MCAT Content Version 3
1/829
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
830 Terms
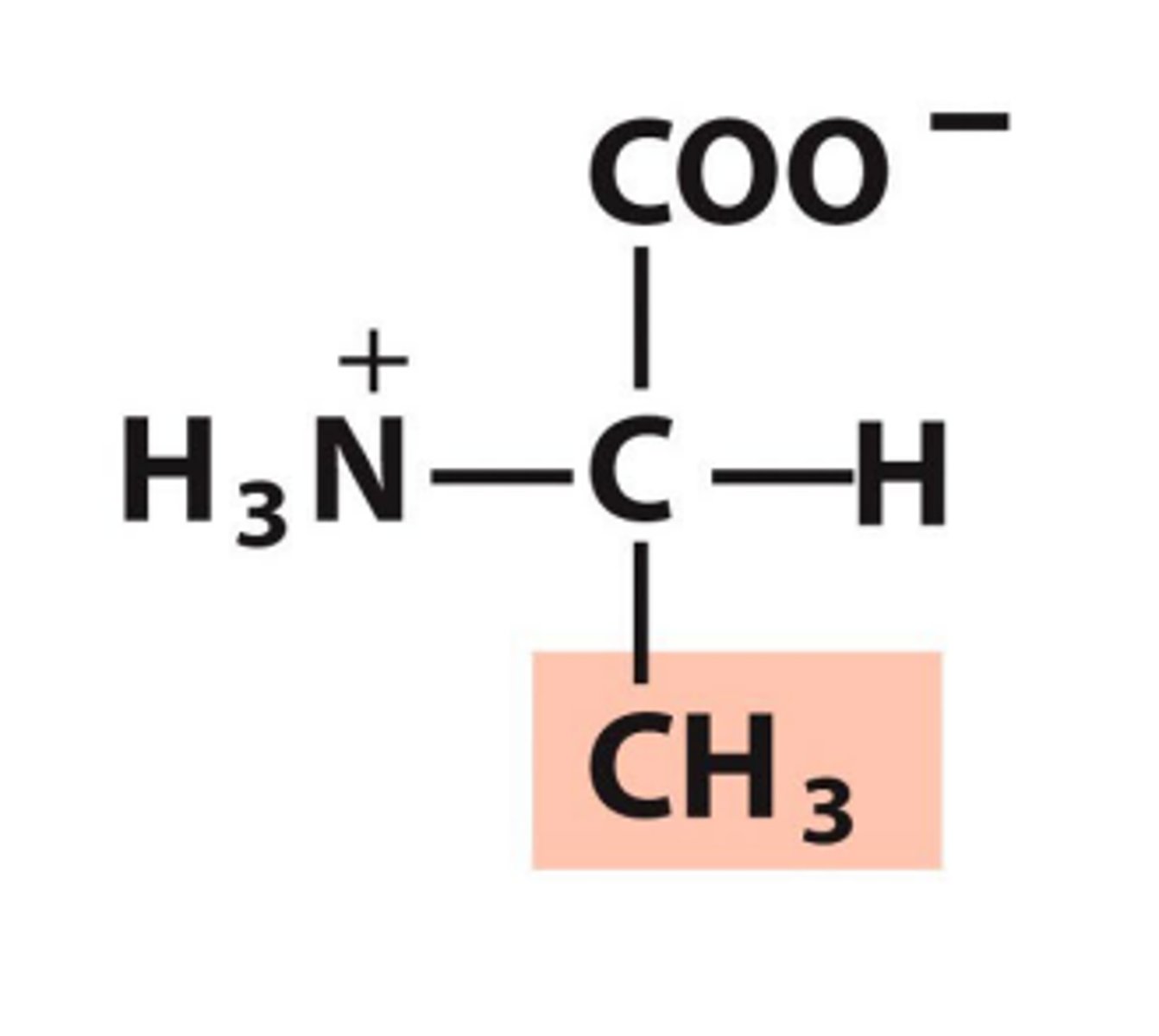
Alanine, Ala, A
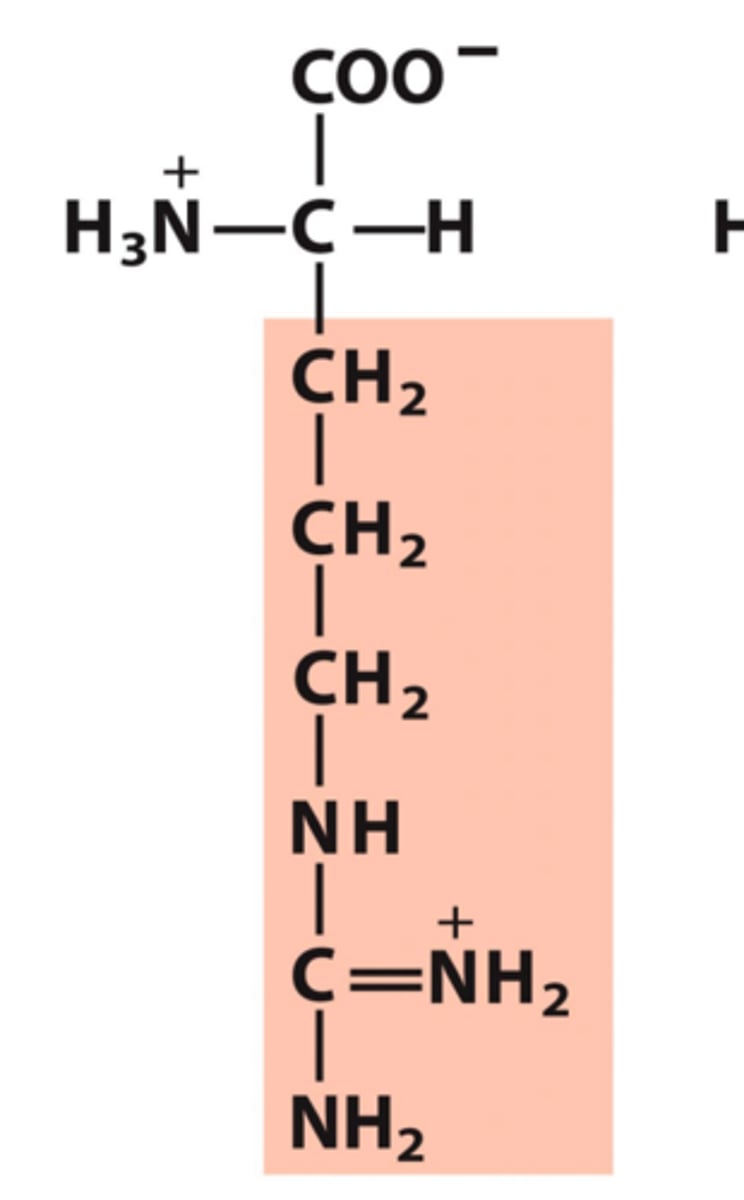
Arginine, Arg, R
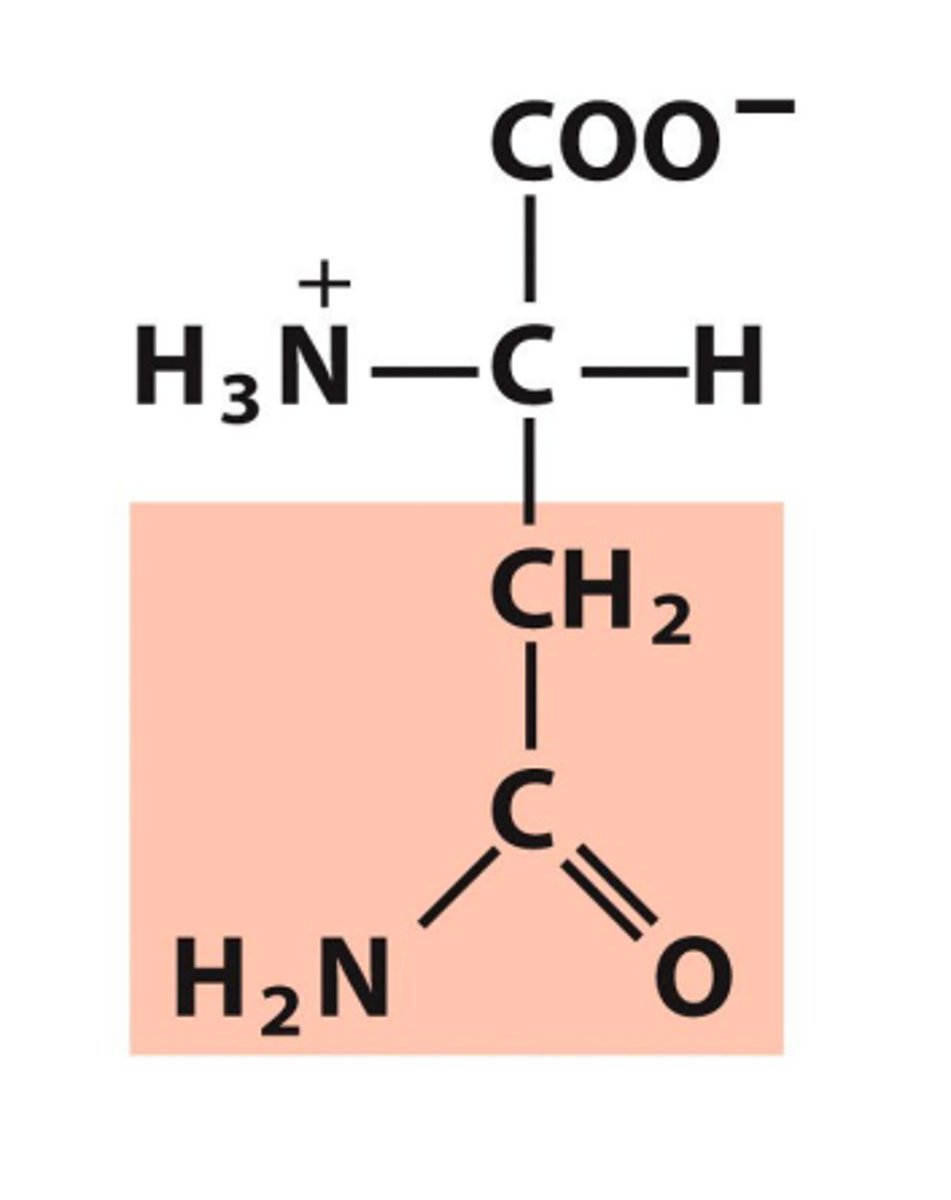
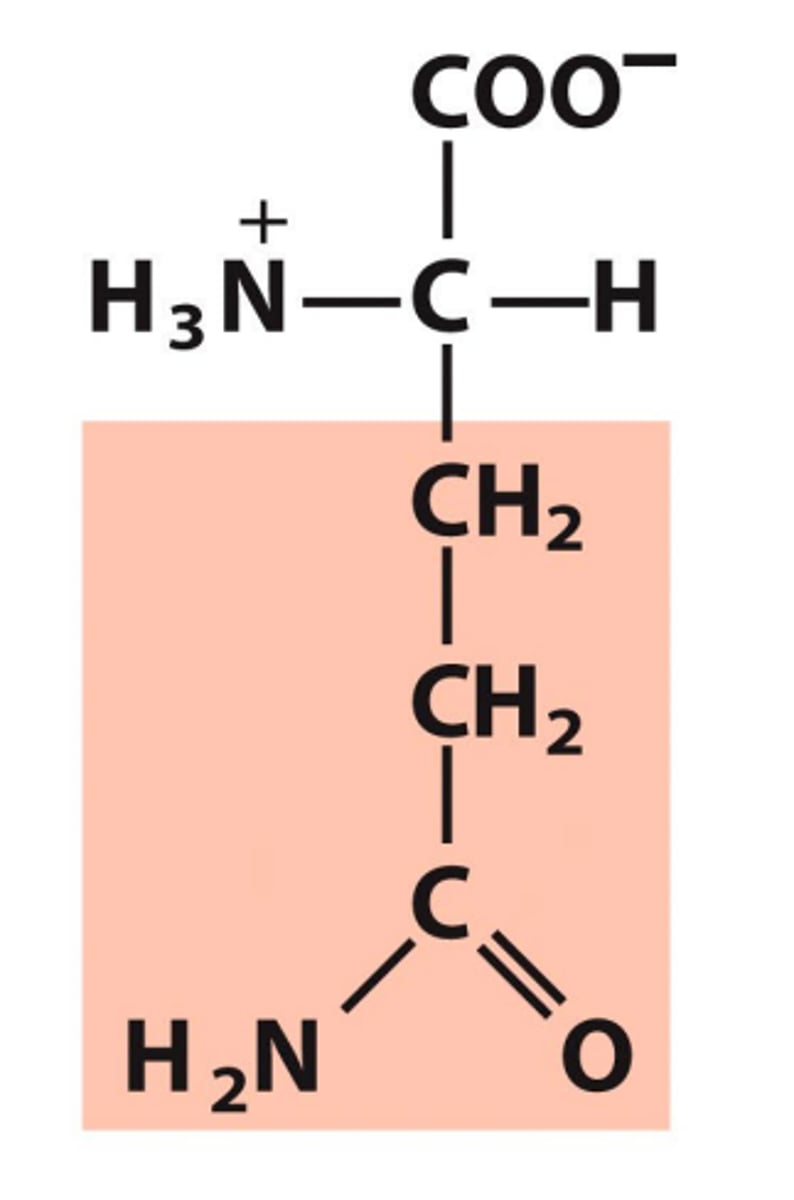
Asparagine, Asn, N
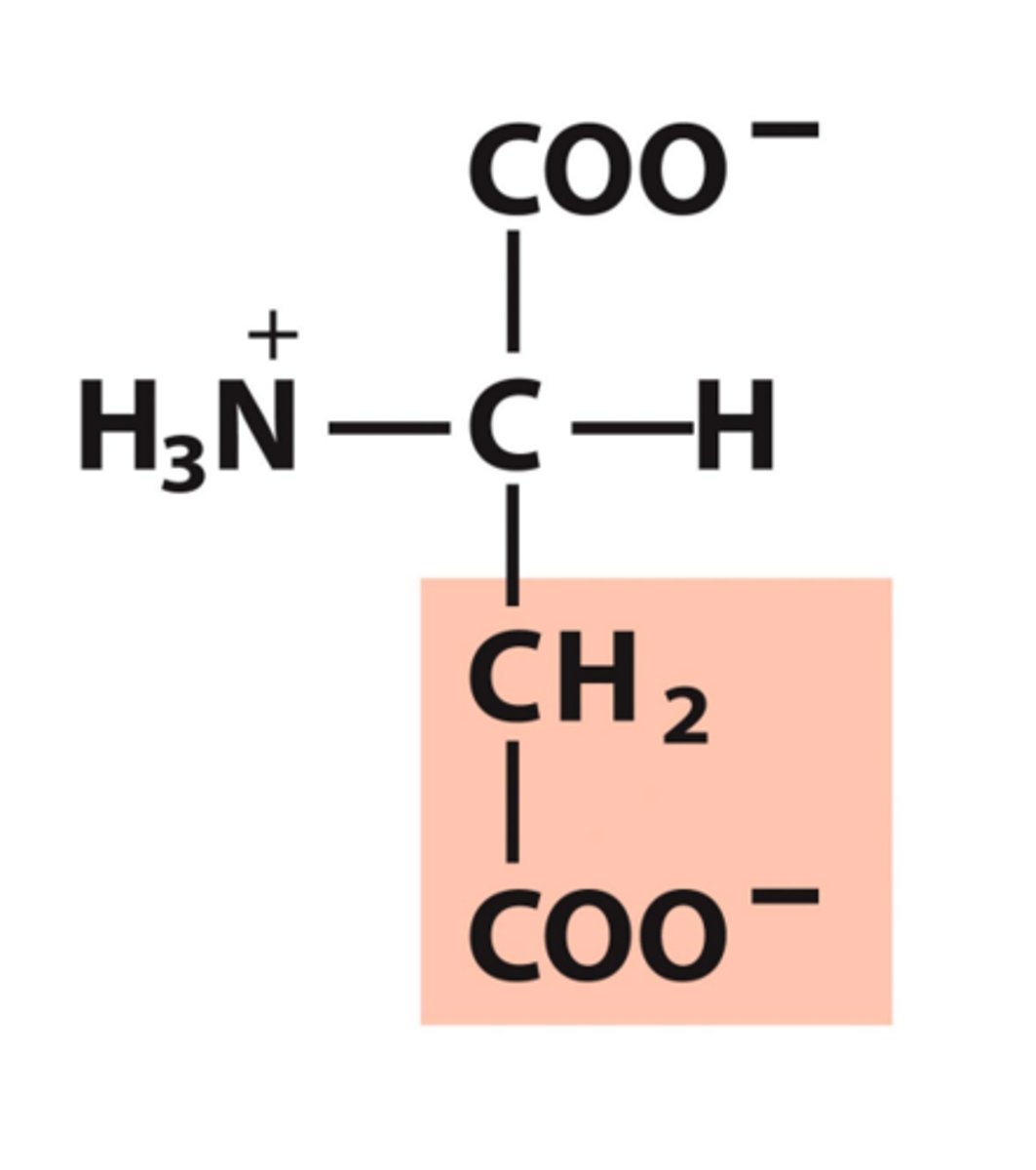
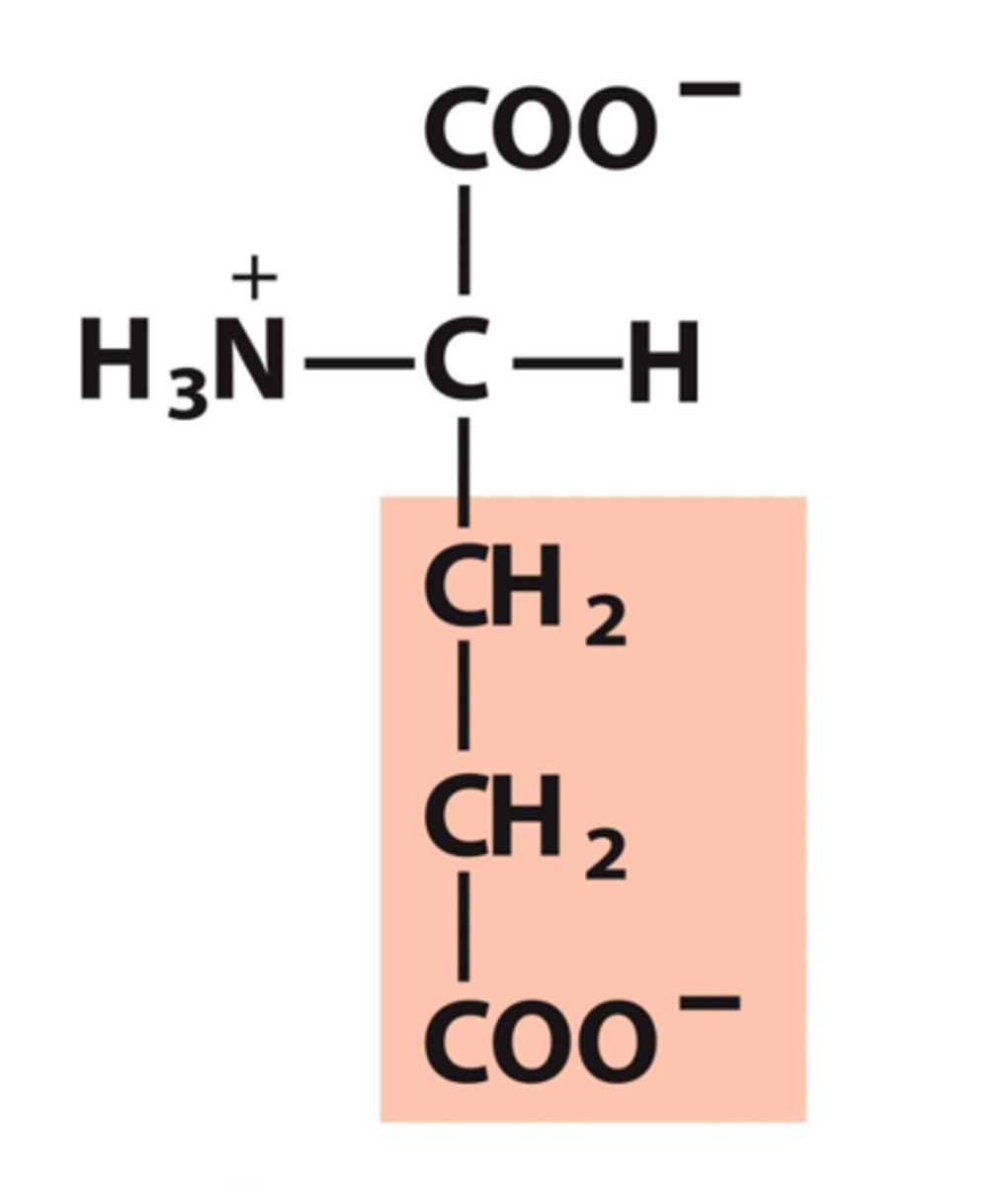
Aspartate, Asp, D
Cysteine, Cys, C
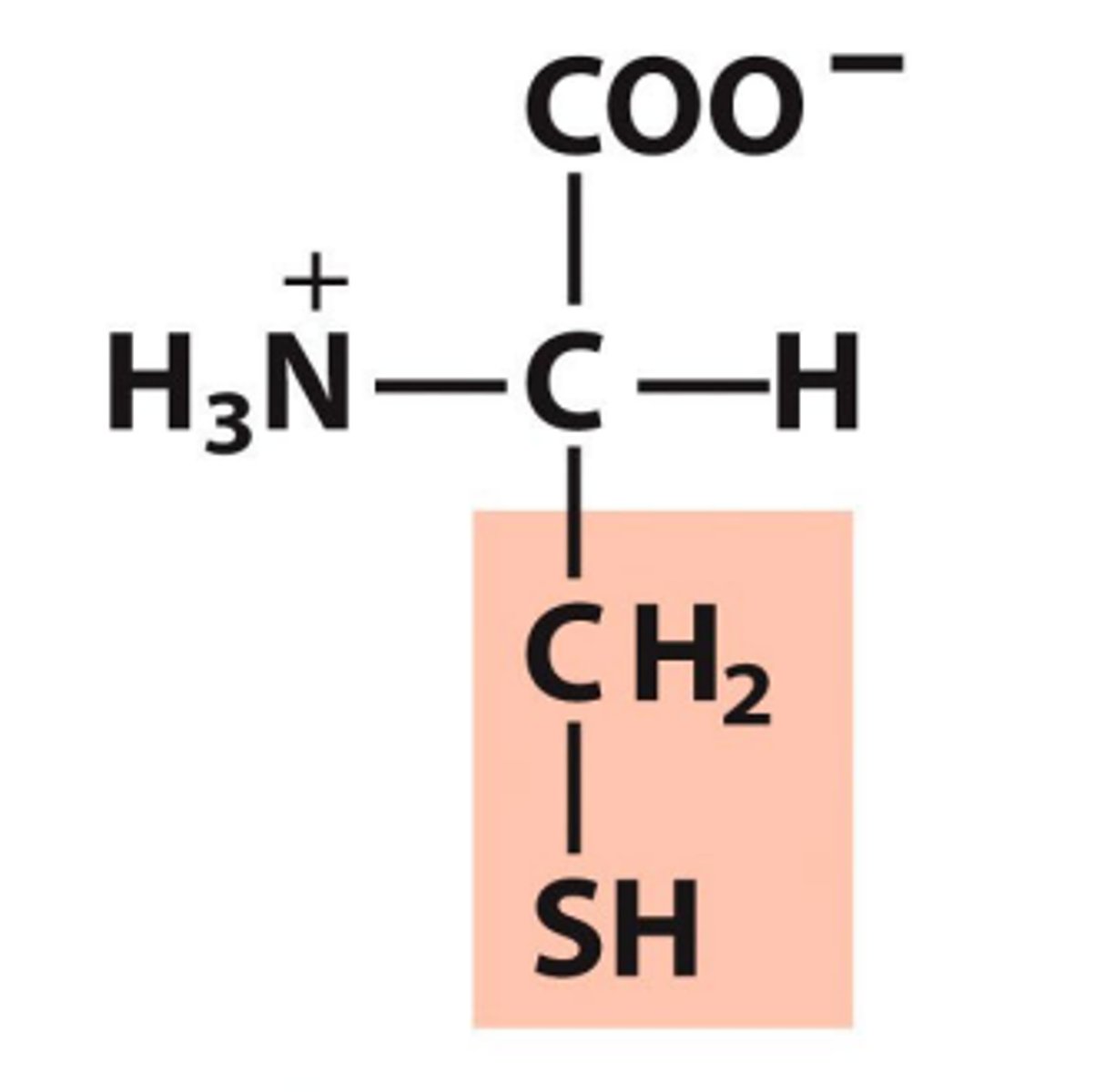
Glutamate, Glu, E
Glutamine, Gln, Q
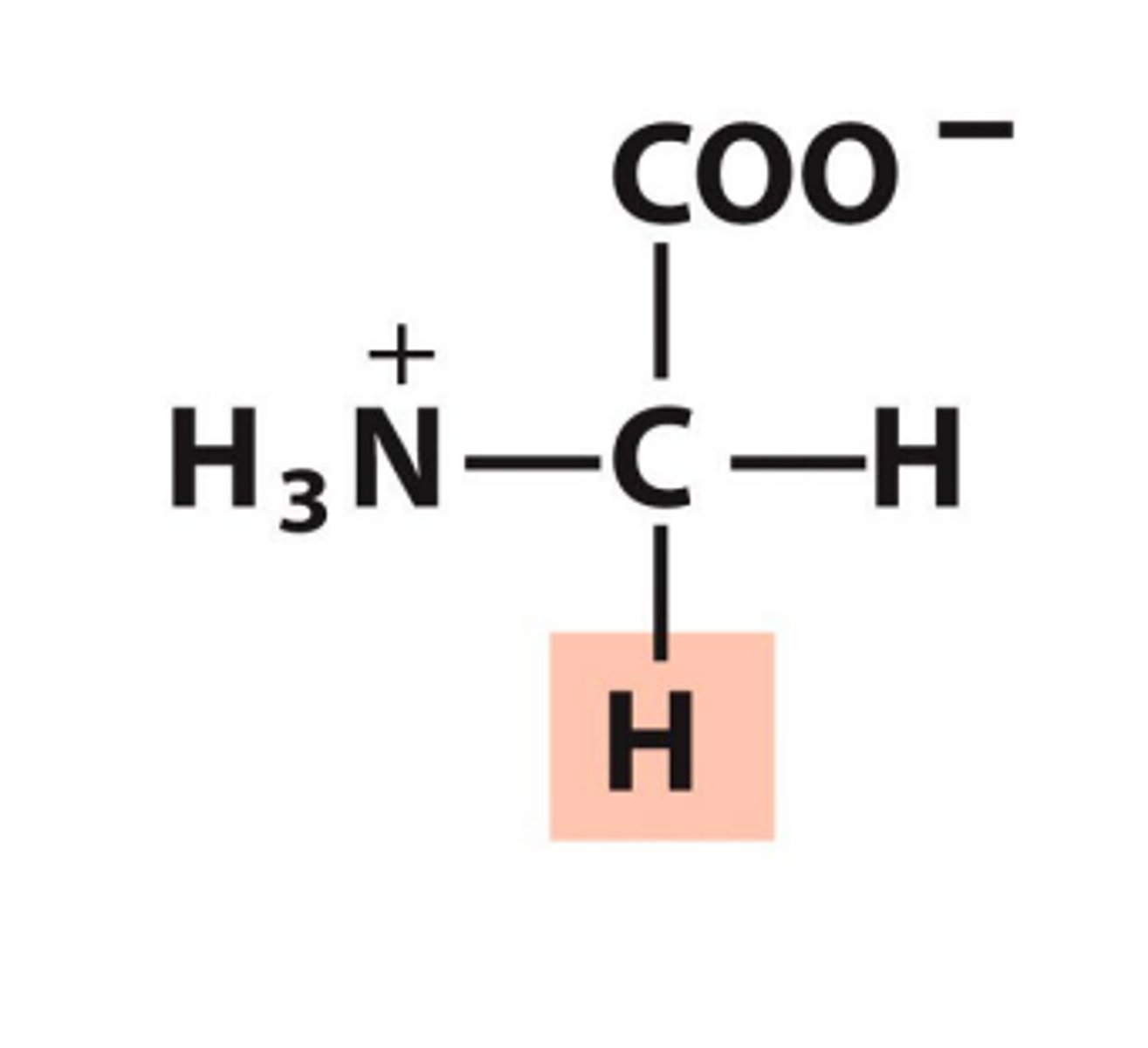
Glycine, Gly, G
Histidine, His, H
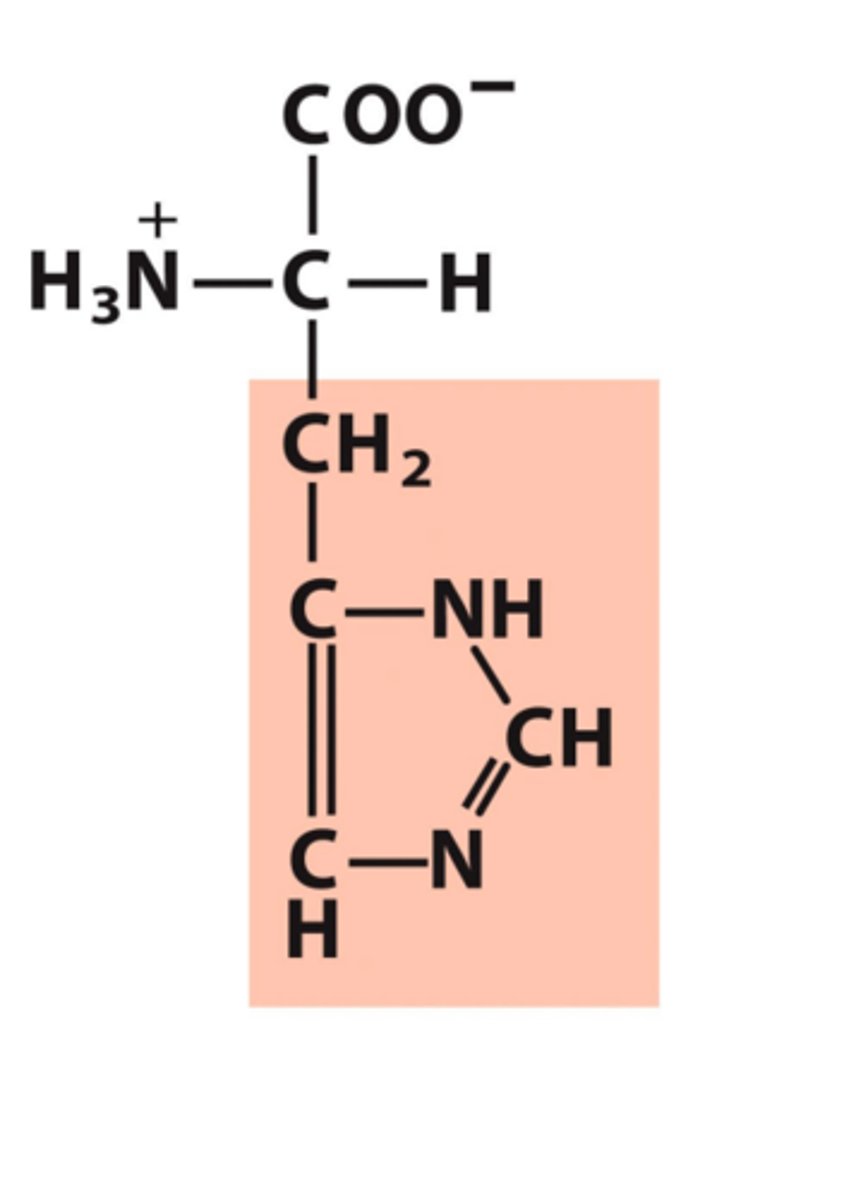
Isoleucine, Ile, I
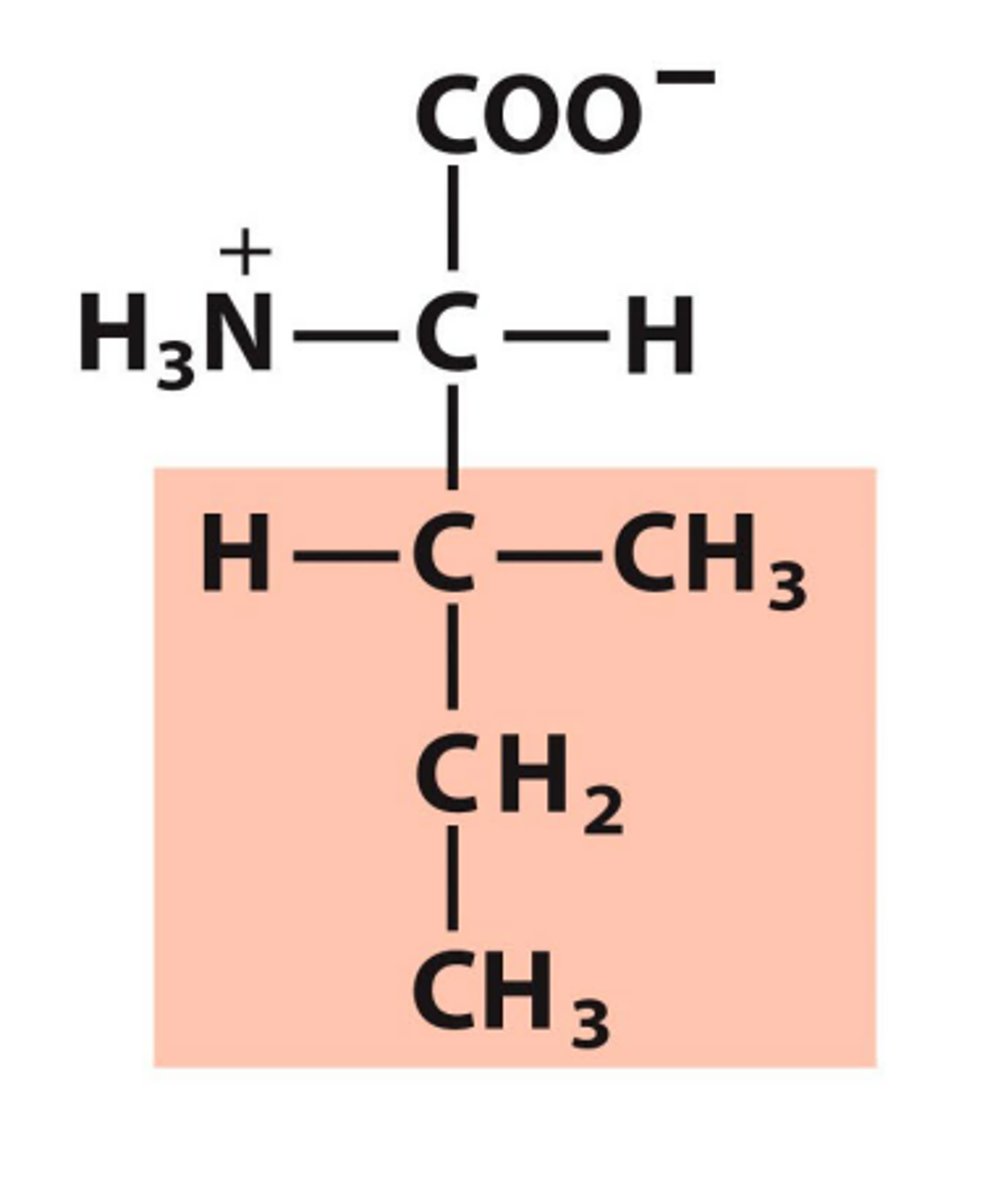
Leucine, Leu, L
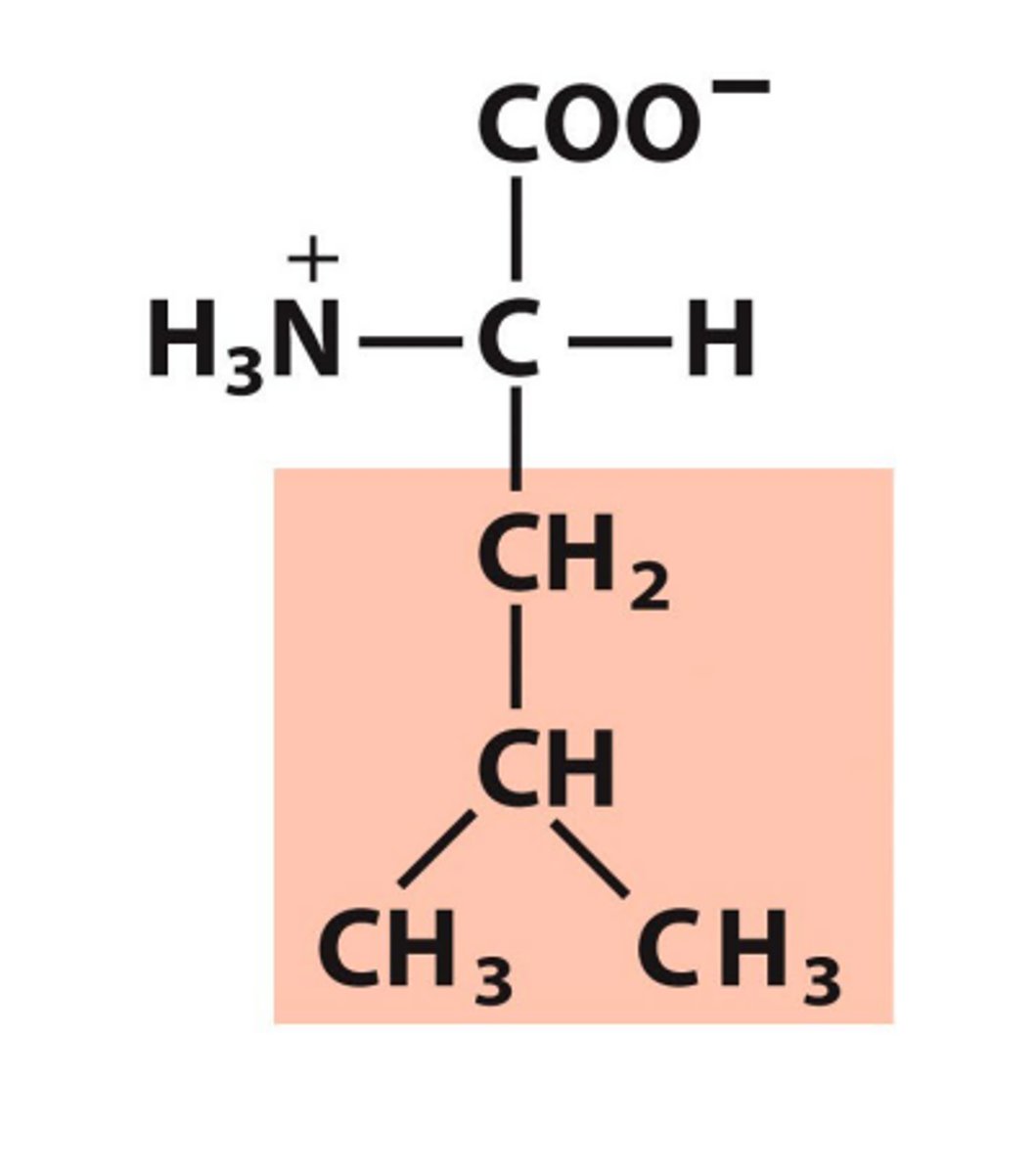
Lysine, Lys, K
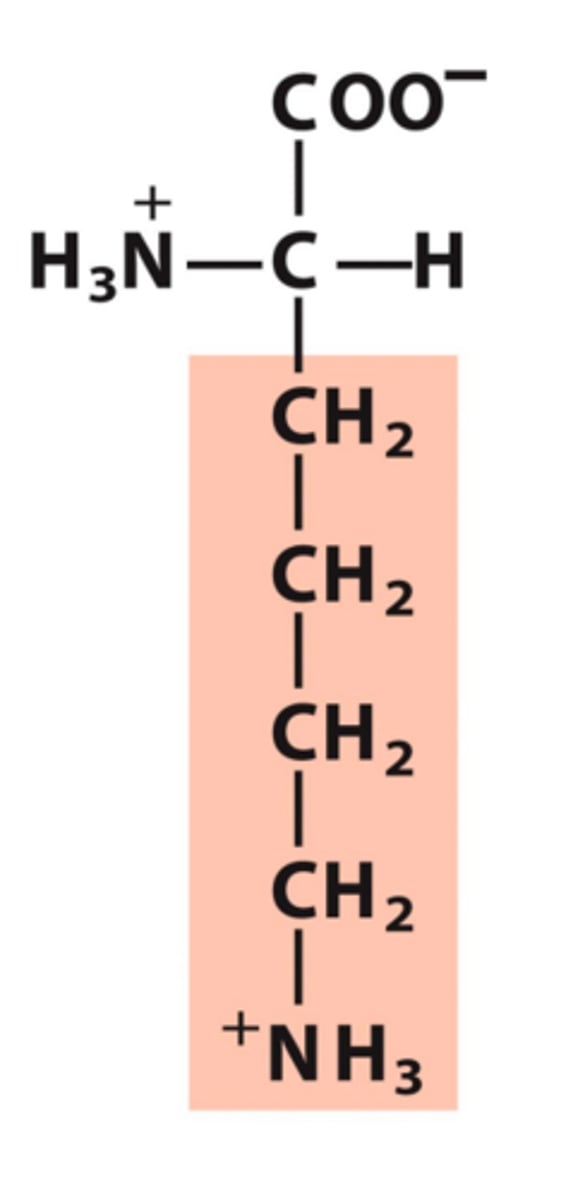
Methionine, Met, M
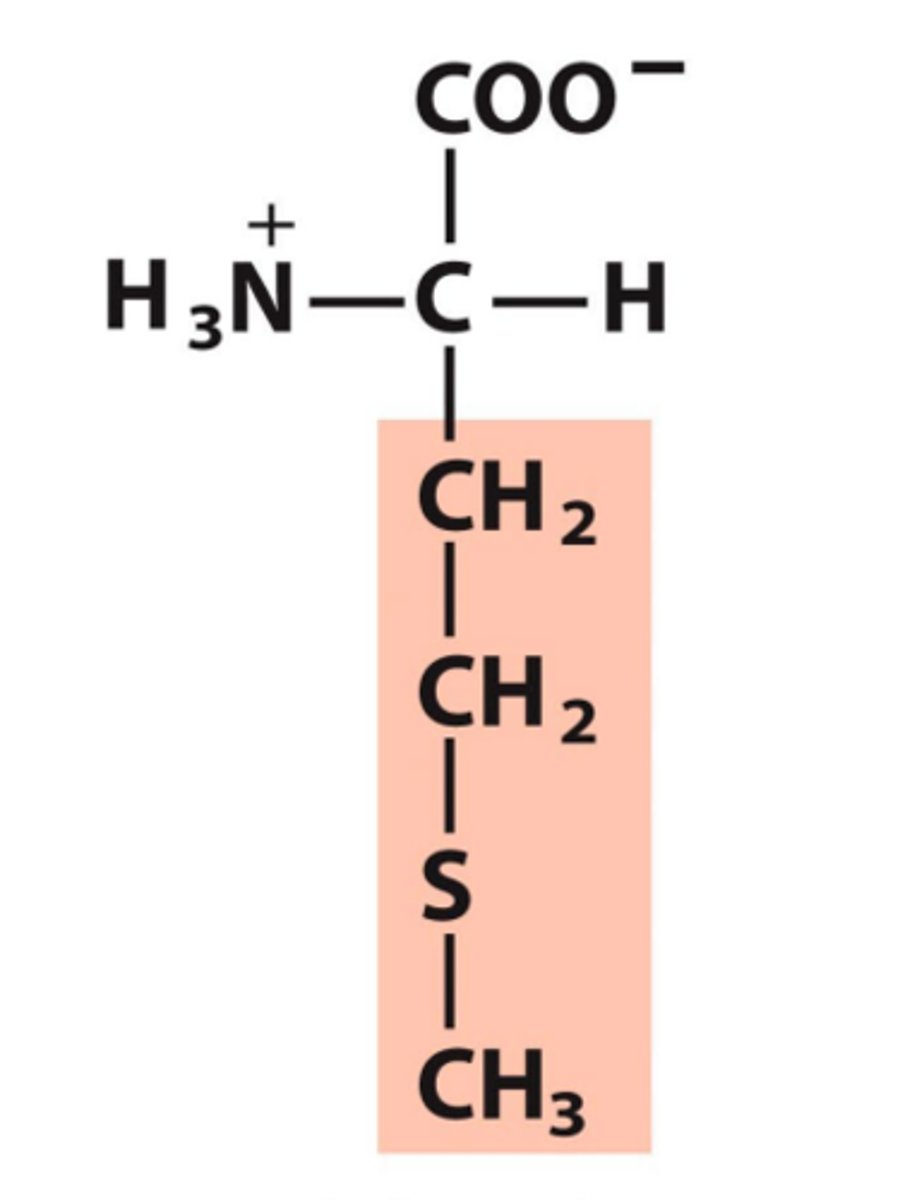
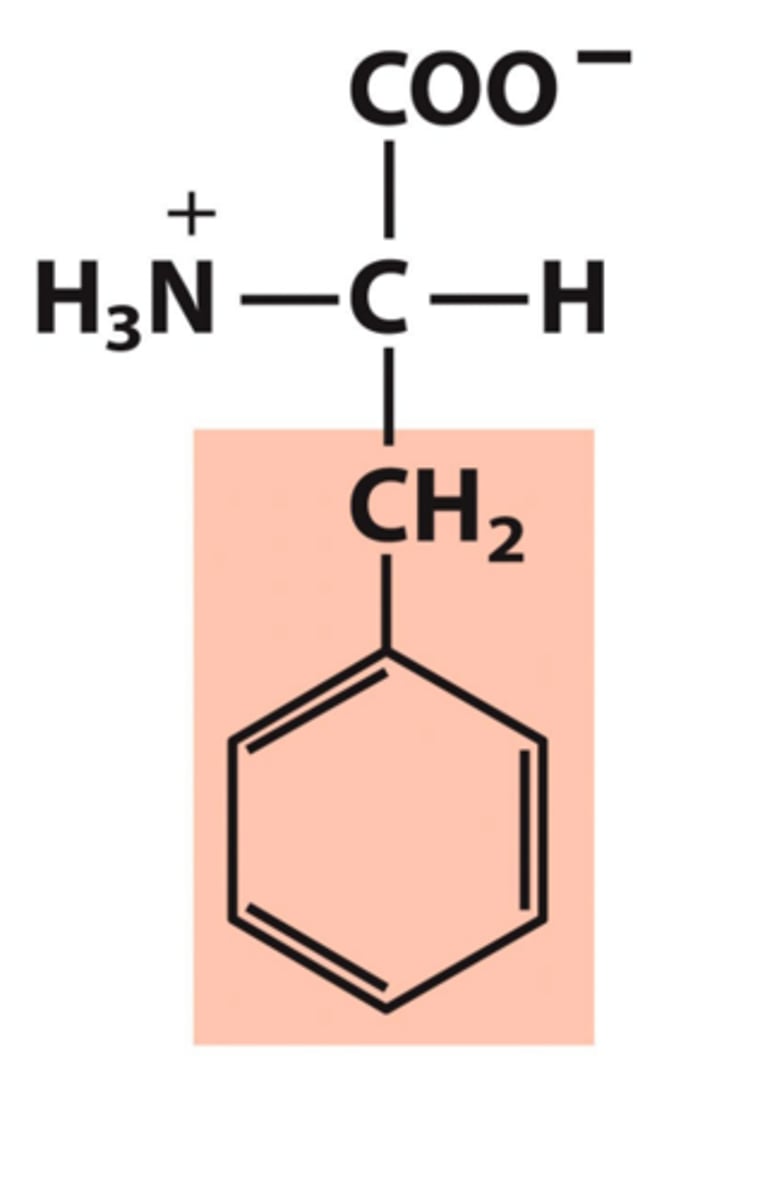
Phenylalanine, Phe, F
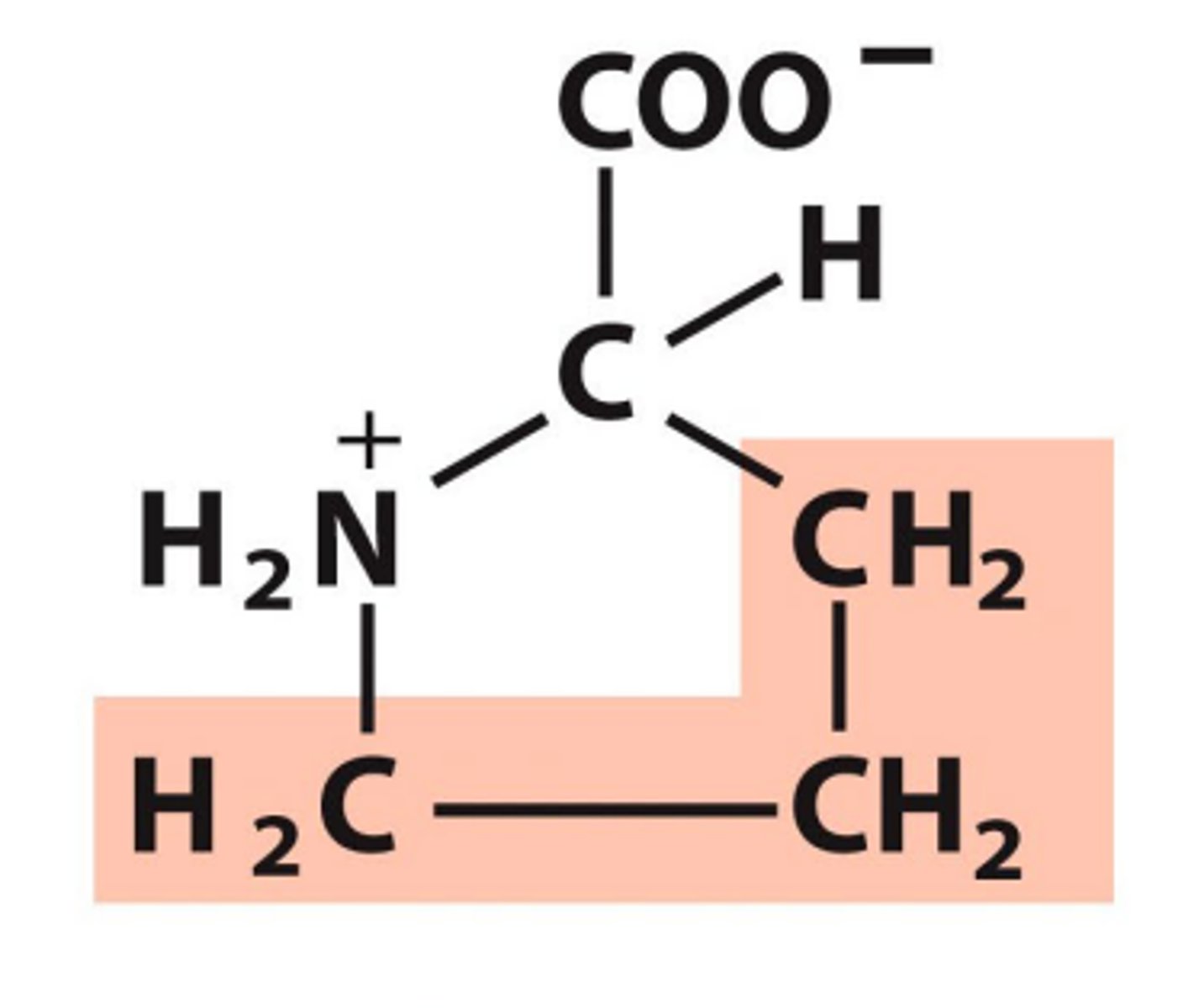
Proline, Pro, P
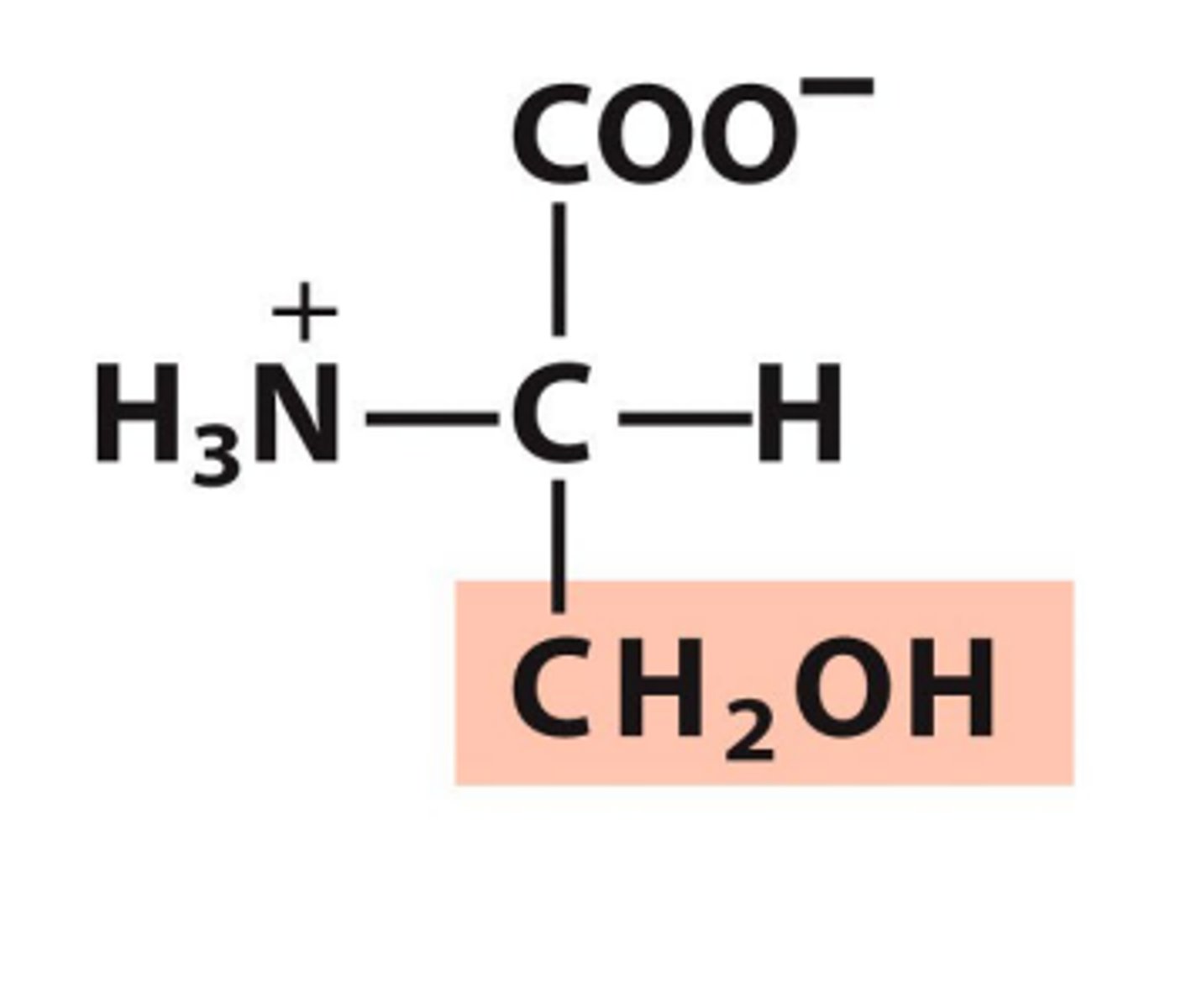
Serine, Ser, S
Threonine, Thr, T
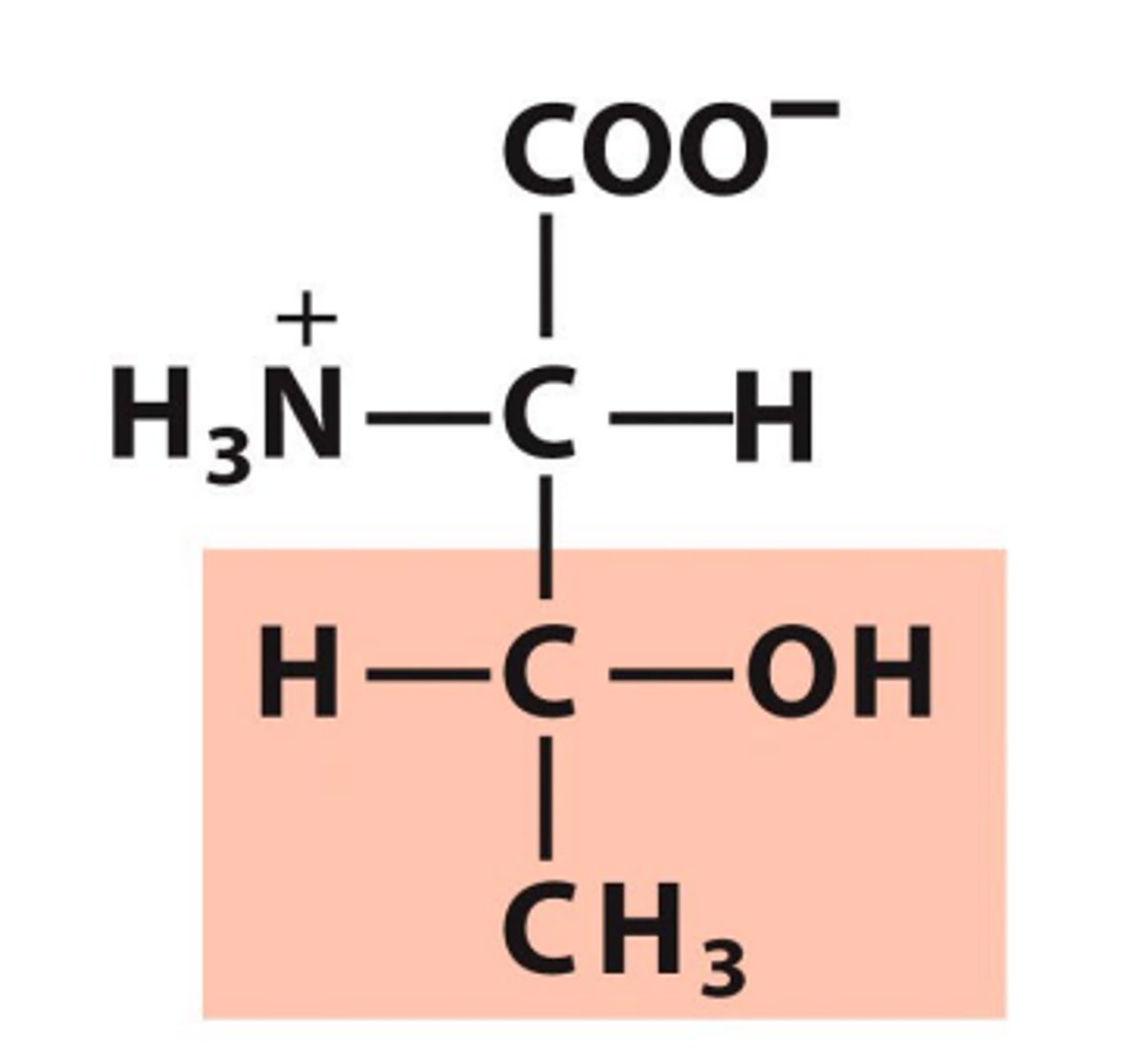
Tryptophan, Trp, W
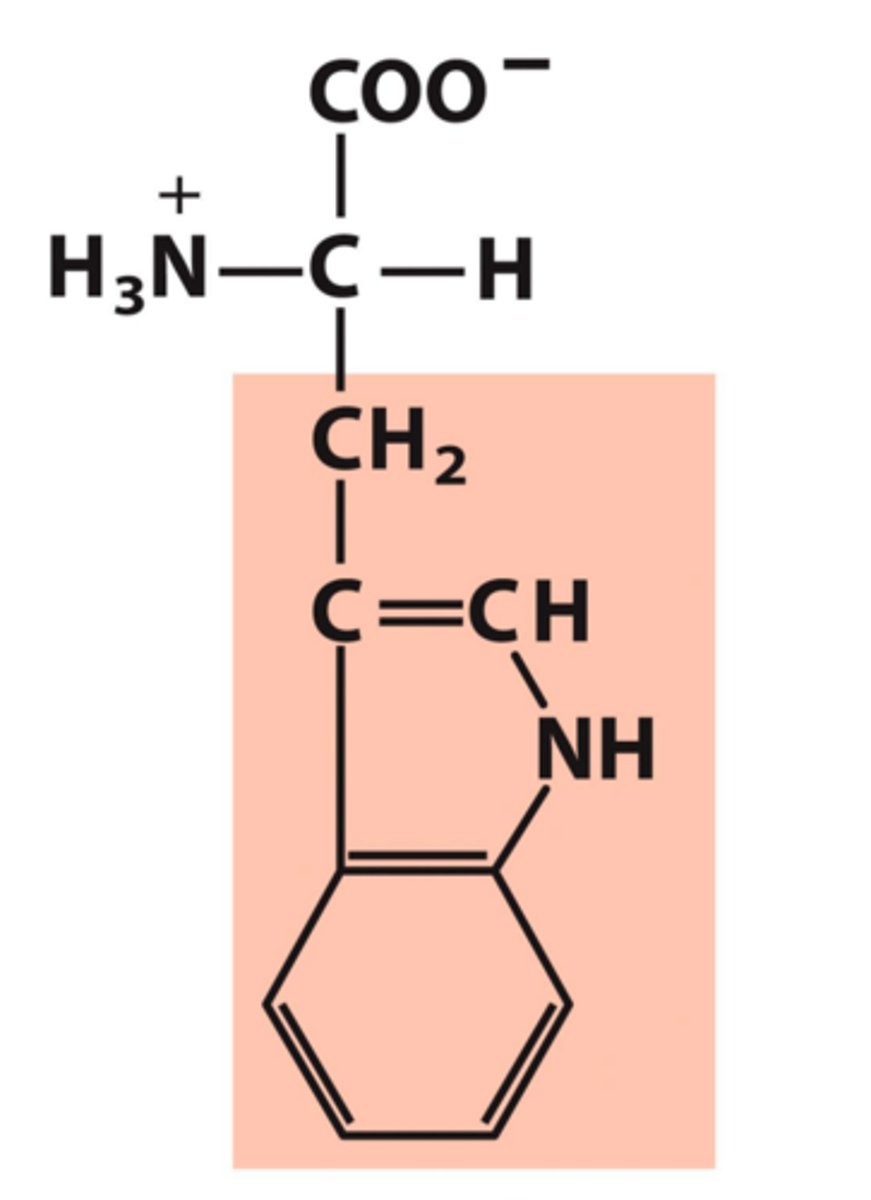
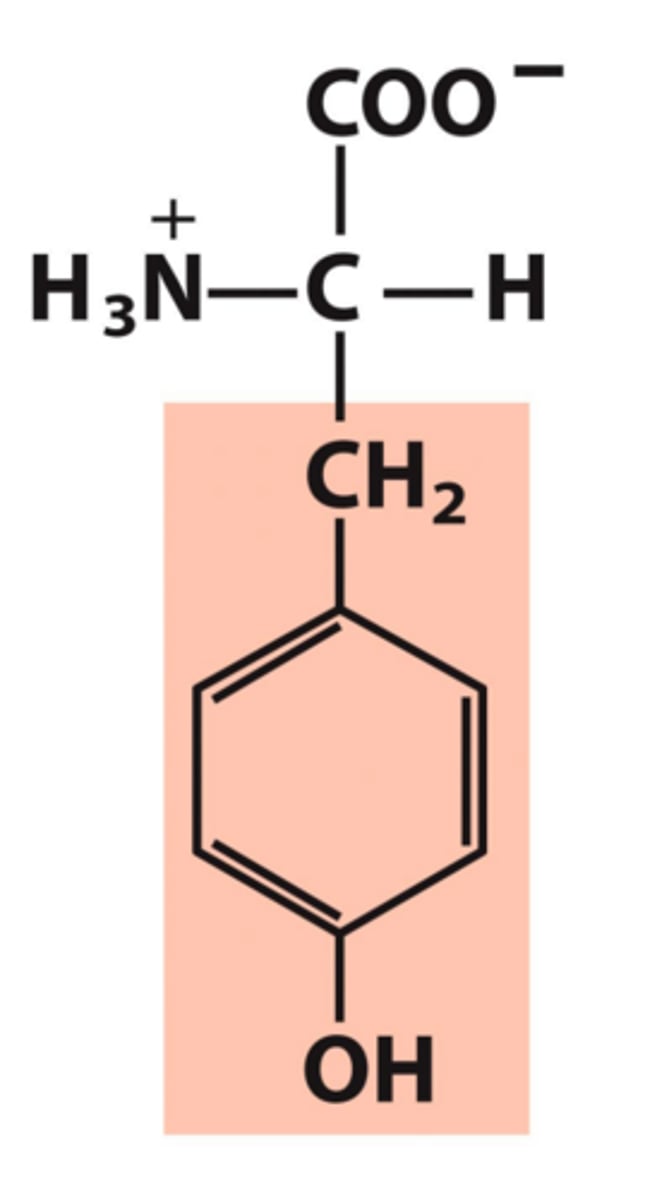
Tyrosine, Tyr, Y
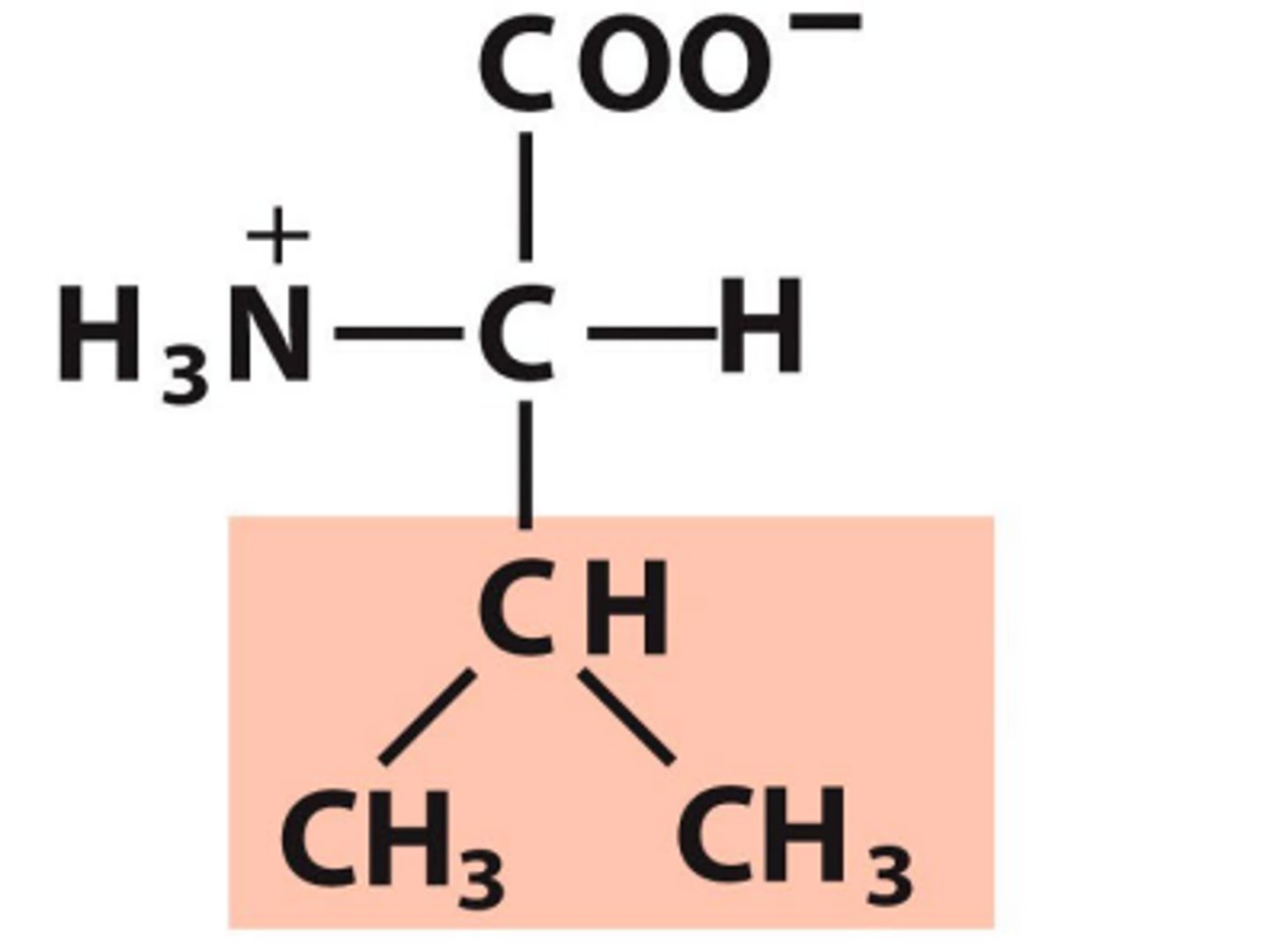
Valine, Val, V
glucose
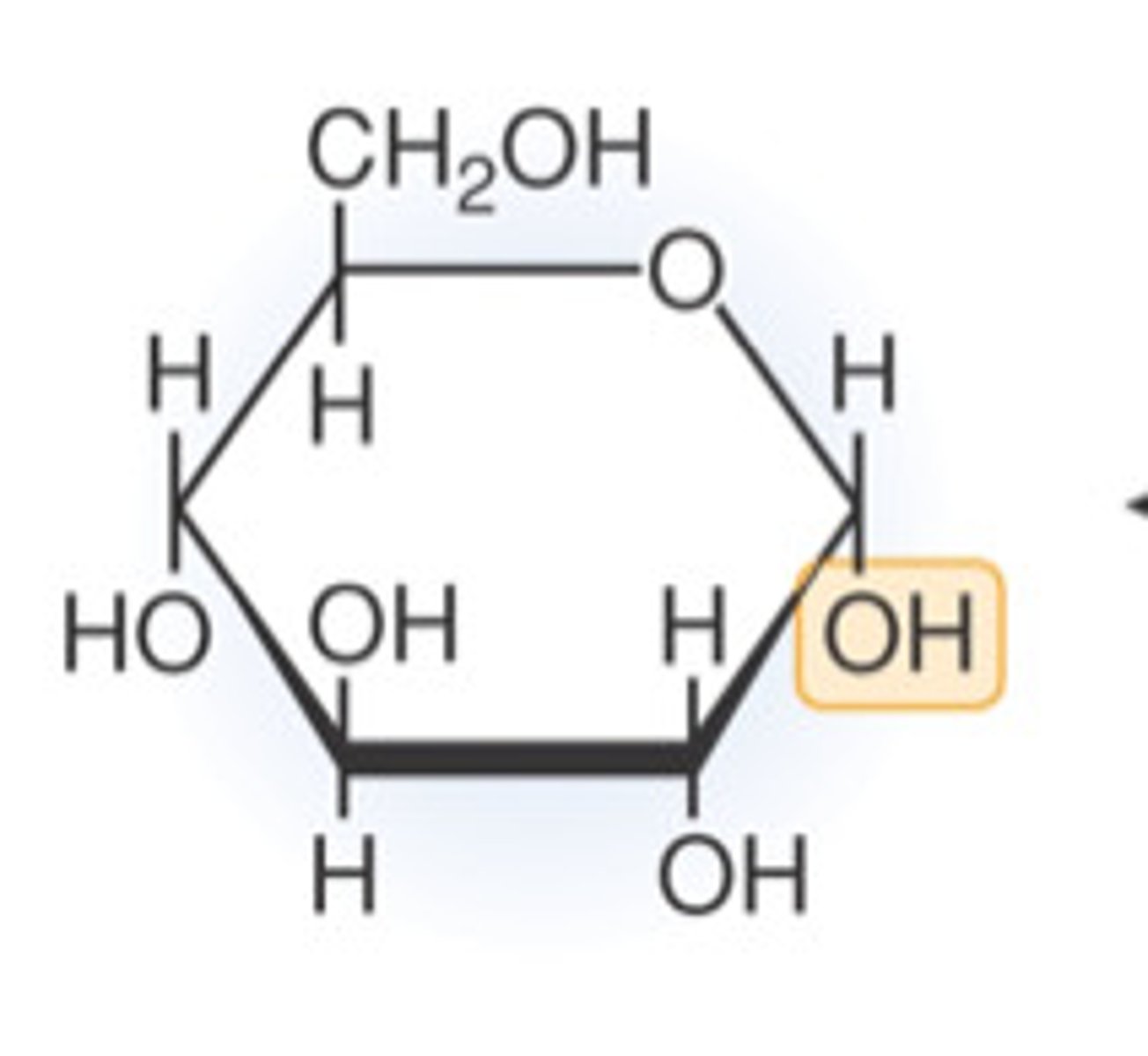
glucose-6-phosphate
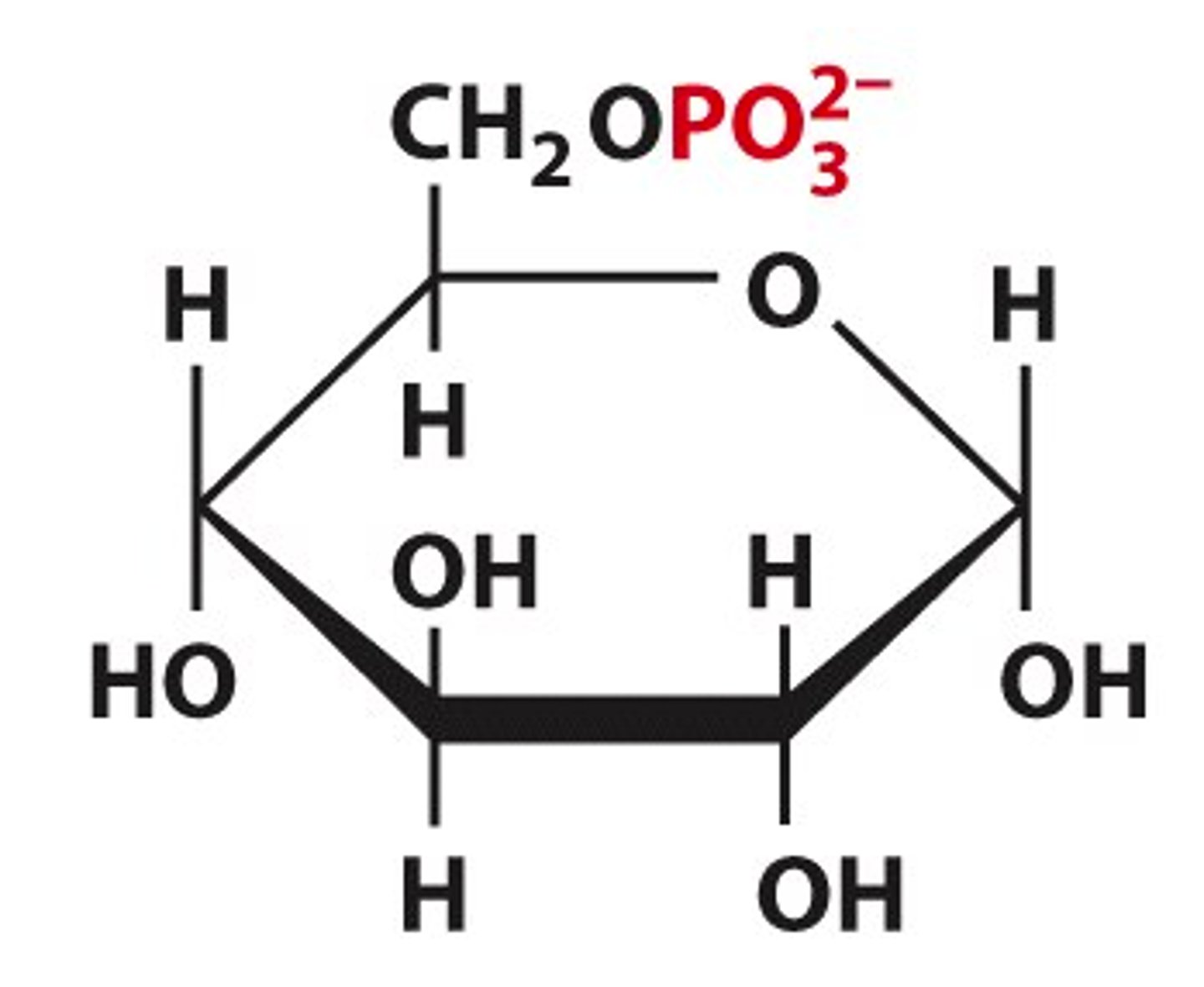
fructose-6-phosphate
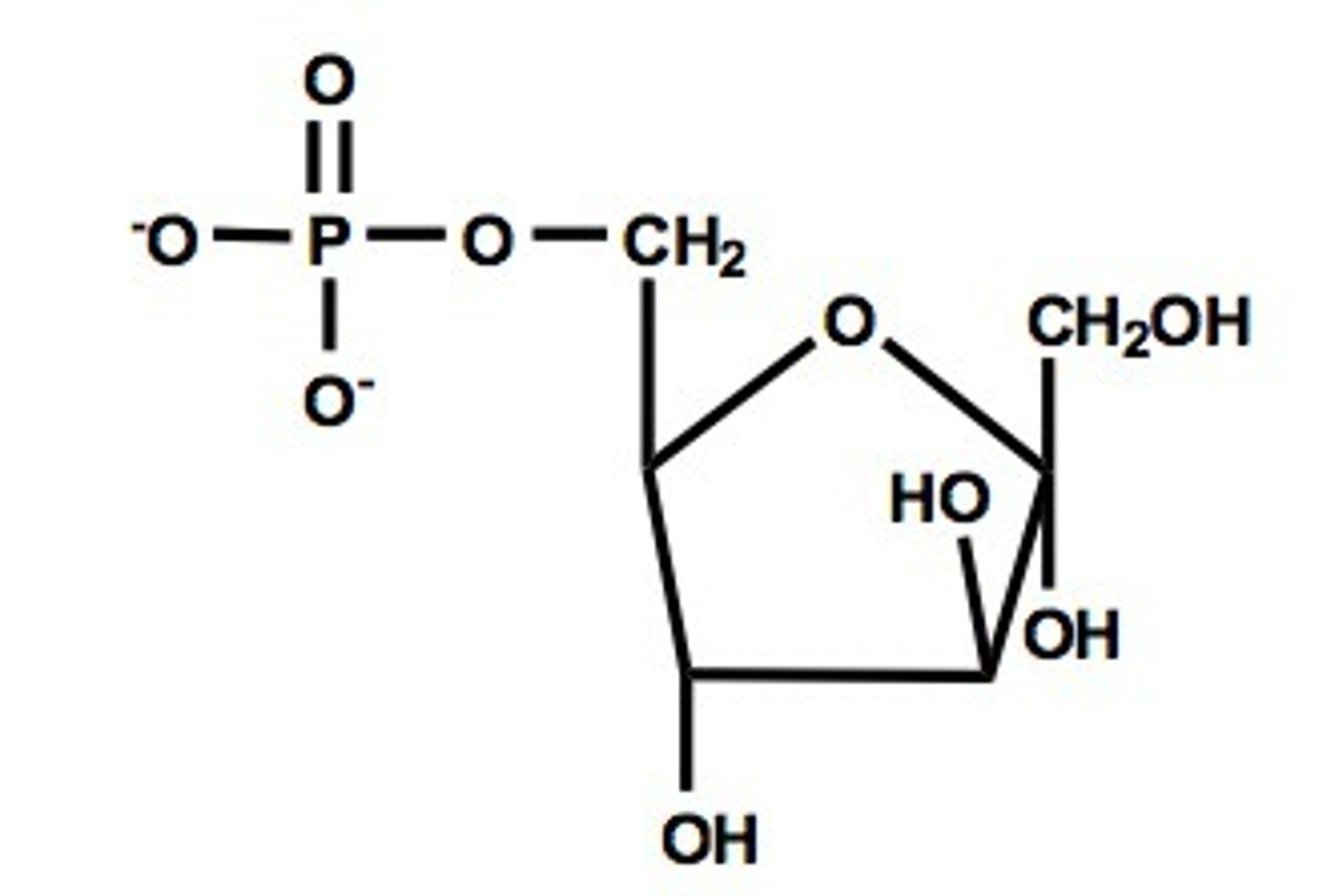
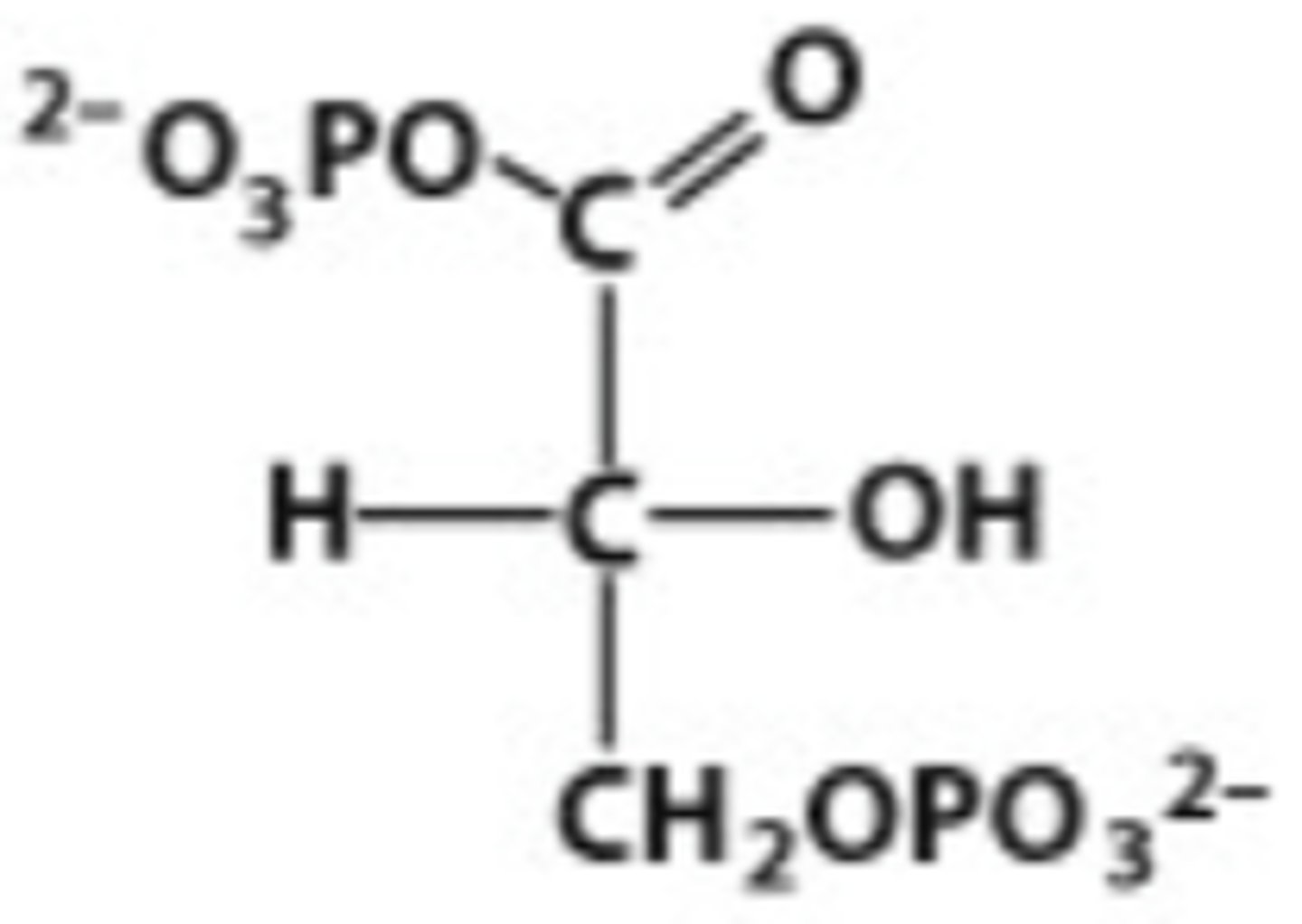
fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
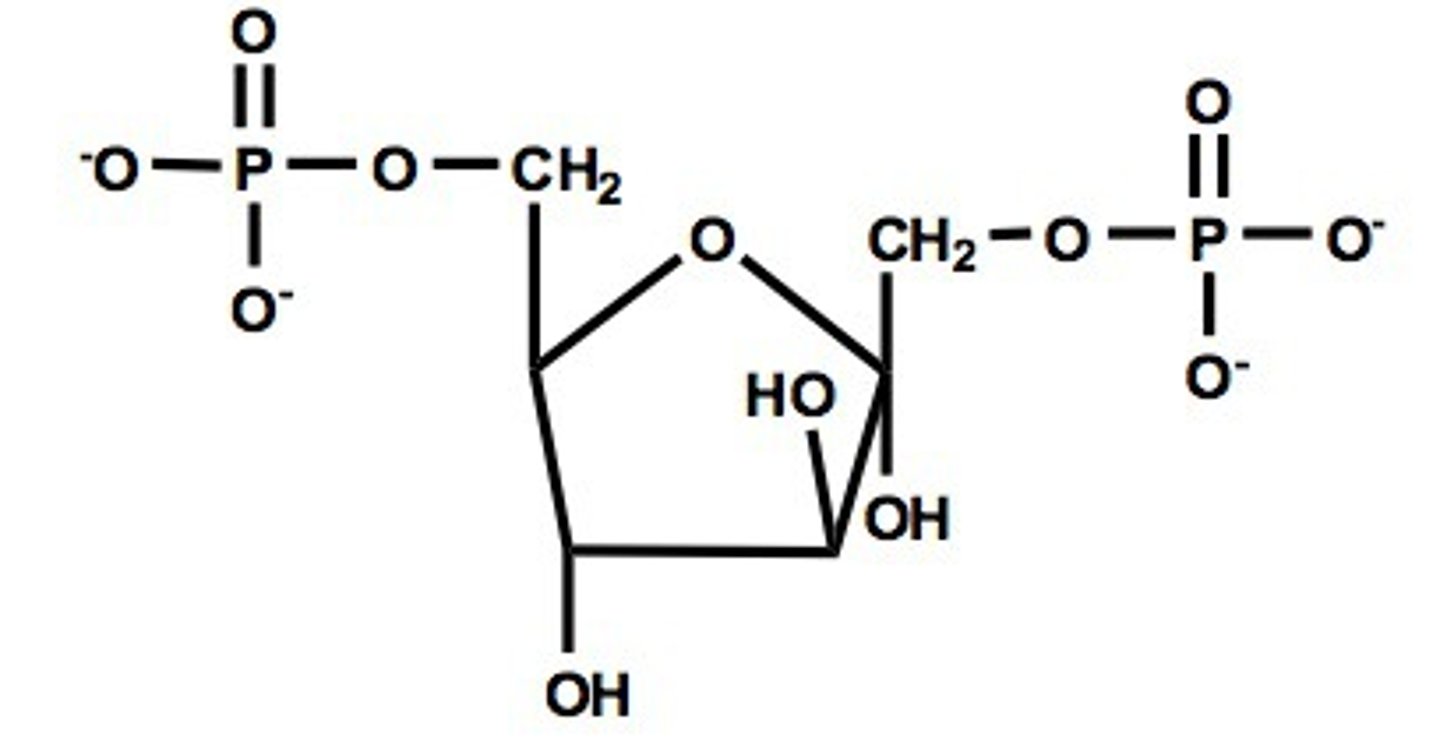
DHAP
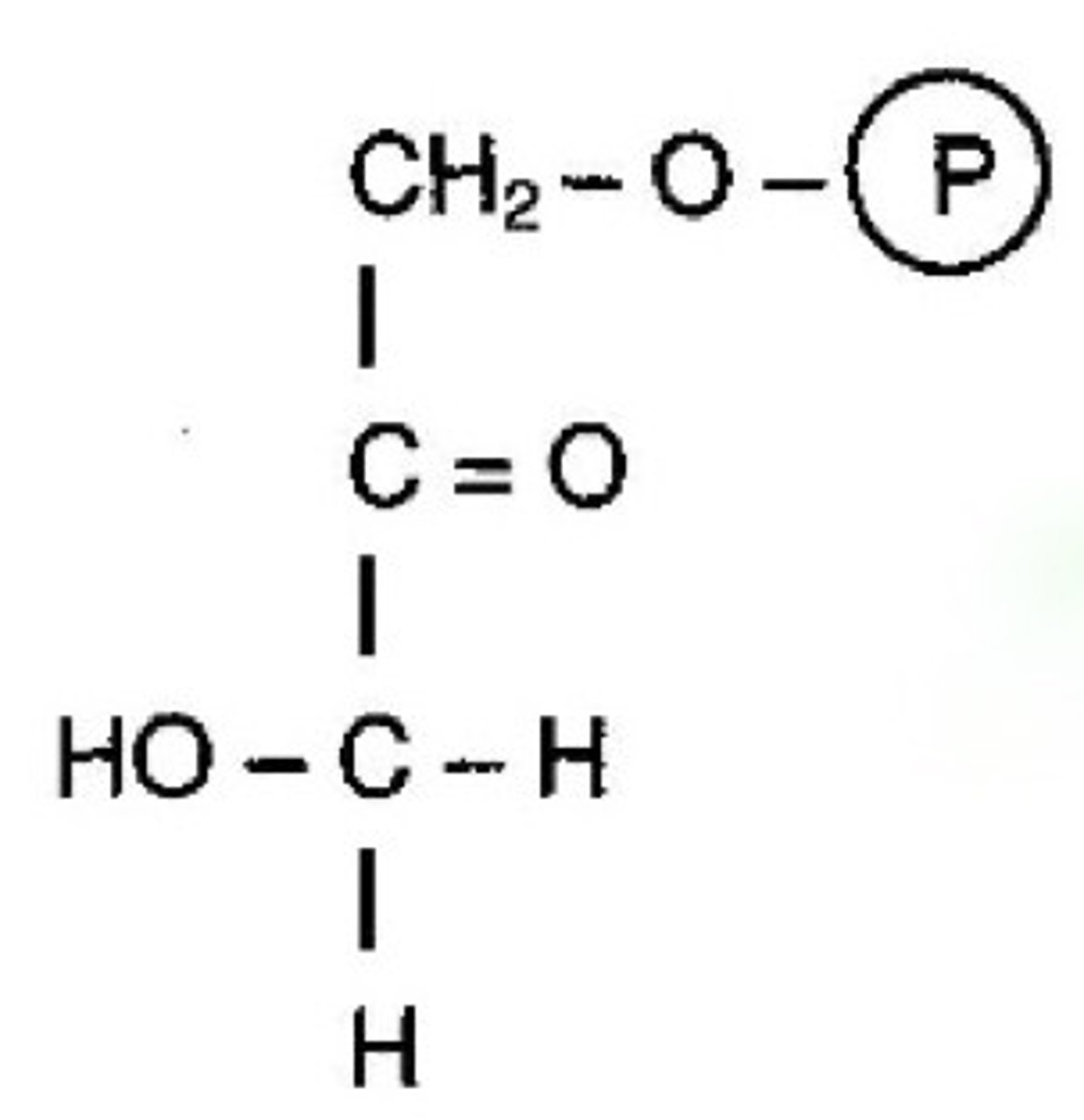
G-3-P
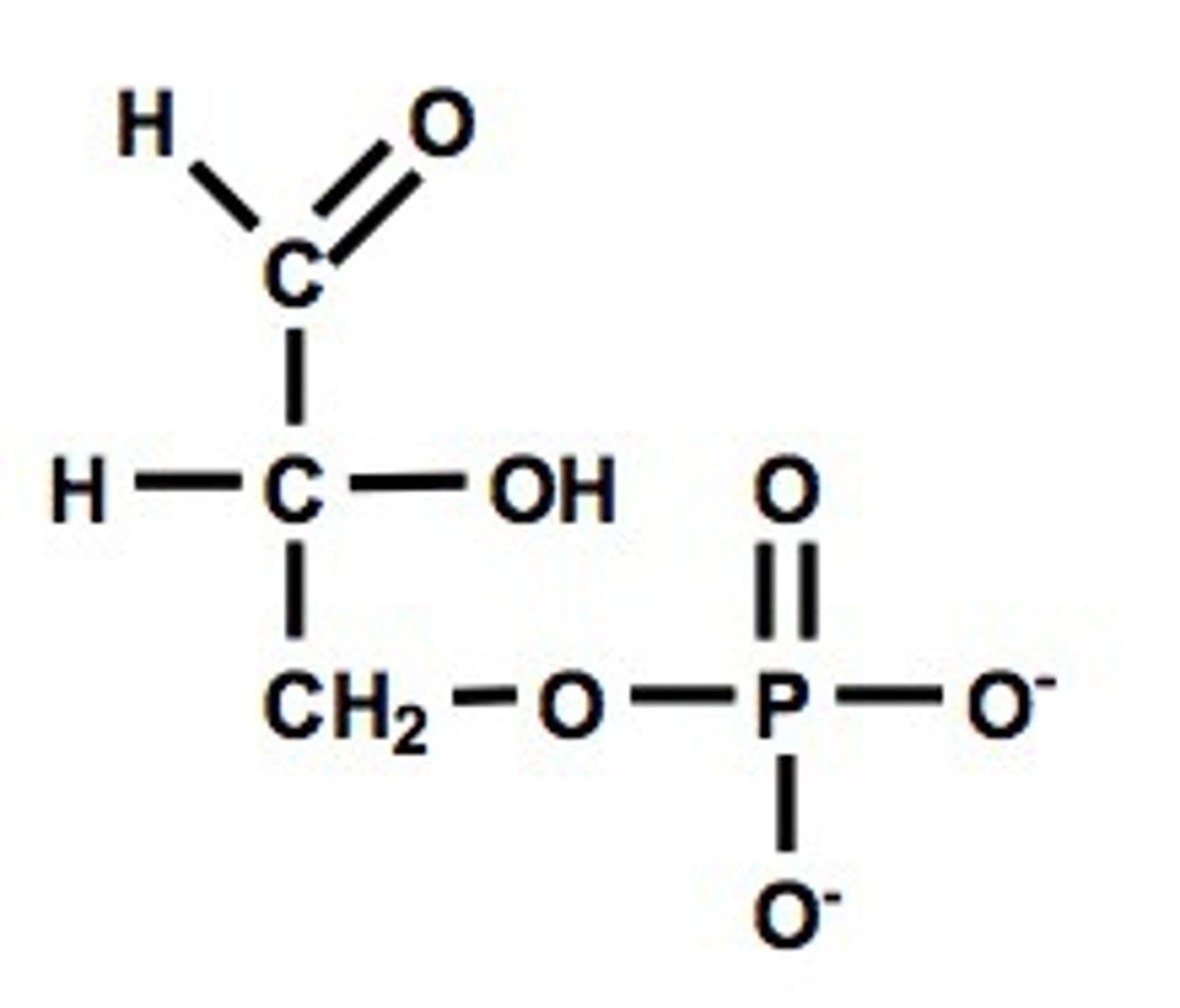
1,3-BPG
3-PG
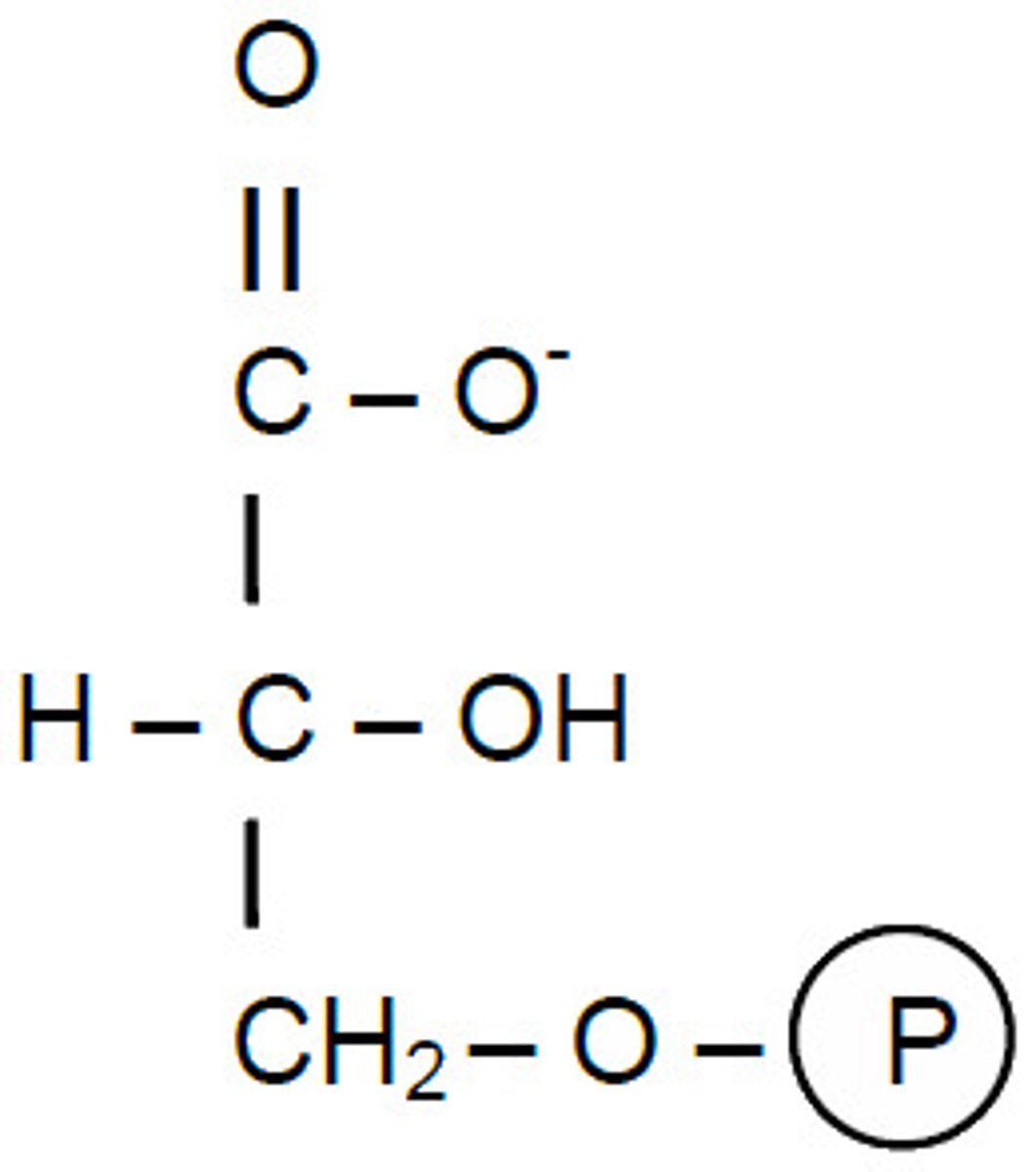
2-PG
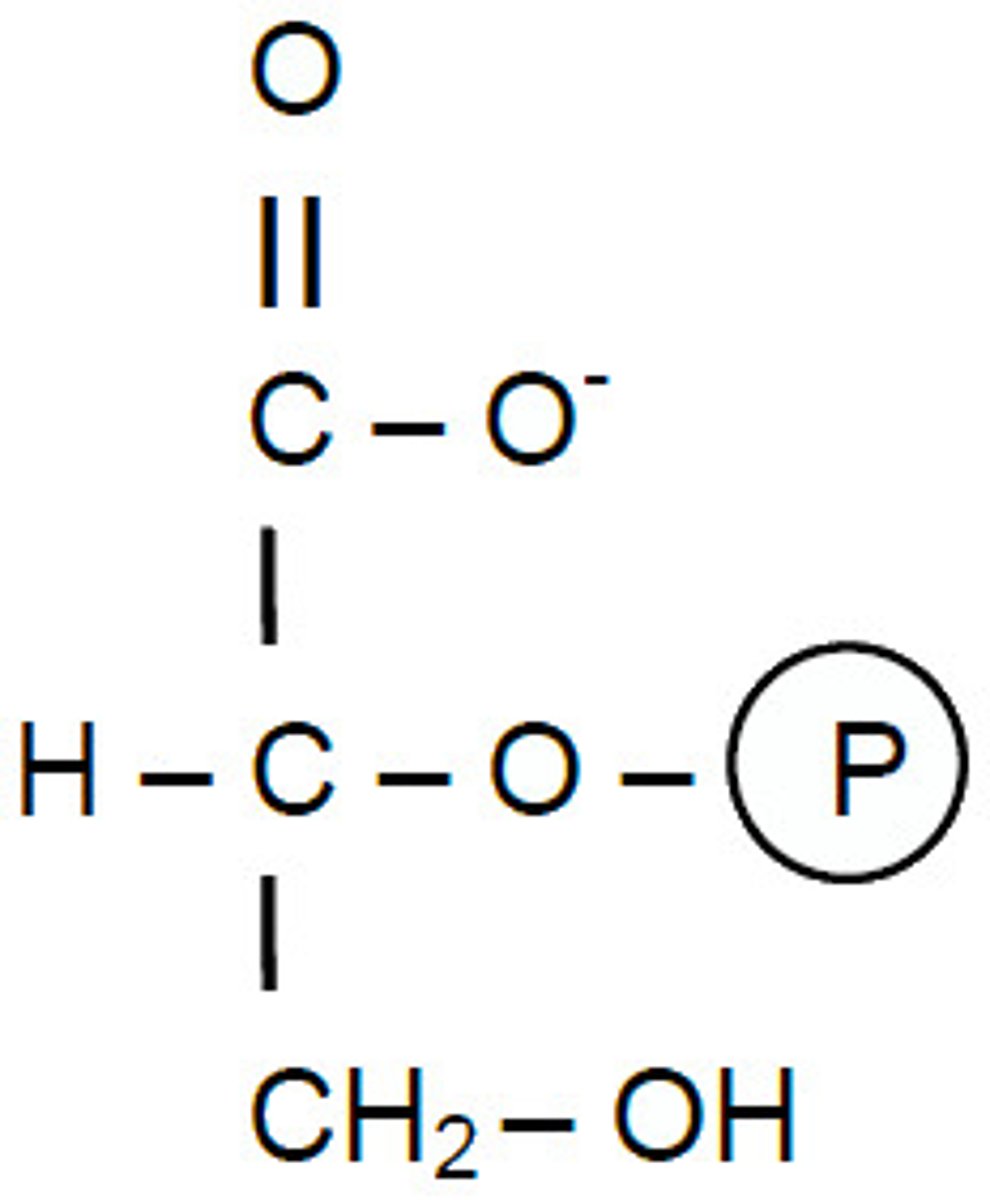
PEP
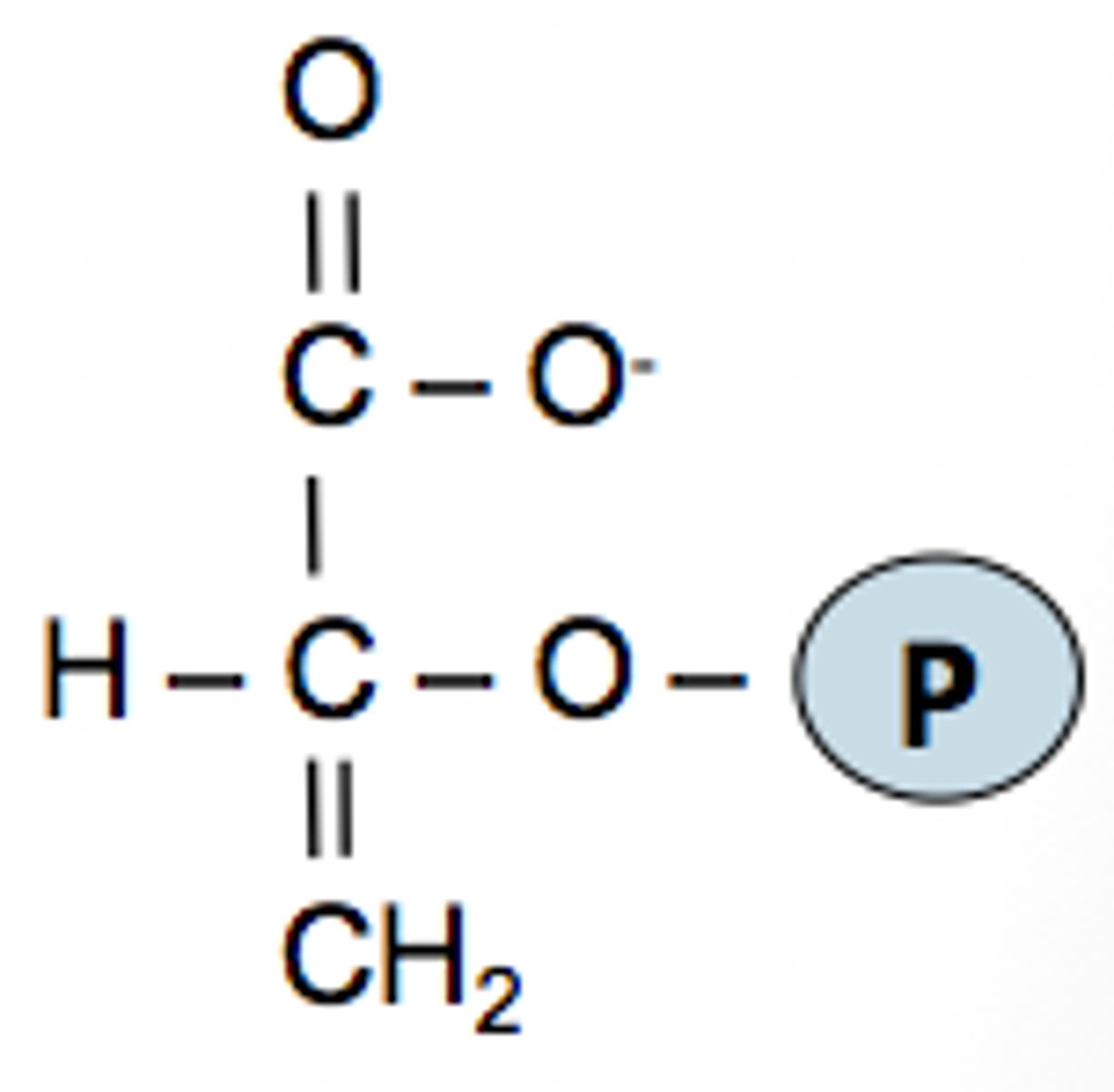
pyruvate
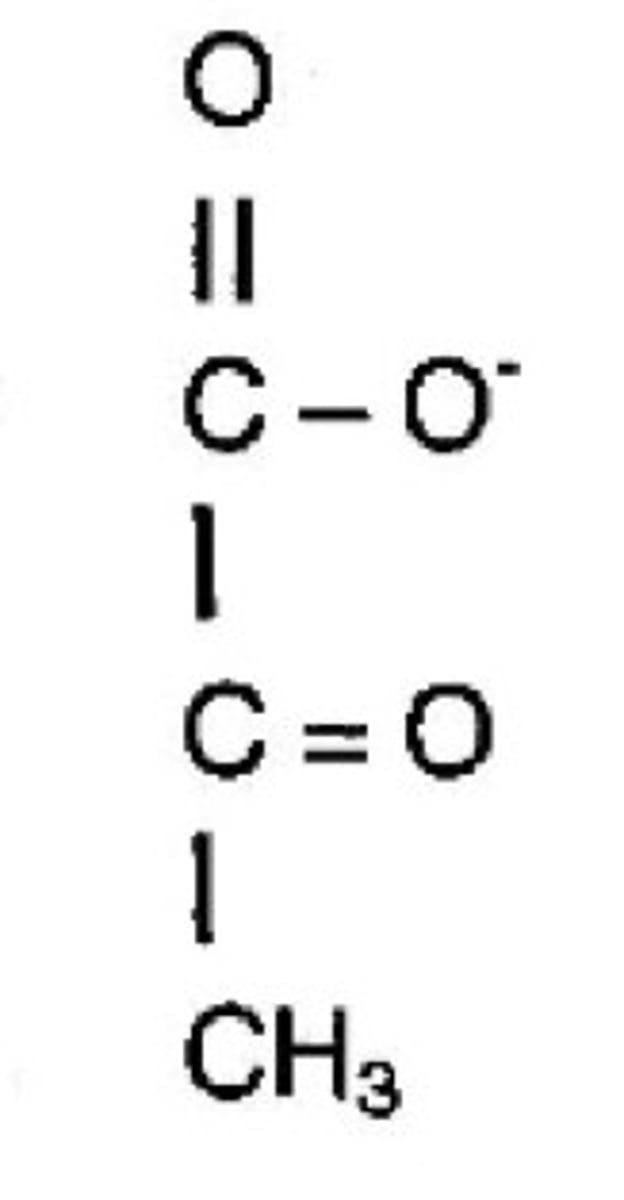
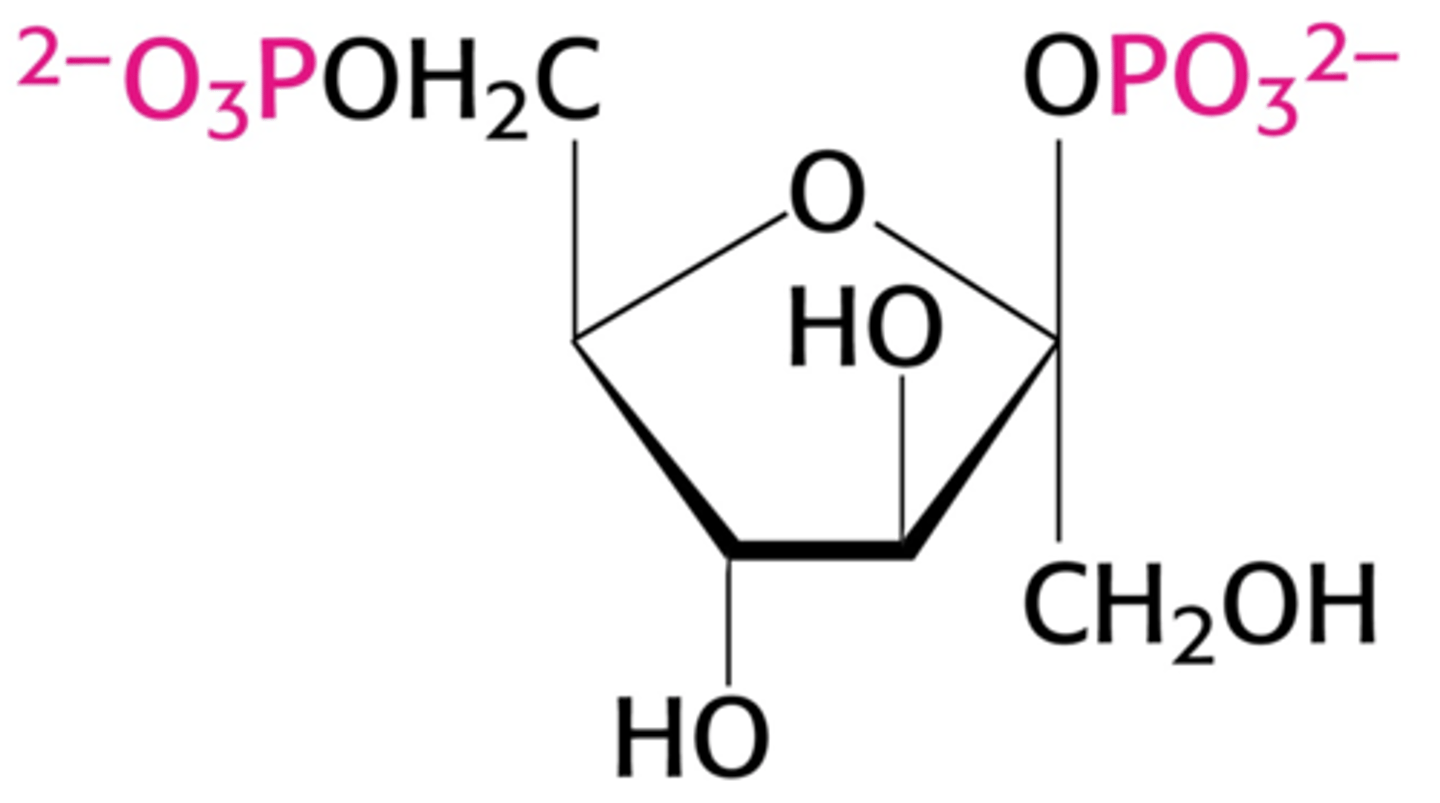
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
acetyl-CoA
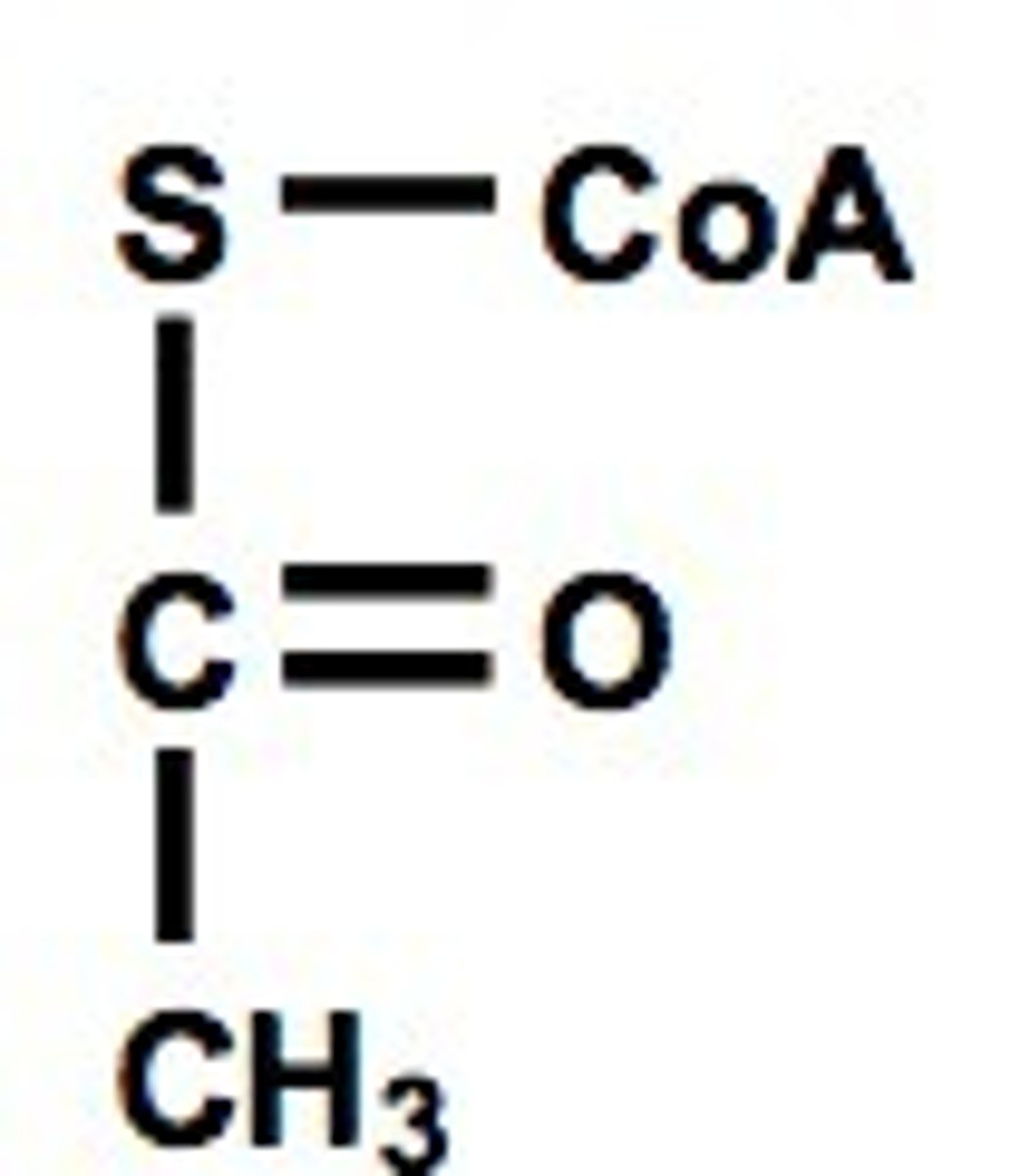
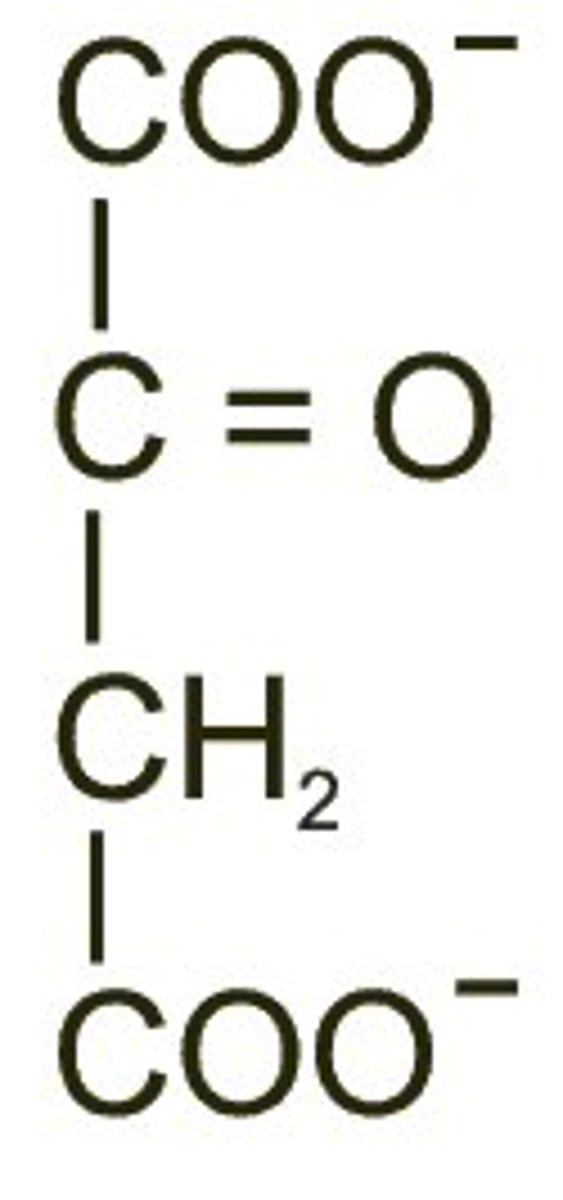
oxaloacetate
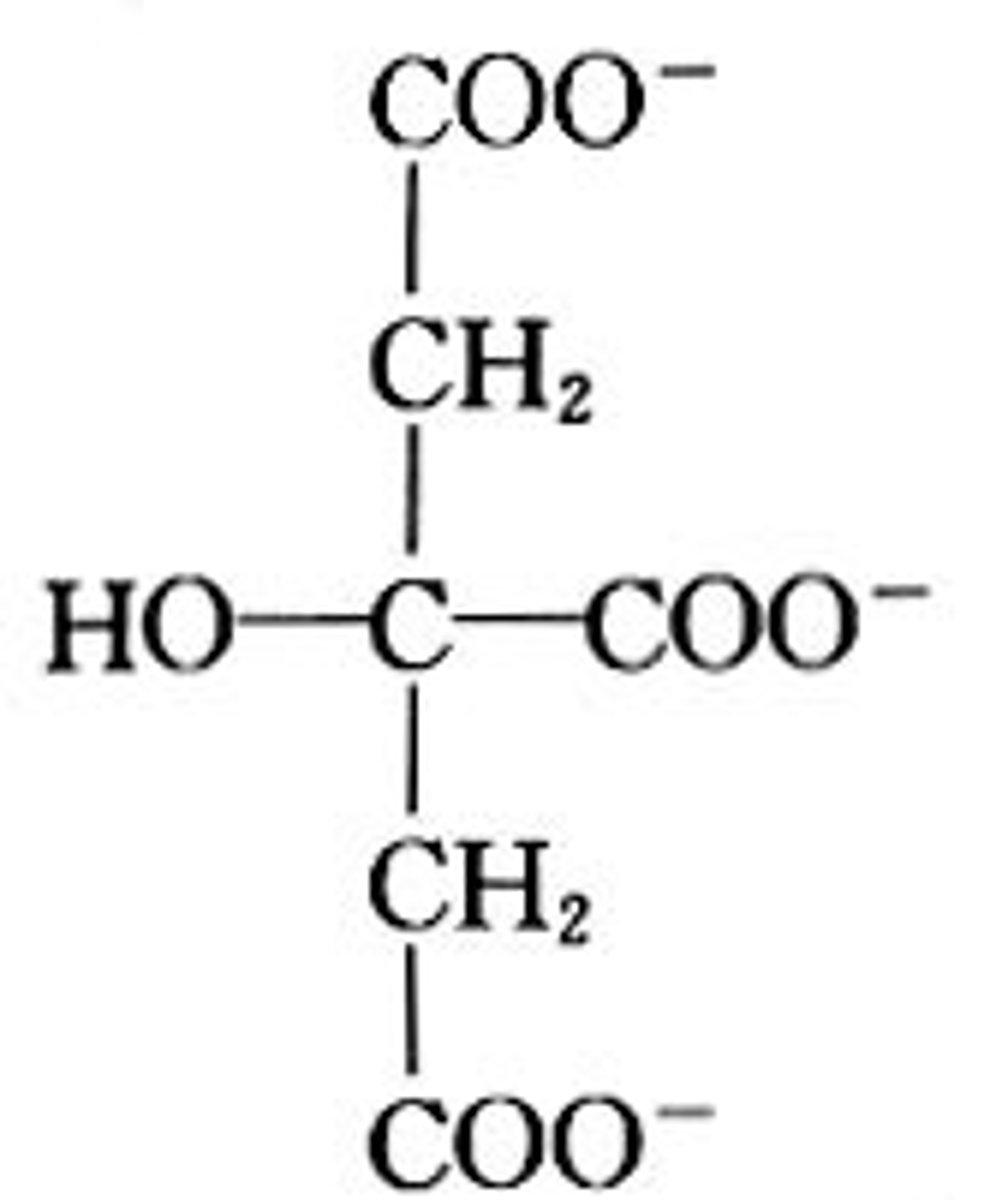
citrate
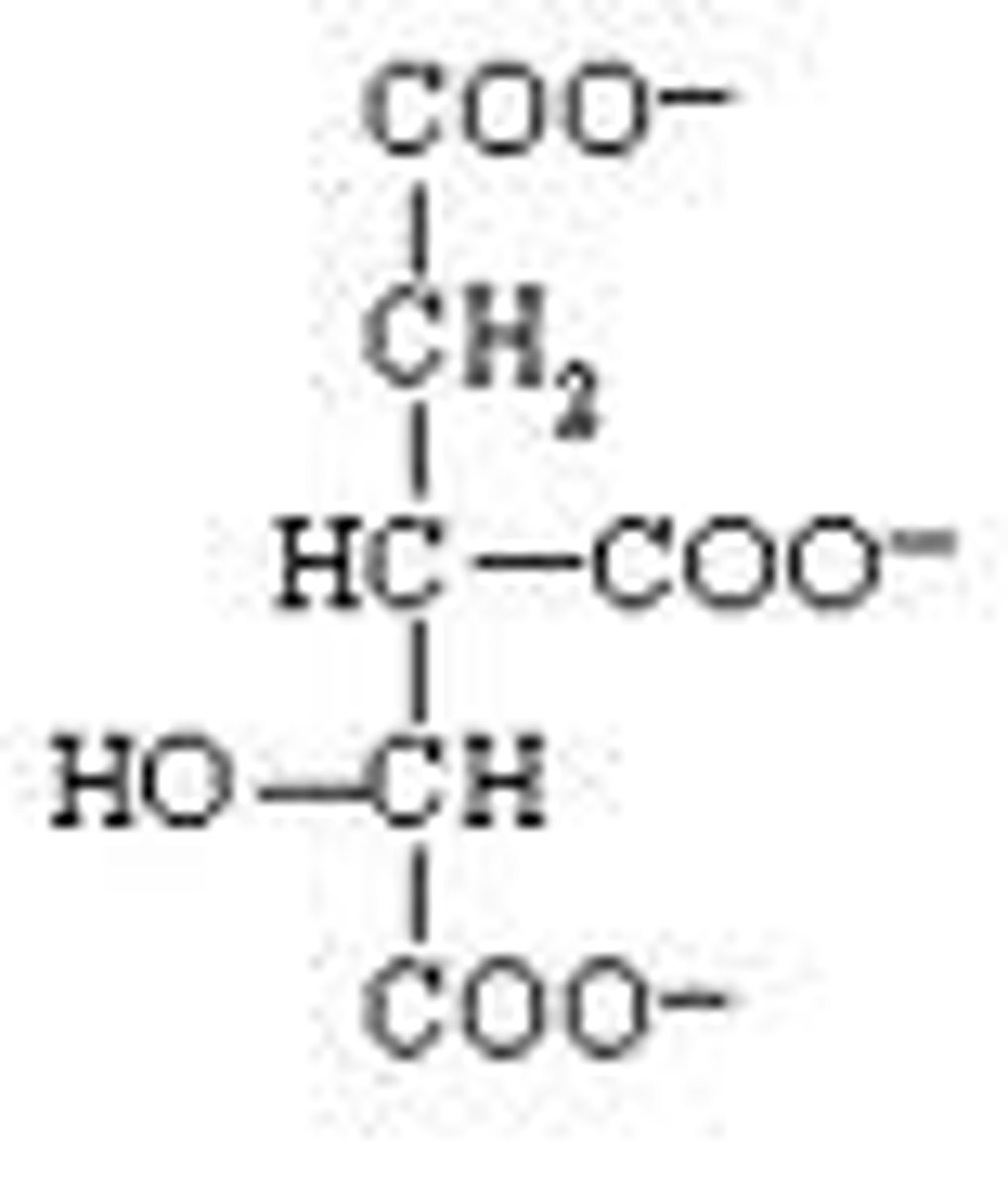
isocitrate
alpha-ketoglutarate
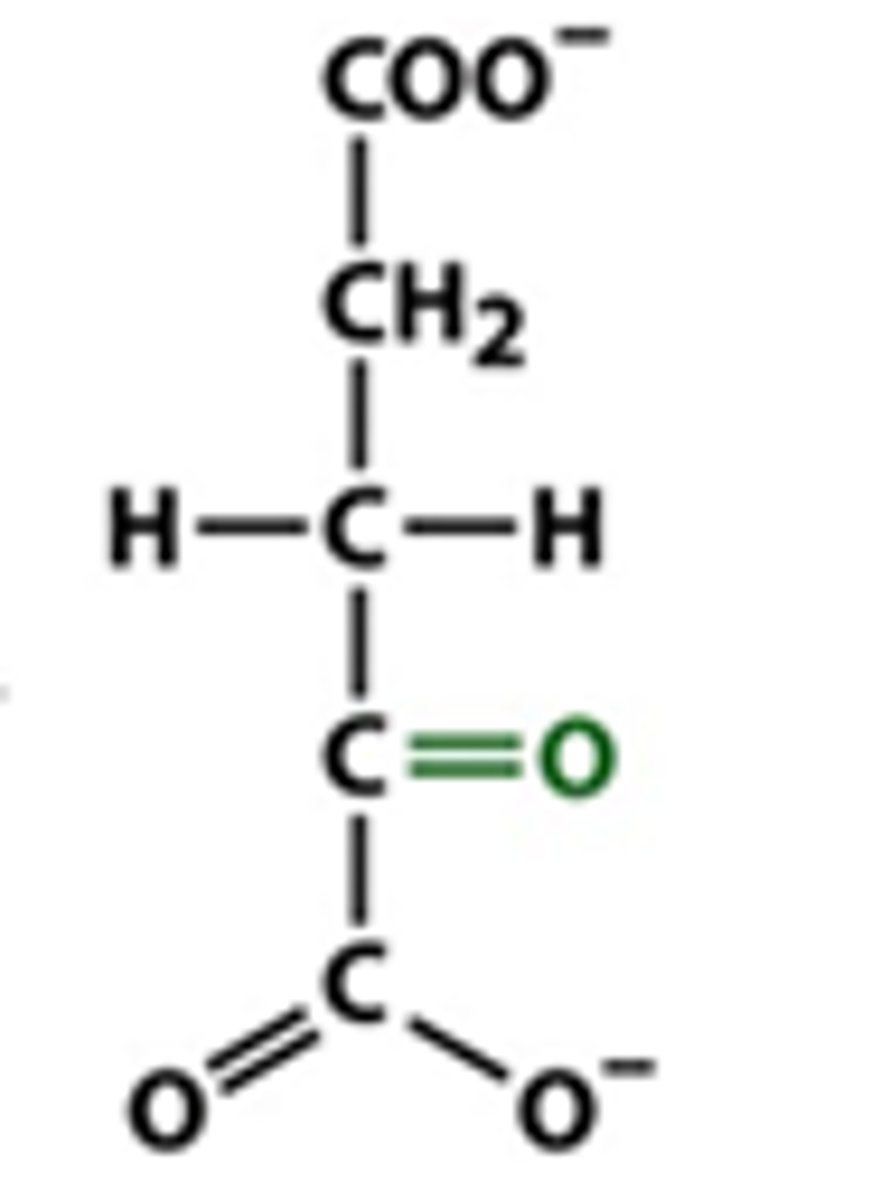
succinyl-CoA
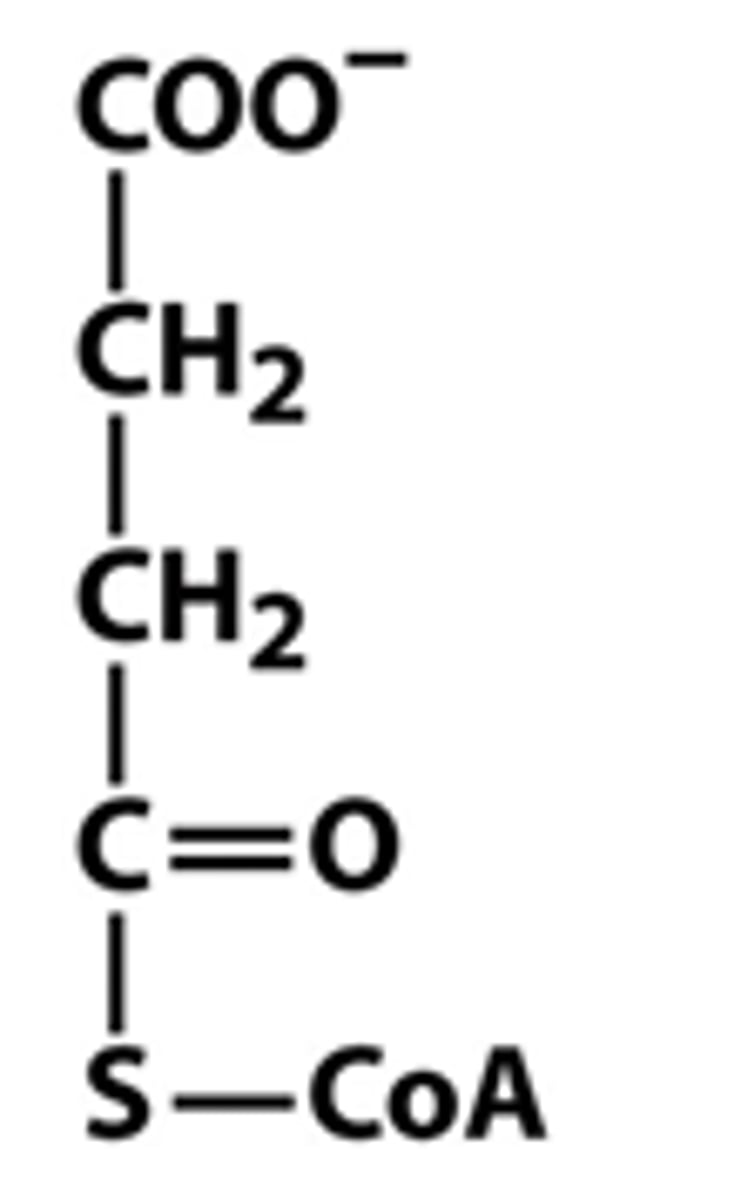
succinate
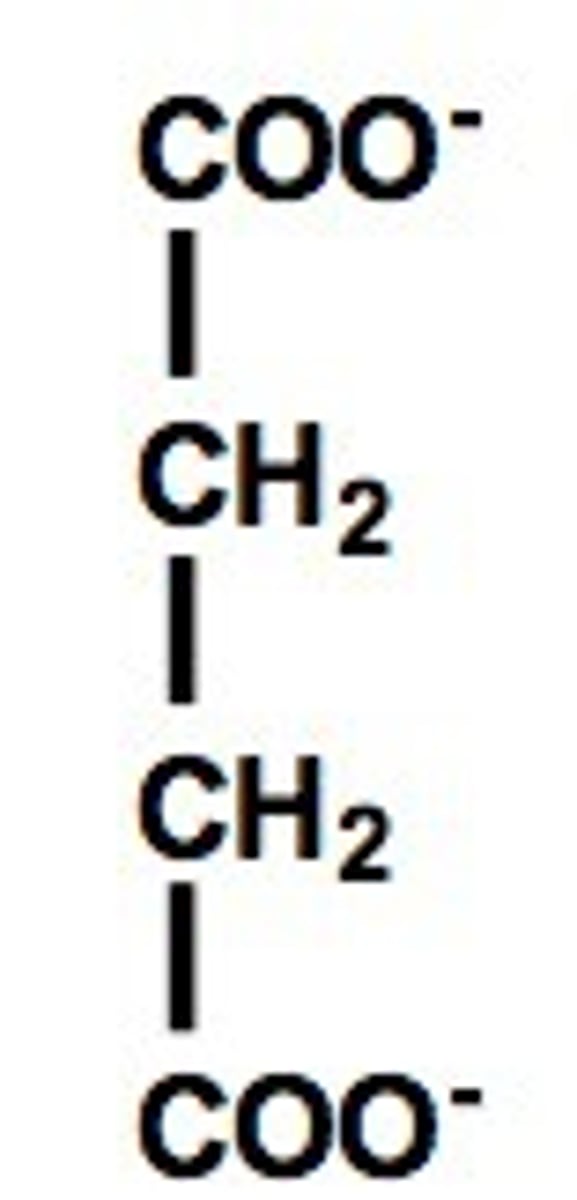
fumarate
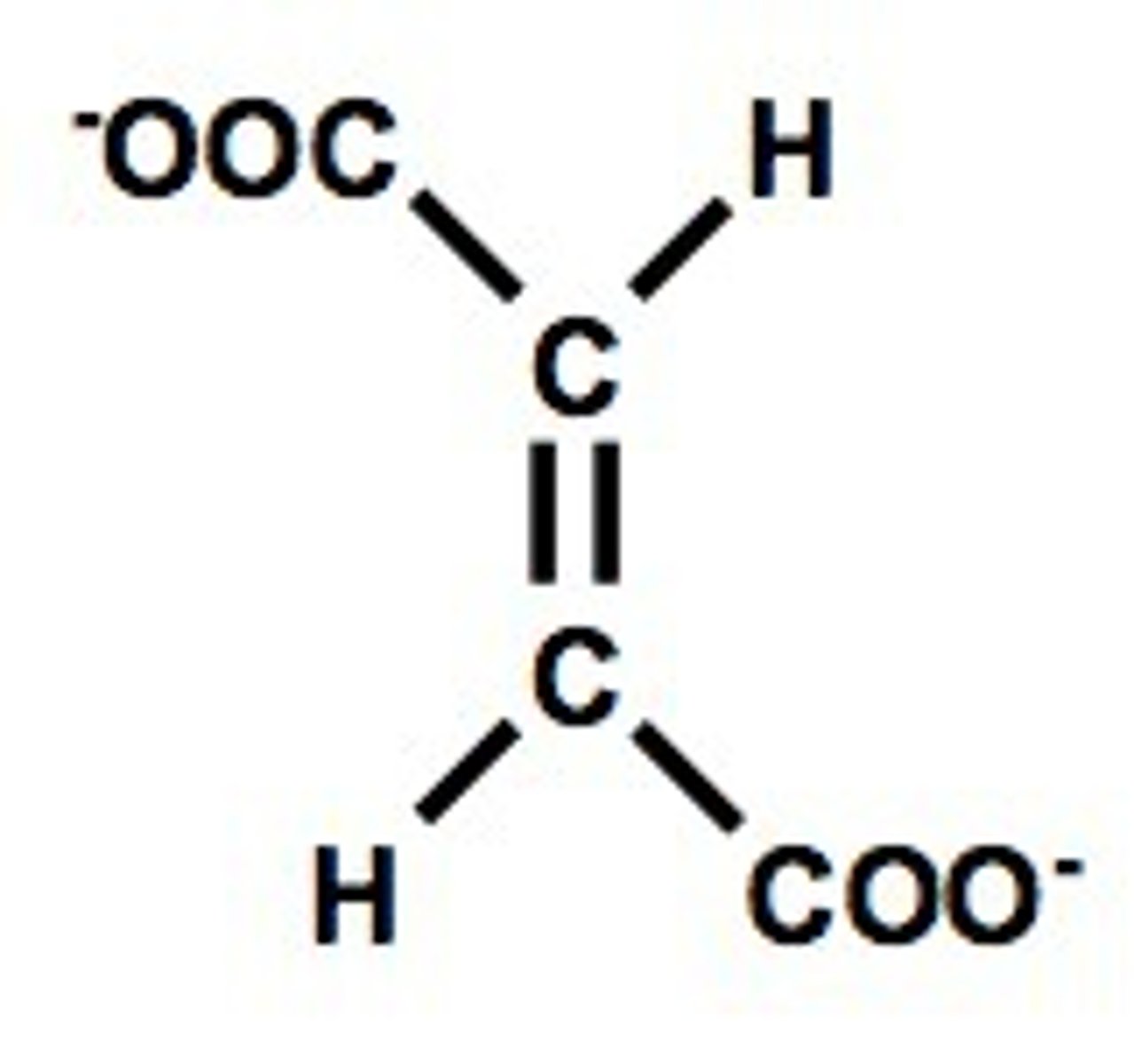
malate
What is the work done by a person holding a stationary object?
Zero. Work requires displacement in the direction of force.
What happens during prophase I of meiosis?
Crossing over occurs between homologous chromosomes.
What separates in anaphase I vs anaphase II of meiosis?
Anaphase I: homologous chromosomes. Anaphase II: sister chromatids.
Are polar bodies produced during meiosis I or II?
Polar bodies are produced during both meiosis I and II in oogenesis.
What type of inhibitor binds to both E and ES complex with unequal affinity?
Mixed inhibitor.
What does a noncompetitive inhibitor do to Vmax and Km?
It decreases Vmax but does not change Km.
What is the role of the allosteric site on an enzyme?
It is a regulatory site where effectors bind to modulate activity.
What happens to fluid pressure as height increases in a vertical pipe?
Pressure decreases to maintain total energy (Bernoulli’s principle).
What happens to fluid velocity when cross-sectional area decreases?
Velocity increases due to the continuity equation (A1v1 = A2v2).
What is the relationship between pressure and velocity in a narrowing pipe?
As velocity increases, pressure decreases (Bernoulli’s principle).
What is the Bohr effect in hemoglobin oxygen dissociation?
A decrease in pH or increase in CO₂ shifts the curve right, promoting O₂ release.
What is the function of the glomerulus in the nephron?
It filters blood to form filtrate, influenced by glomerular pressure.
Why are steroid hormones able to cross the cell membrane?
They are nonpolar and lipid-soluble, so they diffuse through membranes.
What is the function of helper T cells?
They activate B cells and cytotoxic T cells by releasing cytokines.
How does GPCR signaling terminate?
The G protein hydrolyzes GTP to GDP and rebinds to the βγ subunit.
Lineweaver-Burk x-intercept
-1/Km
Lineweaver-Burk y-intercept
1/Vmax
Power formula (average velocity)
P = F × v_avg
Continuity equation
A₁v₁ = A₂v₂
Bernoulli’s equation
P + ½ρv² + ρgh = constant
How does a narrowing pipe affect pressure and velocity?
Velocity increases, pressure decreases due to Bernoulli's principle.
What does Torricelli's Law state about fluid speed from a hole in a container?
v = √(2gh), where h is the depth of the hole below the fluid surface.
If water is falling under gravity, which kinematics formula helps find new velocity?
v = v₀ + gt, assuming downward direction as positive.
What happens to pressure if velocity increases in Bernoulli’s equation?
Pressure must decrease if height remains constant.
What is the change in entropy when a protein folds?
Entropy decreases because folding leads to a more ordered state.
What is the Second Law of Thermodynamics?
The total entropy of the universe always increases over time.
When is a reaction spontaneous given ΔH and ΔS?
If ΔH < 0 and ΔS > 0, the reaction is always spontaneous.
What is the Third Law of Thermodynamics?
A perfect crystal at absolute zero has zero entropy.
What kind of signal is sent by afferent vs efferent neurons?
Afferent: from tissue to CNS. Efferent: from CNS to muscles or glands.
What are the sensory vs motor roles of the nervous system?
Sensory = afferent (input), Motor = efferent (output).
What are the functions of phosphodiesterase in GPCR signaling?
Breaks down cAMP into AMP to terminate signaling.
What does protein kinase A do in a GPCR pathway?
Phosphorylates target proteins in response to increased cAMP.
Why do steroid hormones bind intracellular receptors?
Because they are lipid-soluble and pass through the cell membrane.
What kind of transport requires membrane-spanning proteins and ATP?
Primary active transport.
How does hypertonic solution affect a cell?
Water exits the cell, causing it to shrink.
What is the function of tight junctions in epithelial cells?
They prevent leakage between cells via the paracellular pathway.
What does Henry’s Law relate in the context of respiratory physiology?
Concentration of a gas = solubility × partial pressure.
What is the Bohr shift caused by increased lactic acid?
pH drops, shifting the oxygen dissociation curve right.
What is the primary stimulus that regulates breathing rate?
Changes in blood pH, specifically CO₂-induced H⁺ concentration.
What structure produces erythrocytes?
Bone marrow.
What’s the function of baroreceptors?
Detect changes in blood pressure.
What’s the direction of blood through the heart starting from the body?
Body → superior & inferior vena cava → right atrium → tricuspid valve → right ventricle → pulmonary valve → pulmonary artery → lungs → pulmonary veins → left atrium → mitral valve → left ventricle → aortic valve → aorta → body
Where are B cells activated?
In lymph nodes, upon encountering antigen.
What cells use perforin to kill infected cells?
Cytotoxic T cells and natural killer (NK) cells.
What is the function of somatic hypermutation?
To increase the diversity and affinity of antibody variable regions.
Which MHC class do cytotoxic T cells recognize?
MHC Class I.
What is a naïve T helper cell?
A T helper cell that has not yet encountered its specific antigen.
What are isoprene units made of?
Each isoprene contains 5 carbon atoms.
What is the basic structure of waxes?
Long-chain fatty acids linked to alcohols forming esters.
What does McDonaldization describe?
A process where society becomes more efficient, calculable, predictable, and controlled.
What hormone is released by the adrenal medulla in stress response?
Epinephrine.
What hormone is released by the adrenal cortex in stress and metabolic regulation?
Cortisol.
What are the key characteristics of steroid hormones?
Derived from cholesterol, lipid-soluble, bind intracellular receptors.
Which enzyme converts ATP to cAMP in GPCR signaling?
Adenylate cyclase.
What does Protein Kinase A phosphorylate?
Serine, threonine, and tyrosine residues on target proteins.
How does aldosterone affect ion exchange in the kidney?
It increases Na+ reabsorption and K+ secretion in the distal tubule.
What is the function of renin in blood pressure regulation?
Initiates the RAAS pathway to increase blood pressure.
Where does renin come from?
Juxtaglomerular cells of the kidney.
What is the basic unit of glycogen?
Glucose.