Separation and Identification of Amino Acids by paper chromatography
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
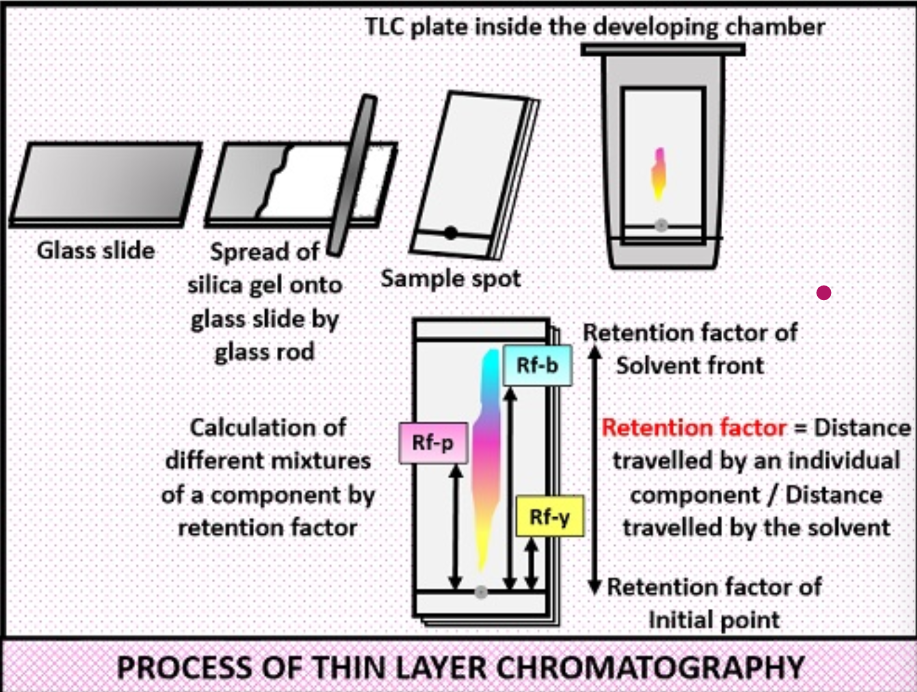
what is retention factor (Rf)
ration of the distance travelled by the solute to the distance travelled by the solvent
what happens if the Rf value is zero?
if the Rf value is zero, the solute remains in the stationary phase and thus is immobile
what happens if the Rf value is 1?
if the Rf value is 1 then the solute has no affinity for the stationary phase and travels with the solvent front
the higher the Rf value, the?
the higher the rf value, the greater affinity of the solute to the solvent
retention factor is also used to?
used to determine the affinity of solute to the solvent
values can be compared to unknown sample with Rf values of known compound
from the Gk words: chroma means?
color
from the Gk words: graphein means?
to writing
who was the first to employ chromatography?
first employed by a russian botanist in 1903 Mikhail Semenovish Tswett, who studied coloring material in plants
what is chromatography and its purpose?
a separation technique which involves separation of components of a mixture through differential migration across a stationary phase
what is differential migration?
refers to compounds of a mixture travelling at different levels or rate depending on:
a. their affinity to the solvent that carries/pick up solutes composing the mixture
b. relative solubility of the solute to the solvent
c. effective charge of the solute (acidic, basic or neutral(
d. size
what is paper chromatography?
a technique used for the separation & identification of relatively small chemical substances by a moving solvent on sheets or strips of filter paper
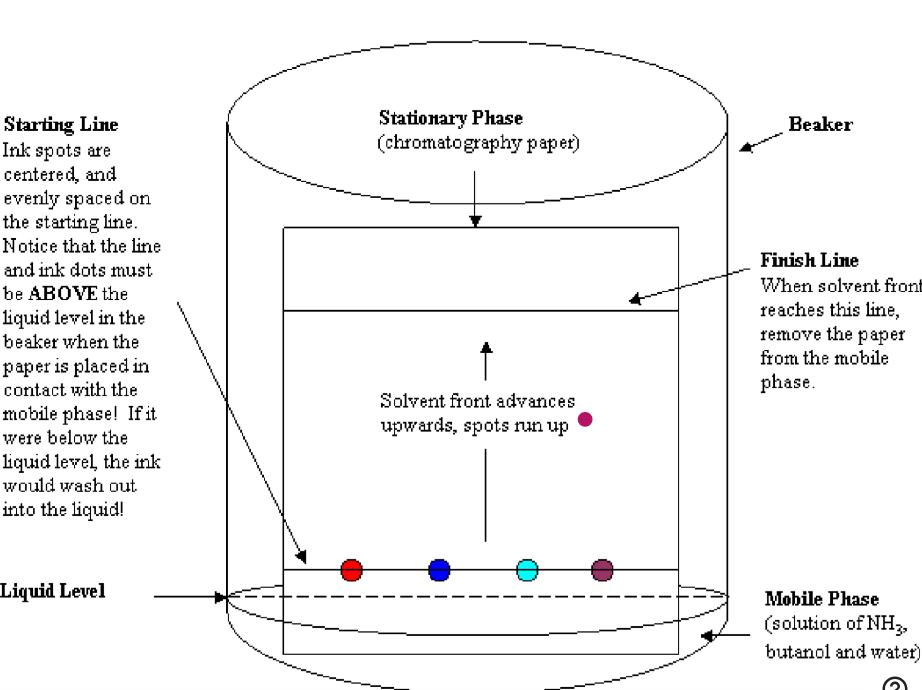
substances to be identified are “spotted” near one end of the filter paper
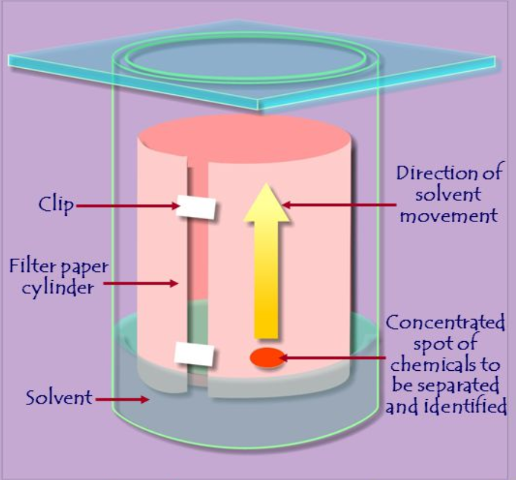
what is the technique of paper chromatography used for?
the technique is use for small molecules such as amino acids, small peptides and sugars
as the solvent moves up the paper, different molecules move at different rates with the smallest molecules moving the fastest
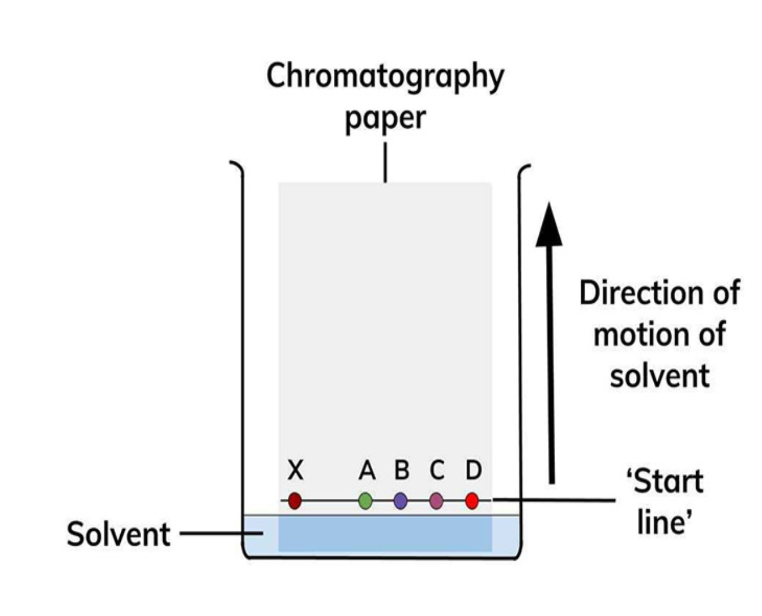
paper chromatography: how it works
a drop of solution to be separated is placed at one end of the filter paper which is placed in a sealed glass jar that contains a small amount of solvent
the end of the paper is dipped in solvent
the solvent travels through capillary action as it takes up unknown substances which are deposited in the spots
thin layer chromatography
similar to paper chromatography
filter paper is replaced by as glass/ plastic plate coated with a thin layer of chromatographic material (silica/alumina)
what is thin layer chromatography?
is a technique used for the separation of mixtures of chemical compounds on a thin layer of adsorbent material.
Thin Layer Chromatography
Its is one of the most widely used technique for the separation and final purification of organic compounds.
what is the principle of TLC?
it is based on the principle of adsorption chromatography or partition chromatography or combination both, depending on adsorbent, its treatment and nature of solvents employed
the components with more affinity towards stationary phase travels slower
components with less affinity towards stationary phase travels faster
process of thin layer chromatography
prepare the plate
spot the sample
prepare the solvent (mobile phase)
develop the TLC plate
removed and dry the plate
visualize the spots
analyze the results
what is gel filtration chromatography?
also called “gel permeation molecular sieve or size exclusion”
separates protein on the basis of their size and shape using porous beads made of hydrated polymers of polyacrylamide (biogel) or carbohydrate dextran (sepalex)
separation is according to difference of size or molecular weight (MW)
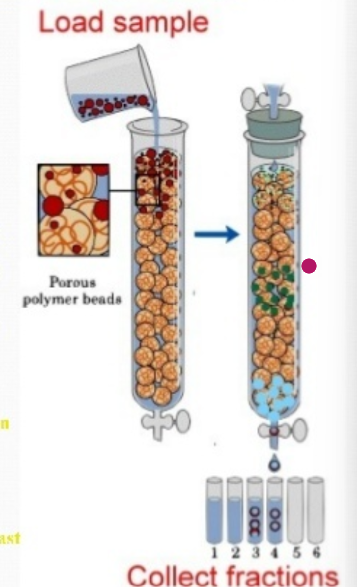
characteristics of gel filtration chromatography
beads are packed in a column
large and elongated protein cannot enter the beads and migrate through the column faster, emerging out the bottom first
smaller molecules move slowly and elute later
for de-salting a protein or to estimate the molecular mass of the protein
in gel filtration, what phase does it occur when beads are of hydrated, porous polymer?
stationary phase (column matrix)
in gel filtration chromatography, what phase is the buffer or solvent?
mobile phase

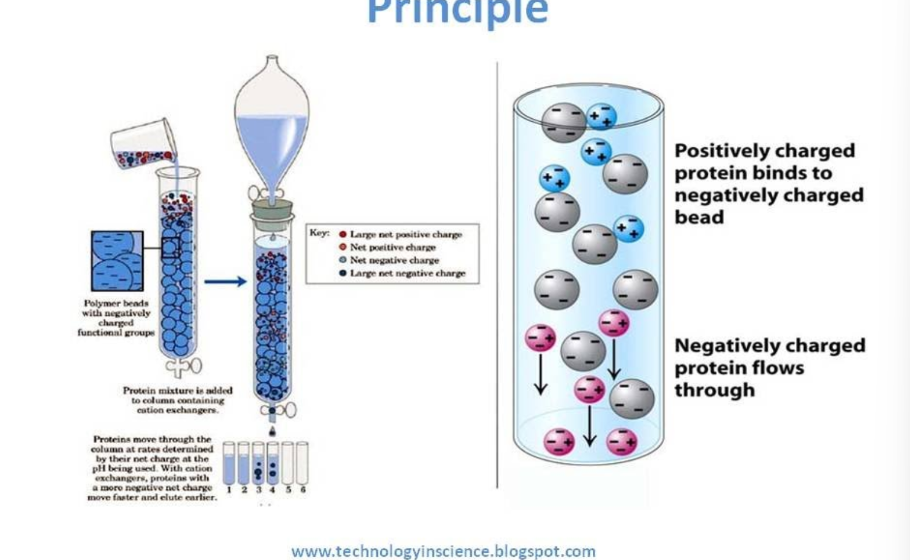
ion exchange chromatography involves the use of?
involves the use of cationic (polysulfonate) and anionic (polyamine) resins
in ion exchange chromatography, proteins are separated on the basis of their overall net charge at?
pH 7
in ion exchange chromatography, negatively charged proteins (acidic amino acids) will?
negatively charged proteins (acidic amino acids) will bind to a column with positively charged beads
in ion exchange chromatography, neutral and positively charged AA will?
neutral and positively charged AA will not bind to the column
what ions compete with protein for the positively charged groups in the column?
chloride ions
eluted proteins are washed with varying conc. of?
NaCI
in ion exchange chromatography, what happens to proteins with low density?
proteins with low density of negative charges are eluted first, followed by with a higher density of negative charges
what is the principle of IEC?
positively charged protein binds to negatively charged bead
negatively charged protein flows through
what is adsorption chromatography?
one of the oldest types of chromatography around
it utilizes a mobile liquid or gaseous phase that is adsorbed into the surface of a stationary solid phase
solutes are adsorbed according to their affinity to the solid adsorbent
what are the common adsorbents of adsorption chromatography?
common adsorbents: aluminum, oxide, silica gel, carbon and powdered sugar
in adsorption chromatography, solvent range from?
solvents range from polar liquids (alcohols), to non polar liquids (hexane)
in adsorption chromatography, chromatography on aluminum oxide will?
chromatography on aluminum oxide will separate aromatic from aliphatic hydrocarbons
what is chromatogram?
result attained from a chromatographic analysis
pattern formed in the absorbent medium by layers of chromatography
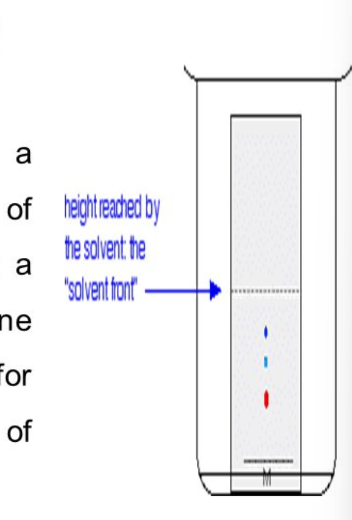
what is solvent front?
maximum distance travelled by the solvent mixture when it was allowed to travel through paper by capillary action
what is stationary phase?
part of the chromatographic system through which the mobile phase flows where the distribution of the solutes between the phases occurs
the stationary phase may be?
may be solid or liquid that is immobilized or adsorbed on a solid
what is mobile phase?
carries the solutes through the stationary phase
either liquids or gases