KIN223FINAL
1/290
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
291 Terms
With the subject in the anatomic position, one can best see the dorsum of the manus from a(n) _________blank view.
a) posterior
b) superior
c) inferior
d) anterior
e) lateral
a) posterior
A professional fighter hit in the mental region might have damage to the
shoulder.
knee.
nose.
jaw.
ear.
jaw
Choose the statement that best exemplifies the interrelated nature of anatomy and physiology.
Multiple Choice
The ovaries are involved in the production of gametes as well as the production of hormones that regulate the menstrual cycle.
The stomach is involved in mechanical and chemical digestion, and secretes many enzymes as well as hormones.
The iris of the eye consists of two layers of smooth muscle innervated by the autonomic nervous system.
Simple squamous epithelium consists of a single layer of flattened cells, which is appropriate for organs where filtration and diffusion occur.
Simple squamous epithelium consists of a single layer of flattened cells, which is appropriate for organs where filtration and diffusion occur.
Gross anatomy refers to the study of
structures formed by cells.
structures not visible to the unaided eye.
structures visible to the unaided eye.
nasal secretions.
cells.
structures visible to the unaided eye.
The word "anatomy" comes from
Multiple Choice
Italian and means "form."
Latin and means "to be born."
German and means "body."
Hebrew and means "shape."
Greek and means "to cut apart."
Greek and means "to cut apart."
When a blood vessel is damaged, platelets attach and recruit more platelets to the area. These new platelets recruit even more, quickly increasing the number of platelets until the damage is sealed with a blood clot. This amplification is an example of
Multiple Choice
negative feedback.
positive feedback.
positive feedback
A(n) _________blank plane separates the body into superior and inferior parts.
Multiple Choice
coronal
frontal
oblique
transverse
sagittal
transverse
The pleural cavity is the
the serous membrane lining the abdomen.
potential space between the two serous membranes surrounding a lung.
same as the mediastinum.
space within which the heart sits.
potential space between the two serous membranes surrounding a lung
If you are cold and your body alters the circulation near the skin in order to conserve heat, what characteristic of life is this representing?
Organization
Metabolism
Regulation
Reproduction
Regulation
The cranial cavity houses the
eyeball.
nasal structures.
spinal cord.
brain.
ear canals.
Brain
The best term for referring to the rear or "tail end" is
caudal.
superior.
inferior.
lateral.
cephalic.
caudal
The directional term that means "away from the midline of the body" is
Multiple Choice
superior.
inferior.
caudal.
lateral.
medial.
lateral
The term that refers to the ability of organisms to react to changes in the environment is
Multiple Choice
organization.
reproduction.
development.
metabolism.
responsiveness.
responsivness
Which anatomical term describes the wrist region?
Multiple Choice
Carpal
Digital
Tarsal
Olecranal
Perineal
carpal
The smallest structural unit that exhibits the characteristics of living things is
Multiple Choice
a cell.
an individual.
tissue.
a system.
an organ.
a cell
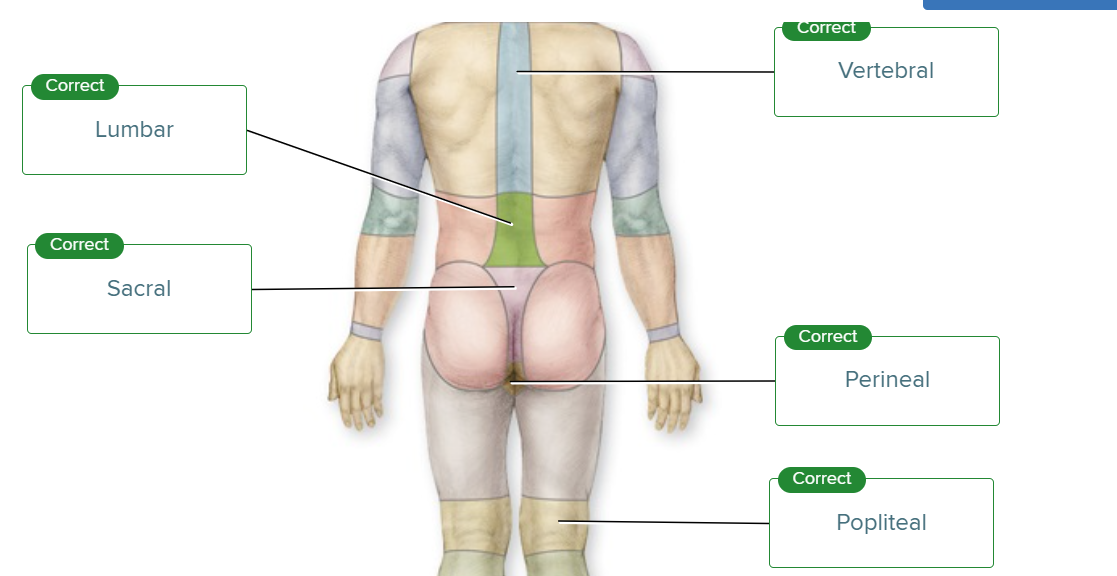
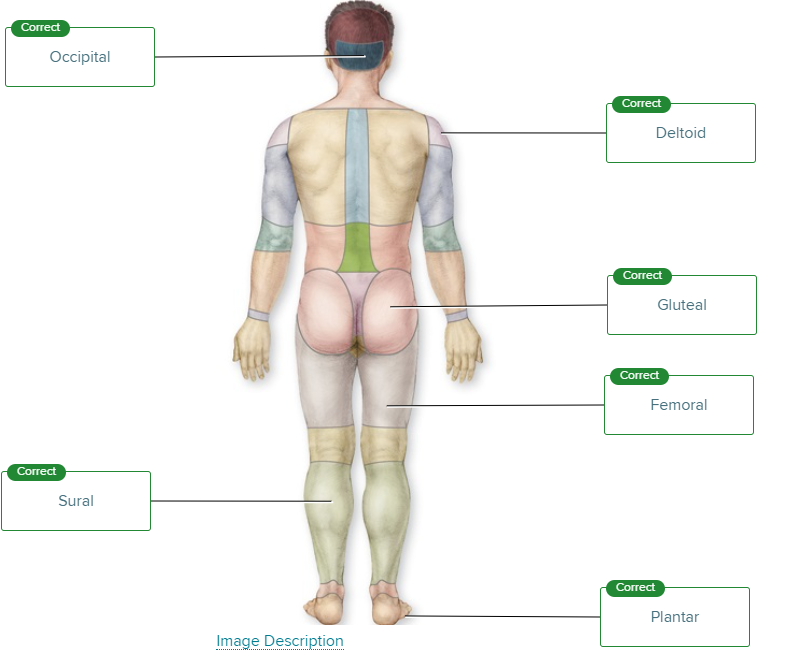
For accuracy and clarity, the initial point of reference for body regions or parts is anatomic position. An individual is in this position if they are _____ with the feet ______ . The upper limbs are at _____ and the palms face____ . The head should be ____ and the eyes _____.
standing upright, parallel and flat on the floor, sides of the body, anteriorly, level, looking forward
Which of the following is an organic molecule?
Multiple Choice
O2O2
HCl
NaOH
C6H12O6C6H12O6
C6H12O6C6H12O6
The three parts making up a nucleotide are
Multiple Choice
a phosphorous, a deoxygenated ribose, and an amino acid.
a five-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
a purine, a pyrimidine, and a ribose sugar.
a double helix, a single strand, and a chromosome.
an adenine, a guanine, and a cytosine.
a five-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
All organic compounds contain _________blank, hydrogen, and usually oxygen.
Multiple Choice
phosphorus
carbon
nitrogen
sulfur
carbon
The molecular formula of chlorine gas is Cl2Cl2 . One molecule of this gas would be attracted to another by
Multiple Choice
ionic bonds
polar covalent bonds.
hydrogen bonds.
intermolecular forces between nonpolar molecule
intramolecular forces.
intermolecular forces between nonpolar molecules
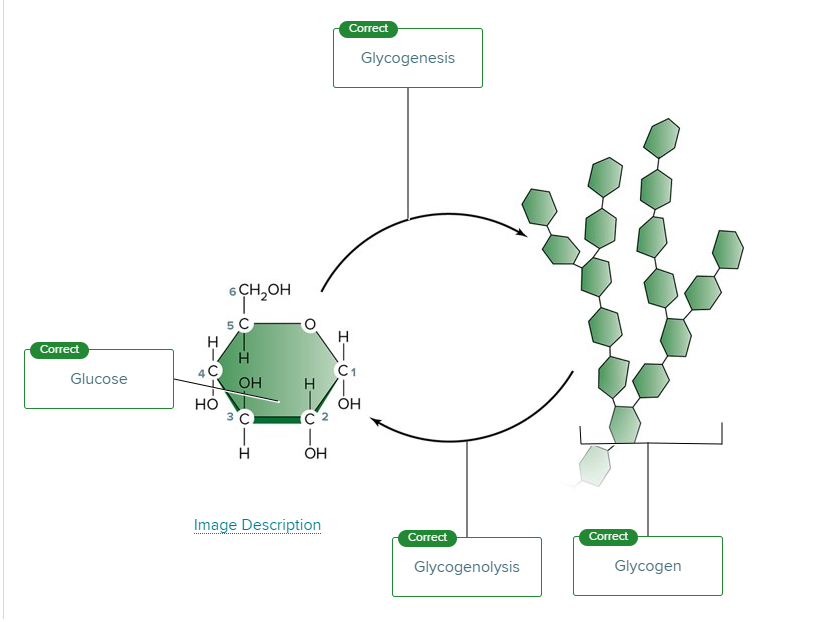
Skeletal muscle tissue can break down glycogen, a carbohydrate polymer, into its individual monomers to be used for energy. What are the monomers produced?
Multiple Choice
Nucleic acids
Polysaccharides
Glucose molecules
Amino acids
Glucose molecules
Hemoglobin in blood, components of the cytoskeleton, and enzymes in the digestive system are all examples of
Multiple Choice
catalysts.
amino acids.
proteins.
lipids.
carbohydrates.
proteins.
The primary sequence of a protein contains proline. What can you predict about its folded structure at that region?
Multiple Choice
There is a disulfide bond at that region.
There is a bend at that location.
There is an alpha helix at that location.
That is the very beginning of a polypeptide chain.
There is a bend at that location.
Hydrogen bonds form between molecules containing _________blank bonds; the hydrogen bond is between a hydrogen atom of one molecule and a partially _________blank charged atom of another.
Multiple Choice
polar covalent; negatively
nonpolar covalent; positively
ionic; positively
nonpolar covalent; negatively
polar covalent; positively
polar covalent; negatively
Mixing water and oil together is an example of a(n)
Multiple Choice
emulsion
solution.
colloid.
emulsion
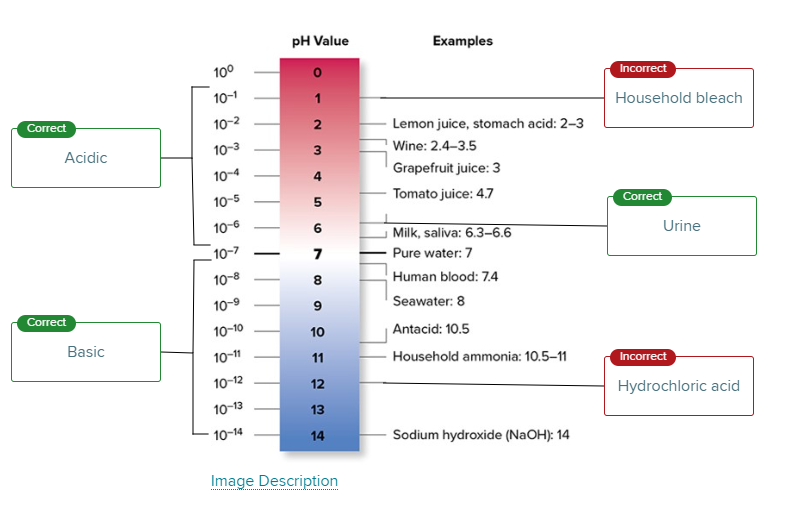
Generally, a chemical buffer is described as
Multiple Choice
a weak acid that makes a solution slightly more basic by its presence.
a weak acid and weak base that help prevent big changes in pH.
a neutral molecule that does not influence the pH in any way.
a strong acid or strong base that brings the pH of a solution to 7.0.
a weak acid and weak base that help prevent big changes in pH.
What type of organic molecule comprises the majority of a potato?
Multiple Choice
Glycogen
Monosaccharides
Polysaccharides
Disaccharides
Polysaccharides
Which of the following is an accurate description of hydrocarbons?
Multiple Choice
Most of them contain sulfur.
They are nonpolar molecules.
They are polar molecules.
Most of them contain phosphorus.
They are nonpolar molecules.
Ionic bonds involve
Multiple Choice
electrostatic interactions between anions and cations.
the release of protons by negatively charged particles.
the attraction between water and salts.
the sharing of electrons between two atoms of the same element.
electrostatic interactions between anions and cations.
Water and a nonpolar substance will need to be forcibly mixed. This best describes a(n)
Multiple Choice
solution.
colloid.
emulsion
emulsion
Lipids ____ polymers.
Lipids ____ in water.
Lipids function as stored _____.
The most common form of lipids are _____
are not
are insoluble
nutrients
triglycerides
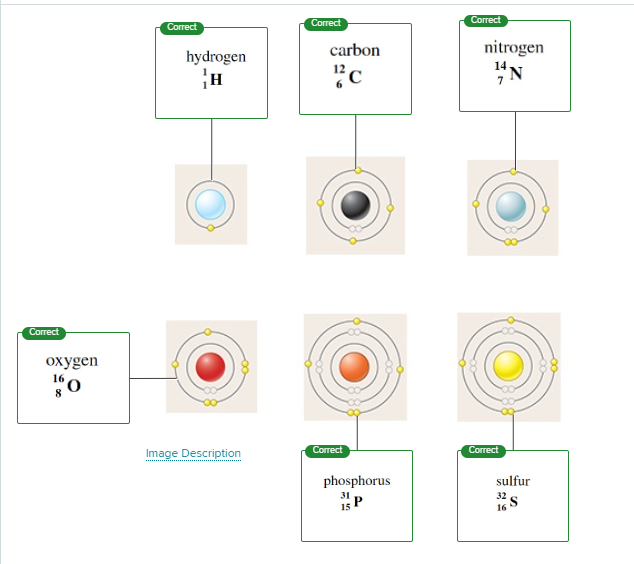
The smallest part of an element that maintains the properties of the element is defined as a(n) _____.
Of the three basic components of an atom, _____ have a negative charge and are not located in the nucleus of the atom.
All atoms of the same element have the same number of positive subatomic particles, ______, also known as the atomic number. Neutrons have a ______ charge and when combined with protons, determine the atomic mass.
Sulfur has an atomic mass of 32 and an atomic number of ______. With this information, the total number of electrons for this element is 16 Correct.
If the atomic number of nitrogen (N) is 7, then the total number of electrons is equal to _______ .
atom
electrons
protons, neutral
16
7
pls ignore that I got it wrong lol
count # of electrons, it’s the bottom #
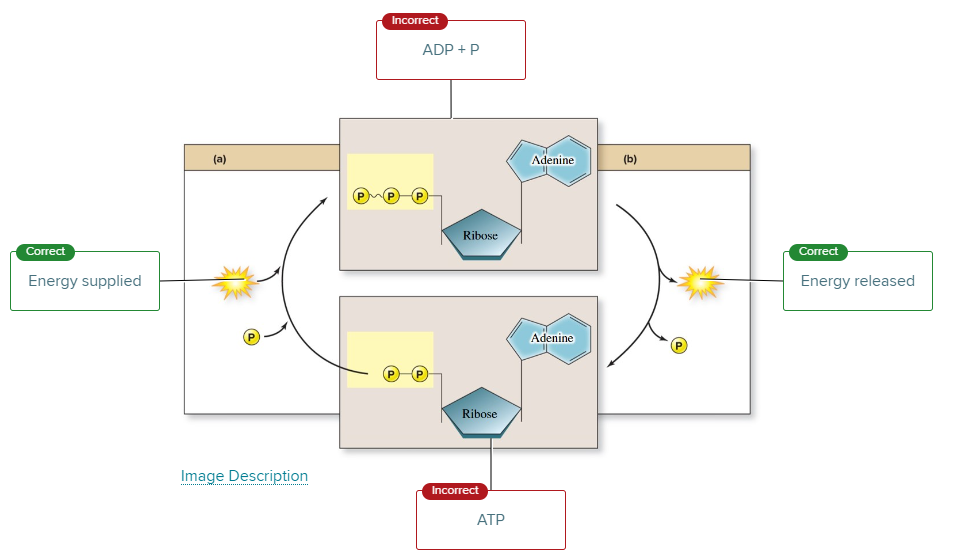
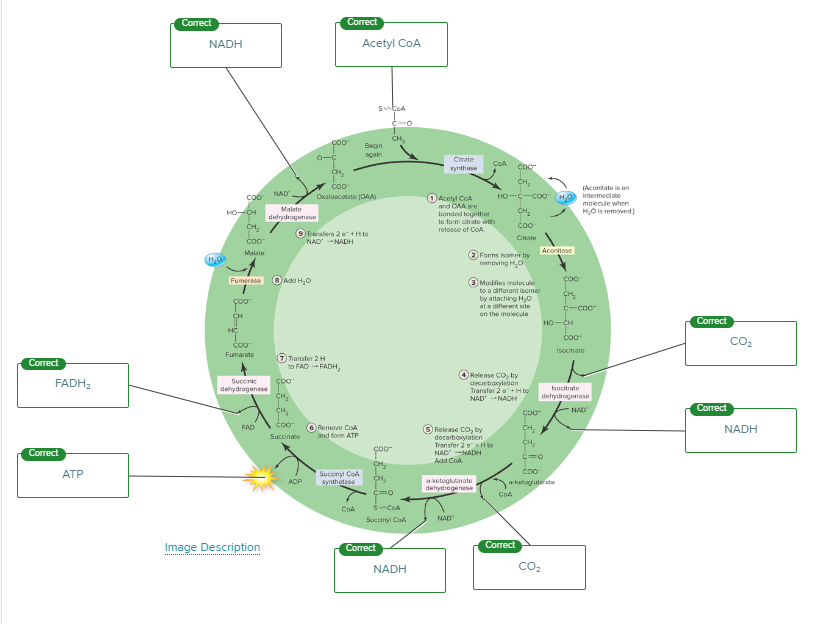
The more common way that ATP is produced in cells is
Multiple Choice
the direct pathway known as substrate-level phosphorylation.
the indirect pathway known as oxidative phosphorylation.
the indirect pathway known as substrate-level phosphorylation.
the direct pathway known as oxidative phosphorylation.
the indirect pathway known as oxidative phosphorylation.
Which of the following molecules is produced, along with the oxidation of NADH, when oxygen levels are limited?
Multiple Choice
Oxygen
Pyruvate
Lactate
CO2CO2
Citrate
Lactate
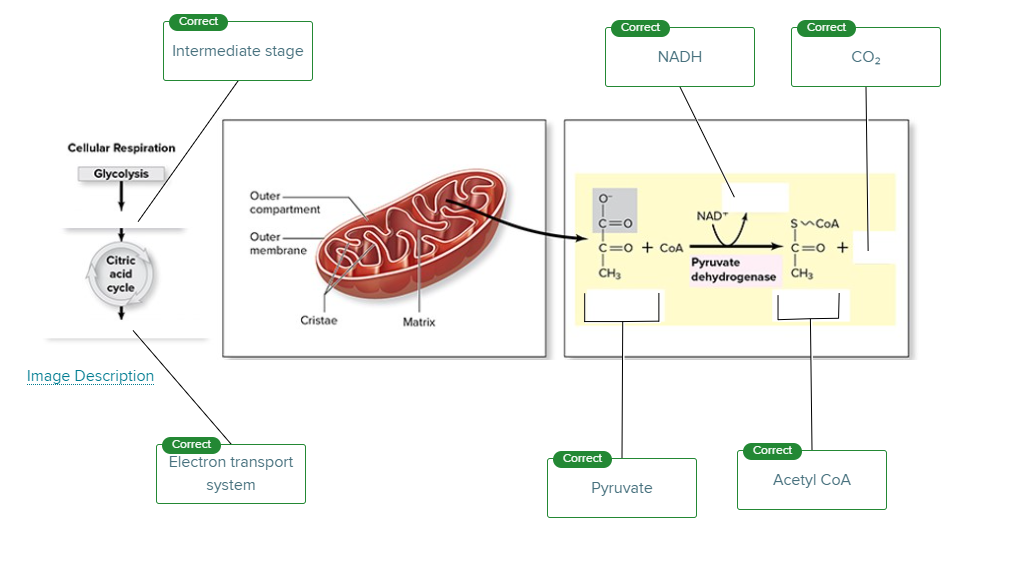
Fatty acids and some amino acids are converted directly into _________blank for ATP production.
Multiple Choice
glucose
pyruvate
NADH
acetyl CoA
FADH2
acetyl CoA
The enzyme RNA polymerase is synthesized
Multiple Choice
at the Golgi apparatus, and it is embedded in the cell membrane.
in the nucleus, and it is converted to RNA for export outside the cell.
at a ribosome, and it remains within the cell.
at the rough endoplasmic reticulum, and it is secreted from the cell.
at a ribosome, and it remains within the cell.
How many ATP are produced using the energy from each NADH?
Multiple Choice
1
3
2
4
3
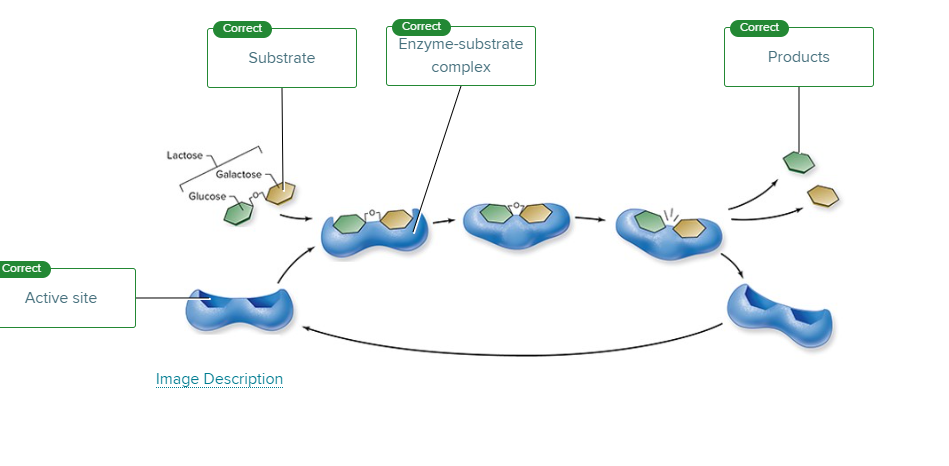
In the final step of enzymatic catalysis,
Multiple Choice
the product is completed and the enzyme is inactivated.
the enzyme and substrate form chemical bonds with each other resulting in a new product.
the products are released and the enzyme is free to bind other substrates.
the substrate is released and the enzyme is inactivated.
equilibrium is obtained so that the enzyme does not catalyze further reactions.
the products are released and the enzyme is free to bind other substrates.
Which stage of cellular respiration is catalyzed by pyruvate dehydrogenase?
Multiple Choice
Citric acid cycle
Electron transport system
Glycolysis
Fermentation to lactate
Intermediate stage
Intermediate stage
The sodium level inside and outside of a resting cell is an example of the
Multiple Choice
potential energy of a concentration gradient, because sodium is more abundant outside the cell.
conversion of potential energy to kinetic energy, because sodium can never move across the cell membrane and must move across its surface.
kinetic energy of sodium rushing out of a cell down its concentration gradient.
kinetic energy of the large difference in sodium concentration on the inside versus the outside of the cell.
potential energy of an electron transport chain, because sodium has an extra electron to donate.
potential energy of a concentration gradient, because sodium is more abundant outside the cell.
The optimum temperature for most enzymes is around body temperature. If the body temperature is slightly elevated, what effect will this have on enzymatic reactions?
Multiple Choice
Increased reaction rates
Enzymes may denature
Less kinetic energy, so less likely for enzyme and substrate to contact
Stiffer, more rigid enzymes
Increased reaction rates
Why does pyruvate need to be converted to lactic acid in order for glycolysis to continue in the absence of oxygen?
Multiple Choice
Lactic acid carries high energy electrons to the mitochondria in the absence of oxygen.
Glycolysis would otherwise shut down due to an overabundance of NAD+NAD+ .
In the absence of oxygen, NADH is not converted to NAD+NAD+ by the electron transport chain, and NAD+NAD+ levels fall.
In the absence of oxygen, NADH is not converted to NAD+NAD+ by the electron transport chain, and NAD+NAD+ levels fall.
Which of the following is a common feature of electron carriers?
Multiple Choice
They are all reduced when electrons are lost.
They all contain iron to attract the electrons.
They can be reversibly oxidized and reduced.
They gain electrons when they are oxidized.
They all use FAD as an intermediate.
They can be reversibly oxidized and reduced.
According to the second law of thermodynamics, when energy is transformed from one kind to another
Multiple Choice
chemical bonds must be broken.
some of it is converted to heat.
some energy is destroyed.
homeostasis is maintained.
new energy is created.
some of it is converted to heat.
During cellular respiration, decarboxylation occurs when
Multiple Choice
a carbon atom is removed from and an oxygen atom is added to fructose.
a carboxyl group is released from pyruvate.
a carbon dioxide molecule is removed from the cytosol.
a carbon atom is removed from glucose.
all carbon and oxygen atoms are released from a high-energy molecule
a carboxyl group is released from pyruvate.
the term "activation energy" refers to the amount of energy
Multiple Choice
required to initiate only catabolic reactions.
released by an endergonic reaction.
released by an exergonic reaction.
required to initiate any chemical reaction.
released by a catabolic reaction.
required to initiate any chemical reaction.
PLS I DIDN”T SEE THERE WAS A CORRECT ANSWER BUTTON
One mechanism for regulating enzymes is by either adding a phosphate group through _______ removing a phosphate group by _______. The enzymes that transfer phosphate from ATP generally called ________, whereas enzymes that remove the phosphates are called ________.
phosphorylation
dephosphorylation
protein kinases
phosphatases
Chemical reactions can occur when sufficient _____ is supplied to overcome the activation energy. In the lab, heating a mixture of ______ often overcomes the activation energy. An elevation in temperature ________the kinetic energy of the molecules. This provides enough energy to _______ chemical bonds. This is not feasible in living cells because a change in temperature of this type will cause the proteins to _____ and cause cell death Correct. To assist with this problem, cells use biologically active protein catalysts called _____ to facilitate chemical changes
energy
reactants
increases
break
denature
enzymes
Which are the smallest components of the cytoskeleton?
Multiple Choice
Centrioles
Centrosomes
Intermediate filaments
Microtubules
Microfilaments
Microfilaments
Mucus is moved along the lining of the trachea by extensions from cell membranes known as
Multiple Choice
cilia.
microvilli.
stereovilli.
flagella.
cilia.
Another name for the intracellular fluid is
Multiple Choice
cytoplasm.
cytosol.
interstitial fluid.
cisternae.
intercellular matrix.
cytosol.
If the nutrient glycogen is found stored inside a cell, it is considered a(n)
Multiple Choice
inclusion.
pigment.
non-membrane-bound organelle.
membrane-bound organelle.
inclusion.
The _________blank are responsible for synthesizing most of a human body cell's ATP.
Multiple Choice
nucleoli
ribosomes
lysosomes
microfilaments
mitochondria
mitochondria
Proteins that are embedded within, and extend across, the phospholipid bilayer are called _________blank proteins.
Multiple Choice
cytoskeleton
peripheral
integral
catalytic
integral
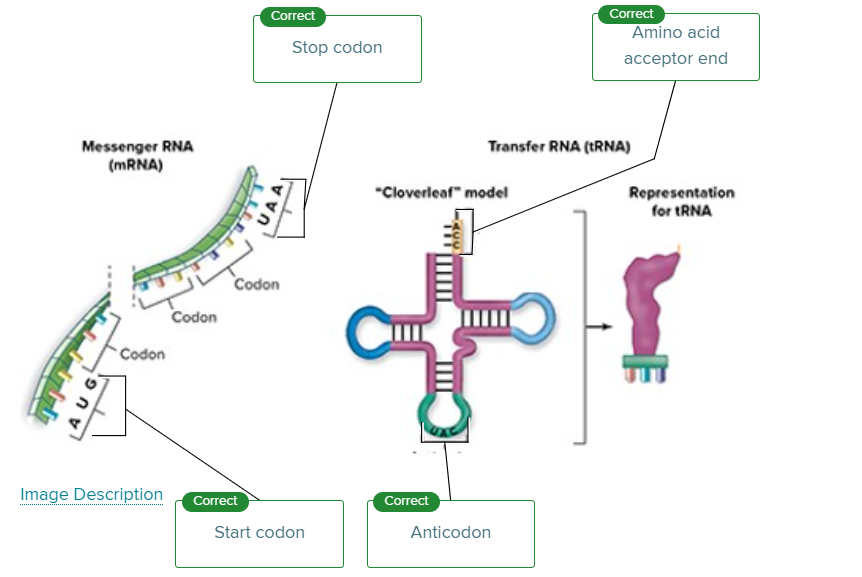
Which of the following is considered a required enzyme for the process of transcription?
Multiple Choice
RNA polymerase
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
Amine transferase
DNA polymerase
RNA polymerase
The folds of the internal membrane of a mitochondrion are called
Multiple Choice
vacuoles.
vesicles.
cristae.
cisternae.
cristae
The lipid that stabilizes the membrane at extreme temperatures and is found in the hydrophobic regions of the bilayer is
Multiple Choice
the nonpolar tails.
the polar head.
glycocalyx.
cholesterol.
glycolipid.
cholesterol.
The phase of mitosis that begins as spindle fibers pull sister chromatids apart at the centromere is
Multiple Choice
anaphase.
metaphase.
interphase.
prophase.
telophase
anaphase.
Channel-mediated diffusion is a subtype of
Multiple Choice
simple diffusion.
facilitated diffusion.
active transport.
endocytosis.
carrier-mediated diffusion.
facilitated diffusion.
During transcription
Multiple Choice
a protein is formed as a DNA sequence is read.
a DNA sequence is formed as a RNA sequence is read.
a protein is formed as a RNA sequence is read.
an RNA molecule is formed as a DNA sequence is read.
an amino acid is transferred to a ribosome as a DNA sequence is read.
an RNA molecule is formed as a DNA sequence is read.
The last part of interphase is called
Multiple Choice
the S phase.
the first "gap" phase.
the second "gap" phase.
anaphase.
telophase.
the second "gap" phase.
To maintain a resting membrane potential, the sodium-potassium pump
Multiple Choice
actively transports 3 potassium ions out of the cell and 2 sodium ions into the cell.
passively transports 3 sodium ions out of the cell and 2 potassium ions into the cell.
passively transports 3 potassium ions out of the cell and 2 sodium ions into the cell.
actively transports 3 sodium ions out of the cell and 2 potassium ions into the cell.
actively transports 3 sodium ions out of the cell and 2 potassium ions into the cell.
The uptake of material through the plasma membrane by the formation of a vesicle is _________blank, whereas the fusion of a vesicle with the plasma membrane and the release of its contents outside of the cell is called _________blank.
Multiple Choice
endocytosis; exocytosis
endocytosis; pinocytosis
pinocytosis; endocytosis
exocytosis; pinocytosis
endocytosis; exocytosis
Contains the information necessary to produce proteins through gene expression ____
Carries amino acids to the ribosome_____
Contains the information from DNA known as the genetic code _____
Is combined with proteins to make ribosomes _______
DNA
tRNA
mRNA
rRNA
______ provide a means of regulating the movement of substances across the plasma membrane. These proteins include channels, carriers, and pumps.
______ bind ligands, such as neurotransmitters and hormones.
______ are proteins or glycoproteins that communicate to other cells that they belong to the body.
_____ catalyze chemical reactions and may be attached either to the internal or external surface of a cell.
_______ are proteins that secure the cytoskeleton to the plasma membrane.
_______ form cell-to-cell attachments.
Transport proteins
Cell surface receptors
Identity markers
Enzymes
Anchoring sites
Cell-adhesion proteins
If you gently rub your thumb and forefinger together, each finger is contacting
Multiple Choice
keratinized simple squamous epithelium.
nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium.
nonkeratinized simple squamous epithelium.
simple squamous epithelium.
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium.
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium.
Which type of epithelial tissue would be the least protective?
Multiple Choice
Simple squamous
Stratified nonkeratinized
Transitional
Simple columnar
Stratified keratinized
Simple squamous
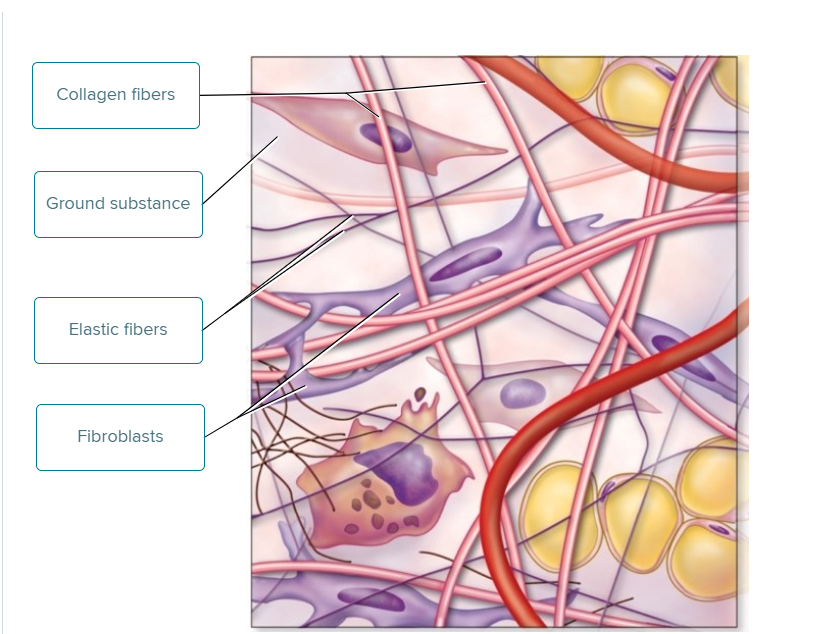
What feature of your ear accounts for its ability to regain its shape after it has been deformed or compressed?
Multiple Choice
The elastic fibers in the ear's skin that contract after being stretched
The elastic fibers present in the ear's cartilage
The abundance of reticular fibers forming a dense meshwork
The ear's built-in memory based upon its overall size and shape
The elastic fibers present in the ear's muscles
The elastic fibers present in the ear's cartilage
f you were examining a microscope slide containing a type of muscle tissue and observed a branching network of striated cells, each with one or two central nuclei, you could conclude that you were looking at _________blank muscle.
Multiple Choice
cardiac
voluntary
smooth
skeletal
osseous
cardiac
When hyperplasia proceeds out of control, a tumor may develop. This condition is termed
Multiple Choice
fibrosis.
hypertrophy.
neoplasia.
metaplasia.
atrophy
neoplasia
Which of the following is not a function of epithelial tissue?
Multiple Choice
Secretion
Selective permeability
Physical protection
No exceptions; these are all functions of epithelial tissue
Sensation
No exceptions; these are all functions of epithelial tissue
From which primary germ layer is the epidermis of the skin derived?
Multiple Choice
Endoderm
Mesenchyme
Ectoderm
The epidermis is derived from all three primary germ layers.
Mesoderm
Ectoderm
There are four types of body membranes. Select the exception.
Multiple Choice
Cartilaginous
Synovial
Serous
Cutaneous
Mucous
Cartilaginous
The type of epithelial tissue that is only one cell-layer thick is called _________blank; the type of epithelial tissue that is two or more cell-layers thick is called _________blank.
Multiple Choice
squamous, transitional
simple; stratified
stratified; columnar
pseudostratified, cuboidal
simple; stratified
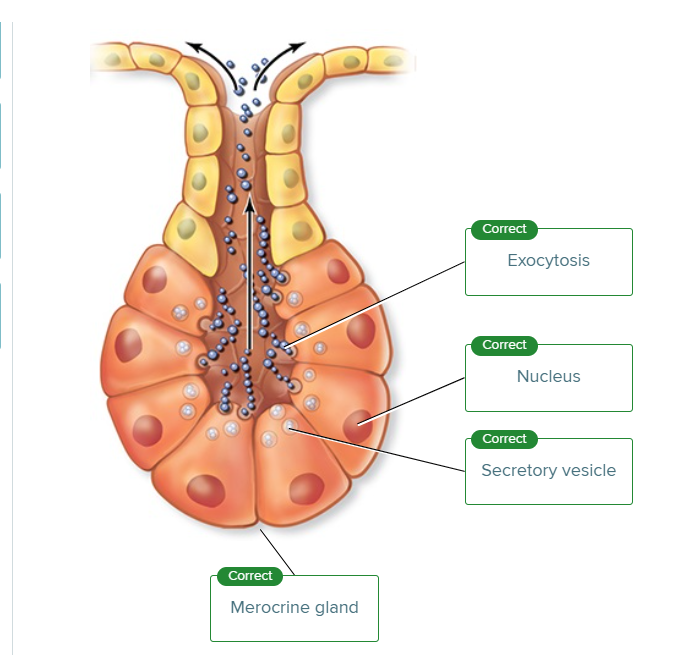
The type of exocrine gland in which the entire cell disintegrates, liberating any accumulated products, is the _________blank gland.
Multiple Choice
apocrine
merocrine
goblet cell
holocrine
None of the choices is correct.
holocrine
Microscopic folds that extend from the apical surface of certain epithelia to increase the surface area for absorption and secretion are called
Multiple Choice
cilia.
desmosomes.
mucus.
flagella.
microvilli.
microvilli.
Plasma is
Multiple Choice
a liquefied ground substance that includes several dissolved cells.
platelets, red blood cells, and white blood cells.
a liquid ground substance containing dissolved proteins
a dissolved ground matrix and a lining of epithelial cells.
platelets and a watery ground substance.
a liquid ground substance containing dissolved proteins.
A skeletal muscle fiber is
Multiple Choice
a skeletal muscle cell.
a contractile filament within the osteon of bone.
found only in cardiac muscle.
an elongated series of muscles held together by dense connective tissue.
a collection of several muscles bound together by a membrane.
a skeletal muscle cell.
The largest of the body membranes, commonly called the skin, is the _________blank membrane.
Multiple Choice
synovial
cutaneous
mucous
cartilaginous
serous
cutaneous
Epithelial tissue
Multiple Choice
cells secrete a ground substance composed of hydroxyapatate.
cells can be cube or column shaped.
is composed of cells, matrix and ground substance.
cells are typically scattered in a random fashion in the matrix they produce.
cells can be cube or column shaped.
The outermost layer of the skin (the epidermis) protects the underlying structures from the environment. __________
The epithelium of the skin is a barrier to water and reduces water loss from the body. _______
The epithelium of the skin prevents the entry of many toxic molecules and microorganisms into the body. ________
Simple squamous epithelium allows carbon dioxide to diffuse from the blood into the lungs. _________
Mucous glands and the enzyme-secreting portions of the pancreas secrete their products into ducts that subsequently deliver their products to other areas of the body. ________
The plasma membranes of certain epithelial tissues contain carrier proteins that regulate the absorption of materials. _______
The epithelium of the oral cavity protects the underlying structures from food as it is being chewed.____________
The epithelial cells of the intestine absorb digested food molecules, vitamins, and ions. ____________
Protecting underlying structures
Acting as barriers
Acting as barriers
Permitting the passage of substances
Secreting substances
Absorbing substances
Protecting underlying structures
Absorbing substances
In the body, _______ are a group of similar cells that perform a common function, and _____ are structures that are composed of _____ or more of these. Tissues ____ an organ's function. The key to organ structure is that the _____ tissue types must work in concert.
tissues
organs
two
support
different
After the egg is fertilized, the first tissues that appear are called the _______ .
The mucous membrane of the digestive tract emerges from the ________ .
Muscle, bone, and blood all emerge from ______ , which is derived from the ______ layer.
_____ arises from all three primary germ layers.
The____ and spinal cord both arise from _____ .
primary germ layers
endoderm
mesenchyme, mesoderm
epithelium
brain, ectoderm
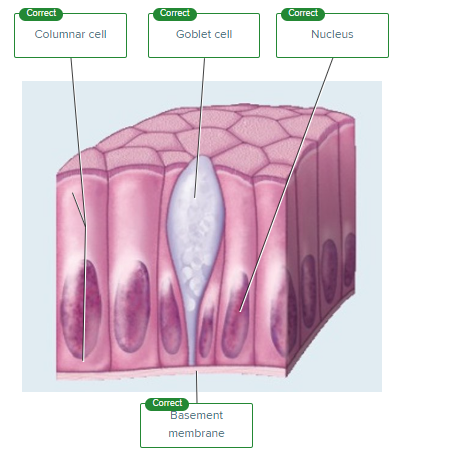
The oily, waxy secretion called sebum is produced by
Multiple Choice
sweat glands.
apocrine glands.
sebaceous glands.
the dermis.
hair follicles.
sebaceous glands.
Which statement is true regarding the subcutaneous layer (hypodermis)?
Multiple Choice
It is a keratinized, squamous epithelium.
It is the superficial region of the dermis.
It is responsible for the ridges known as fingerprints.
It stabilizes the position of the skin and binds it to underlying structures.
It stabilizes the position of the skin and binds it to underlying structures.
Reddened skin reflects
Multiple Choice
dilated blood vessels, sending more blood to the dermis.
eating too many carrots.
inheriting extra melanin.
constricted blood vessels, sending more blood to the epidermis.
dilated blood vessels, sending more blood to the dermis.
The part of the hair that extends beyond the skin surface is called the
Multiple Choice
papilla.
alopecia.
bulb.
root.
shaft.
shaft