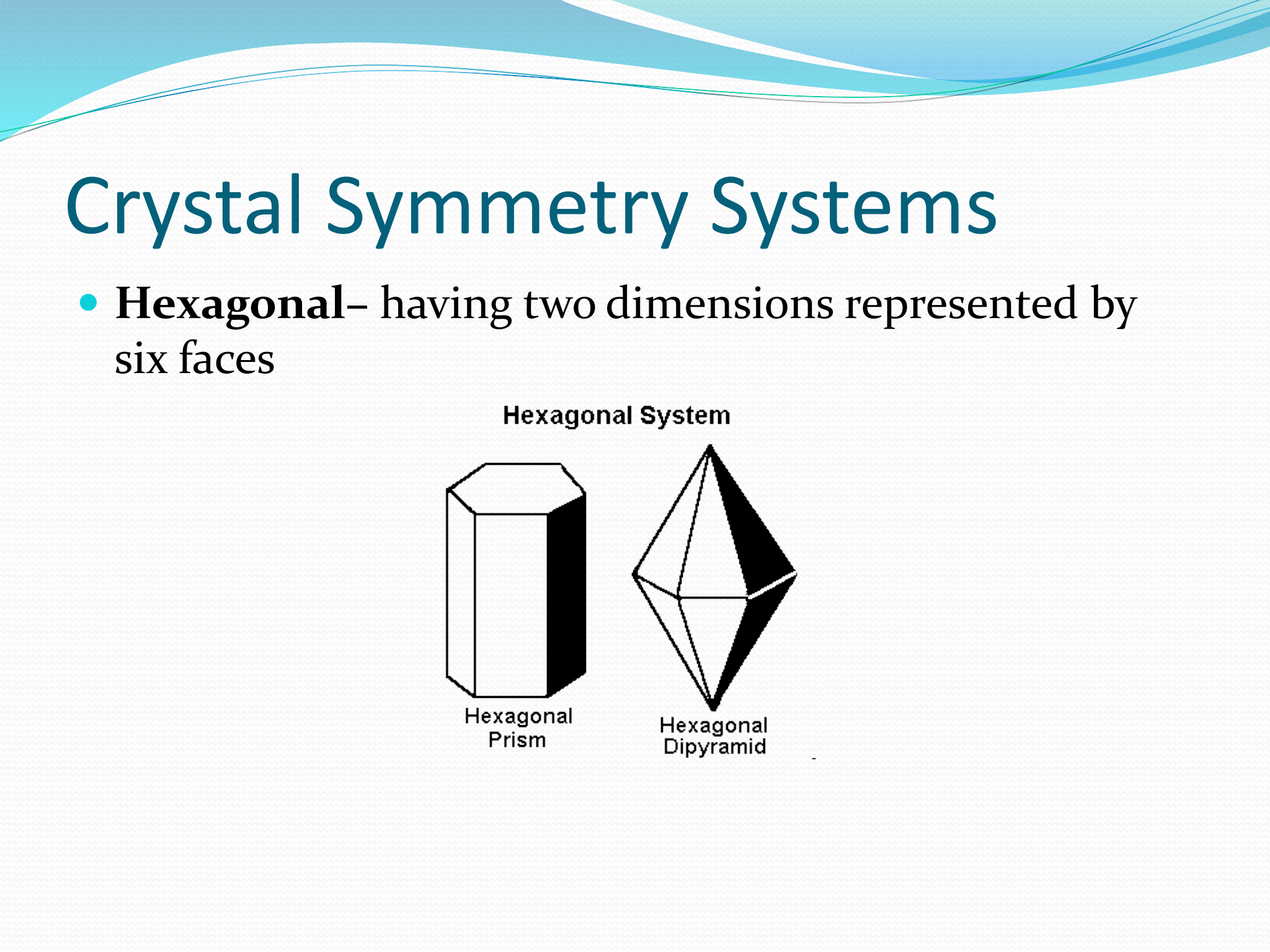
Hexagonal Symmetry
having two dimensions represented by six faces
What are polymorphic minerals? Give an example:
minerals with the same chemical composition but arranged in a different internal structure
ex: Diamond & Graphite
Name the different mineral properties
color
streak
luster
hardness
Specific Gravity
Luster
Defined as the wat the mineral “scatters light”
Silky, Glassy, Satiny, Resinous, Pearly, Earthy, Metallic
Hardness of a mineral
the mineral’s ability to resist being permanently “scratched”
Frederich Mohs Scale: higher numbers can leave a “mark” on lower numbers.
What are the different types of Crystal Habits?
Bladed: slender and flattened
Sheet: muscovite, biotite, lepidolite
Columnar: only revealing crystal faces in two dimensions, irregular at edges
Fracture: glassy “minerals” like obsidian have no real cleavage, instead they break with what is called “conchoidal fracture”
Cleavage: the tendency of a mineral to break along planes (cleavages) of weakness related to the atomic structure of the mineral
Which are the most abundant class of Mineral?
Oxides
Silicates
Sulfides
Sulfates
Halides
Carbonates
Native Metals
Silicates
What are the building blocks of all silicates?
silica tetrahedron (SiO4)
What are the 4 types of magma in order from greatest → least amount of silica?
Felsic
Intermediate
Mafic
Ultramafic
The MORE volatiles present in magma, the ___________________ (lower/higher) the viscosity. The LESS volatiles present, the ____________________ (lower/higher) the viscosity.
lower; higher
The higher the silica content present in magma, the _________________ (lower/higher) the viscosity.
higher
Intrusive Structure: Dikes
vertical, tubular bodies
Intrusive Structure: sills
horizontal, tubular bodies
Intrusive structures: Laccoliths
essentially a sill which is continuously supplies with new magma, which then bulges upward
Intrusive Structure: Plutons
blob-shaped bodies of magma which rise through the crust as a single entity before (for some reason) stopping their progress and cooling in place
Intrusive Structure: Batholiths
essentially HUGE HUGE plutons
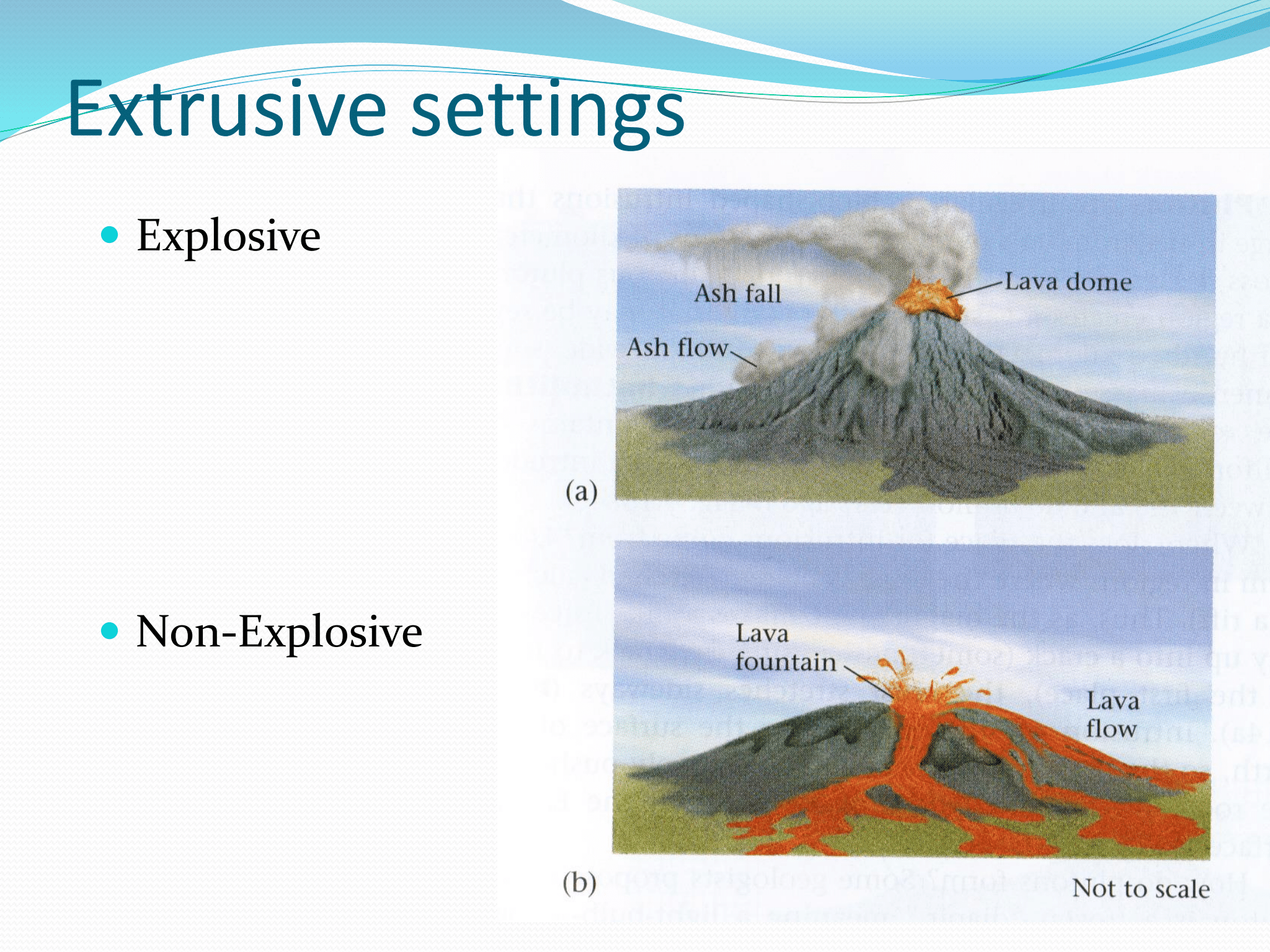
What are the 2 Extrusive Settings?
Explosive: Ash fall, Lava domes, Ash flow
Non-Explosive: Lava fountain, Lava flow
What three factors control the rate of cooling?
Depth: deeper the site of cooling = slower cooling
Morphology: more spherical magma body = slower cooling
Presence of Groundwater: presence of groundwater = fast cooling
Describe ALL of the 3 Igneous Textures
Fragmental: igneous “fragments” that have been welded together. Typically produced by extrusive processes
Glassy: have few or no crystals at all
Crystalline
Phanaretic: large crystals
Aphanitic: small crystals
Porphyritic: large crystals of one or more minerals “floating” in a matrix of smaller crystals (invisible) of other minerals
Categorize Different Types of Lava Flows
Andesitic: glacier like
Ryolitic: high viscosity, tend to form domes
Columnar joints
Basaltic: Lava tubes
Pahoehoe
a’a
Pyroclastics
Andesitic Pyroclastics
Ash
Pyroclastic Flow
Basaltic Pyroclastics
Lapilli: formed by popping gas pockets which ejects the material
Bombs: big lapilli
Pelee’s hair
Deposits
Tephra: unconsolidated pyroclastics of all types
Tuff: ash mixed with lapilli
Ignimbrite: a cohesive sheet of tuff formed from pyroclastic flow
Blocks: chunks of previously existing volcano torn loose by the eruption
Debris flow: blocks mixed with melted snow
Lahar: saturated mixture of debris
Fissure

Crater

Caldera

Shield Volcanos

Cindercone Volcano

Stratovolcanos
Eruptive Style: Effusive
Eruptive Style: Explosive
consisting mainly of low-viscosity lava flows, tends to create shield volcanos
consisting of both high-viscosity lava, pyroclastics and ash fall, tends to create cindercones