2.5 Continuity
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Continuous Number

Definition l implicitly requires three things if f is continuous at a:
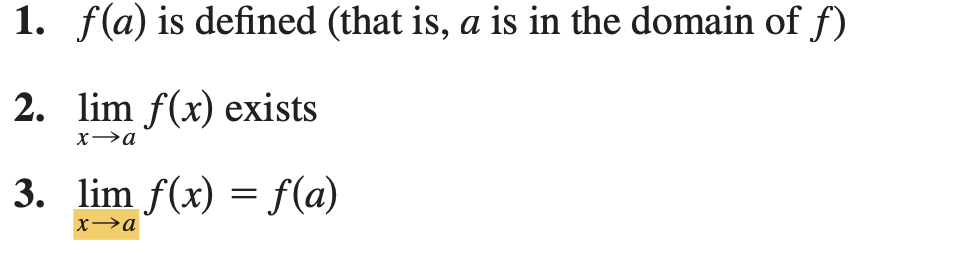
Discontinuity
If f is defined near a (in other words, f is defined on an open interval containing a, except perhaps at a), we say that f is discontinuous at a (or f has a discontinuity at a) if f is not continuous at a.
Continuity
A function f is continuous from the right at a number a and continuous from the left at a if

Continuous on an interval
A function f is continuous on an interval if it is continuous at
every number in the interval.

If f and g are continuous at a and c is a constant then the following
functions are also continuous at a:
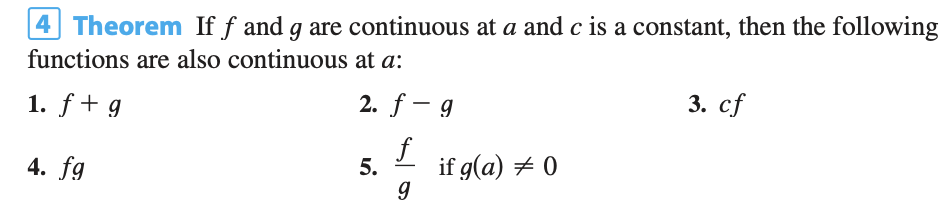
The following theorem was stated in Section 2.3 as the Direct Substitution Property.

The following types of functions are continuous at every number in
their domains:
polynomials, rational functions, root functions, trigonometric, functions, inverse trigonometric functions, exponential functions logarithmic functions
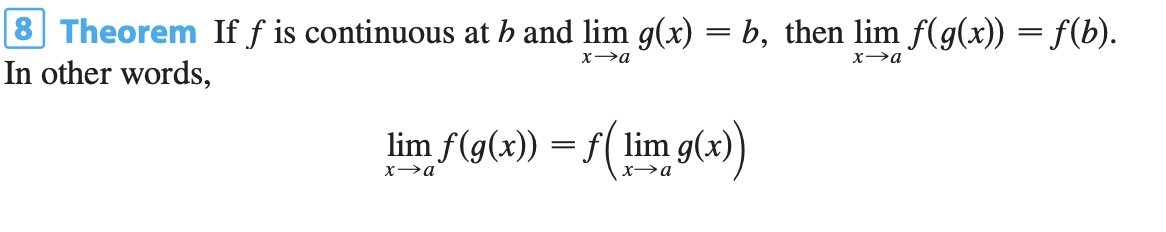

The Intermediate Value Theorem (IVT)
f is continuous on a closed interval [a,b]
N is any number between f(a) and f(b)
Then there exists at least one number c in the open interval (a,b)(a,b) such that f(c)=N.