Biochemistry- All key words and Theory
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
The three fundamental groups of organisms
Eukaryotes (humans, mammals etc)
Well defined nucleus within each cell.
(multiple celled)Bacteria
(single celled)Archea (single celled)
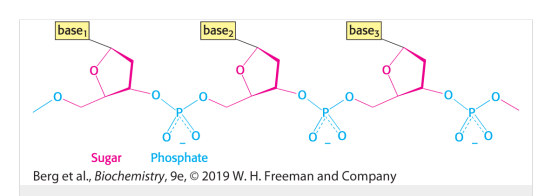
DNA
Stores genetic information
Constructed from four building blocks (bases)
- Adenine (A)
- Cytosine (C)
- Guanine (G)
- Thymine (T)DesoxyNucleacAcid
Double helix where the bases bond through hydrogen bonds
Covalent bonds
The sharing of electrons between two atoms creating a bond
Non-covalent bonds
Ionic interactions
hydrogen bonds
Van der waals interactions
Hydrophobicinteractions
Properties of water
polar molecule
Highly cohesive(strong interactions with itself)
Hydrophobic effect
The tendency of nonpolar molecules to asscociate with eachother and unlikelyness to associate with the polar solvent.
Ionic interaction energy
K = is a proportionality constant (k = 1389, for energies in units of kilojoules per mole, or 332 for energies in kilocalories per mole).
q1 and q2 are the charges on the two atoms (in units of the electronic charge)
r is the distance between the two atoms (in angstroms)
D is the dielectric constant
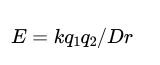
Homologs
Molecules that have been derived from the same ancestor
Paralogs ( differ in function)
Orhtologs ( similar in function)
Conservative substitution
Replaces one amino acid with another that is similar in size and chemical properties
Nonconservative substitution
An amino acid is replaced by one that is structurally dissimilar
Divergent evolution
Proteins that are derived from common ancestors
Convergent evolution
Different evolutionairy pathways leading to the same solution
RNA
Ribonucleic Acid
Single stranded molecule
Used to transfer information from dna
3D structure vs Sequence identity
3D structure is more conserved
Enzymes
proteins that catalyze specific chemical reactions in biological systems
Side chain (R group)
The variable group attached to the central carbon in an amino acid
L amino acid
Naturally occuring form of amino acids
Zwitterion
A dipolar ion , both negative and positive
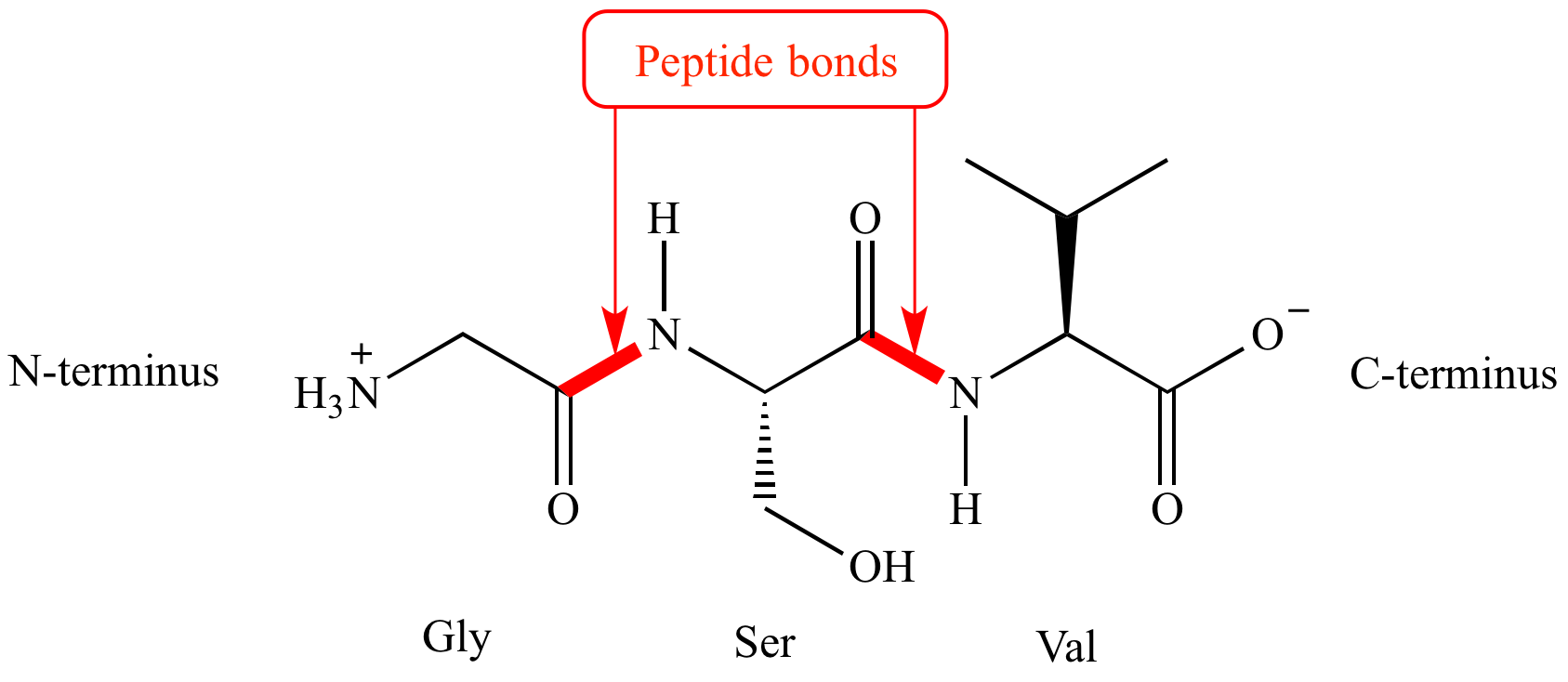
Peptide bond
A covalent bond between the carboxyl group of a amnino acid and the amino group of another. Forms proteins
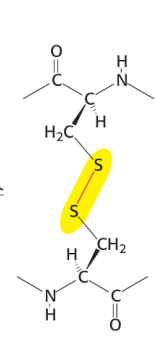
Disulfide bonds
provides stability for secondary proteins
Primary structure
The linear sequence of amino acids in a protein
Torsion angle
Angles that describe rotation around bonds in the protein backline
Phi (ϕ) angle
The torsion angle around the bond between the nitrogen and alpha carbon (N–Cα) of an amino acid.
Psi (ψ) angle
The torsion angle around the bond between the alpha carbon and the carbonyl carbon (Cα–C) of an amino acid.
Secondary structure
Local folding patterns of the polypeptide chain
alpha helix
A right handed helical structure stabalized by hydrogen bonds psi and phi below 100
β pleated sheet
A sheet-like secondary structure formed by hydrogen bonds between β strands.
β strand
A single sgment of a polypeptide chain
Tertiary structure
The overall 3D structure of a single polypeptide chain
Globular protein
A compact spherical protein
All Hydrophilic Proteinogenic Amino Acids
Serine (Ser,S)
Threonine (Thr,T)
Asparagine (Asn,N)
Glutamine (Glu,Q)
Tyrosine (Tyr,Y)
Aspartic acid (Asp,D)
Glutamate (Glu, E)
Lysine (Lys,K)
Arginine (Arg,R)
Histidine (His, H)
All hydrophobic Proteinogenic Amino Acids
Glycine (Gly,G)
Alanine (Ala, A)
Valine (Val,V)
Leucine (leu,L)
Isoleucine (Ile,I)
Methionine (Met,M)
Proline (Pro,P)
All aromatic proteinogenic aminoacids
Phenylalanine (Phe,F)
Tyrosine (Tyr,Y)
Tryptophen (Trp,W)
All acidic proteinogenic amino acids
Aspartic acid(aspartate) (Asp, D)
Glutamic acid( Glu, E)
All Basic proteingenic amino acids
Lysine (Lys,K)
Arginine (Arg,R)
Histidine (His,H)
Proteome
The functional representation of a genome
Assay development
A Sspecific test that detects the unique activity or property of the target protein.
Specific Activity
The ratio of enzyme activity to the amount of protein in the mixture
Homogenate
A homogenate is a mixture resulting from breaking open cells to release their contents, creating a uniform solution of cellular components for further analysis or purification. Can be achieved by centrifusion.
Protein purification techniques
Proteins can be purified based of:
- Solubility
- Size
- Charge
- Binding affinity
Techniques:
Salting out (solubility)
Dialysis (size)
Gel-Filtration (size)
Ion-Exchange chromatograpy (charge)
Affinity chromatography
HPLC
Gel electrophoresis
A molecule with a net charge will move in an electric field. This phenomenon, termed electrophoresis.
The velocity of migration (v) of a protein (or any molecule) in an electric field depends on the electric field strength (E), the net charge on the protein (z), and the frictional coefficient (f ).
v = Ez/f
f = 6πηr
Isoelectric focusing
Electrophoretical separation of proteins based ontheir relative acidic and basic residue contents
The isoelectric point (pI) of a protein
The pH at which its net charge is zero
Two-dimensional electrophoresis
Isoelectric focusing can be combined with SDS-PAGE to obtain very high resolution separations by two-dimensional electrophoresis
Ultracentrifugation
Used to separate biomolecules and determine their masses
Sedimentation coefficient (s)
Rate of movement of a particle when experiencing centrifugal force.
s = m*(1-vρ)/f
m= mass particle
v = partial specific volume
ρ = density of the medium
f= frictional coefficient
Antibody ( immunoglobulin)
responds to an antigen
polyclonal antibodies
Polyclonal antibodies are a mixture of antibodies produced by different B cells that recognize and bind to multiple sites (epitopes) on the same antigen.
Monoclonal antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies are identical antibodies produced by a single B cell clone that recognize and bind to one specific epitope on an antigen.
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
Assay that makes use of an enzyme that can produce a coloured product. Helps detecting and quantifying proteins
Western blotting
Western blotting is a technique used to detect specific proteins in a sample by separating them by size using gel electrophoresis, transferring them to a membrane, and probing with antibodies.
co- immunoprecipitation
A technique used to detect and study protein-protein interactions by using an antibody to capture a target protein and any interacting partners from a sample, allowing for their identification and analysis.
Fluorescence microscopy
makes the target protein fluorescent
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI)
A technique used to ionize large biomolecules for spectral analysis
Electrospray ionization
A method of ionizing molecules by applying voltage to a liquid
Time-Of-Flight analyzer
A mass spectrometer that measures the time it takes ions to reach a detector
Edman degradation
A method for sequencing proteins by sequentially removing one amino acid at a time from the N-terminus.
Phenyl isothiocyanate
A reagent used in Edman degradation for labeling the amino acid being removed.
Tandem mass spectrometry
A technique that involves multiple stages of mass spectrometry to identify and analyze peptides or proteins.
Overlap peptide
Peptides that overlap in sequence and are used to confirm protein identification through mass spectrometry.
Peptide mass fingerprinting
A method of identifying proteins by analyzing the masses of peptide fragments generated by digestion.
Fourier transform
A mathematical technique used to analyze signals, commonly used in NMR and mass spectrometry.
Chemical shift
A change in the resonance frequency of nuclei in NMR spectroscopy, providing information about their environment.
Enzyme
A biological catalist, usually of the protein classq
Substrate
The reactant that a enzyme binds upon during a enzyme substrate reaction
Cofactor
A non protein compound required for an enzymes activity.
(Can be a metal ion or organic compound)
Apoenzyme
The protein portion of an enzyme
Haloenzyme
The complete protein incl cofactor
Free energy (ΔG)
The energy available to do work in a chemical reaction
Active site
The region on the enzyme where the subtrate binding and catalysis occurs
Michaelis–Menten Equation
An equation describing the relation between enzymatic rate and substrate concentration
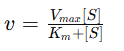
Kₘ (Michaelis constant)
The substrate concentration at which the reaction rate is half of Vmax
Shows the enzymes affinity for the substrate( lower Km = higher affinity)
Vmax
The maximum rate of enzymatic reactions
Lineweaver–Burk Equation
A linear transformation of the michaelis -menten equation, used to graphically determine Km and Vmax
(the reciprocal of the mm equation)
Turnover effect K_cat
The number of substrate molecules converted into product when the enzyme is saturated with substrate
k_cat/Km ratio
a measure of catalytic efficiency
Competitive inhibition
Inhibitor competes with substrate for binding at active site
Uncompetitive inhibition
Inhibitor only binds to enzyme-substrate complex
Noncompetitive inhibition
Inhibitor binds to a non active site
Substrate analog
a molecule that mimics the substrate, binds to enzyme and deactivates it
Suicide inhibition
Irreversible reaction where an enzyme converts the inhibtor into a reactive form that covalently binds and deactivates
Binding energy
The energy released when an enzyme binds to its substrate
Induced fit
A model where enzymes change shapoe upon binding with the substrate in order to improve reactivity
Covalent catalyis
A mechanism where an enzyme forms a temporary covalent bond with the substrate
General acid base catalysis
Enzyme catalysis that involves donation or acceptance of a proton to stabalize reactin intermediates
Metal ion catalysis
The use of metal ions in enzyme catalysis to stabalize charges or start reactions
Catalytic triad
A group of three coordinated amino acids in an enzymes active site that work together to catalyze reactions
Oxyanion hole
A pocket in an enzymes active site that stabalizes the negatively charge intermediate
Protease inhibitor
A molecule that binds to and blocks the activity of a protease enzyme
Proton shuttle
A series of residues or molecules that facilitate the movement of protons during enzymatic reactions
Methylases
Enzymes that add methyl groups to DNA or proteins
P-loop
a protein motif that binds the phosphate groups of nucleotides like atp
Nucleotide
the building block of nucleic acids, consisting of a sugar , phosphate and nucleic base
Deoxyribose
the sugar found in DNA
Ribose
The sugar found in RNA
Nucleoside
A molecule that contains a sugar and nucleic base without a phosphate group
DNA polymerase
An enzyme that polymerises DNA by adding nucleotides to a growing strand
Template
The strand of DNA or RNA that guides the synthesis of the complementary strand
Primer
A short DNA or RNa piece that provides the starting point of polymerization
mRNA
messenger RNA, molecule that carries genetic information from DNA to the ribosome