Equations and Variables
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
What does r’d mean
dynamic resistance
What is the equation linking capacitance, charge stored and voltage across
c = q/v
What is the equation for energy stored in a capacitor
1/2CV
What is the equation for capacitance
plate area x dielectric constant / plate separation
What is the equation for dialectic constant
Material permittivity/permittivity of free space
What is the equation linking voltage and turns in transformers
Vs/Vp = Ns/Np
What is the equation linking current and turns for transformers
Is/Ip =Np/Ns
What does Vp(out) mean
Peak voltage output
What is the equation for time constant
T = RC
What is the equation for time period
1/f
What is the equation for ripple factor
Vr(p-p)/Vdc
What is Vr(p-p)
Ripple voltage
What is VDC
The DC magnitude carried by the wave form
What is Vz (diodes)
Zener voltage
What is Zz
Zener impedance
What is the equation for Zener impedance
Change in Zener voltage/change in current
What is Izk
The minimum amount of current needed to keep the diode in the Zener region
What is Izm
The maximum about of Zener current that can be sustained before the diode damages
What is the equation for Izm
Pd/Vz
What is PD (diodes)
The max power the diode can take
What is Beta (BJTs) and where is it found
The DC gain and found in the data sheet
What is Hfe another name for
Beta
Why are BJTs better at amplification than FETs
As they have a higher value of gain, meaning they have a higher amplification factor
What is alpha (BJT’s)
The ratio of Ic to Ie
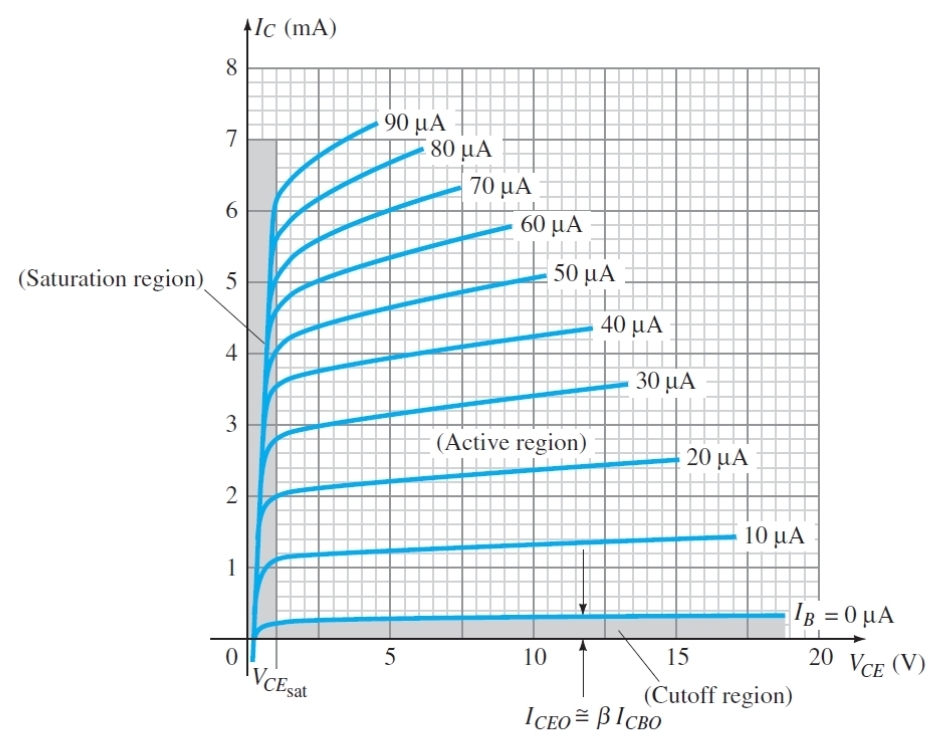
What does VCEsat stand for (BJTs)
The collector - emitter saturation voltage
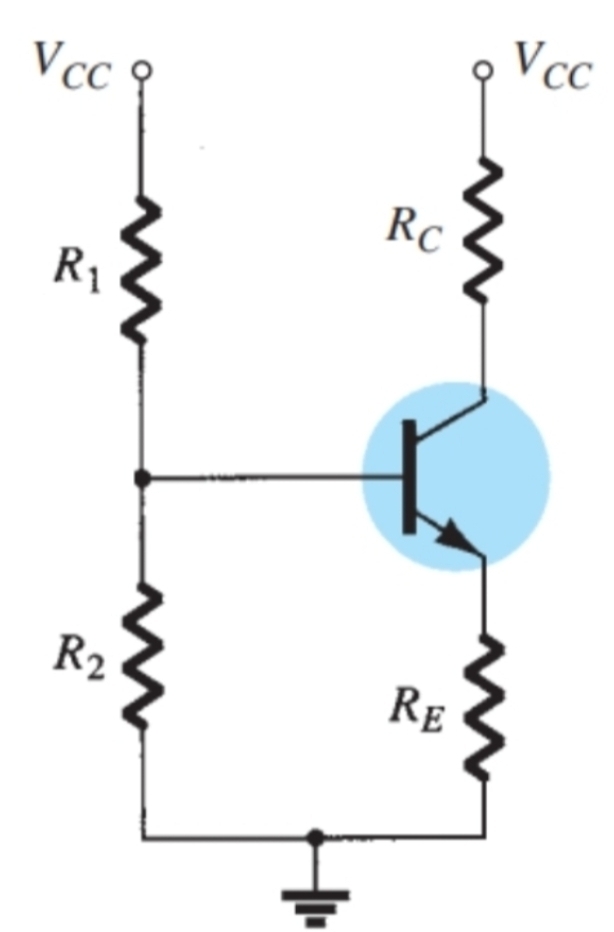
How do you calculate Rth
add r1 and r2 in parallel
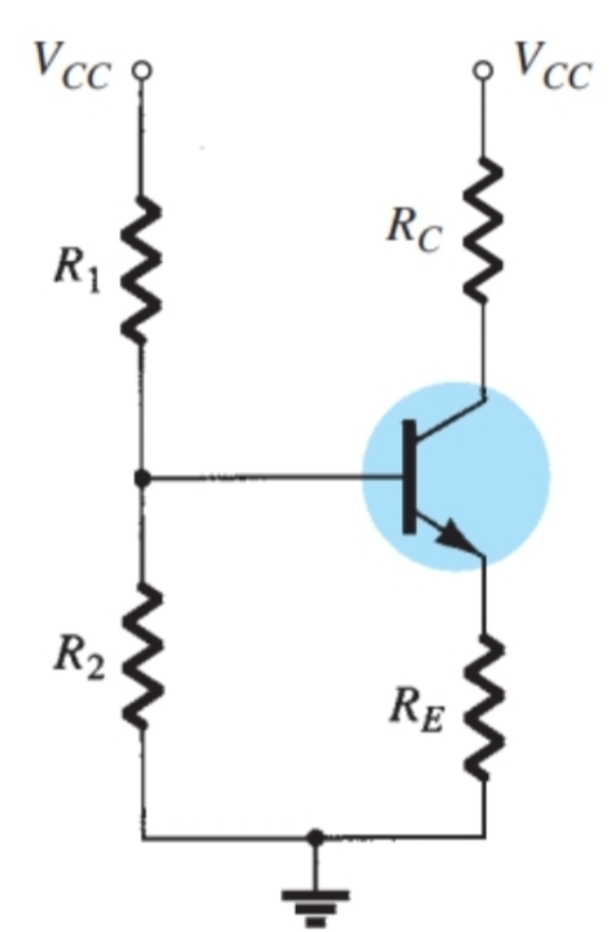
How do you work out Eth
Voltage divider to work out r2
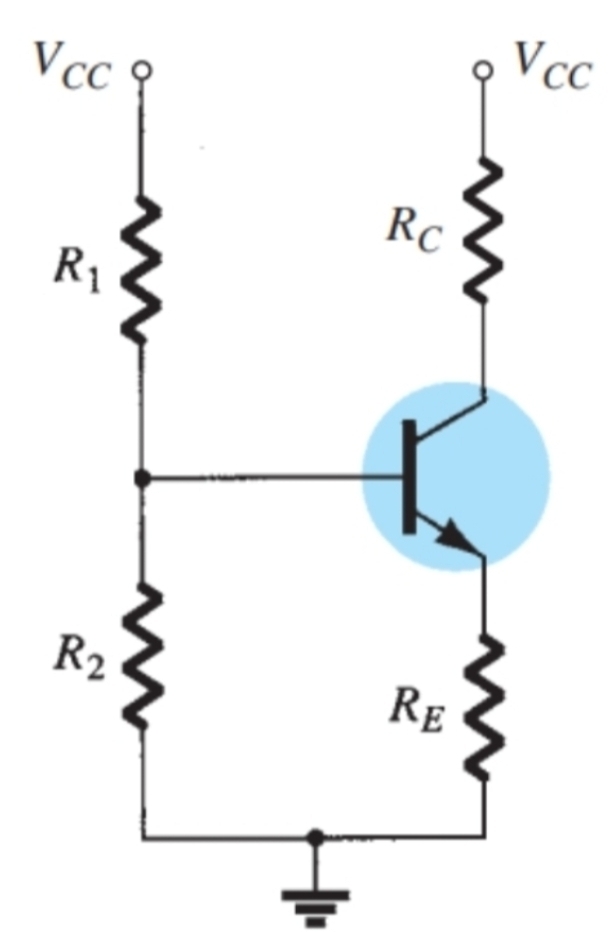
What condition must be met to use approximate analysis on this configuration
Beta times Re must be greater than or equal to 10R2
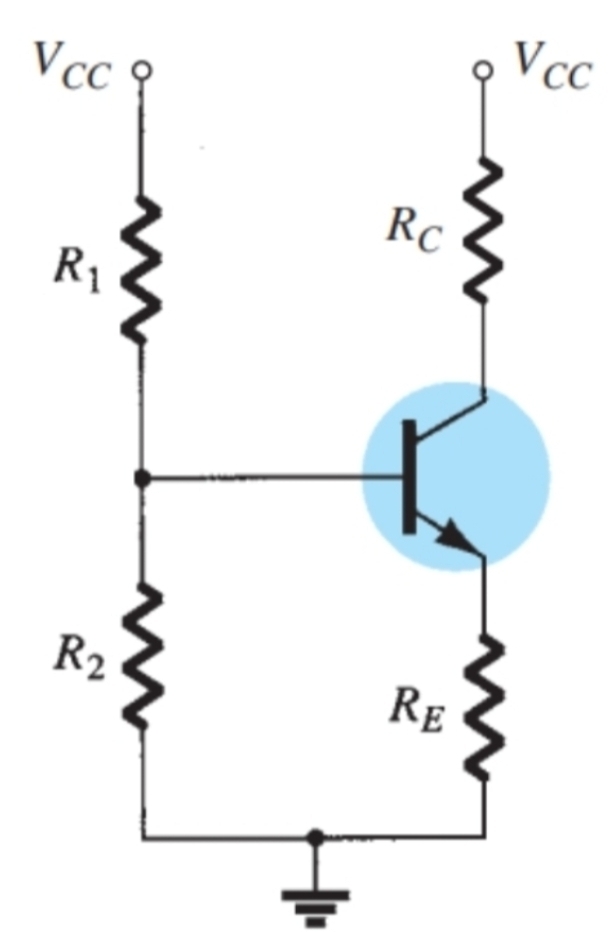
What approximation is made when using the approximate analysis
Ib = 0
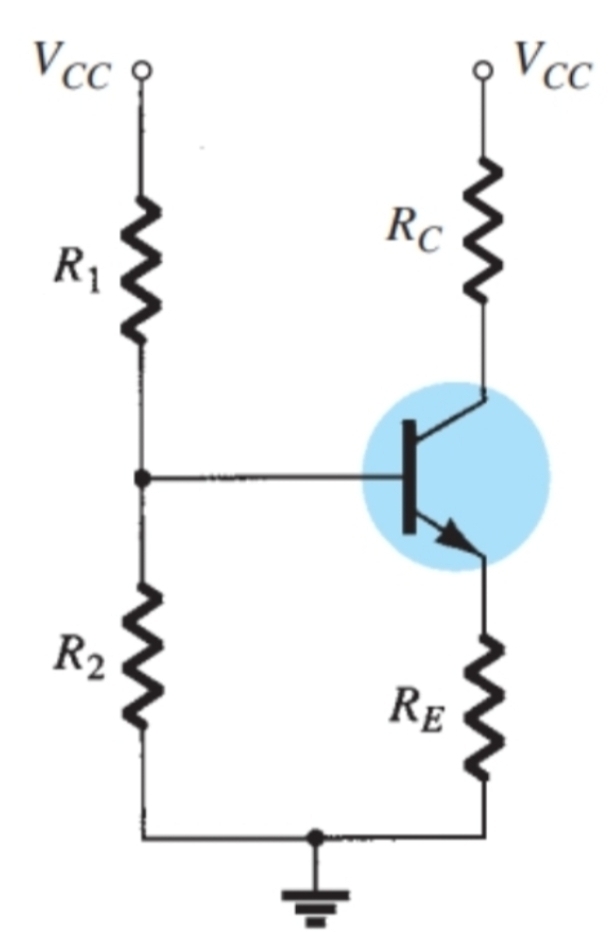
How is VB calculated for the approximate analysis
Voltage divider for r2
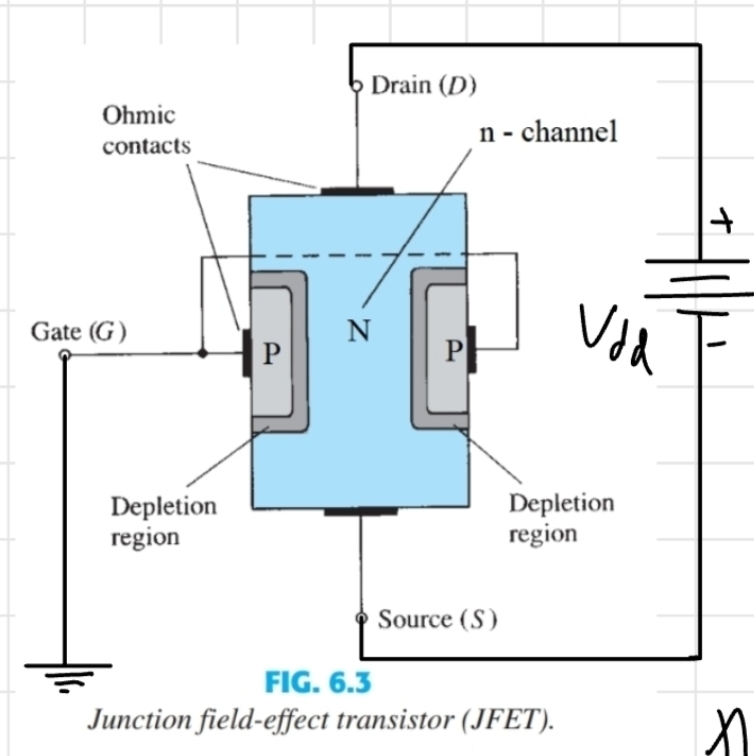
What is the current flowing through the N region for a JFET know as
Id
What is the controlling element for FETs
Vgs
What is the pinch point (JFETs)
Where the depletion region has expanded and joined at the top
What is VP (JFETs)
Pinch off voltage
What is IDSS
The current at the saturation point, where the current will not increase anymore
What is VO (OP-AMP)
Voltage output
What is the equation for the output of an OP-AMP
V0*A
What is A (OP-AMP)
Gain
How is the differential voltage calculated (OP-AMP)
Vd = V1 - V2
What is VD (OP-AMP)
Differential voltage
What is VD equal to when the input is different (OP-AMP)
V1-v2
In common mode how do you work out Vd (OP-AMP)
V1 - V2
What is the input for common mode treated as (OP-AMP)
Average of the 2 inputs
What is the final output for common mode
AcVc + AdVd
How is common mode rejection ratio calculated (OP-AMP)
Ad/Ac
If common mode rejection ratio is calculated with logs, what would it be multiplied with (OP-AMP)
20log10
What is the equation for gain (OP-AMP)
V1/V0
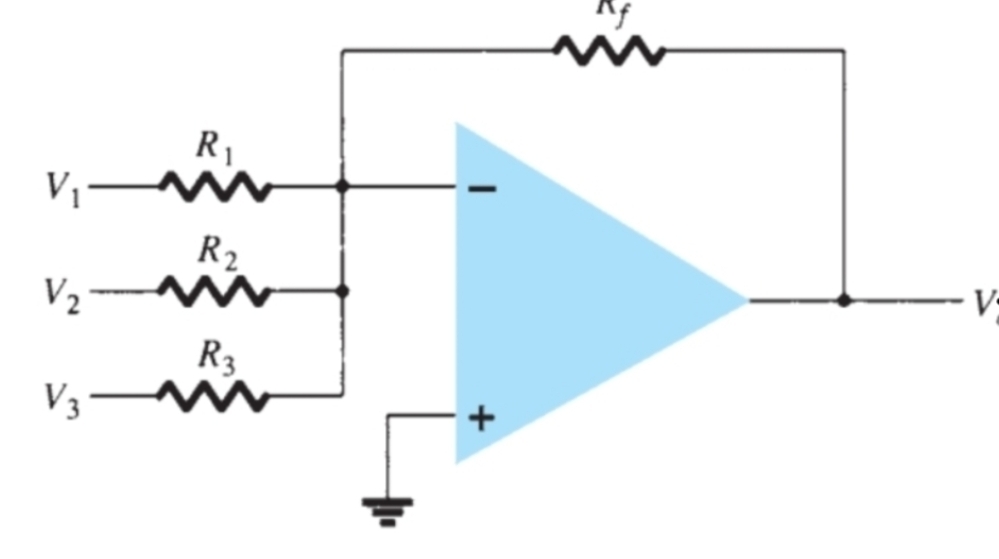
How is the gain for each input calculated for this circuit
Rf/Rx
What is the resistance given by a capacitor (unrationalised)
1/jwc
What is the resistance given by a capacitor (rationalised)
-j/wc
What does wc equal (capacitor)
s
What is capacitor resistance in laplace
1/sC
What is xc (OM-AMP)
Capacitor resistance
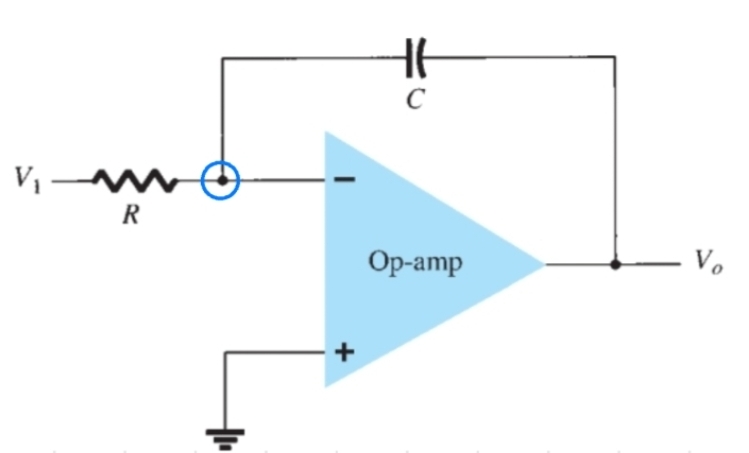
What does 1/s mean
Integrate
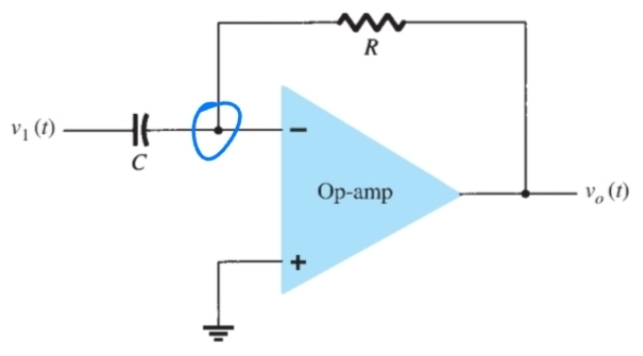
What does S mean
Differentiate
What is the closed loop gain for a oscillator circuit
A times beta
What is beta in an oscillator circuit
The gain form the feedback circuit
What is VBR (thyristor Shockley diode)
Breakover voltage
What is breakover voltage (thyristor Shockley diode)
The minimum voltage to turn the device on
What is IA (thyristor Shockley diode)
The current passing though the device
What is VAK (thyristor Shockley diode)
The voltage applied over the anode and cathode
What is Is (thyristor Shockley diode)
Switchover current
What is switchover current (thyristor Shockley diode)
The current at the point where the device starts conducting
What is IH (thyristor Shockley diode)
Holding current
What is holding current (thyristor Shockley diode)
The minimum current required to keep the device is on state