Understanding Heat Transfer: Conduction in Solids
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Conduction
The transfer of thermal energy through matter, from high to low temperature, without the movement of matter.
Heat (thermal) energy store
A commonly used form of energy that can be transferred through conduction, convection, and infrared radiation.
Thermal Conduction
The process by which hot particles vibrate more and collide with cooler particles, transferring thermal energy.
Thermal Source
An origin of heat that causes particles to gain energy and vibrate more.
Thermal conductivity
A material property that indicates how much thermal energy per second (J/s, or Watts) a substance can conduct.
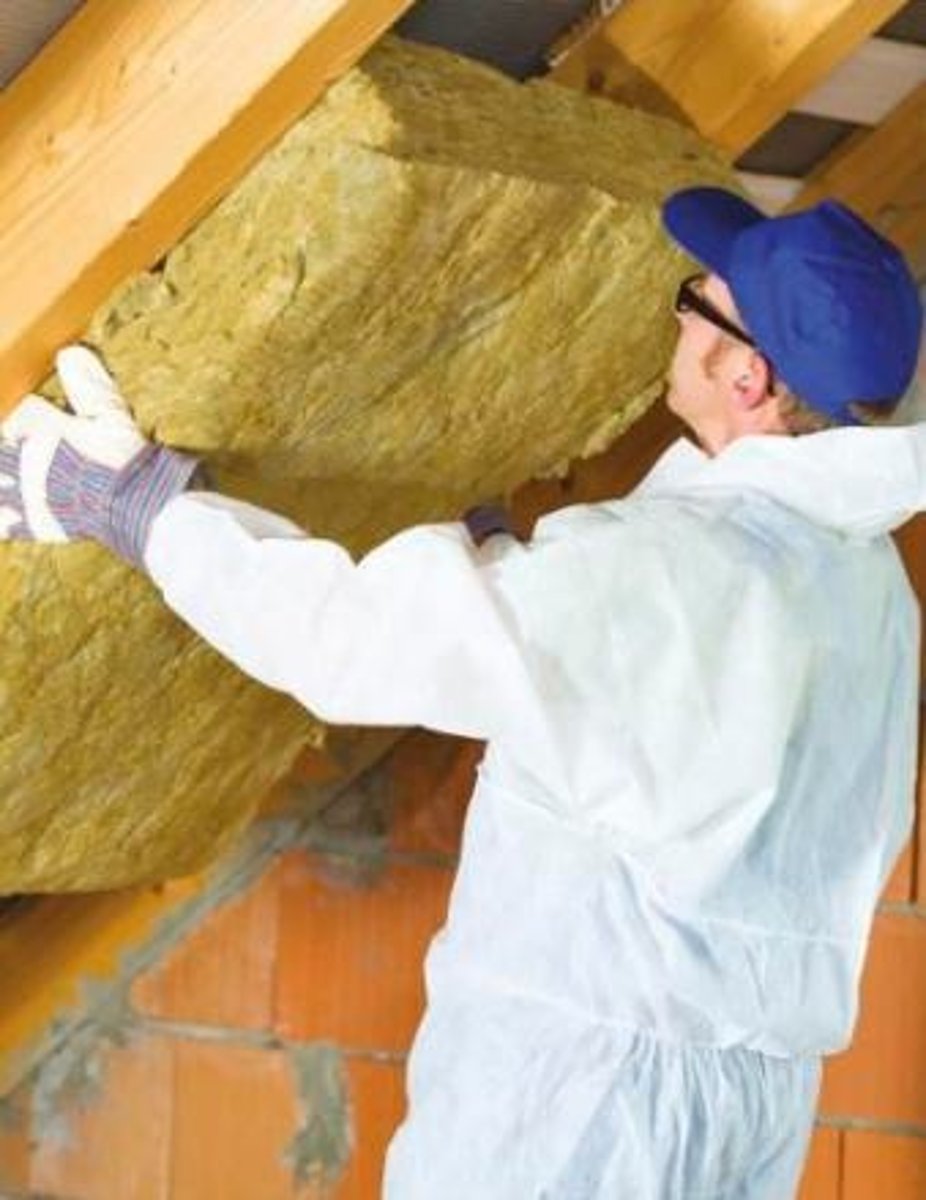
Insulators
Materials that are bad conductors of heat and have low thermal conductivity.
Conductors
Materials that allow heat energy to transfer efficiently, with metals being excellent conductors.
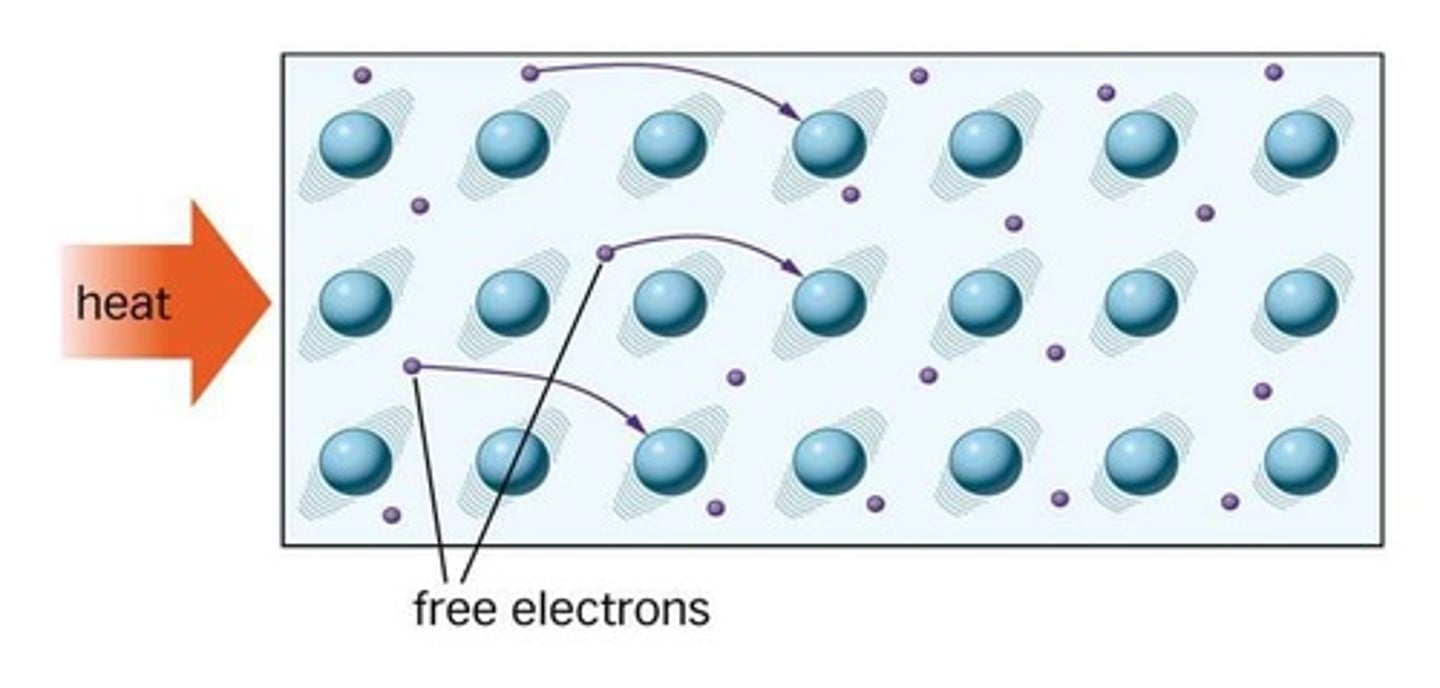
Free electrons
Electrons in metals that can move freely and transfer energy by colliding with vibrating atoms.
Metallic Conductor
A type of conductor that allows energy transfer faster due to free electrons.
Key HEAT Processes
The main methods of heat transfer: conduction, convection (in fluids), and infrared radiation.
Non-metal solids
Materials that are usually poor heat conductors compared to metals.
Gases and liquids
States of matter that are really bad conductors of heat due to particles being much further apart.
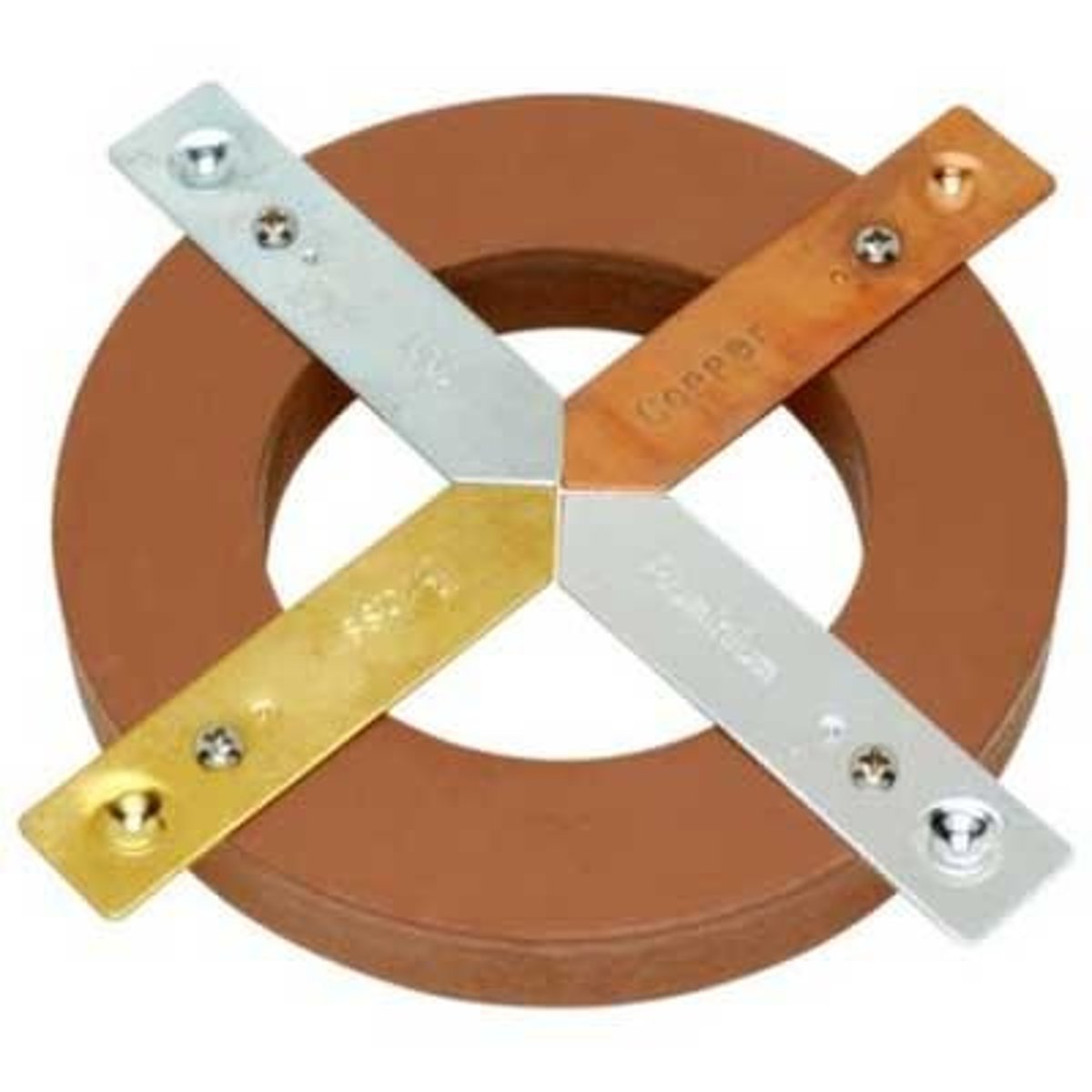
Metal Strips Experiment
An investigation to determine if all metals conduct heat at the same speed and which is the best conductor.

Temperature difference
The variation in temperature across a material that affects the effectiveness of an insulator.
Thickness of material
A factor that influences the insulating properties of a material.
Thermal conductivity of the material
A characteristic that determines how well a material can conduct heat.
Wood vs Metal Spoon
Wood feels warmer than metal at room temperature because it does not transfer heat energy well.
Particle-to-particle transfer
The method of heat transfer in solids where hot particles collide with cooler neighbor particles.
Vibrating particles
Particles that gain energy and vibrate more when heated, contributing to thermal conduction.
Conclusion of Metal Strips Experiment
All metals are good conductors, but some are better than others based on their thermal conductivity.
Keeping warm in winter
An application of insulation to reduce heat loss from homes.

R-A-G
A method to update organizers with understanding of each topic.