Community and Public Health Nursing: Concepts, Models, and Disaster Management
1/249
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
250 Terms
Health
a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity (WHO, n.d.).
Community
a group or collection of individuals interacting in social units and sharing common interests, characteristics, values, and goals (geopolitical vs phenomenological).
Population
a group of individuals with common personal or environmental characteristics. Aggregates are subgroups or subpopulations.
Public/Community Health Nursing
the practice of promoting and protecting the health of populations using knowledge from nursing, social, and public health sciences.
Community-Based Nursing
application of the nursing process and caring for individuals, families, and groups where they live, work, or go to school or as they move through the health care system.
Population-Focused Nursing
Concentrates on specific groups of people and focuses on health promotion and disease prevention regardless of geographic location.
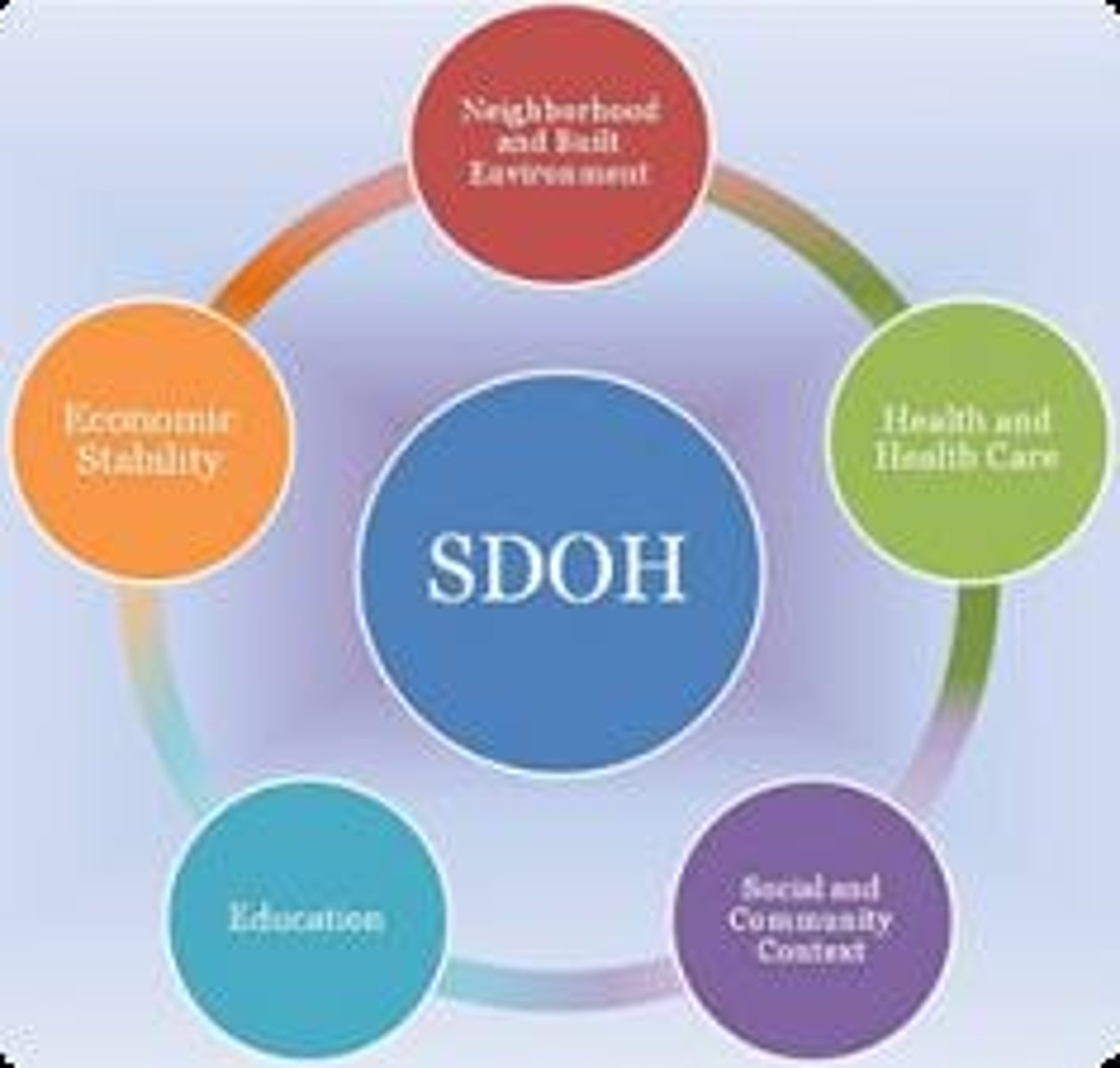
Social Determinants of Health
Economic Stability, Education access and Quality, Healthcare Access and Quality, Neighborhood and Built Environment, Social and community context.
World Health Organization
the United Nations agency that connects nations, partners and people to promote health, keep the world safe and serve the vulnerable so that everyone can attain the highest level of health.
CDC
a US agency that collaborates to create the expertise, information, and tools that people and communities need to protect their health through health promotion, prevention of disease, injury and disability, and preparedness for new health threats.
World Bank
international organization owned by 187 countries - whose role is to reduce poverty by lending money to the governments of its poorer members to improve their economies and to improve the standard of living of their people.
US Department of Health and Human Services
a US organization aimed to enhance the health and well-being of all Americans, by fostering sound, sustained advances in the sciences underlying medicine, public health, and social services.
Healthy People 2030
a US based framework derived with the goal of creating principles for all people to achieve their full potential for health and well-being across the lifespan.
Diversity
Variety across many variables, including gender, race, ethnicity, age, religion, sexual orientation, economic situation, physical abilities, political beliefs.
Public Health Intervention Wheel
Population based approaches that utilize surveillance, referral and follow-up, health teaching, collaboration, and advocacy to inflict health and wellness changes.
Primary Prevention
Prevention of a problem before it occurs
Secondary Prevention
Early detection and intervention
Tertiary Prevention
Correction and prevention of deterioration of a disease state
Upstream Intervention
Taking early action to recognize a problem before it comes to fruition to ensure better outcomes
Downstream Intervention
Taking action to problems after they've occurred and/or after they are an overwhelming issue
Microscopic focus
Individual assessment and treatment, more immediate, downstream thinking
Macroscopic focus
More global thinking, looks at prevalence and causes across populations, upstream thinking
Risk
Likelihood or probability of exposure
Risk factor
Specific exposure, internal or external (age, sex, or genetics)
Penders Health Promotion Model
Defined as the process of empowering individuals and communities to make healthy lifestyle choices to improve overall health and wellness, where health is 'a positive dynamic state not merely the absence of disease.'
Health Belief Model
Predicts that a specific health behavior is more or less likely based on an individual's perceptions of disease severity and personal susceptibility to the disease combined with perceived benefits and barriers to that behavior
Theory of Planned Behavior
Assumes that individuals act rationally, according to their attitudes, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control
Transtheoretical Model stages of change
Suggests that individuals move through six stages of change: precontemplation, contemplation, preparation, action, maintenance, and termination
Knowles Assumptions
The Adult Learning Theory is the concept or study of how adults learn and how it differs from children. The six assumptions include: adults' self-concept, learning experiences, readiness to learn, motivation, need to know, and problem-centered learning.
Disaster
Community is disrupted and experiences great loss, resources are overwhelmed
Disaster Risk
Function of hazard, exposure, vulnerability, and capacity (UNDRR)
Disaster Resilience
Capacity to absorb, adapt, and continue to thrive
All Hazards Approach
Focus on capacities/capabilities instead of one specific threat
Patterns of Health and Disease
Countries with relatively strong economies and stable societies often have a heavy burden of chronic disease
Older population
Mortality often due to causes such as stroke, heart disease
Tobacco
Countries with less stability and less developed economies often have a heavy burden of infectious disease
Younger population
Mortality often due to causes such as diarrheal diseases, infections.
Population Trends and relation to health
United States: Slower population growth, Aging population, Greater diversity. Global: Slower population growth, Higher dependency ratio for many countries, ex European countries, Aging populations.
Levels of Prevention
Upstream and Downstream thinking, Micro/macroscopic focus on health.
Risk/ Risk factors
Factors that increase the likelihood of negative health outcomes.
Transtheoretical Model
A model that describes the stages of change individuals go through to alter behavior.
Empowerment Models
Models that focus on empowering individuals and communities.
Health Education Empowerment
Empowering individuals through education to make informed health choices.
Community Empowerment
The process of enabling communities to increase control over their lives.
Community-Based Participatory Research/Community-Engaged Scholarship
Research that involves community members in the research process.
Disaster vulnerability assessment
Systematic process used to identify individuals or groups who are at increased risk for poor health outcomes due to social, economic, environmental, or biological factors.
Culture (N&M 13)
The culture that develops in any given society is always specific and distinctive, encompassing the knowledge, beliefs, customs, and skills acquired by members of that society.
Subculture (N&M 13)
Fairly large aggregates of people who share characteristics that are not common to all members of the culture and that enable them to be a distinguishable subgroup.
Cultural competence
Respecting and understanding the values and beliefs of a certain cultural group so that one can function effectively in caring for members of that cultural group.
Cultural sensitivity
Emphasizes awareness and continuous learning about cultural differences.
Transcultural nursing
A field of study that combines nursing and anthropology.
Dominant value orientation (N&M 13)
Every society has a basic value orientation that is shared by the majority of its members as a result of early common experiences.
Socio-economic status
A composite of the economic status of a family or unrelated individuals based on income, wealth, occupation, educational attainment, and power.
Cultural stereotyping
Tendency to view individuals of common cultural backgrounds similarly and according to a preconceived notion of how they behave.
Quantitative Data
Data represented numerically, including anything that can be counted, measured, or given a numerical value.
Qualitative Data
Categorical data representing information and concepts that are not represented by numbers.
PDSA
An acronym used in QI which is a four step guide through the thinking process as a way to test a change that is implemented.
SMART goal
A strategy used to set a project goal in QI that is specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound.
Patient-Centered Care
Emphasizes tailoring care to individual patient needs, values, and preferences.
Clinical Judgment and Decision-Making
Central to NCLEX success and safe practice, involves applying nursing process steps (assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, evaluation) to real-world scenarios.
Data-Driven Practice
Quality improvement relies on collecting and analyzing data to identify gaps and measure outcomes.
Continuous Quality Improvement (CQI)
Models that rely on collecting and analyzing data to identify gaps and measure outcomes.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration
A cooperative approach in quality improvement that involves multiple disciplines working together.
Error Prevention and Safety Culture
Encourages proactive risk identification and a non-punitive environment for reporting errors.
Medication Safety
Focus on preventing medication errors and ensuring safe medication practices.
Infection Control
Practices aimed at preventing the spread of infections in healthcare settings.
Procedural Accuracy
Ensuring that medical procedures are performed correctly and safely.
Resilience and Burnout Prevention
Building emotional insight, work-life balance, and reflective practices to help nurses thrive under pressure.
Quantitative Data Analysis
Statistical analysis focusing on numerical data to identify trends and outcomes.
Qualitative Data Analysis
Analysis focusing on non-numerical data to develop themes and categorize information.
SMART Goals
Goals that are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
Assessment
Determine need in a community or population.
Planning
Practical intervention strategies based on assessment.
Intervention
Implementing a change based on planning.
Evaluation
Assessing how well a change occurred.
Aggregate
A community composed of people who have common characteristics.
Shoe Leather
Door-to-door assessment, asking questions in groups of people or all people in a community.
Windshield Survey
Systematic observation via walk/drive through an area to make organized observations.
Photovoice
Image selection based on personal interest.
Expressed Need
Demand for services and market behavior of the targeted population.
Normative Needs
Lack, deficit, or inadequacy of services determined by health professionals.
Perceived Needs
Wants and desires expressed by the audience.
Relative Needs
Gap showing health disparities between advantaged and disadvantaged populations.
Epidemiology
Study of the distribution and determinants of health and disease in human populations.
Descriptive Epidemiology
Study of the amount and distribution of disease.
Analytic Epidemiology
Investigation of the causes of disease.
Environment
Modifiable external risk factors that may predispose to or protect against disease, illness, or injury.
Consistency of association
The condition in question must occur when the 'factor' is present not when it is absent.
Strength of association
The greater the correlation between the factor and the condition the greater the possibility the relationship is a causal one.
Specificity
The supposed cause always created the same effect.
Temporal relationship
The supposed cause always occurs before the effect (time factor).
Coherence
The supposition that one event causes another is coherence with other existing knowledge.
Ecosocial Epidemiology
Emphasis on the role of evolving macro-level socioenvironmental (political and economic) factors.
Absolute risk
Probability that anyone in a population will develop a particular condition.
Relative risk
Probability that someone in a group of people will develop the condition when compared to people w/o the characteristic.
Surveillance
Mechanism for the ongoing collection of community health information.
Morbidity
Frequency in which a disease appears in a population.
Mortality
Number/rate of deaths in a given population.
Incidence
Is a measure of the number new cases of a characteristic that develops in a population in a specified period of time.
Prevalence
Is the proportion of the population who have a specified characteristic in a specified period of time.
Portal of Entry
Opening where the pathogen may enter the body