Primary Dentition
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
how many primary teeth are there in total?
20 primary teeth (10 on each arch)
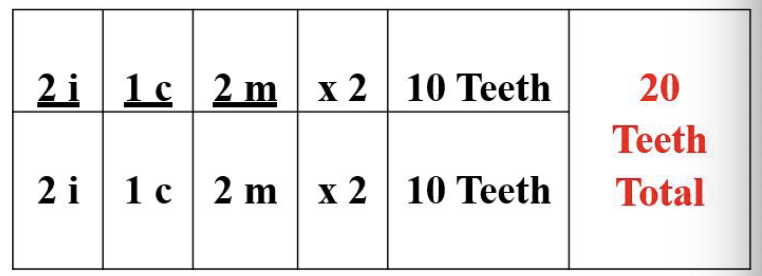
dental formula of primary teeth
i 2/2
c 1/1
m 2/2
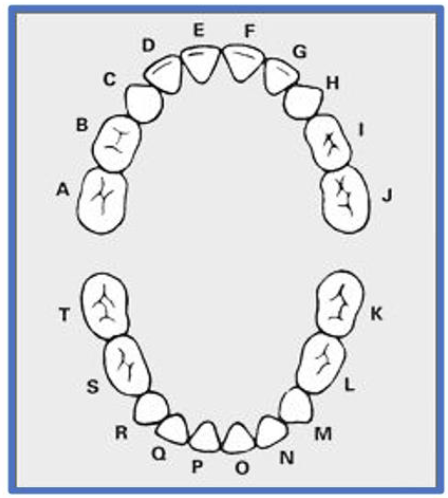
primary teeth are lettered or numbered?
lettered (A-T)
are there premolars in the primary dentition?
no
teeth start to form when in utero?
4-6 weeks
calcification of teeth begin approximately when in utero?
5-6 months
at birth, no teeth are visible. however…?
tooth buds may be noted on radiographs
are ages of eruption exact?
no. infants/children vary in development so age of eruption is an average
describe the order of eruption of primary teeth
centrals
laterlas
first molars
canines
second molars
A, B, D, C, E
which arch of teeth usually erupt first in ideal developmental pattern?
mandibular teeth usually erupt before Maxillary Teeth in an ideal developmental pattern
roots of primary teeth take how long to complete formation after eruption?
1.5 years
a tooth erupts when…?
its root is about half-formed (50%)
estimated eruption for primary maxillary central incisor
7.5 month
estimated eruption for primary maxillary lateral incisor
8-9 months
estimated eruption for primary maxillary canine
16-20 months
estimated eruption for primary maxillary first molar
12-16 months
estimated eruption for primary maxillary second molar
2-2.5 years
estimated eruption for primary mandibular central incisor
6.5 months
estimated eruption for primary mandibular lateral incisor
7 months
estimated eruption for primary mandibular canine
16-20 months
estimated eruption for primary mandibular first molar
12-16 months
estimated eruption for primary mandibular second molar
2.5 years
By __ years of age, there is separation of teeth, usually in the anterior teeth, due to the growth of the Maxilla and to accommodate the larger Permanent teeth
5
By __ years of age, the Permanent First Molars erupt, with this occurrence we see the beginning of the Mixed Dentition Stage.
6
how long does the mixed dentition stage last and the eruption of which teeth begins this stage?
6-12 years (perm first molars)
Permanent Anterior Teeth Erupt ______ to Primary Anterior Teeth
lingual
Permanent Posterior Teeth Erupt _________, in the furcation area of Primary teeth
apical (beneath)
Primary teeth roots are completed approximately ___ years after eruption, then they…?
1.5; resorb
do primary incisors have mamelons?
no but permanent incisors do
the primary molars are replaced by which teeth?
permanent premolar teeth
Primary teeth are smaller and whiter than permanent teeth because…?
less calcified than permanent teeth
Crowns of Primary Teeth are wider in what dimension compared to their crown lengths.
wider mesiodistally (Primary teeth crowns are more “squatty” (disproportionally shorter and thicker)
Roots of Primary Molars are …? beyond the crown to accommodate the Permanent Premolar Teeth
longer, slender, and flare
Primary teeth have prominent ________- on anterior teeth labially and lingually, producing a construction at the cervix of the tooth
cervical ridges or bulges
Primary Molars are _______ at the cervix
narrow (constricted at the cervix)
there are prominent _________ on the maxillary and mandibular first primary molars
buccal cervical ridges
Prominent buccal cervical ridges on the maxillary and mandibular …?
first primary molars
Primary teeth have a ______ occlusal table in part due to a flat slanted surface above the cervical bulge.
narrow
how do roots of primary teeth compare to roots of permanent teeth?
narrower and longer
which primary teeth contact only 1 tooth in the opposing arch?
mand centrals
max 2nd primary molars
t/f: primary teeth have static occlusal relationships.
false. occlusal relationships change with growht
spaces/diastemas develop particularly in what region?
anterior
Primary teeth wear on the…?
incisal and occlusal (because the primary teeth are less well calcified than the permanent teeth)
which tooth stabilizes the occlusion at six years of age.
1st perm molar
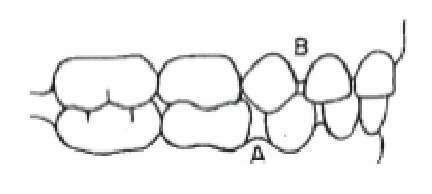
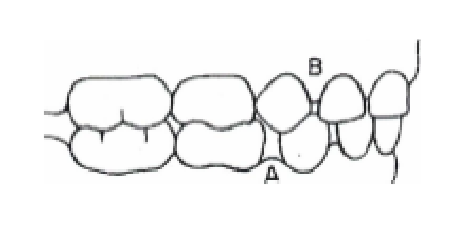
what do A and B represent?
primate spaces
what are primate spaces? how often do they occur?
These spaces originally were to accommodate the long canines of primates. Primate spaces occur in about 50% of children
where are the primate spaces usually found?
maxillary → mesial to canine
mand → distal to canine
what are the 2 possible eruption patterns of the 1st perm molars?
terminal step vs terminal plane
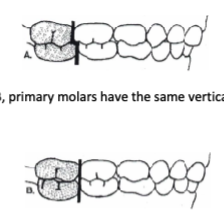
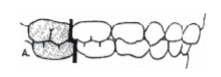
terminal step (ccommodates molars of the same size and creates a normal relationship)
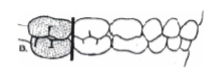
terminal plane (primary molars have the same vertical plane, so the permanent molars will erupt end
to end)
mand primary molars are wider in what direction compared to maxillar? this allows for more what?
mesiodistally
allow more of a mesial shift of the Mandibular First Molars
what is leeway space?
the difference between the combined mesiodistal widths of the deciduous cuspids and molars and their successors
space gained during the transition from primary molars and canines to permanent teeth
leeway space is specifcally referring to size differential between which teeth?
Specifically, the size differential between the Primary Canine, Primary First Molar and Primary Second Molar, and the Permanent Canine, First Premolar, and Second Premolar.
Usually, the sum of the Primary Tooth Widths is greater/smaller than that of their permanent successors.
greater
leeway space occurs in both arches, but which arch has more arch leeway?
mandible has more arch leeway than maxillary
leeway space is taken up by mesial migration of the which teeth during what process?
Permanent First Molars after the loss of the primary molars, and eruption of the second premolar.
Primary anterior teeth are narrower/wider than Permanent Anterior Teeth. Primary molars are narrower/wider than succedaneous premolars
Primary anterior teeth are narrower than Permanent Anterior Teeth.
Primary molars are wider than succedaneous premolars.
primary vs permanent teeth
total teeth
shade
shape
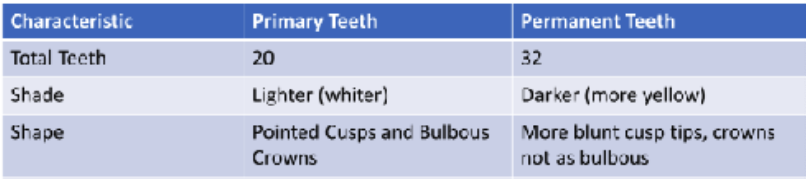
primary vs permanent teeth
occlusal table
roots
size

primary vs permanent teeth
cervical ridge
enamel cap
enamel rods

primary vs permanent teeth
dentin
pulp horns

enamel rods of primary teeth slope in which direction from the DEJ? permanent teeth?
Primary teeth: Slope Occlusally from DEJ
Permanent Teeth: Slope Cervically from DEJ
function of topical fluoride treatments
Inhibits demineralization.
Promotes remineralization.
Effects of topical fluoride on teeth in the oral cavity:
improve enamel crystallinity and recirculates through saliva.
Sources of topical fluoride:
dentifrice
fluoride mouth rinse
professionally applied fluoride (gel or varnish)
what is systemic fluoride?
Fluoride is ingested and the un-erupted teeth are the targets of fluoride activity
Sources of systemic Fluoride:
water fluoridation
dietary sources
fluoride supplements
what is the most efficient and cost-effective public health method for reducing the prevalence of dental caries?
water fluoridation
according to ADA recommendations, what is the optimal level of fluoride in drinking water?
0.7 ppm
Fluoride supplementation depends on
the age of the child
level of water fluoridation in the child’s community
Fluoride supplements should be used until
all the permanent teeth have erupted (approximately 16 years of age).
No fluoride supplementation is recommended before the age of
6 months
Fluoride supplementation should be used in communities where the concentration of fluoride is ______ in the drinking water.
0.6ppm or less
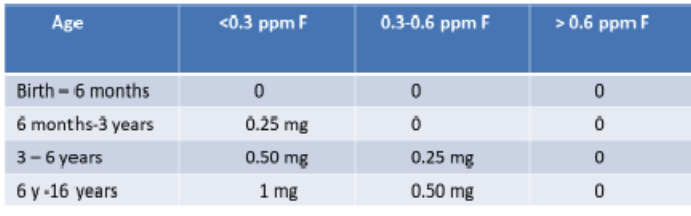
dietary fluoride supplementation by age group for <0.3 ppm F:
birth - 6months
6mo - 3 y
3-6 y
6-16 y
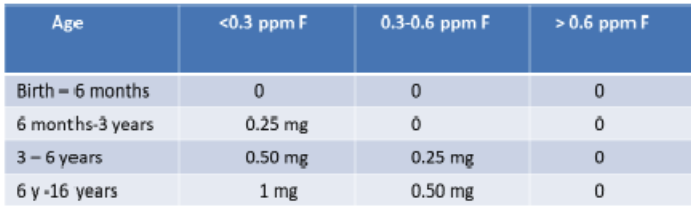
dietary fluoride supplementation by age group for 0.3-0.6 ppm F:
birth - 6months
6mo - 3 y
3-6 y
6-16 y
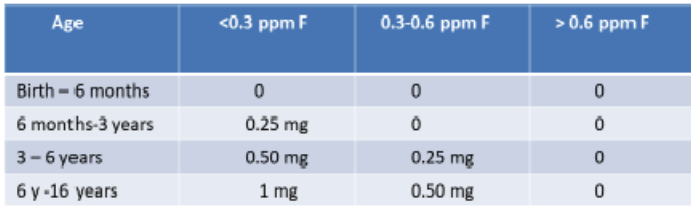
dietary fluoride supplementation by age group for >0.6 ppm F:
birth - 6months
6mo - 3 y
3-6 y
6-16 y