CPIM - Module 1.4
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
performance measurement system
a system for collecting, measuring, and comparing a measure to a standard for a specific criterion for an operation, item, good, service, business, etc. A performance measurement system consists of a criterion, a standard, and a measure.
standards
performance targets - an established norm against which measurements are compared
Principles of Effective Measurement
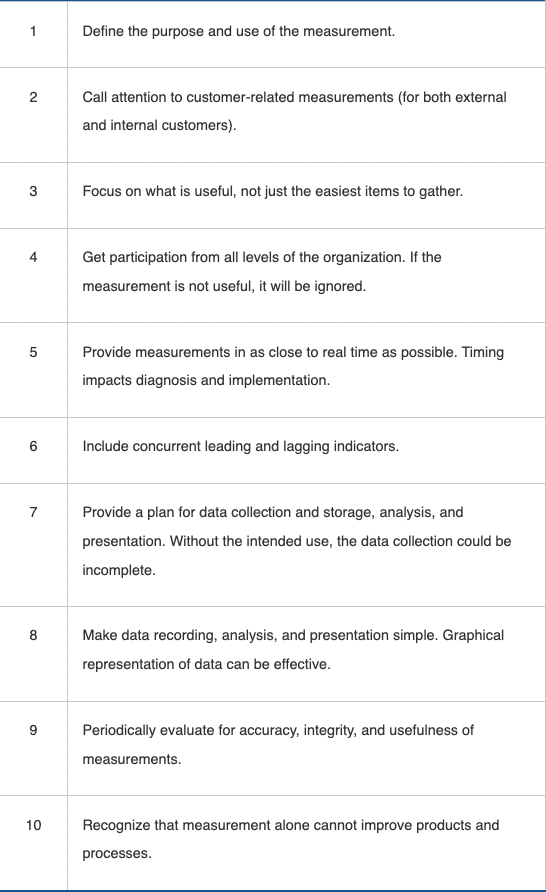
KPIs - Key Performance Indicators
a financial or nonfinancial measure that is used to define and assess progress toward specific organizational goals and that typically is tied to an organization’s strategy and business stakeholders - a KPI should not be a contradictory to other departmental or strategic BU performance measures.
If you cannot measure it, you cannot manage it.
Resilience - Category of performance measurement
Reliability - the ability to perform tasks as expected. Reliability focuses on the predictability of the outcome of a process. Typical metrics for the Reliability attribute include delivering a product on time, in the right quantity and at the right quality level.
Responsiveness - the speed at which tasks are performed and the speed at which a supply chain provides products to the customer. Examples include cycle-time metrics.
Agility - the ability to respond to external influences and marketplace changes to gain or maintain a competitive advantage.
Economic - Category of performance measurement
Costs - the cost of operating the supply chain processes. This includes labor costs, material costs, and management and transportation costs.
Profit - the Profit attribute describes the financial benefit realized when the revenue generated from a business activity exceeds the expenses, costs, and taxes involved in sustaining the activity.
Assets - the ability to efficiently utilize assets. Assets’ strategies in a supply chain include inventory reduction and insourcing rather than outsourcing.
Sustainability - Category of performance measurement
Environmental - The environmental attribute describes the ability to operate the supply chain with minimal environmental impact, including materials, water and energy.
Social - the social attribute describes the ability to operate the supply chain aligned with the organization’s social value, including diversity and inclusion, wage, and training metrics.
SCOR DS Metrics
In SCOR, metrics measure the ability of processes to achieve the strategic objectives associated with performance attributes. SCOR recognizes three levels of predefined metrics: Level 1 metrics are diagnostics for the overall health of the supply chain. Level 2 metrics serve as diagnostics for the level 1 metrics. Level 3 metrics serve as diagnostics for level 2 metrics.
balanced scorecard
a list of financial and operational measurements used to evaluate organizational or supply chain performance. The dimensions of the balanced scorecard might include customer perspective, business process perspective, financial perspective, and innovation/learning perspective. It formally connects overall objectives, strategies, and measurements. Each dimensions has goals and measurements.
4 categories of balanced scorecard
Customer Value
Business Process
Financial Performance
Innovation and Learning - Organizational Capacity
Financial Ratios
Categorized into 5 groups:
Liquidity
Activity
Leverage
Profitability
Market value
Current Ratio
liquidity ratio
Current assets/Current liabilities
Quick Asset Ratio
liquidity ratio
a measure of a firm’s financial stability
(Current Assets - Inventory)/Current Liabilities
Desirable: >1
Inventory turnover
activity ratio
the number of times that an inventory cycles, or turns over, during the year. A frequently used method to compute inventory turnover is:
Annual Cost of Sales/Av. Inventory Level
How to interpret?
higher => inventory is sold and replenished more quickly => the company is tying up less capital
Cash Conversion Cycle (CCC)
the length of time from the purchase of raw materials to the collection of accounts receivable from customers for the sale of products and services.
Cash2Cash Cycle Time
an indicator of how efficiently a company manages its assets to improve cash flow.
Calculated:
Days’ Inventory Outstanding + Days’ Sales Outstanding - Days’ Payable Outstanding
Days’ Inventory Outstanding
(Average Inventory/COGS) x 365
Days’ Sales Outstanding
(Average Accounts Receivable/Net Credit Sales) x 365
Days’ Payables Outstanding
(Average Accounts Payable/COGS) x 365
Total factor productivity
a measure of productivity (of a department, plant, BU…) that combines the individual productivities of all its resources, including labor, capital, energy, material, and equipment. These individual factor productivities are often combined by weighting each according to its monetary value and then adding them.