Lecture 16: Heat transfer
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What are the three main types of heat transfer?
Conduction, convection and radiation
What is conduction?
Heat transfer that occurs through molecular collisions
Takes place within solids, liquids and gases
What is the equation for thermal conductivity?
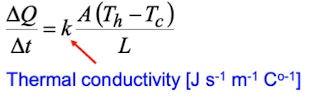
How does having a large or small K value impact conductivity?
Large K: good conductor
Small K: good insulator
How can you further reduce heat loss from a glass window?
Using two panes of glass separated by an air gap will reduce the heat loss more than simply increasing the glass thickness
What is convection?
The process of heat transfer by the mass movement of molecules from one place to another (carrying heat with them)
Occurs in moving fluids, such as liquids and gases
What is natural convection? Give an example
Heat transfer caused by changes in the density of the heated fluid (liquid or air) near the object
eg. during day land warmer than water, at night water warmer than land cool air from land moves towards sea
What is forced convection? Give an example
Heat transfer produced by forcing a fluid past a hot object
eg. car radiator/cooling system: air conditioners and fans
What is radiation?
The transfer of heat in the form of electromagnetic waves, such as infrared radiation, without requiring a medium
This process allows heat to travel through a vacuum
All objects at temperature > 0K radiate and absorb energy
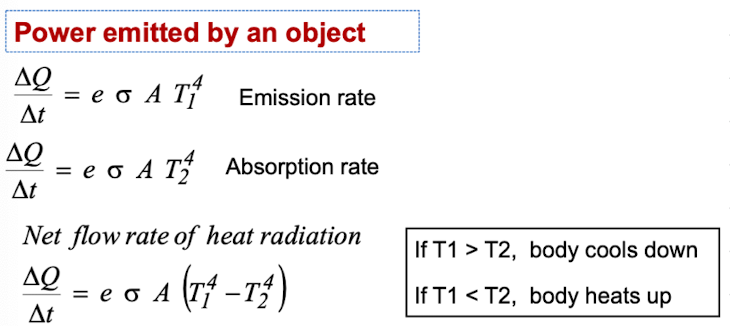
What is the Stefan-Boltzmann equation?
The rate at which an object radiates energy

What does an emissivity value of 0 compared to 1 indicate?
e = 0 (very poor radiator)
e = 1 (perfect radiator ‘black body’)
What is emissivity?
A measure of a material’s radiating efficiency
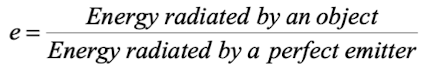
Outline the power emitted and absorbed by an object
Describe radiation from the sun
Heating of an object by radiation from the sun cannot be calculated using stefan-boltzmann equation (this equation assumes a uniform temperature, T2, of the environment surrounding the object, whereas, sun is essentially a point source)
Hence, sun must be treated as a separate source of energy
About 1350J of energy strikes earth's atmosphere per second per square meter of area at right angles to the sun's rays
On a clear day, about 1000 W/m2 reaches the ground on a clear day