period 2: 1607-1754
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Jamestown
(Learning Topic 2.1) The first permanent English settlement in North America, found in East Virginia
Mercantilism
(Learning Topic 2.1) An economic policy under which nations sought to increase their wealth and power by obtaining large amounts of gold and silver and by selling more goods than they bought
Virginia Company
(Learning Topic 2.3) Joint-Stock Company in London that received a charter for land in the new world. Charter guarantees new colonists same rights as people back in England.
-Began as a Corporate colony, but made unwise decisions and was in debt, resulted in King James I revoking the charter and taking direct control, making Virginia the first royal colony.
New England
(Learning Topic 2.3) A region of northeastern United States comprising Maine and New Hampshire and Vermont and Massachusetts and Rhode Island and Connecticut.
-Rocky soil and long winters, farming was limited
-Most farms were small with work done by the family members
-Logging, shipbuilding, fishing, trading, and rum-distilling were the main economic activities.
Middle Colonies
(Learning Topic 2.3) New York, Pennsylvania, Delaware, New Jersey
-Rich soil produced an abundance of wheat for export to the West Indies
-Farms were common
-Known as the "Bread basket"
-Small manufacturing efforts developed: iron making
Southern Colonies
(Learning Topic 2.3) Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia.
-Geography and climate varied greatly, most lived on small subsistence farms, few lived on large plantations and relied on slave labor.
-Tobacco in Chesapeake and North Carolina
-Timber and Naval Stores in Carolinas
-Rice and Indigo in South Carolina and Georgia
Chesapeake Colonies
(Learning Topic 2.3) Term for the colonies of Maryland and Virginia
Virginia House of Burgesses
(Learning Topic 2.3) The first elected assembly in the New World, established in 1619
Plymouth Colony
(Learning Topic 2.3) A colony established by the English Pilgrims. They were radical dissenters who were known as separatists, they wanted to form an independent church. Plymouth became part of Massachusetts in 1691.
-They were heading for Jamestown but miscalculated and arrived at Plymouth.
Puritans
(Learning Topic 2.3) A religious group who wanted to purify the Church of England. They came to America for religious freedom and settled Massachusetts Bay. They were less radical than the pilgrims, and believed the Church of England could be fixed or "purified."
Mayflower
(Learning Topic 2.3) The ship in which the Pilgrim Fathers sailed from England to Massachusetts in 1620.
-Half of those who sailed were separatists, the other half sailed for economic reasons
Mayflower Compact
(Learning Topic 2.3) Pilgrims signed this document that pledged decisions would be made by the will of the majority.
-Most colonists excluded from this, only male property owners could vote for representatives.
Maryland
(Learning Topic 2.3) King Charles I subdivided the Virginia Colony and granted the land of Maryland to George Calvert/Lord Baltimore as a reward for his service to the crown.
-First proprietary colony
-Designed to be a haven for Catholics
Act of Toleration
(Learning Topic 2.3) Several Catholics migrated to Maryland to establish plantations; however, they were outnumbered by the Protestants. Thus, this law was passed granting religious freedom to all Christians, but death for those who denied the divinity of Jesus.
Roger Williams
(Learning Topic 2.3) A dissenter who clashed with the Massachusetts Puritans over separation of church and state and was banished in 1636, after which he founded the colony of Providence, Rhode Island.
-Toleration of religion
-Recognized Native rights and paid them for using their land
-Founded one of the first Baptist churches in America
Anne Hutchinson
(Learning Topic 2.3) Believed in antinomianism, that faith alone is necessary for salvation. She was banished from Massachusetts Bay Colony and founded colony of Portsmouth near Providence.
-She was killed in a Native American uprising after migrating to Long Island
Rhode Island
(Learning Topic 2.3) Roger Williams, in 1644, joined Portsmouth and Providence into Rhode Island by means of a charter.
-This colony tolerated many beliefs, serving as a refuge.
The Fundamental Orders of Connecticut
(Learning Topic 2.3) First written constitution in America
-Representative government consisting of a legislature elected by popular vote and governor chosen by legislature.
The Carolinas
(Learning Topic 2.3) As a reward for helping him gain the throne, King Charles II granted this huge tract of land to 8 nobles.
-SC: Initially based on fur trade, later became plantation based (18th century)
-NC: farmers from Virginia and New England established small self-sufficient tobacco farms
Quakers
(Learning Topic 2.3) English dissenters who broke from Church of England, peace loving Christian sect.
-Religious authority was found within a person's soul, not the Bible.
William Penn
(Learning Topic 2.3) A Quaker that founded Pennsylvania to establish a place where his people and others could live in peace and be free from persecution.
-He was a convert, the royal family owed the Penn family a large debt, paid to William in the form of Pennsylvania.
Georgia
(Learning Topic 2.3) Last colony chartered, only one to receive direct financial support from government in London, defensive buffer between South Carolina and threat of Spanish Florida, penal colony for prisoners in England.
Middle Passage
(Learning Topic 2.4) A voyage that brought enslaved Africans across the Atlantic Ocean to North America and the West Indies
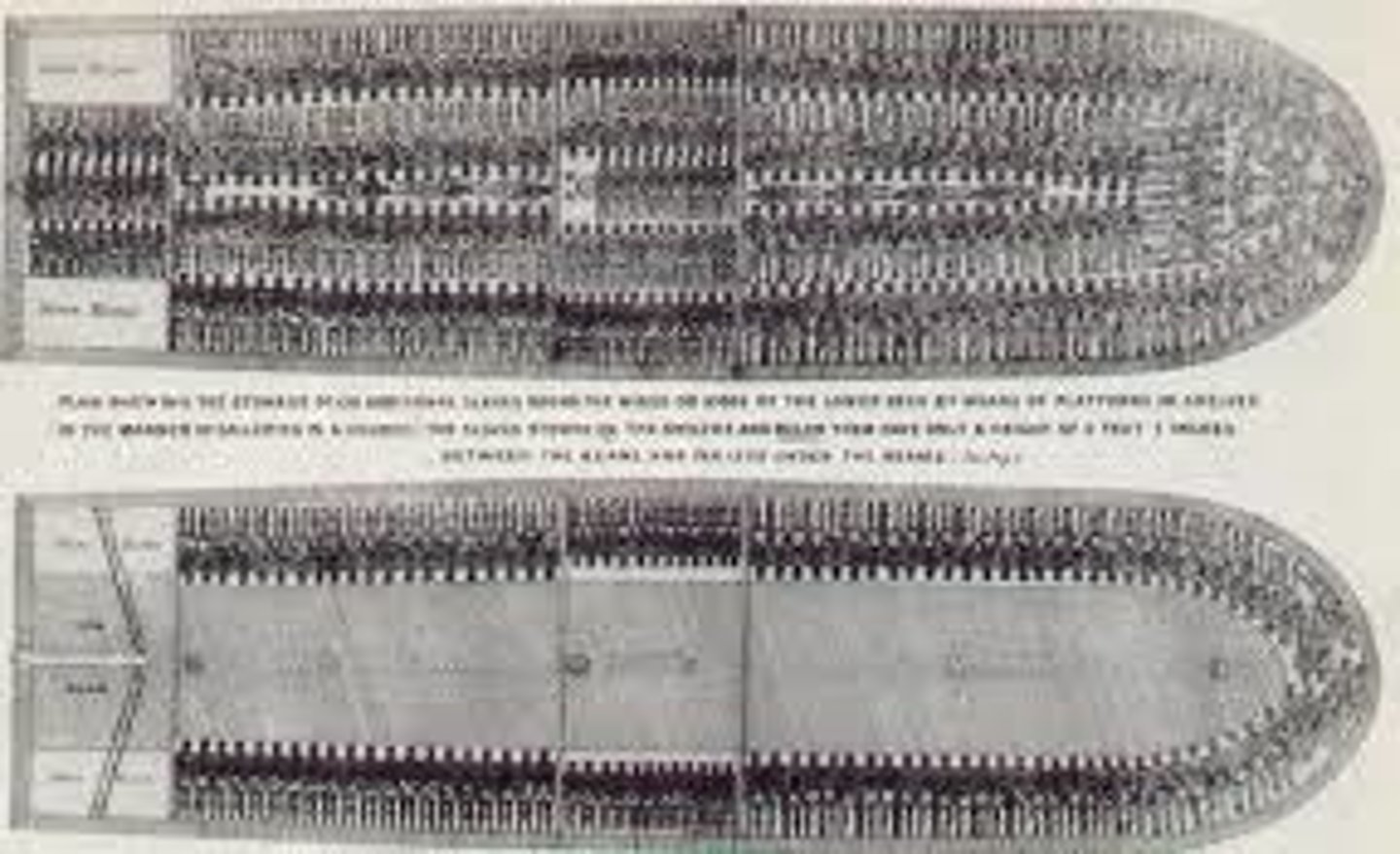
Navigation Acts
(Learning Topic 2.4) Laws that governed trade between England and its colonies. Colonists were required to ship certain products exclusively to England, through the use of only a British vessel, operated by 3/4 British, all goods must go through Britain.. These acts made colonists very angry because they were forbidden from trading with other countries.
Salutary Neglect
(Learning Topic 2.4) An English policy of not strictly enforcing laws in its colonies
Indentured Servants
(Learning Topic 2.4) Colonists who received free passage to North America in exchange for working without pay for a certain number of years.
Metacom's War
(Learning Topic 2.5) Native Americans battle New England colonies; large percentage of Native Americans died, making it one of the bloodiest wars in US; severely damaged the Native American presence in the new world.
-Metacom's father helps the pilgrims greatly, but Metacom himself is hostile.
-English allied with Mohawk Indians and killed Metacom, ending the war
Bacon's Rebellion
(Learning Topic 2.5) A rebellion lead by Nathaniel Bacon with backcountry farmers to attack Native Americans in an attempt to gain more land. Governor Berkely was unfair and did not give the colonists the protection they demanded.
Pueblo Revolt
(Learning Topic 2.5) Native American revolt against the Spanish in late 17th century; expelled the Spanish for over 10 years; Spain began to take an accommodating approach to Natives after the revolt.
Headright System
(Learning Topic 2.7) The Virginia Company's system in which settlers and the family members who came with them each received 50 acres of land
John Winthorp
(Learning Topic 2.7) Successful attorney and manor lord in England who became 1st governor of Massachusetts Bay claiming to have calling from God.
The Enlightenment
(Learning Topic 2.7) A movement in the 18th century that advocated the use of reason in the reappraisal of accepted ideas and social institutions.
Deism
(Learning Topic 2.7) A popular Enlightenment era belief that there is a God, but that God isn't involved in people's lives or in revealing truths to prophets.
John Locke
(Learning Topic 2.7) 17th century English philosopher who opposed the Divine Right of Kings and who asserted that people have a natural right to life, liberty, and property. Against Absolutism
-Heavily influenced the American Revolution
"Government only comes with the consent of the governed"
The Social Contract
(Learning Topic 2.7) Individuals give some freedom to the government/authority figure to maintain security for the greater public good.
Ex- Taxes paid for school
1st Great Awakening
(Learning Topic 2.7) Spectacular, emotional religious revival of the 1730s and 1740s. This event saw an increase in religious sects in the colonies.
Johnathan Edwards
(Learning Topic 2.7) An American theologian and congregational clergyman whose sermons stirred the religious revival (Great Awakening); known for sinners in the hands of an angry god sermon.
-Stayed in New England (not itinerant)
George Whitefield
(Learning Topic 2.7) Spread his ideas throughout the colonies, over 10,000 people came, taught faith and sincerity was enough to understand the gospel without a minister.