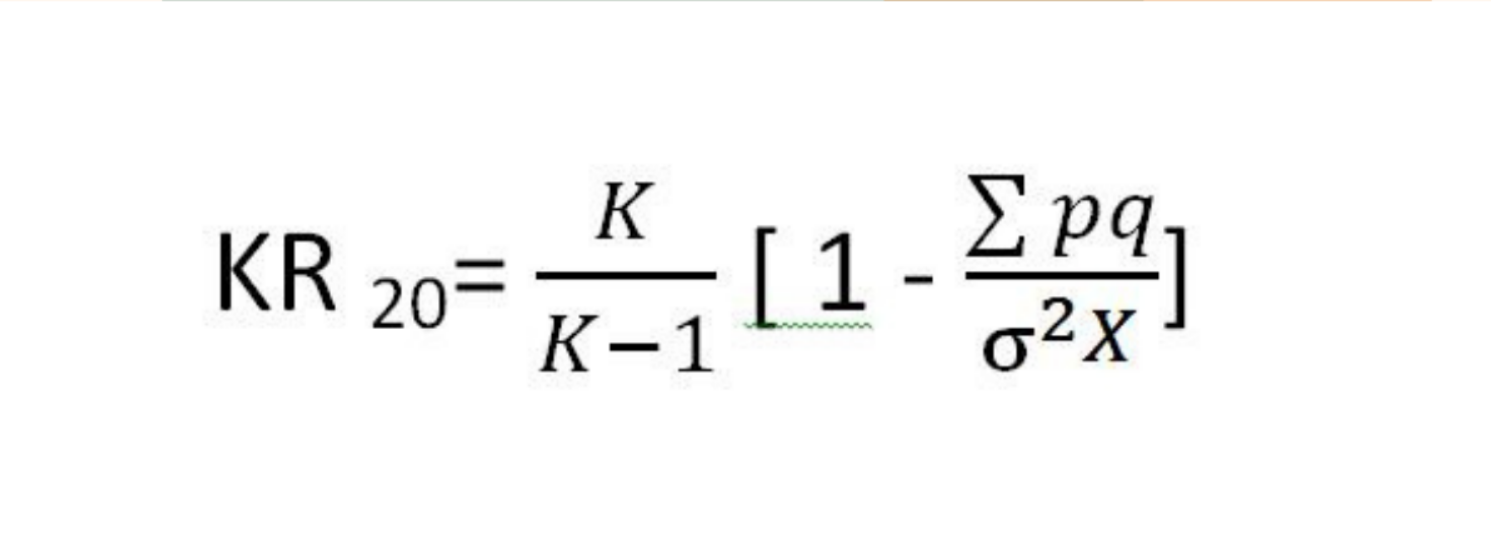IOPSY - 6 EVALUATING SELECTION TECHNIQUES AND DECISIONS
1/26
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Effective Selection Techniques Characteristics (5)
Reliable
Valid
Cost efficient
Fair
Legally defensible
Reliability
the extent to which a score from a selection measure is stable and free from error; how consistent something is
Ways determining Reliability (4)
Test-retest reliability
Alternate-forms reliability
Internal reliability
Scorer reliability
Test-Retest Reliability
the extent to which repeated administration of the same test will achieve similar results; several people take the same test twice, the scores from the first test are correlated with those from the second to see if they are similar
Temporal Stability
the test scores are stable or consistent across time; e.g., when the same test was taken twice and then the first and second test scores are similar
Alternate-Forms Reliability
the extent to which two forms of the same test are similar; it measures the consistency of test results between two different versions of the same test
Counterbalancing
method of controlling for order effects by giving half of a sample Form A first, followed by Form B, and giving the other half of the sample Form B first, followed by Form A
Form Stability
the extent to which the scores on two forms of a test are similar
Internal Reliability
the extent to which responses to test items measuring the same construct are consistent; it measures how well the items on a test work together to measure the same thing
Internal Consistency, Item Stability
The extent to which similar items are answered in similar ways is referred to as ________ __________ and measures ____ _________.
Internal Consistency
the extent to which similar items are answered in similar ways
Item Stability
the extent to which responses to the same test items are consistent
Factors that can affect internal reliability (2)
Length
Item homogeneity
Length
A factor that can affect internal reliability
the longer the test, the higher its internal consistency
Item Homogeneity
A factor that can affect internal reliability
the extent to which test items measure the same construct; the more homogeneous the items, the higher the internal consistency
Methods used to determine Internal Consistency (3)
Split-half
Coefficient (Cronbach’s) alpha
Kuder-Richardson formula 20 (K-R 20)
Split-Half Method
A form of internal reliability
the consistency of item responses is determined by comparing scores on half of thee items with scores on the other half of the items; easiest to use, as items on a test are split into two groups
Spearman-Brown Prophecy Formula
used to correct reliability coefficients resulting from the split-half method; used to adjust correlation
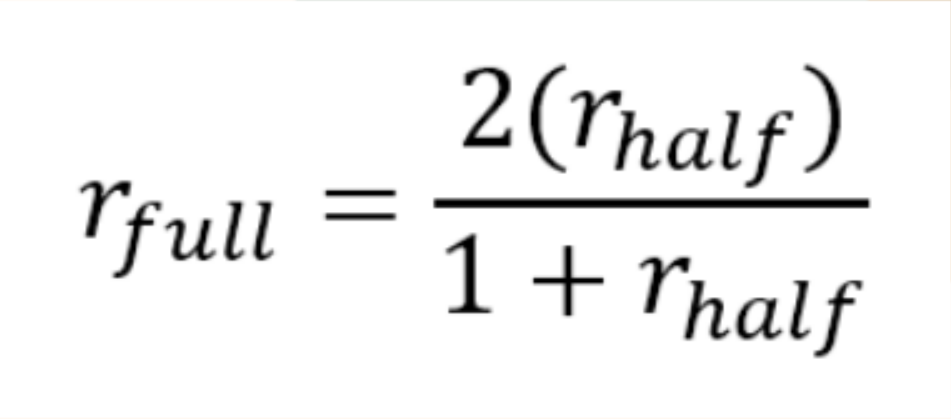
Coefficient (Cronbach’s) Alpha
a statistic used to determine internal reliability of tests that use interval or ratio scales; can be used not only for dichotomous items but also for tests containing interval and ratio items such as five-point rating scales
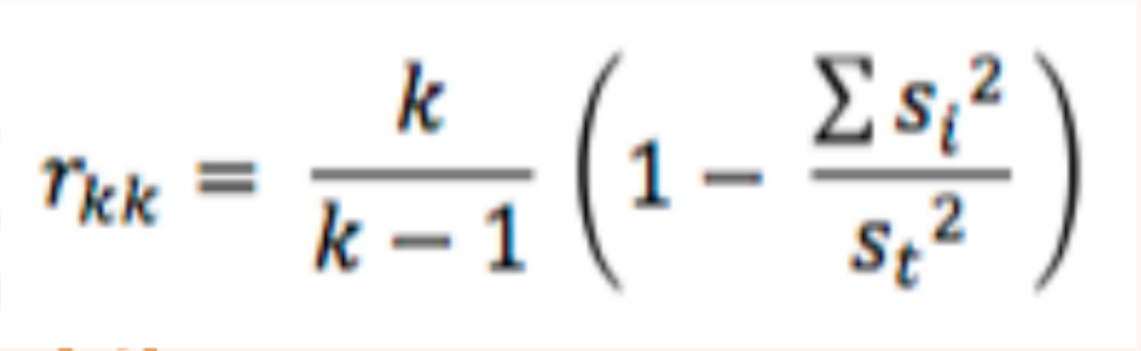
Kuder-Richardson Formula 20 (K-R 20)
a statistic used to determine internal reliability of tests that use items with dichotomous answers (yes/no, true/false)