Human A&P1, Chapter 8
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Joints
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Classes of Joints (by movement)
Diarthrosis, amphiarthroses, and synarthroses
Diathrosis
Freely moveable (limbs, appendicular skeleton)
Amphiarthroses
Slightly moveable
Synthroses
Immovable (stable, axial skeleton)
How joints are joined
Fibrous joints - collagen fibers cross gap between bone matrices
Cartilaginous joints - bones held together by cartilage
Synovial joints - bones separated by lubricating synovial fluid
Fibrous joints
Immovable, joined by connective tissue collagen fibers
No joint cavity, movement depends on length of collagen fibers
Suture, Syndesmosis, Gomphosis
Cartilaginous joints
Immovable, joined by cartilage
No joint cavity
Synchondroses (synarthrotic), Symphyses (amphiarthrotic)
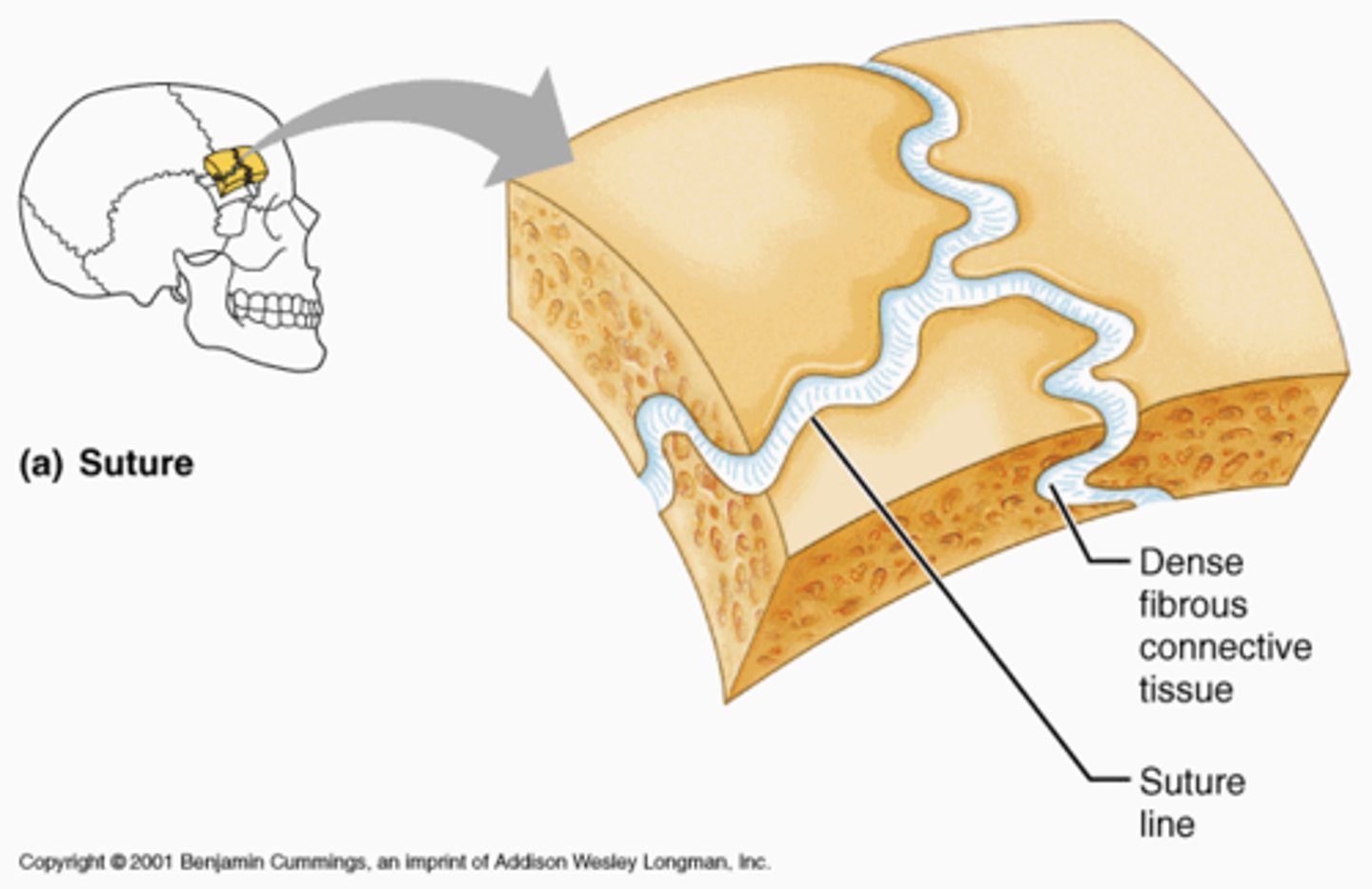
Suture
“Seam”, filled with connective fibers (consistent with periosteum)
Fibrous joint between flat bones of the skull
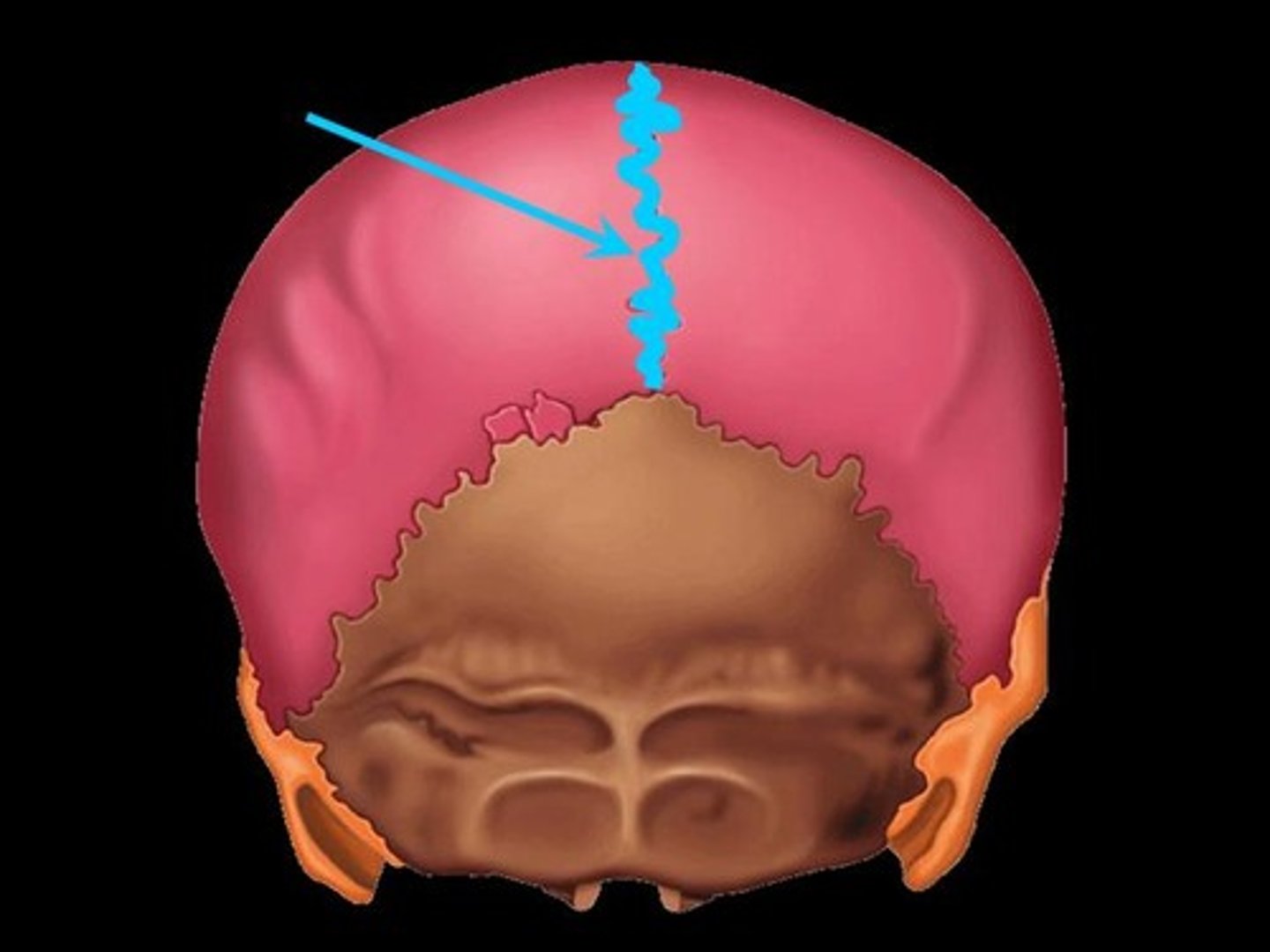
Synostoses
A completely ossified joint; skull bones become a fused joint, occurs at middle age, is protective
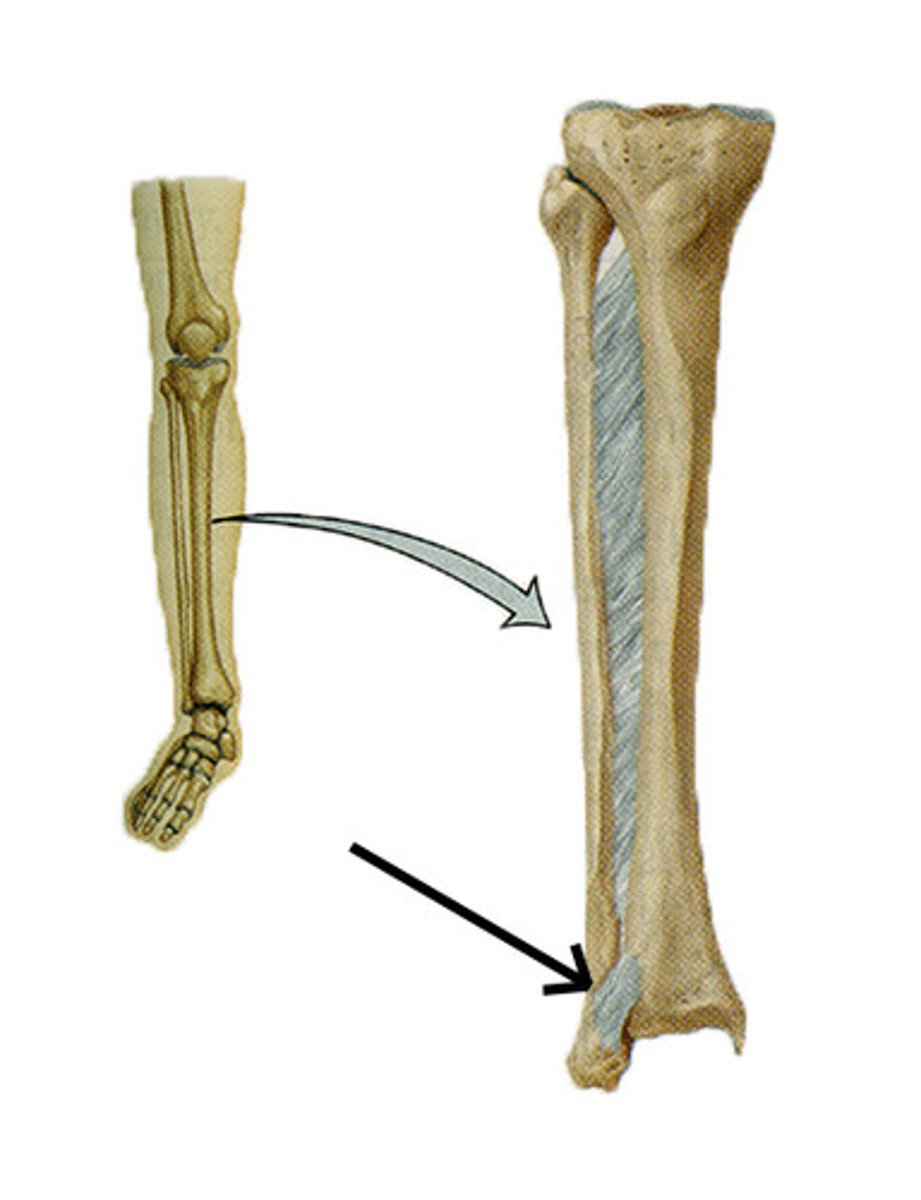
Syndesmosis
Fibrous joint bones united by ligament cords or fibrous connective tissue
Movement depends on connecting fiber lengths: Short fibers (ends of tibia + fibula) = little to no movement/give, long fibers (interosseous membrane) = large amount of movement
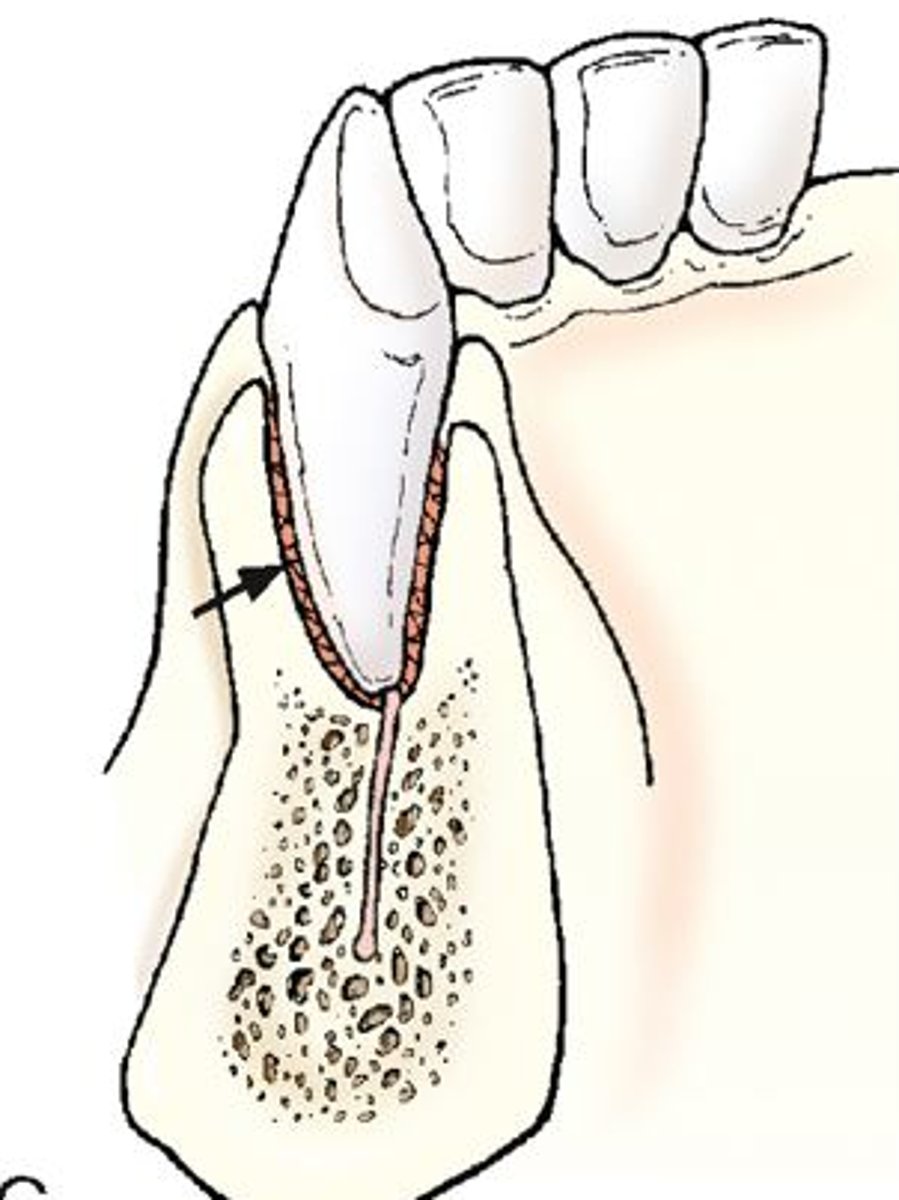
Gomphosis
Fibrous “peg-in-socket” joint such as a tooth (alveolar socket)
The way teeth are embedded in their socket (hammered in
Periodontal ligament is fibrous connection
Synchondroses (synarthotic) joints
Cartilaginous joint, immovable, bones united by hyaline cartilage
“Junction of cartilage”
Epiphyseal plates (in children’s long bones, temporary; eventually become synostoses), joint between costal cartilage (1st rib) + manubrium of sternum
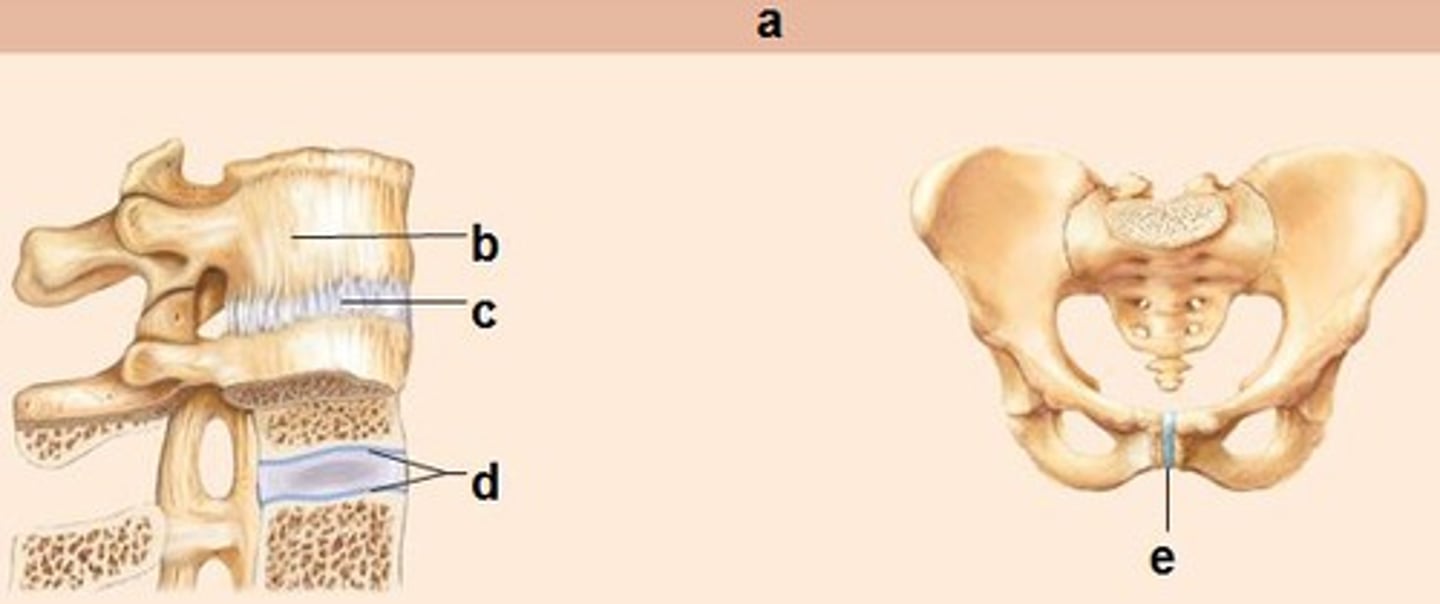
Symphyses (amphiarthrotic) joints
Cartilaginous joint, slightly movable, strenght and flexibility bones united by fibrocartilage (+ hyaline in articular joints)
Intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis of pelvis
Fibrocartilage
Compressible + Resilient, acts as shock absorber and permits limited amount of movement at joint, main element of symphyses
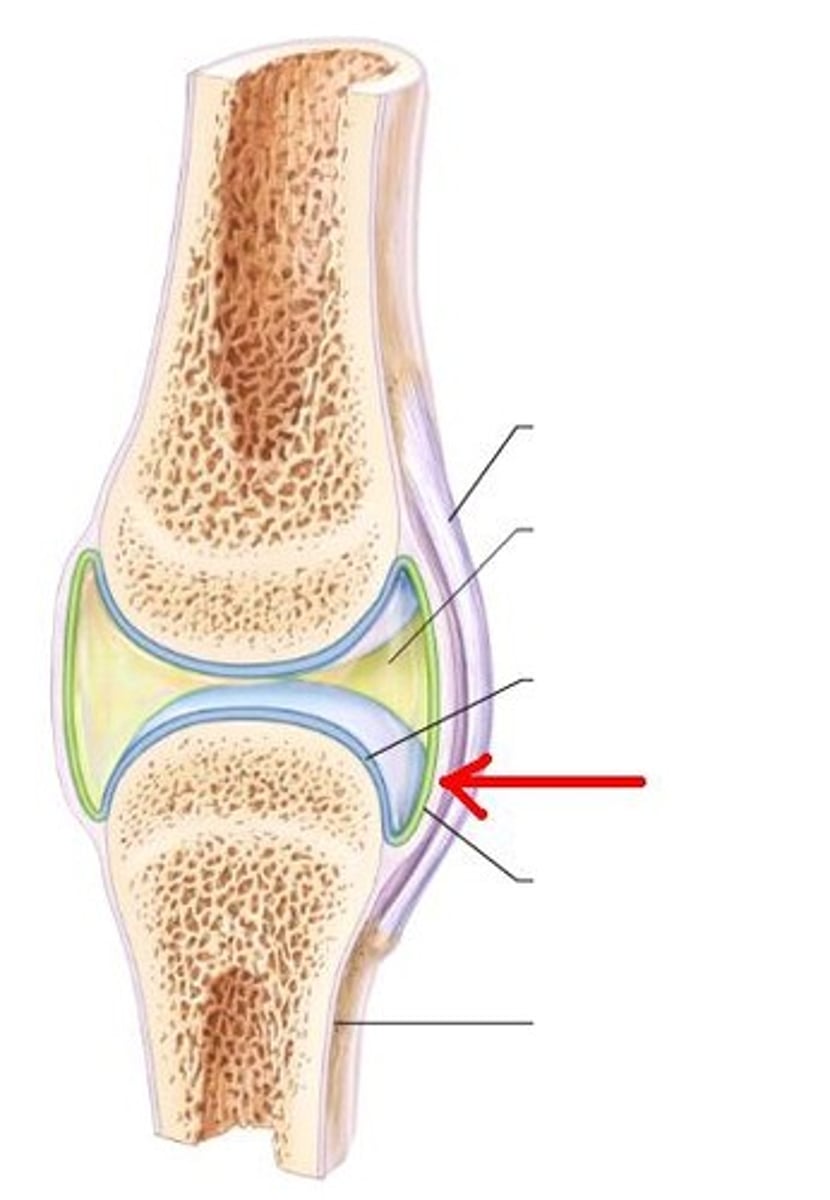
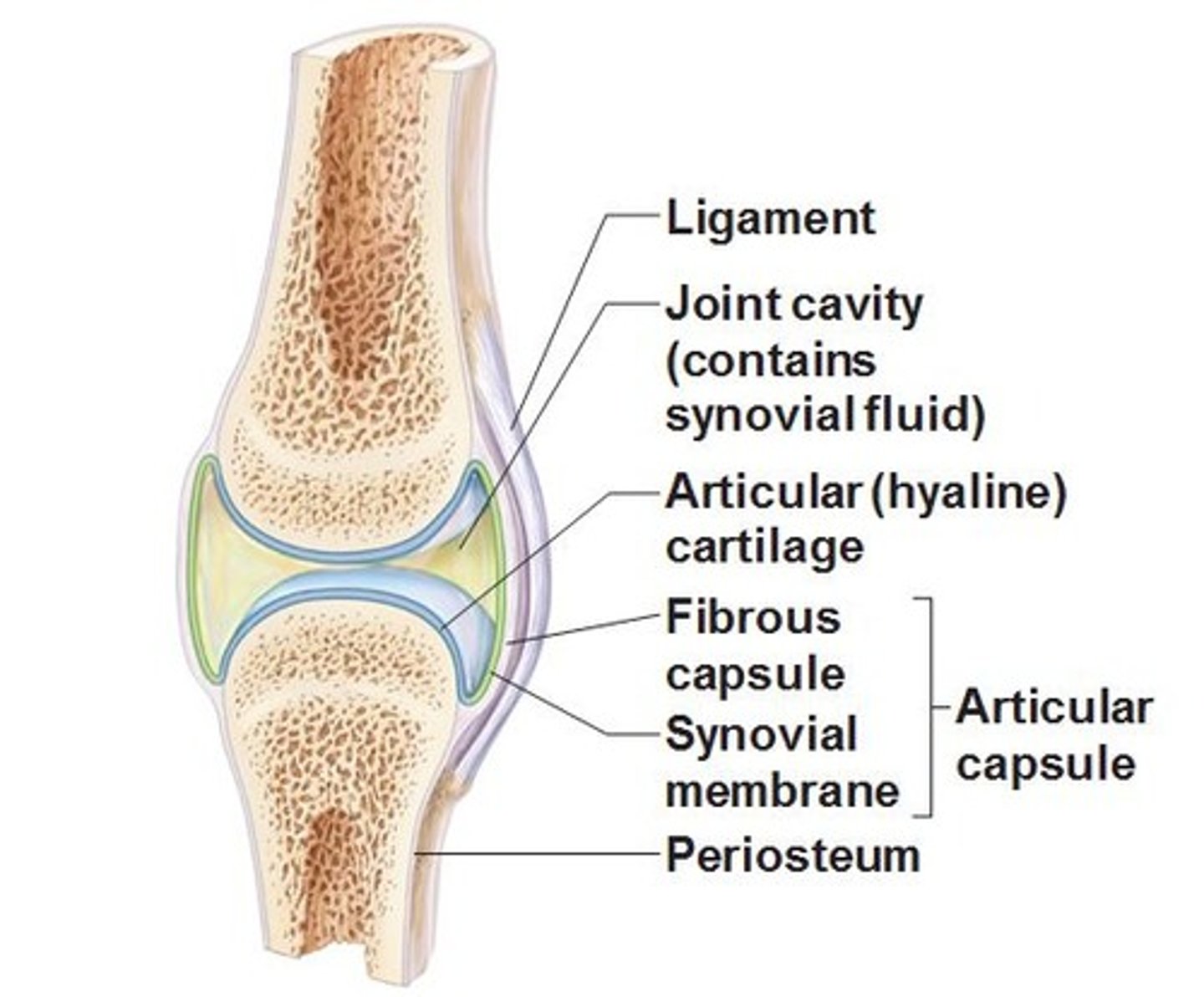
Synovial joints
- Bones separated by a fluid-filled joint cavity
- Adjoining surfaces of bones covered in hyaline cartilage
- Joint capsule encloses the cavity
- Certain joints have a fibrocartilage pad (meniscus)
- Fluid-filled bursae underlie certain muscles
Shoulder, knee, and hip (freely movable)
Synovial fluid
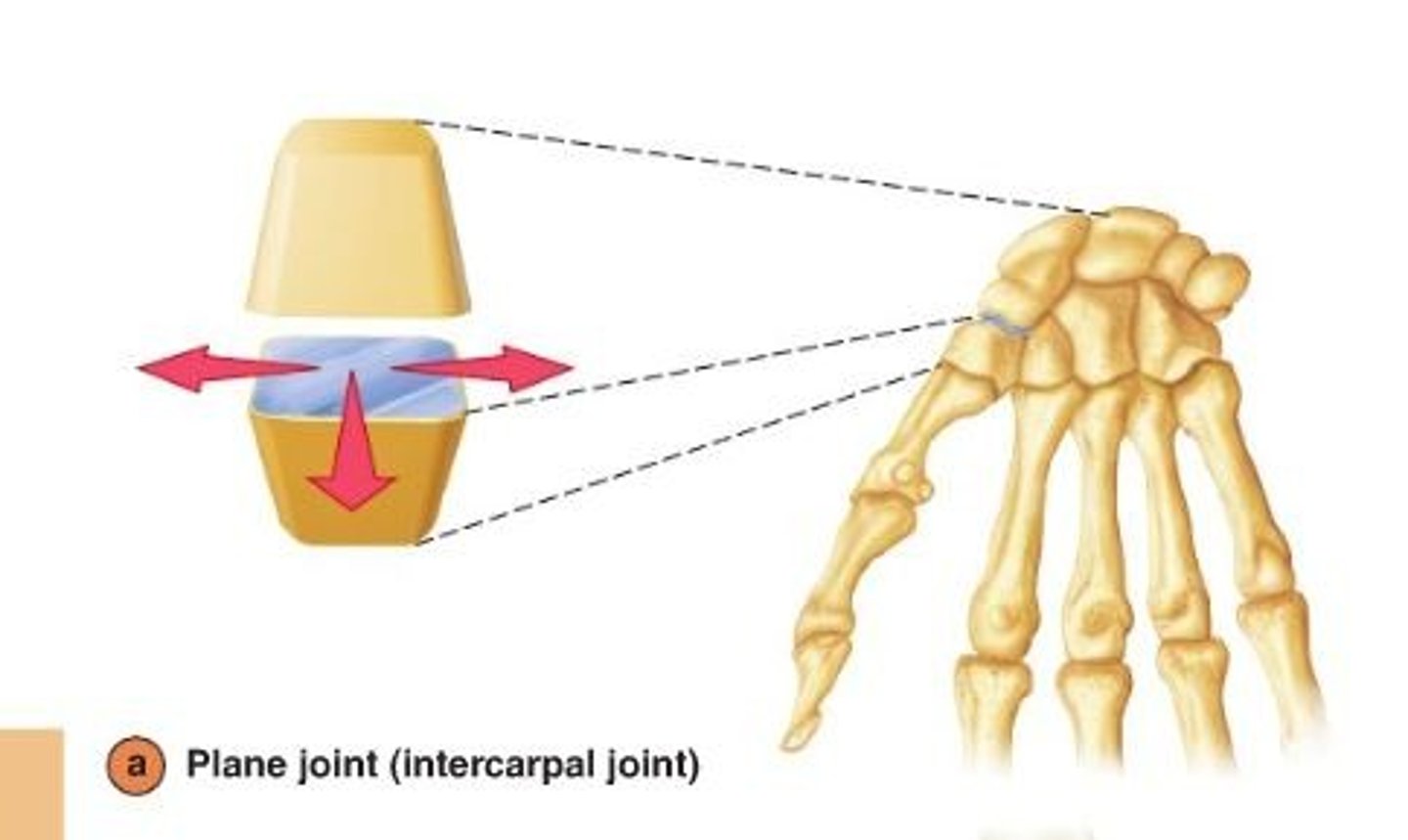
plane synovial joint
flat surface (interracial/tarsal joints and vertebrocostal joints of ribs 2-7)
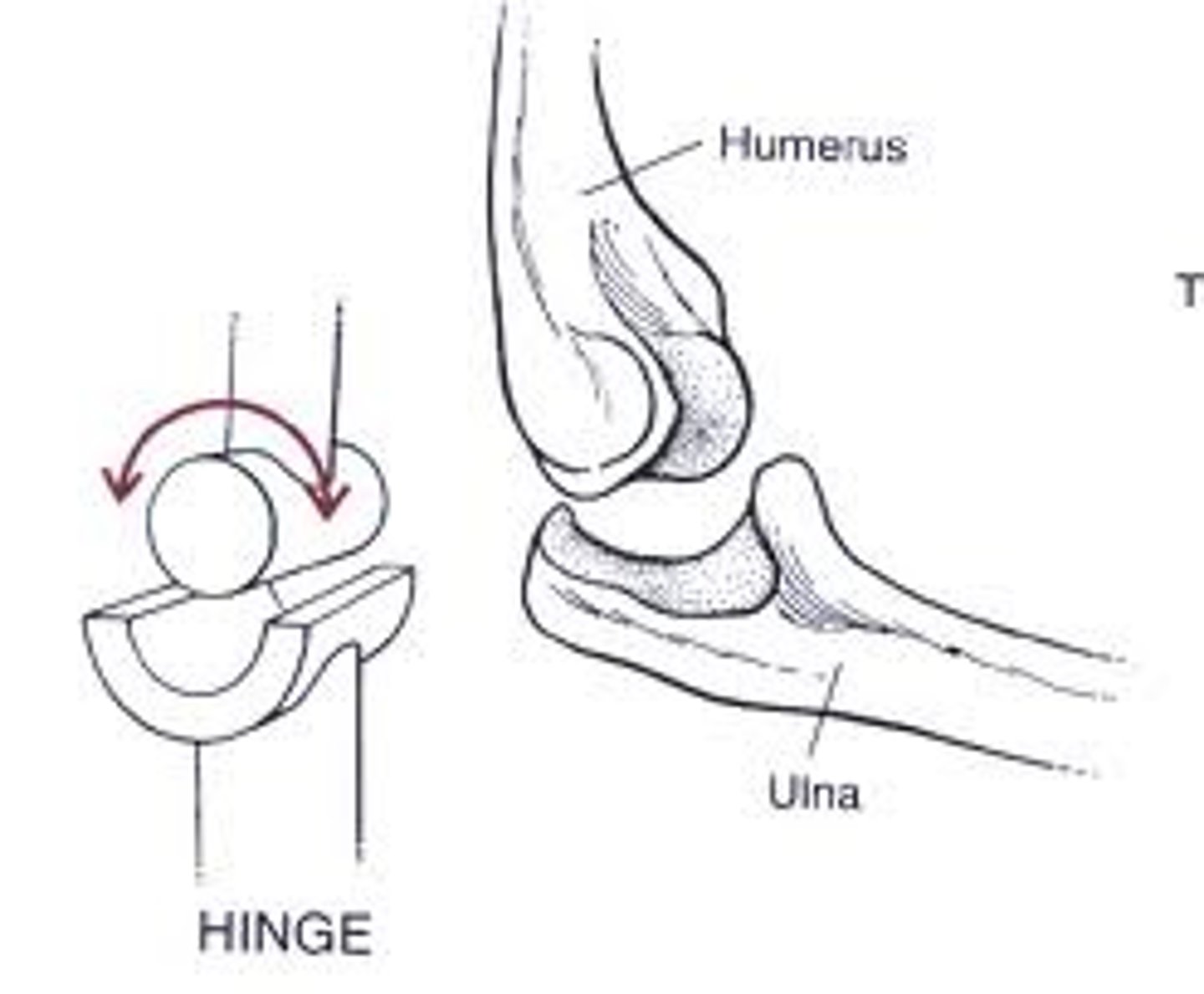
hinge synovial joint
Uniaxial; EX - elbow, ankle, knee, interphalangeal
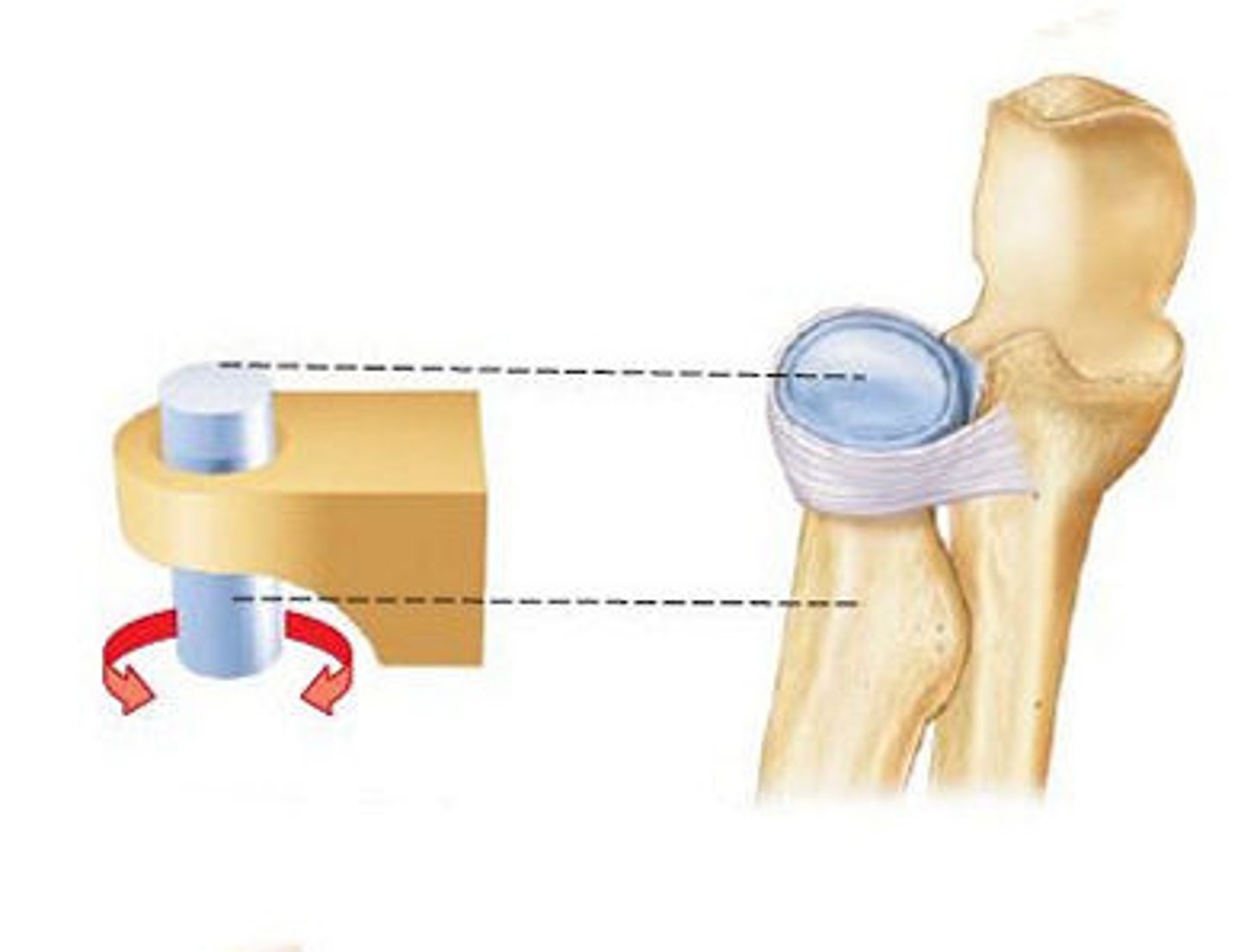
pivot synovial joint
One bone moving around the other (Top of your vertebrae)
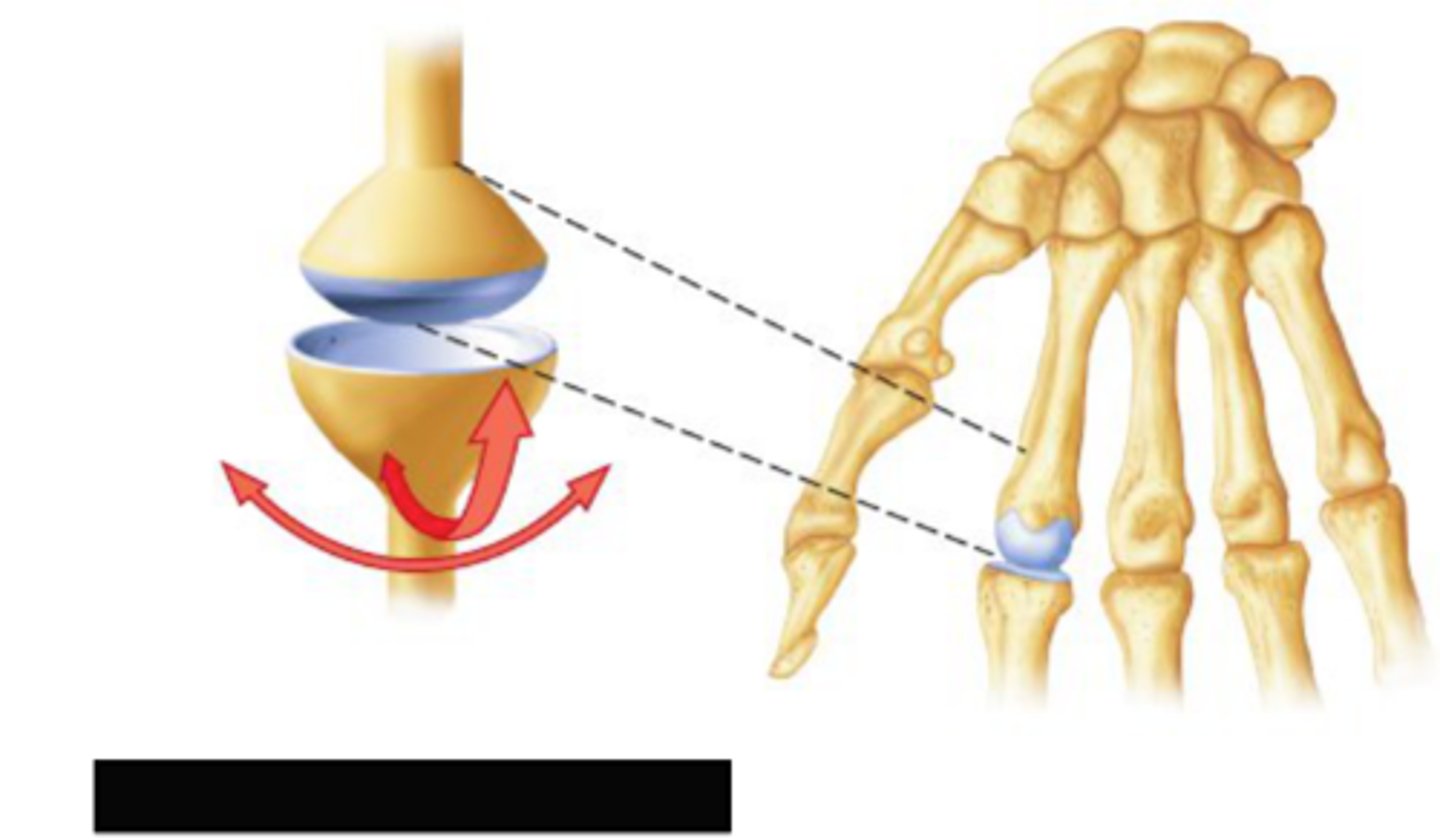
condylar synovial joint
Biaxial; Modified ball-socket; Articular surfaces are ellipsoid instead of spherical; range of motion limited almost to hinge and restricts rotation EX - atlantooccipital, radiocarpal (wrist), TMJ (multiaxial)
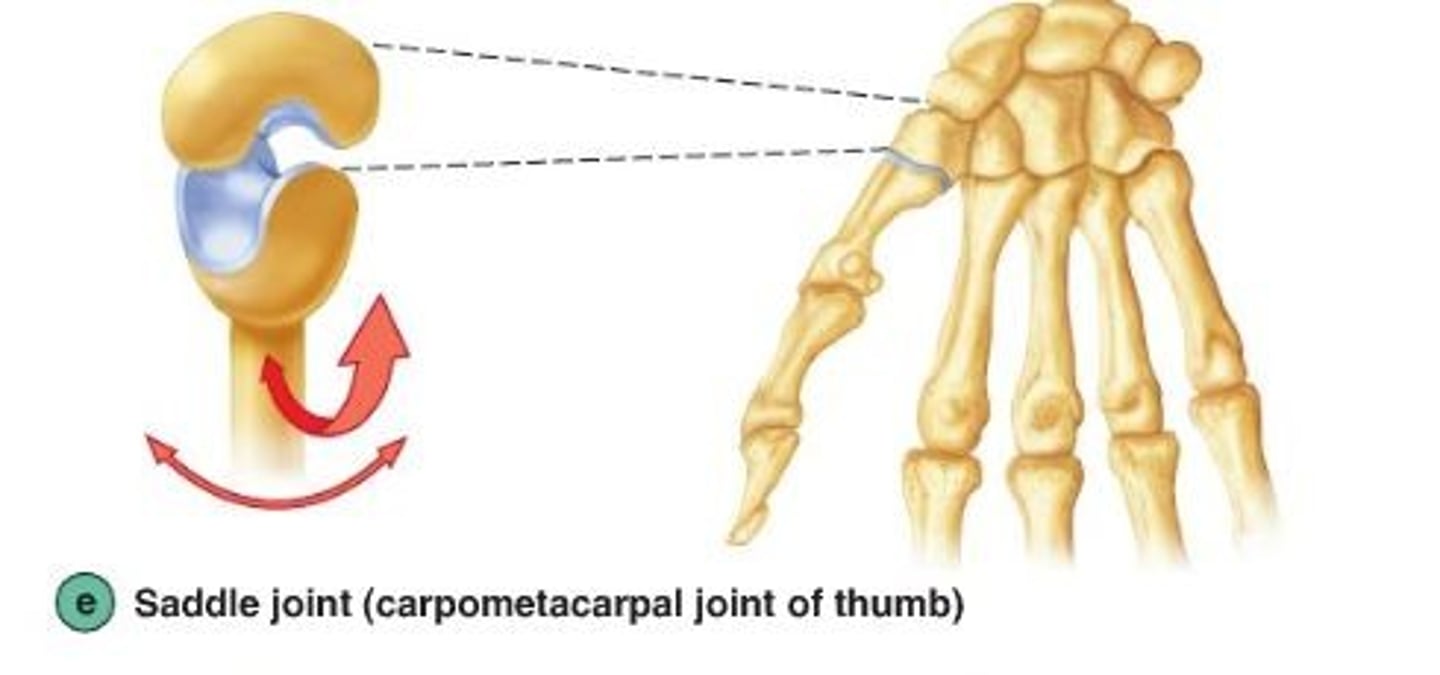
saddle synovial joint
Biaxial; 2 saddle-shaped articulating surfaces oriented at right angles to each other EX - thumb (carpometacarpal pollicis), intercarpal, sternoclavicular
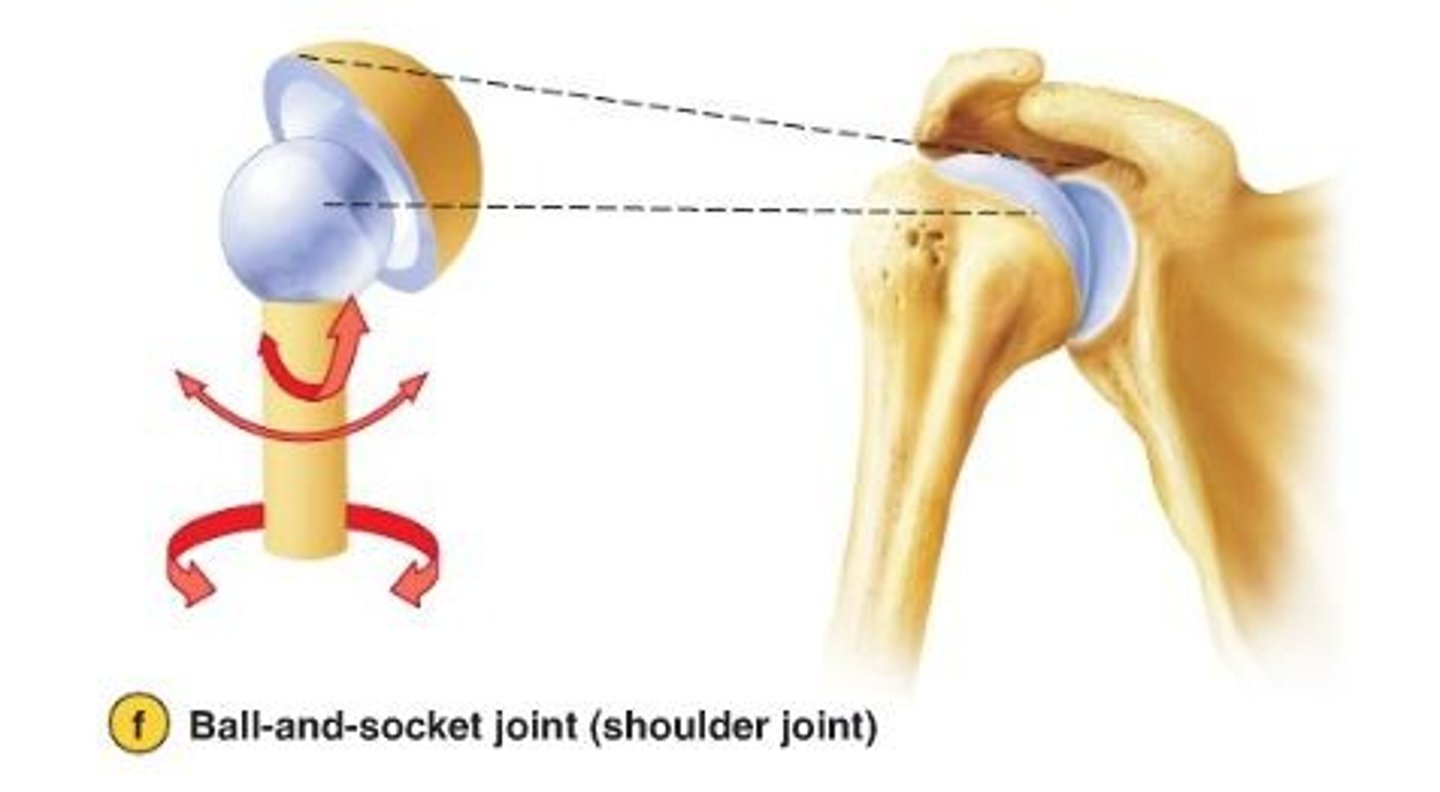
ball and socket synovial joint
Multiaxial; allows a wide range of motion in all directions; EX - shoulder and hip joints
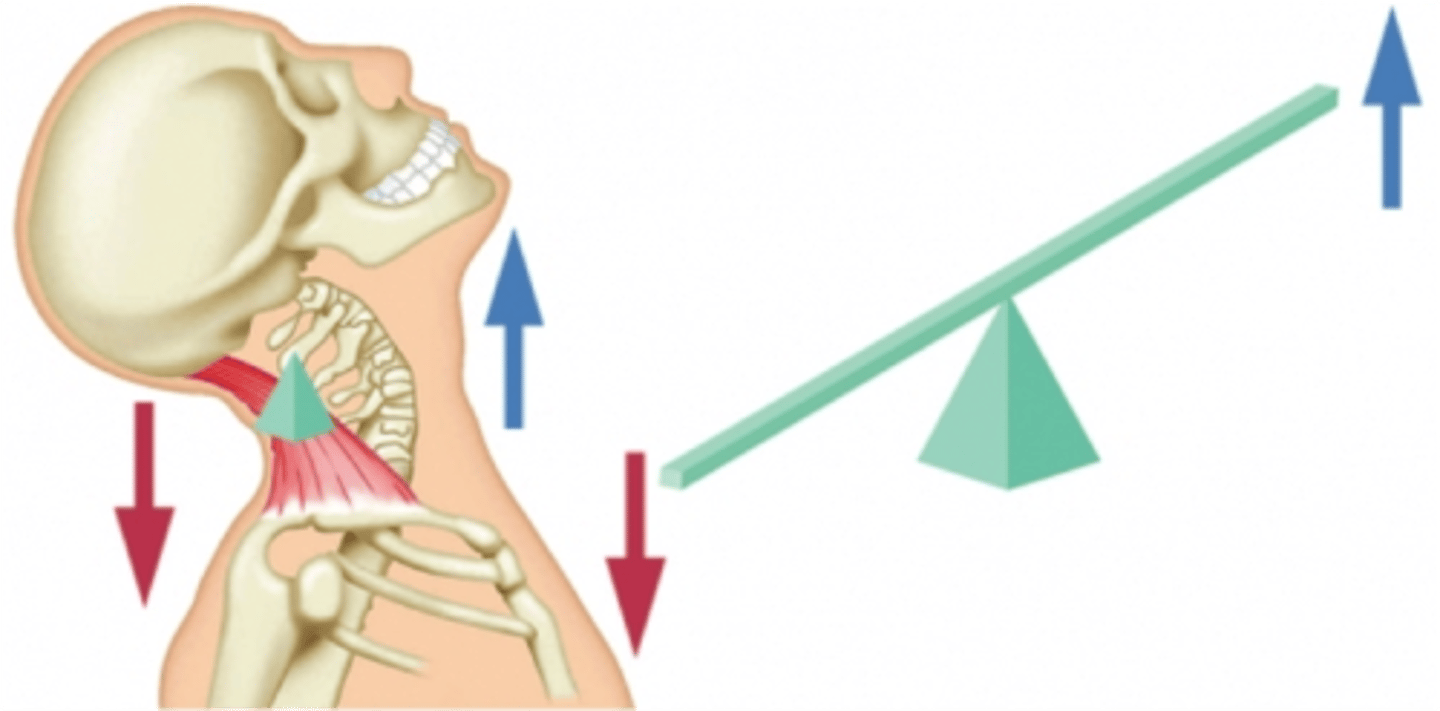
first class lever
The fulcrum is positioned between the effort and resistance
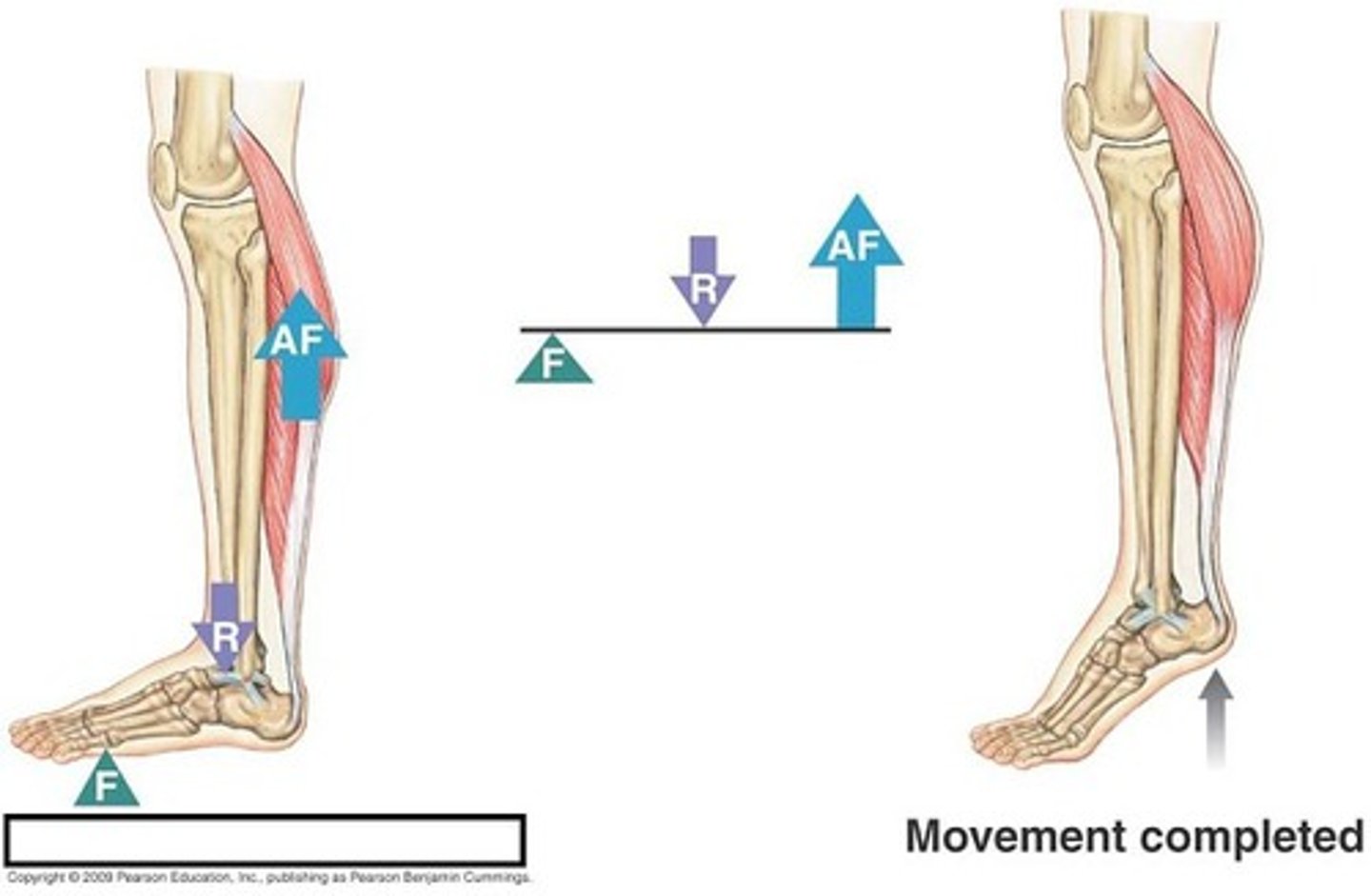
second class lever
the load is between the fulcrum and the effort
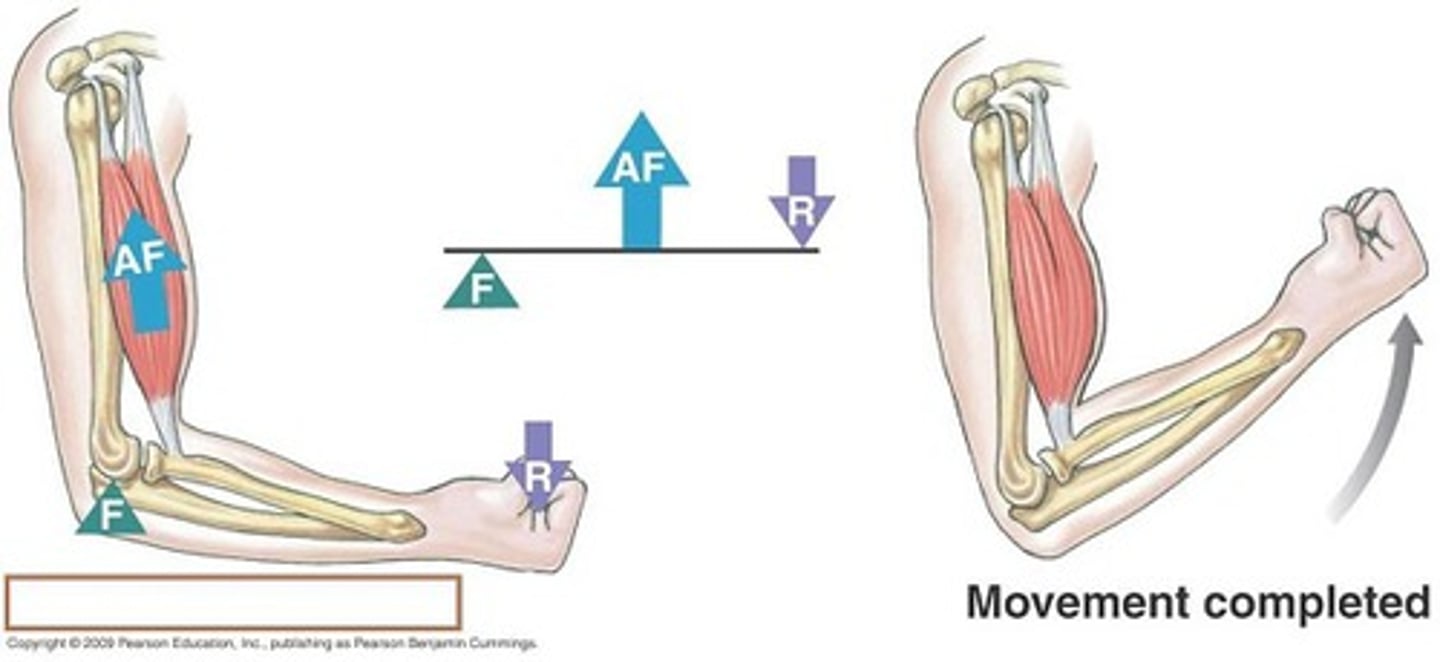
third class lever
The fulcrum is at one end of the bar and the effort is between the fulcrum and the resistance
Flexion
Decreases the angle of a joint
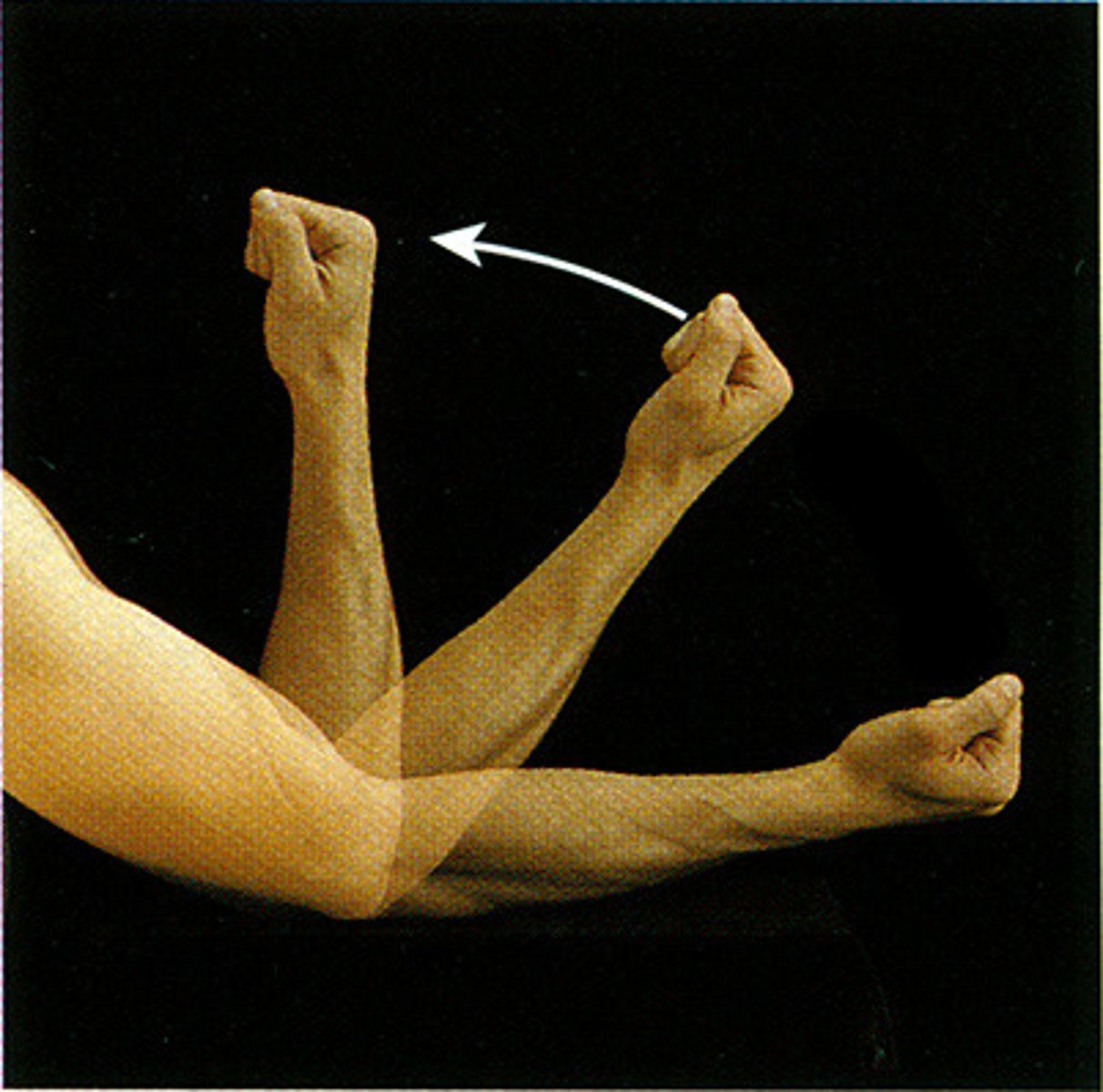
extension
increases the angle of a joint
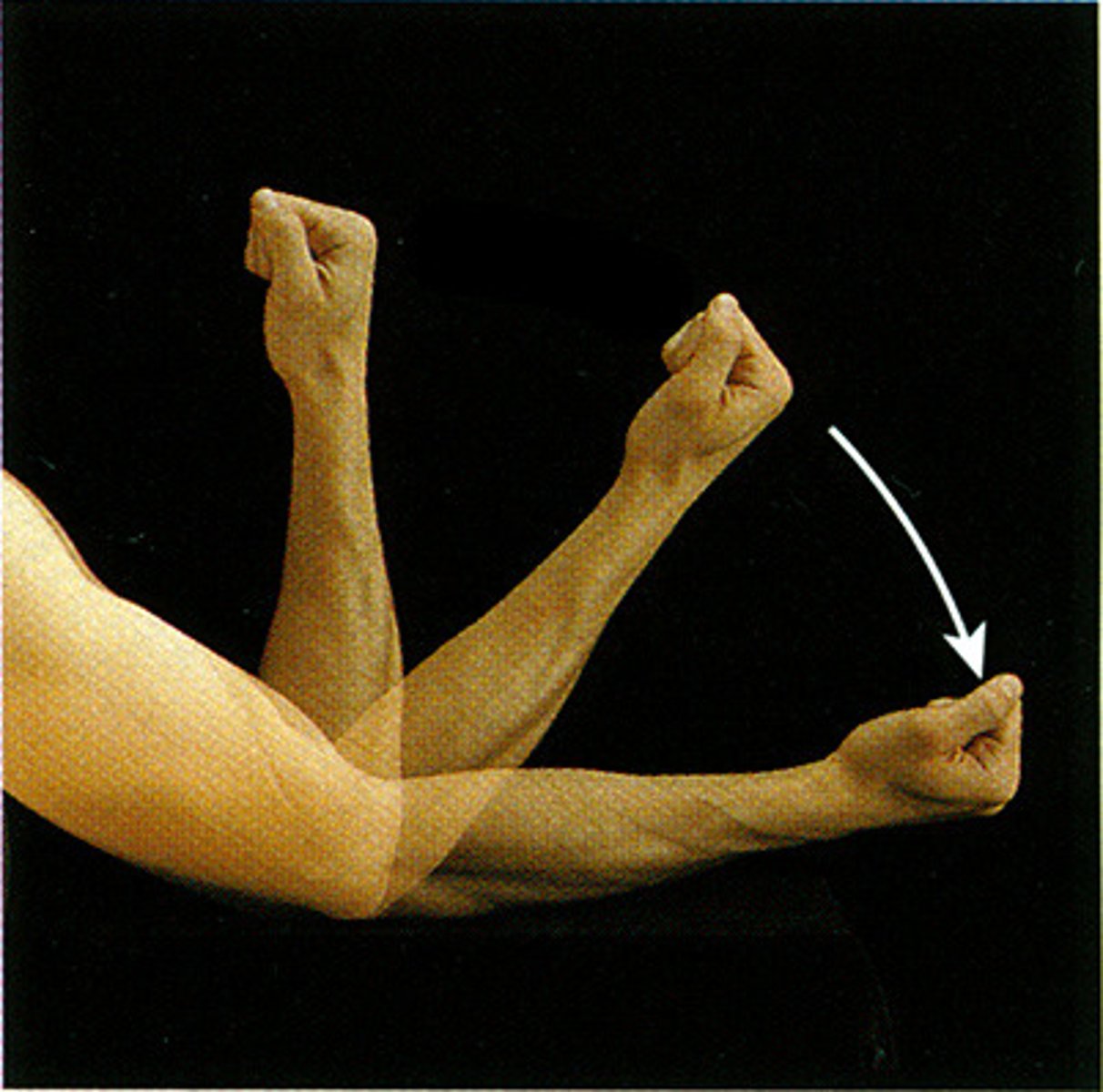
Hyperextension
extension beyond anatomical position
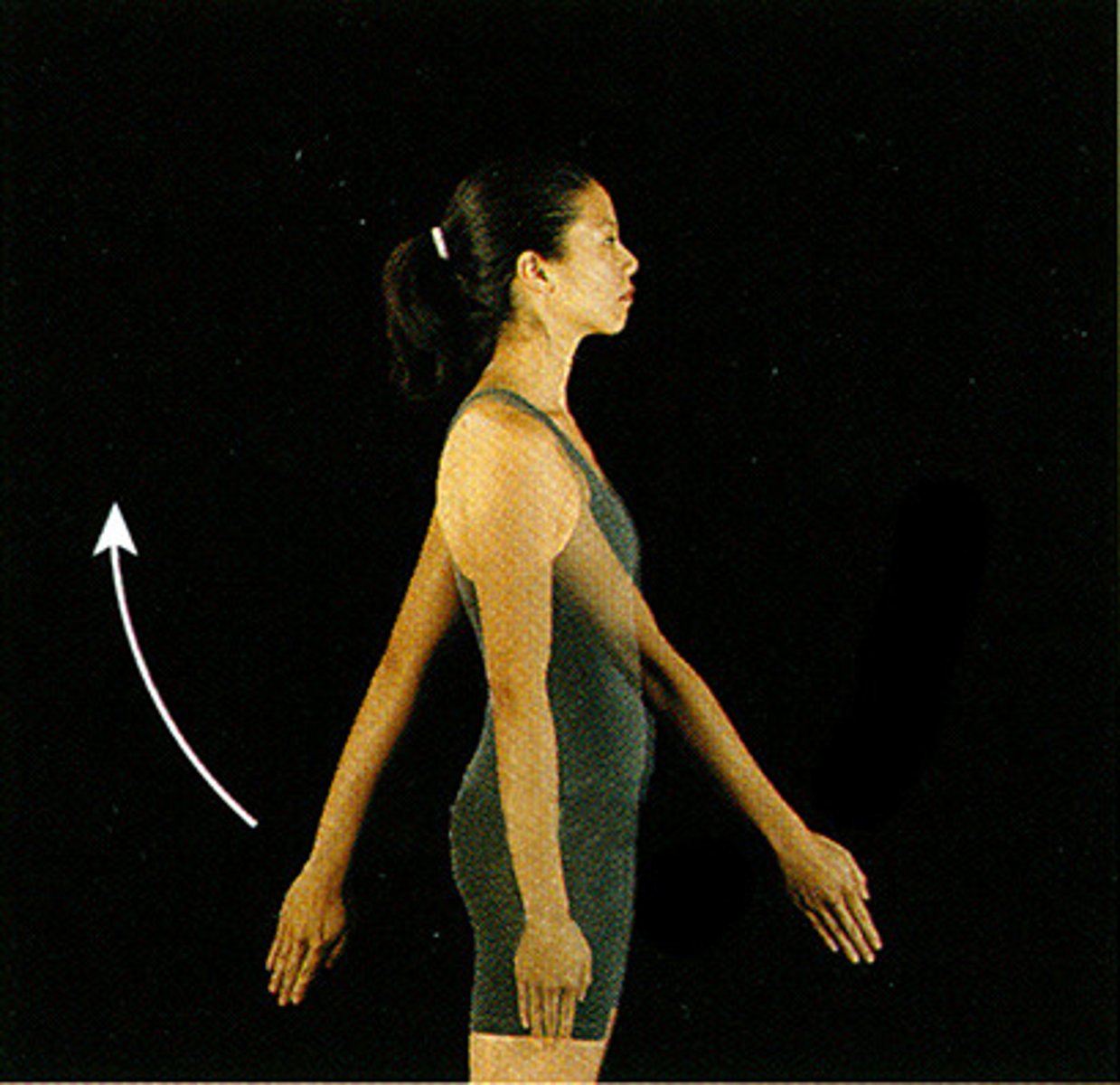
Abduction
Movement away from the midline of the body
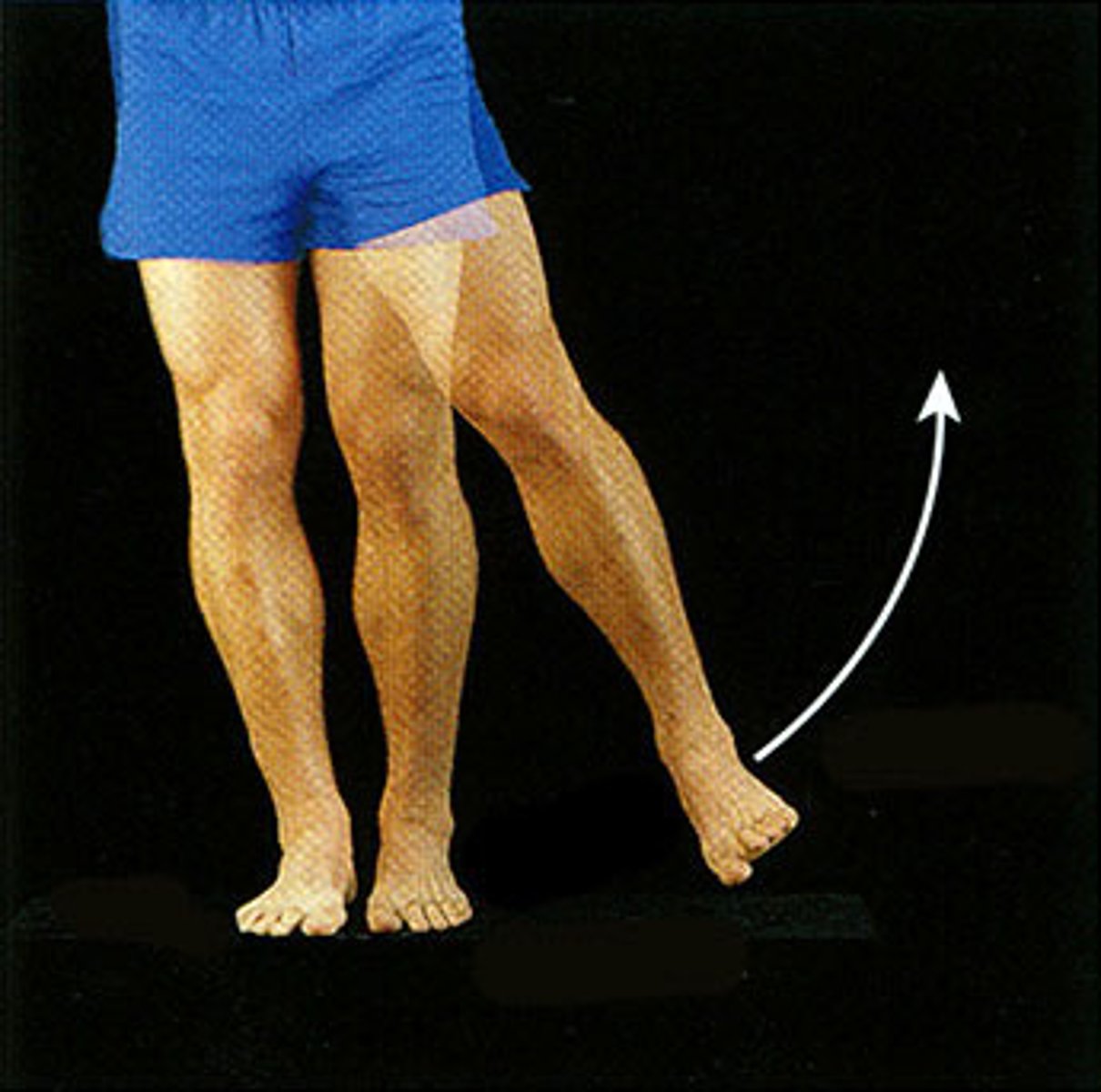
adduction
Movement toward the midline of the body
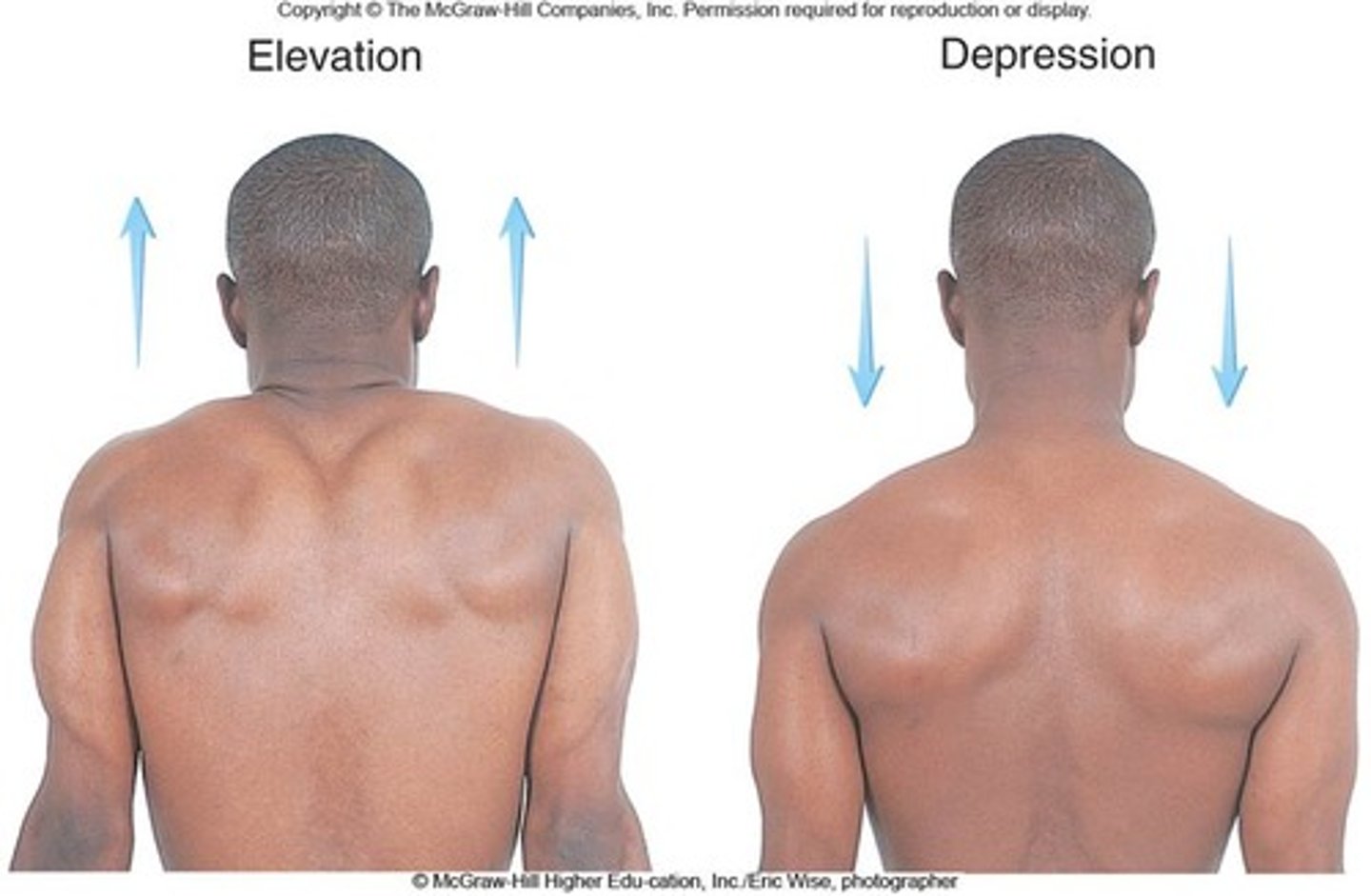
elevation
raising a body part
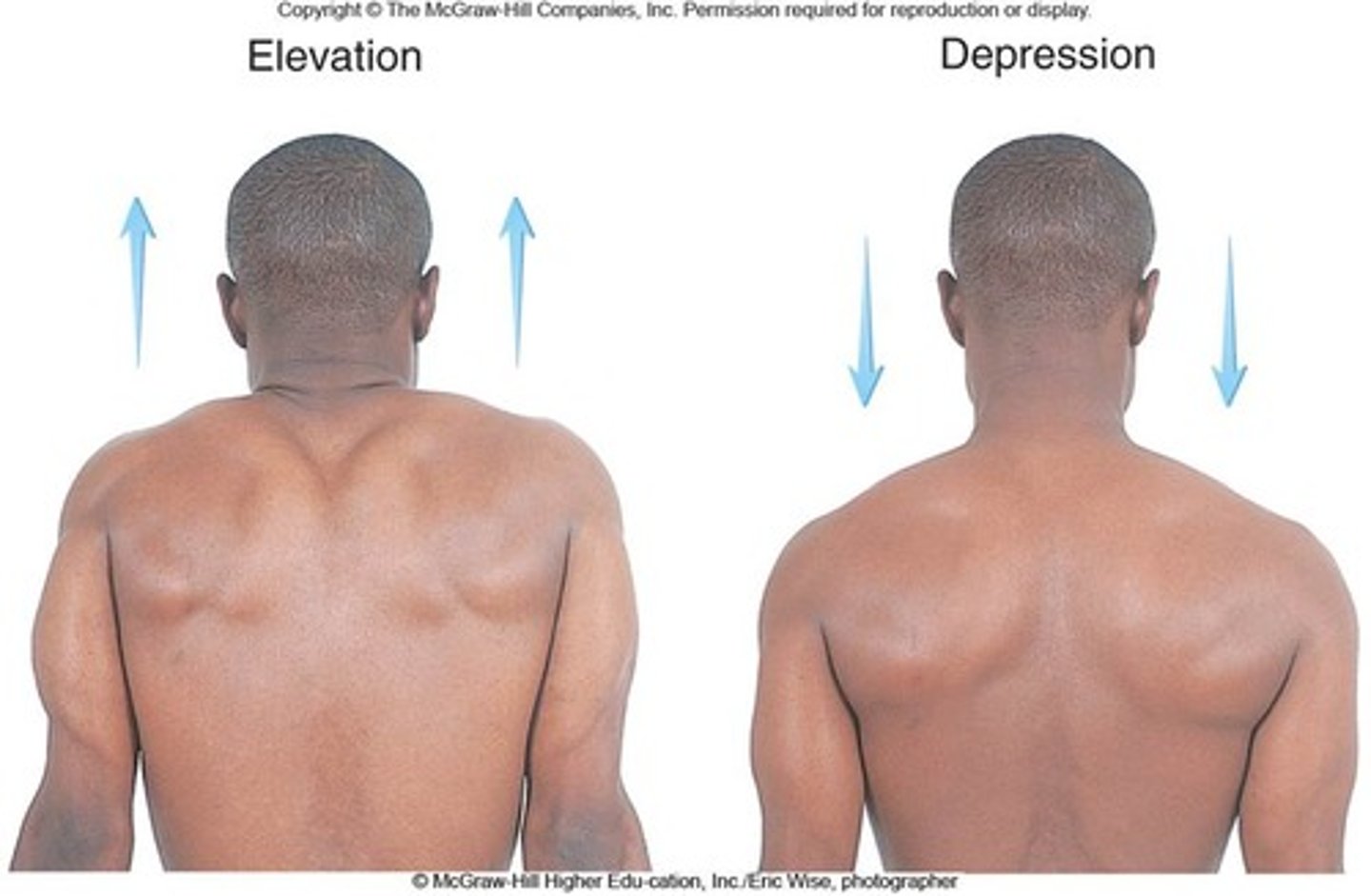
depression
lowering a body part
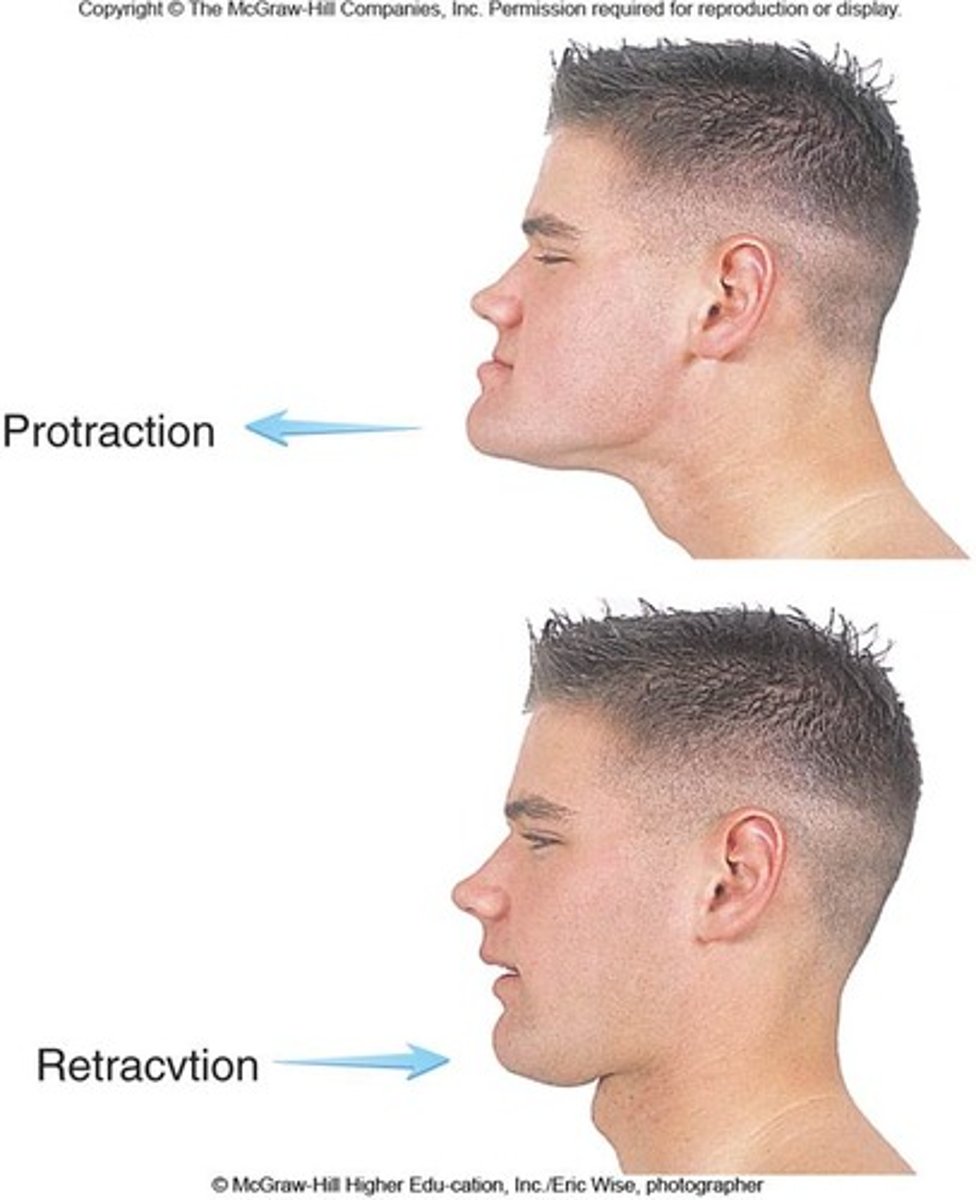
protraction
moving a body part forward and parallel to the ground
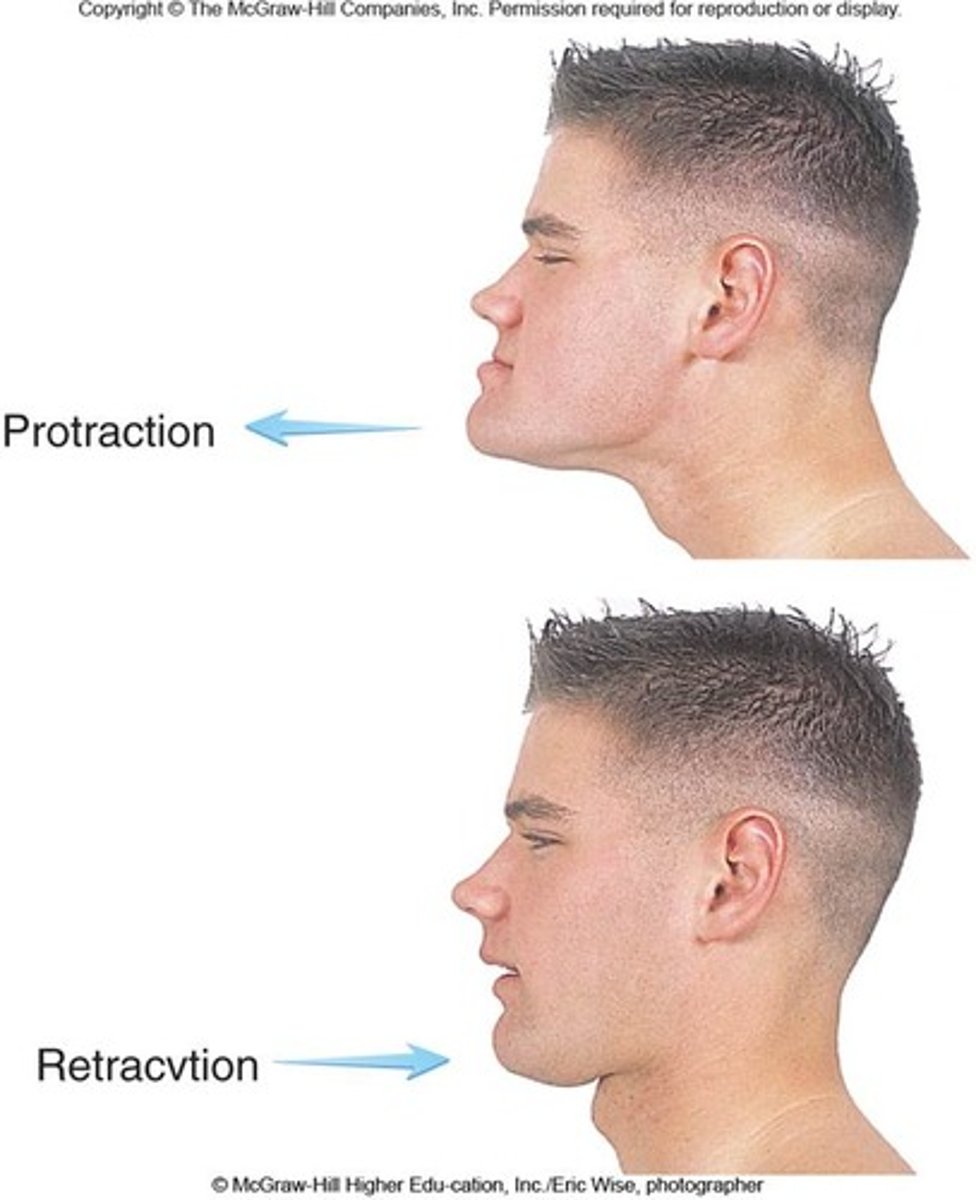
retraction
moving a body part backward and parallel to the ground
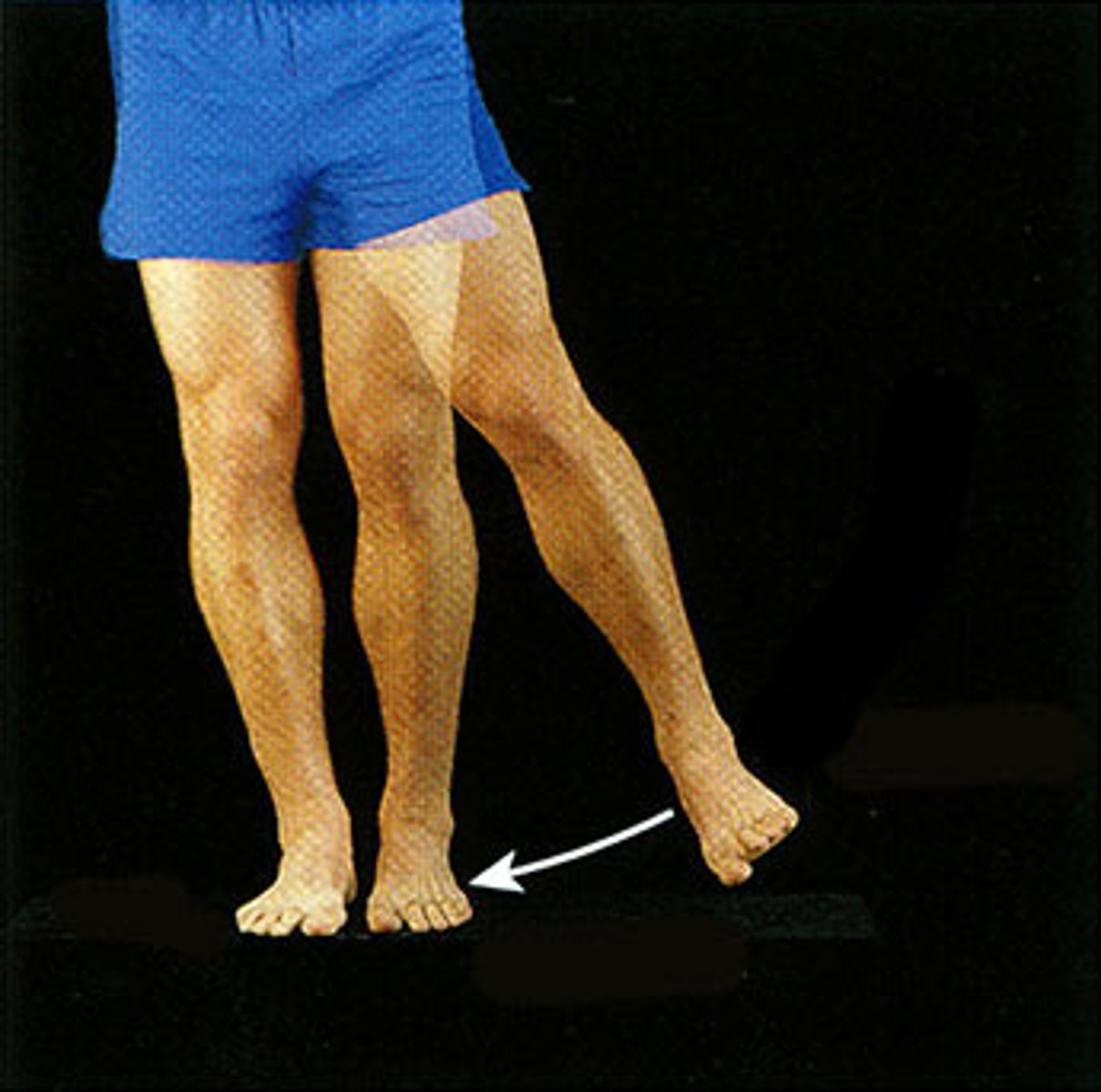
Eversion
turning the sole of the foot outward
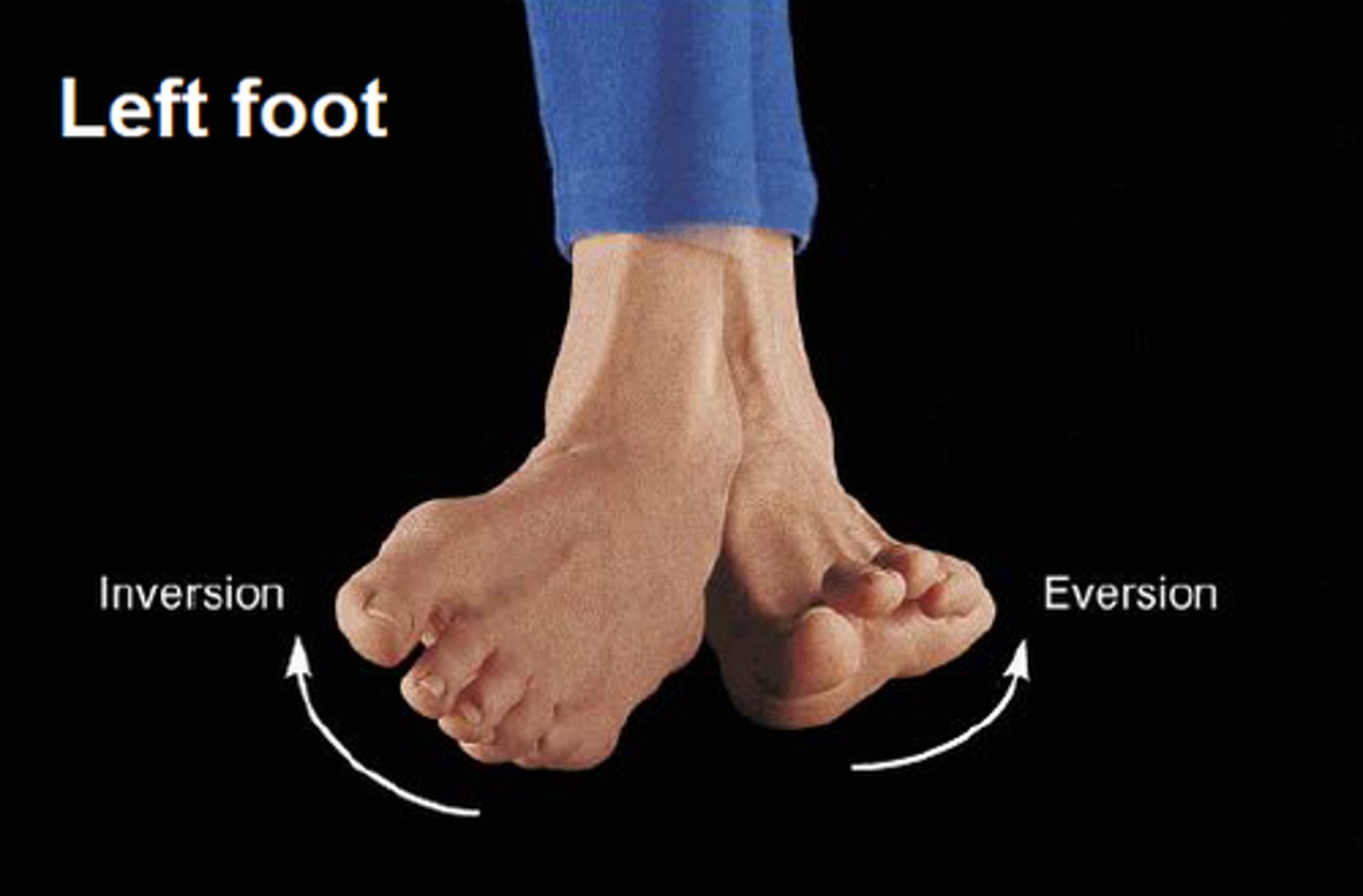
Inversion
Turning the sole of the foot inward
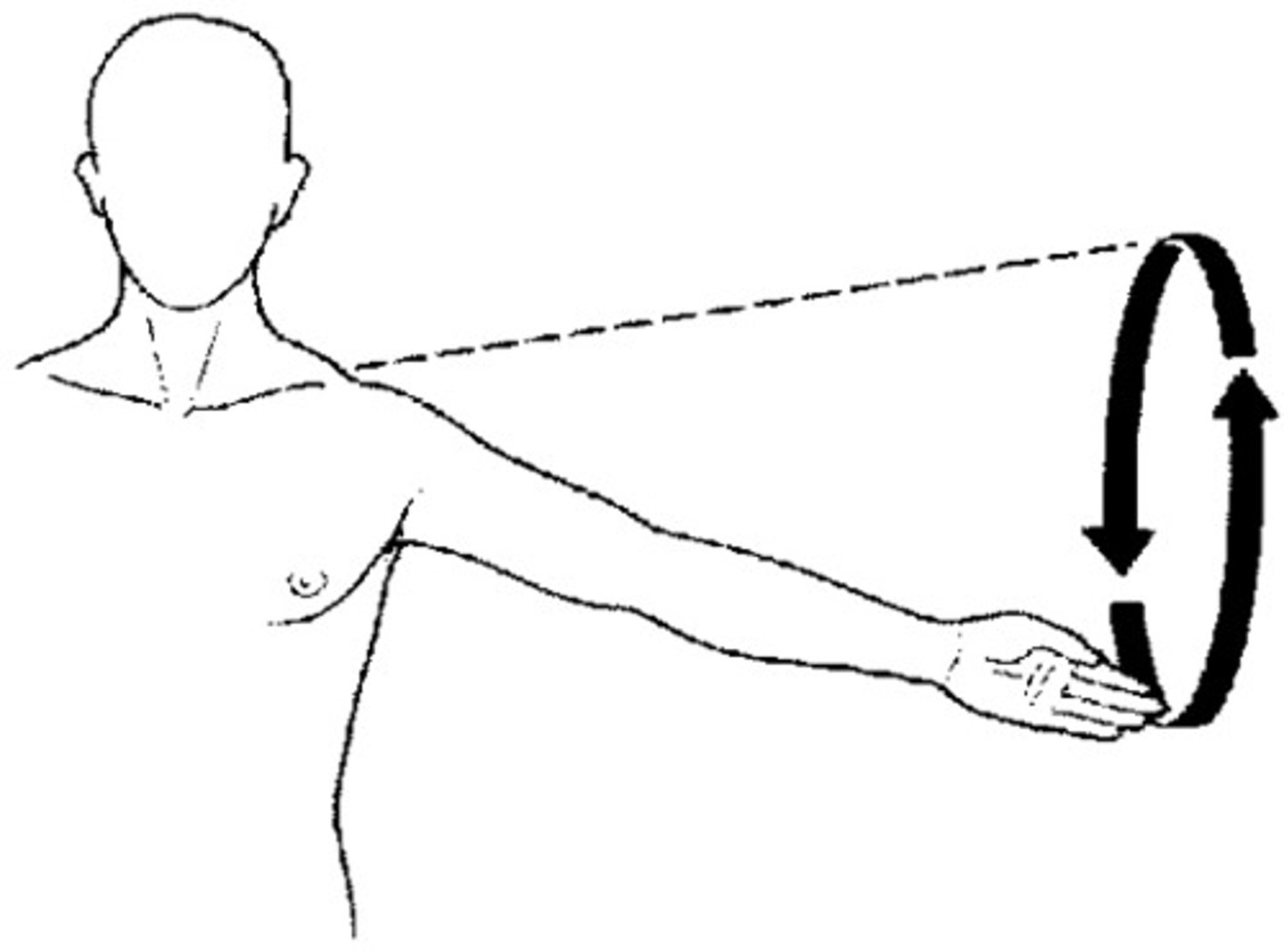
circumduction
the circular movement at the far end of a limb
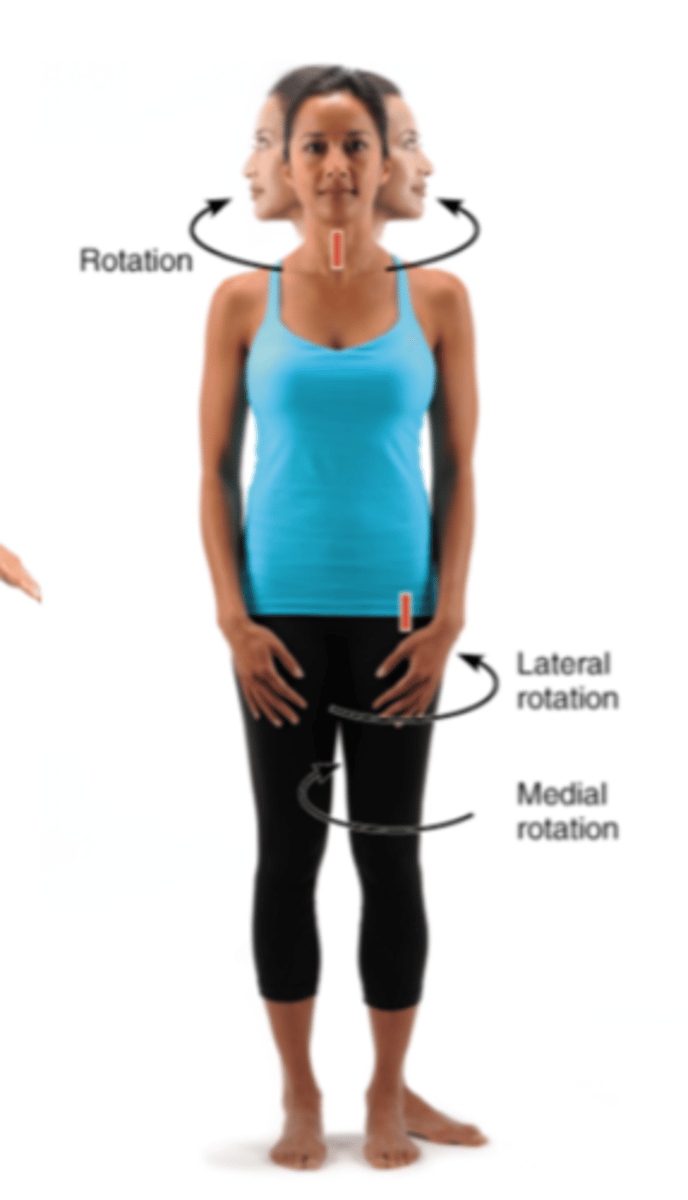
Rotational joint motion
supination
movement that turns the palm up
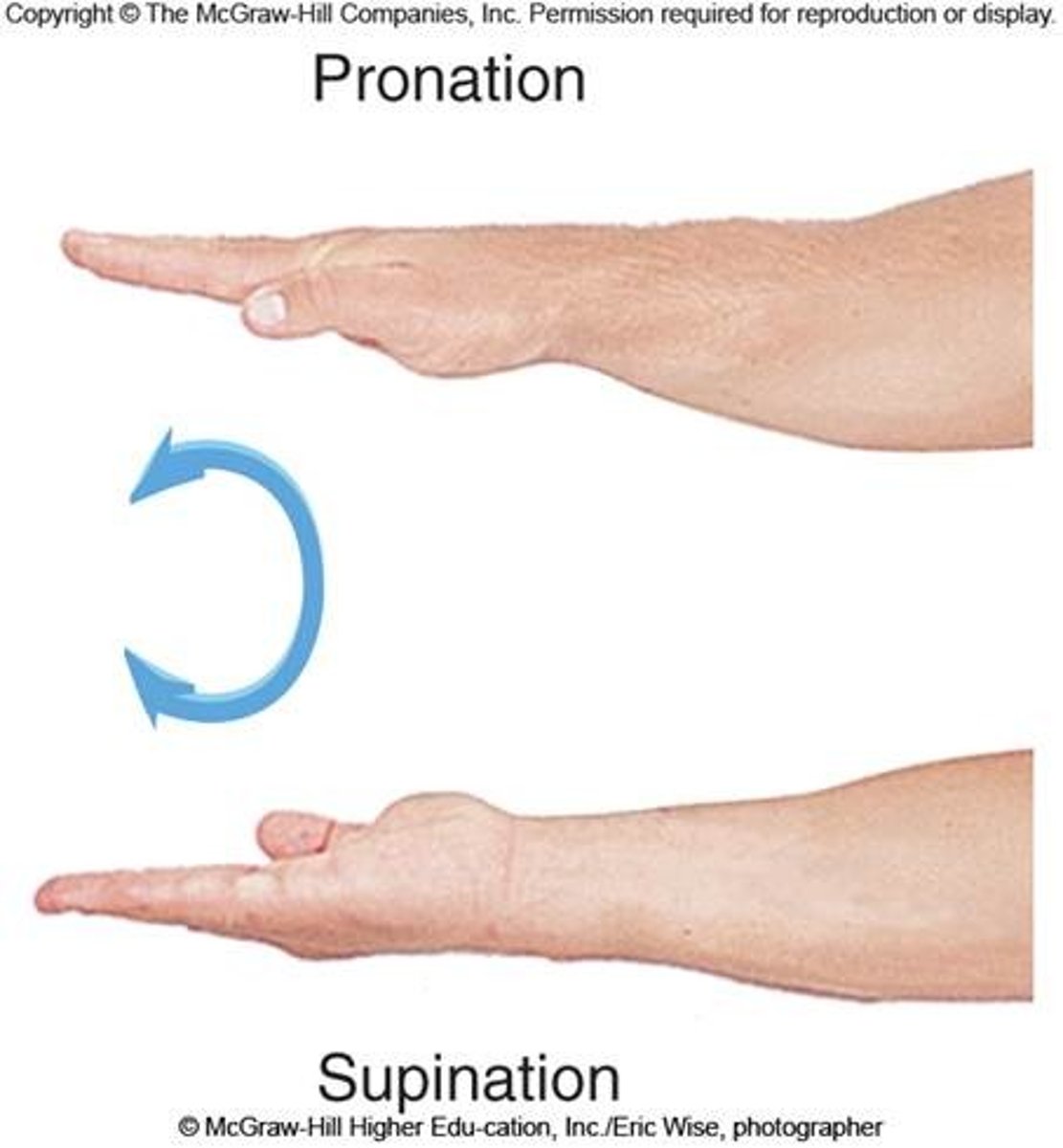
Pronation
palm down
Osteoarthritis
most common chronic arthritis, related to normal aging process, "wear and tear arthritis"
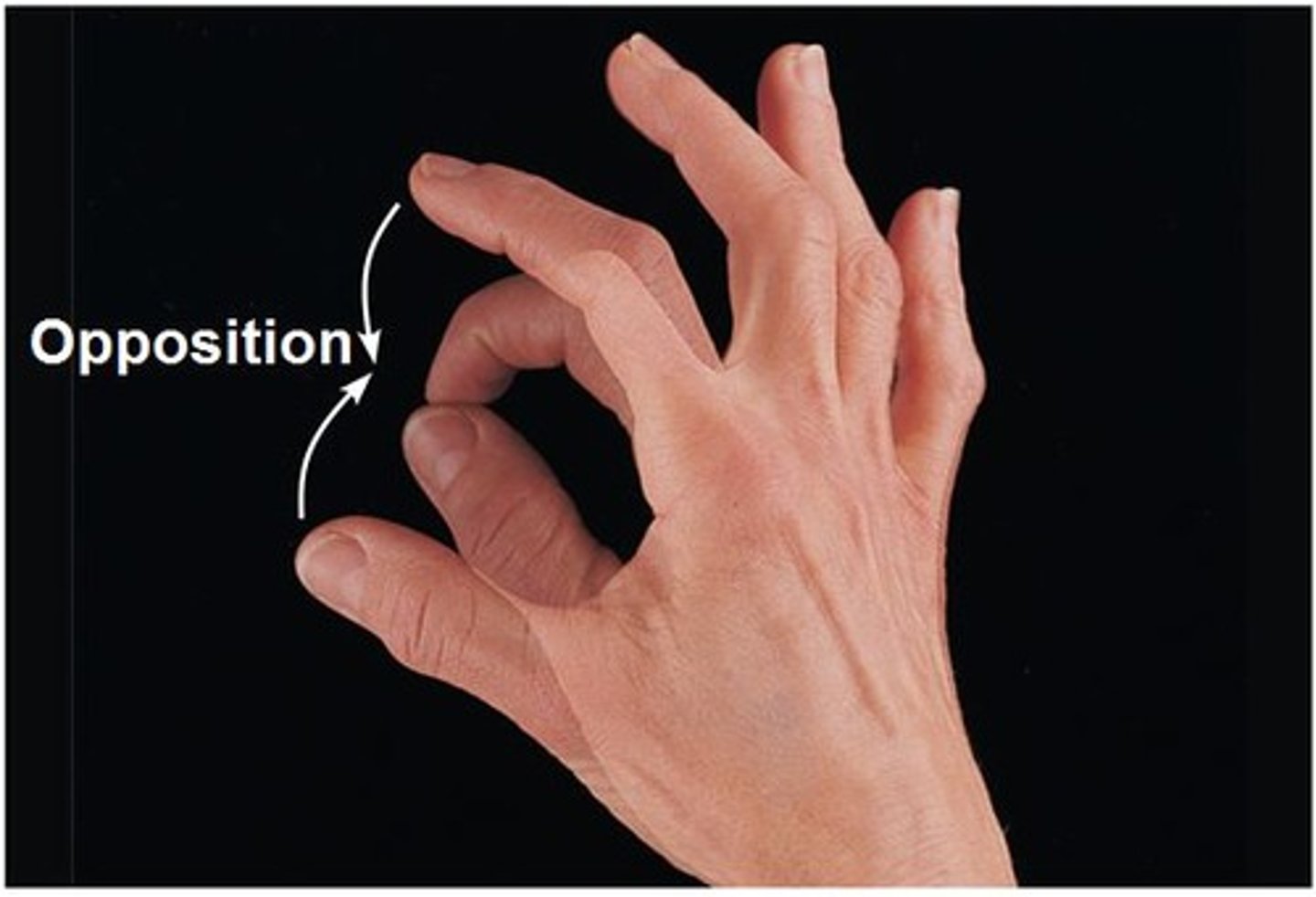
opposition
touching the thumb to any other finger
rheumatoid arthritis
autoimmune disease (immune system attacks the joints), symptoms begin with bilateral inflammation of certain joints, often leans to deformities
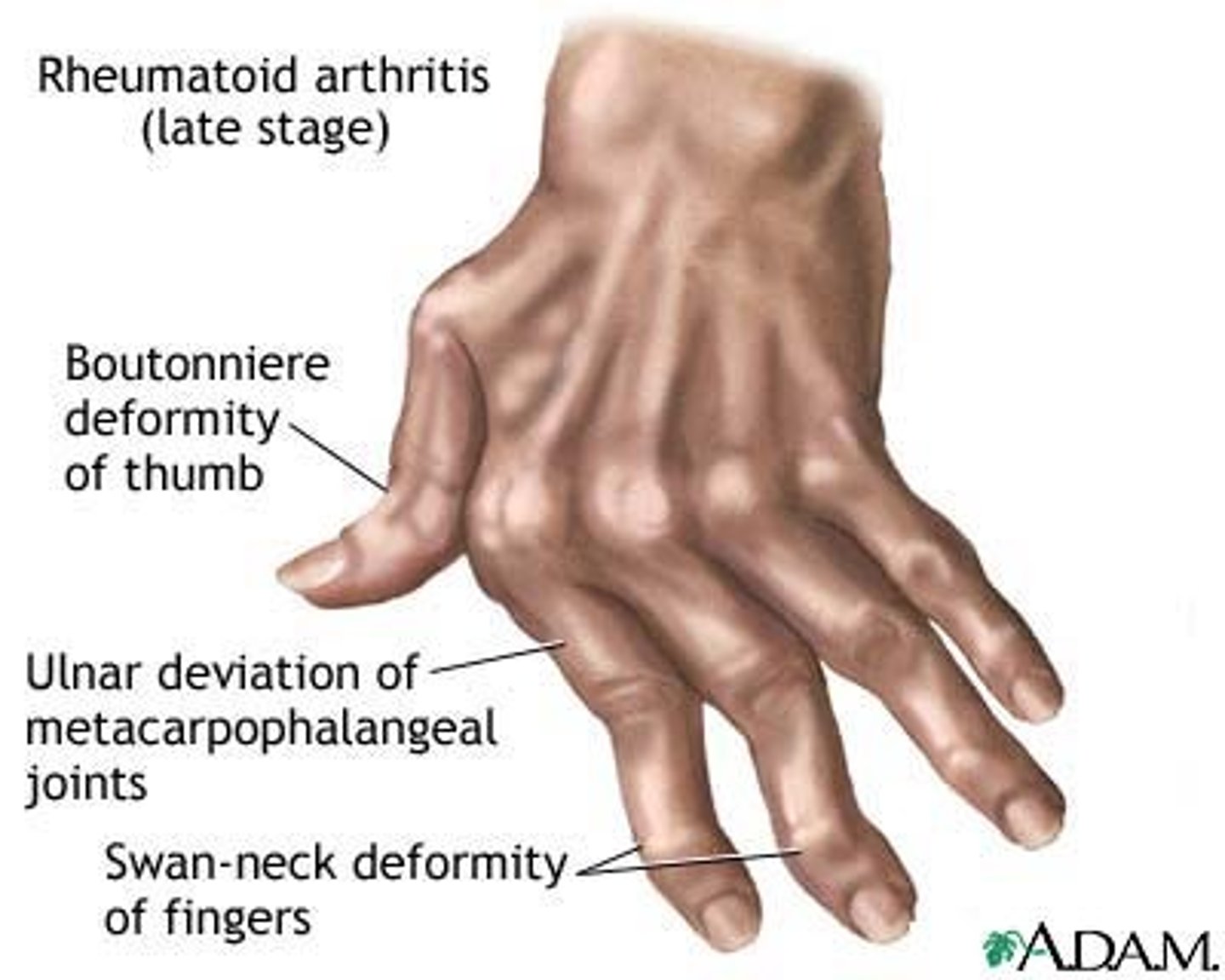
gouty arthritis
inflammation of joints caused by deposition of urate crystals from the blood, genetic cause, can usually be controlled with diet
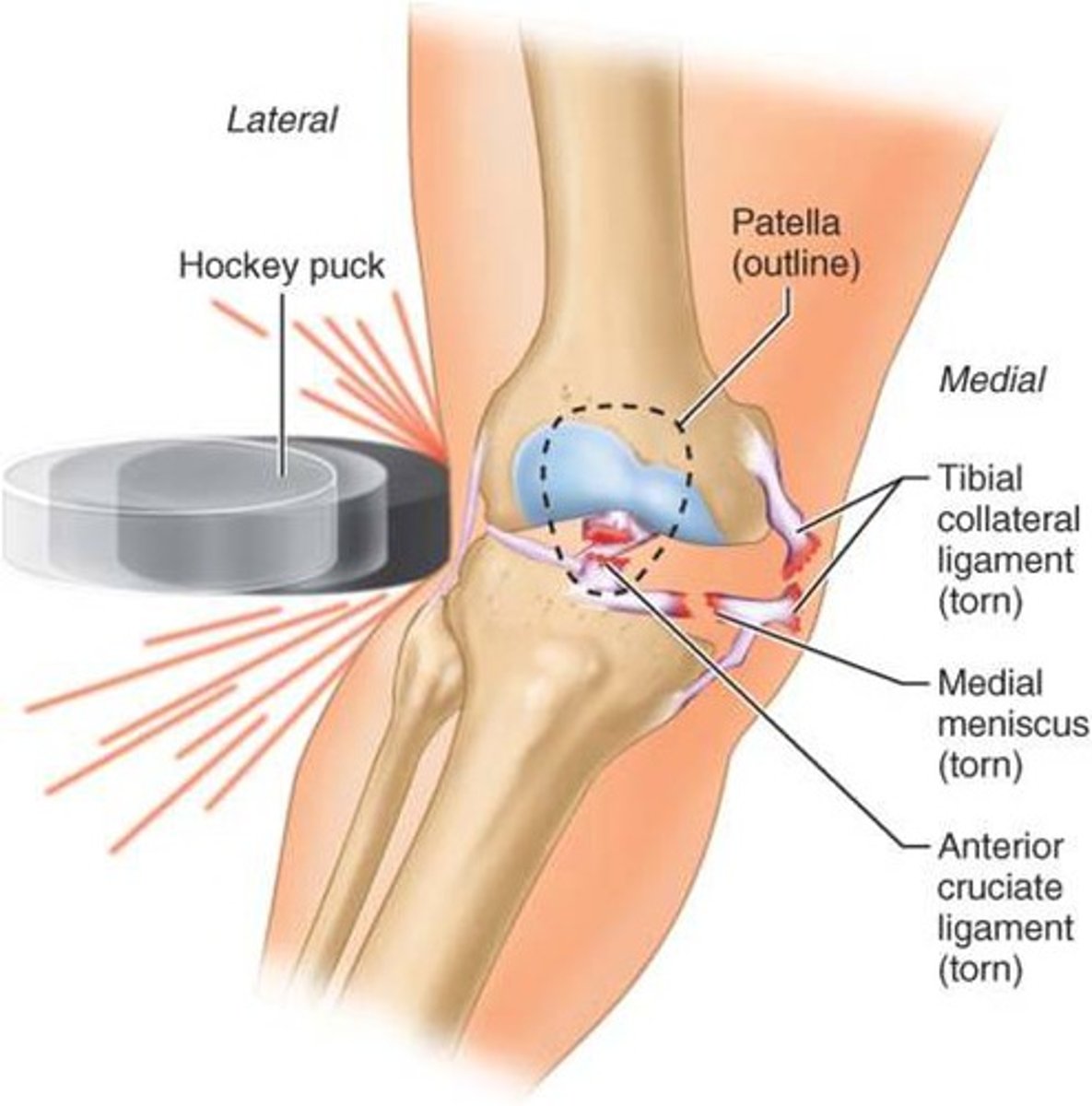
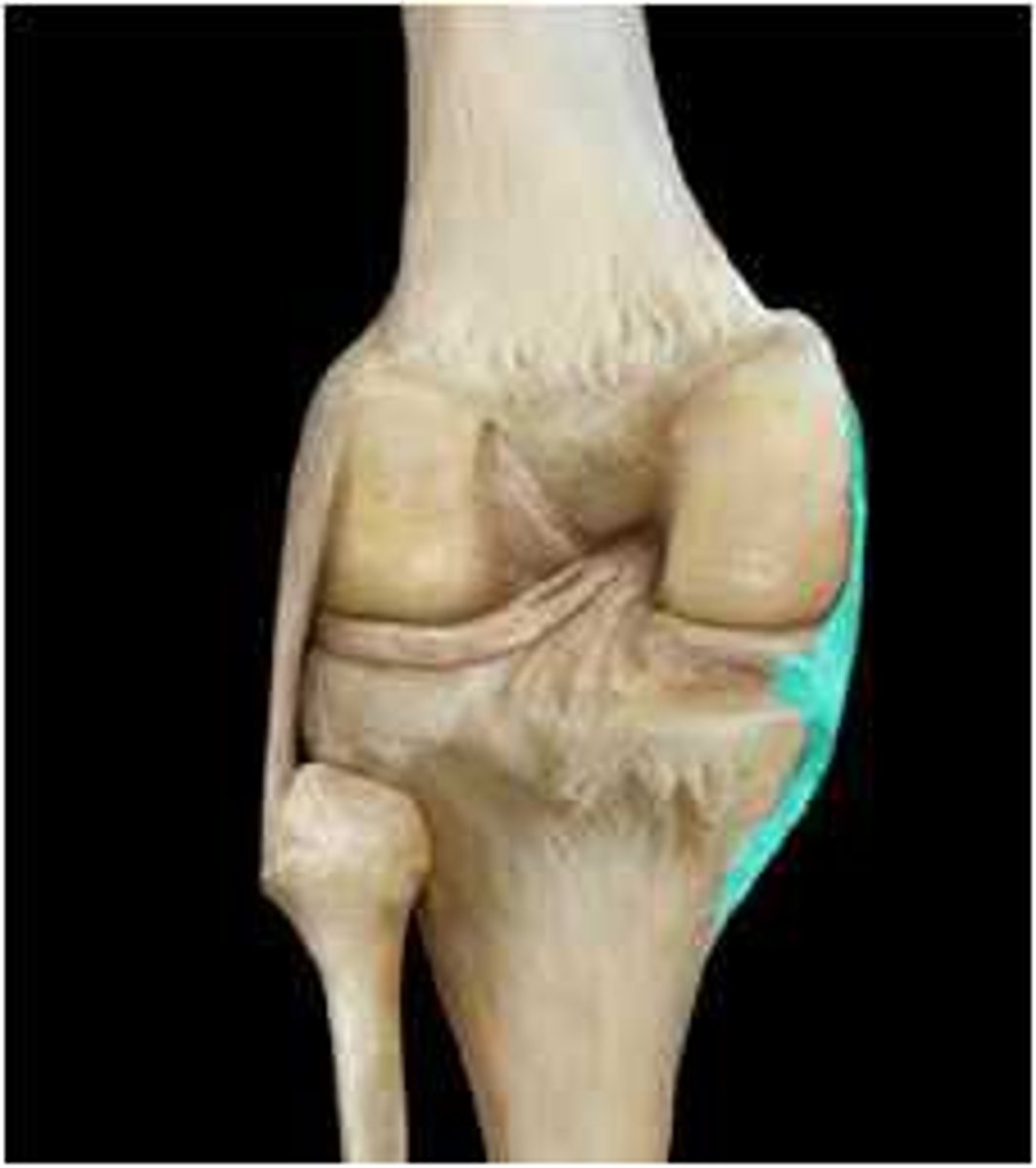
common knee injury
Tibial meniscus, Tibial Collateral Ligament (TCL), and ACL torn
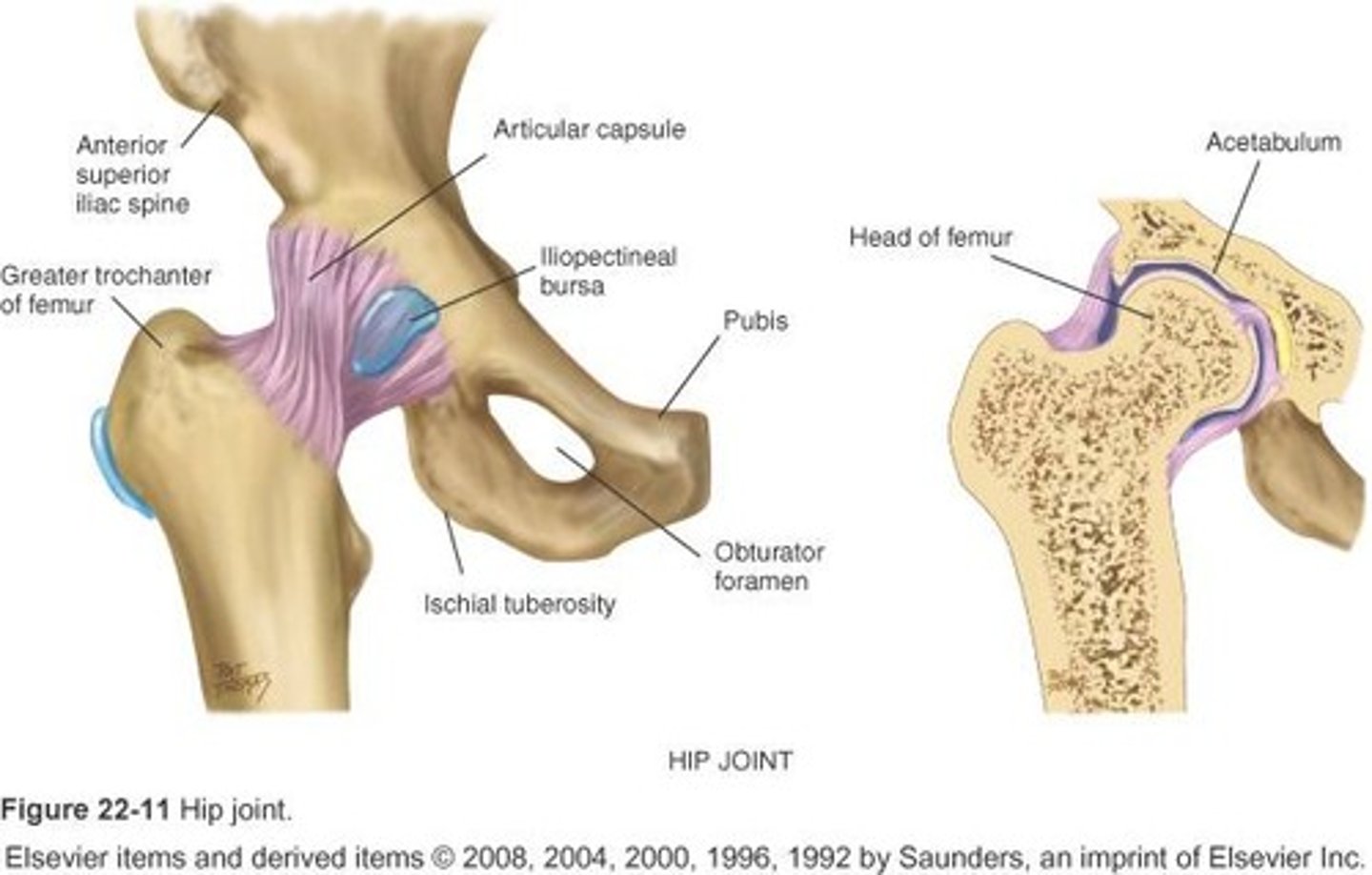
hip joint
joint capsule
The fibrous sac that encloses a joint.
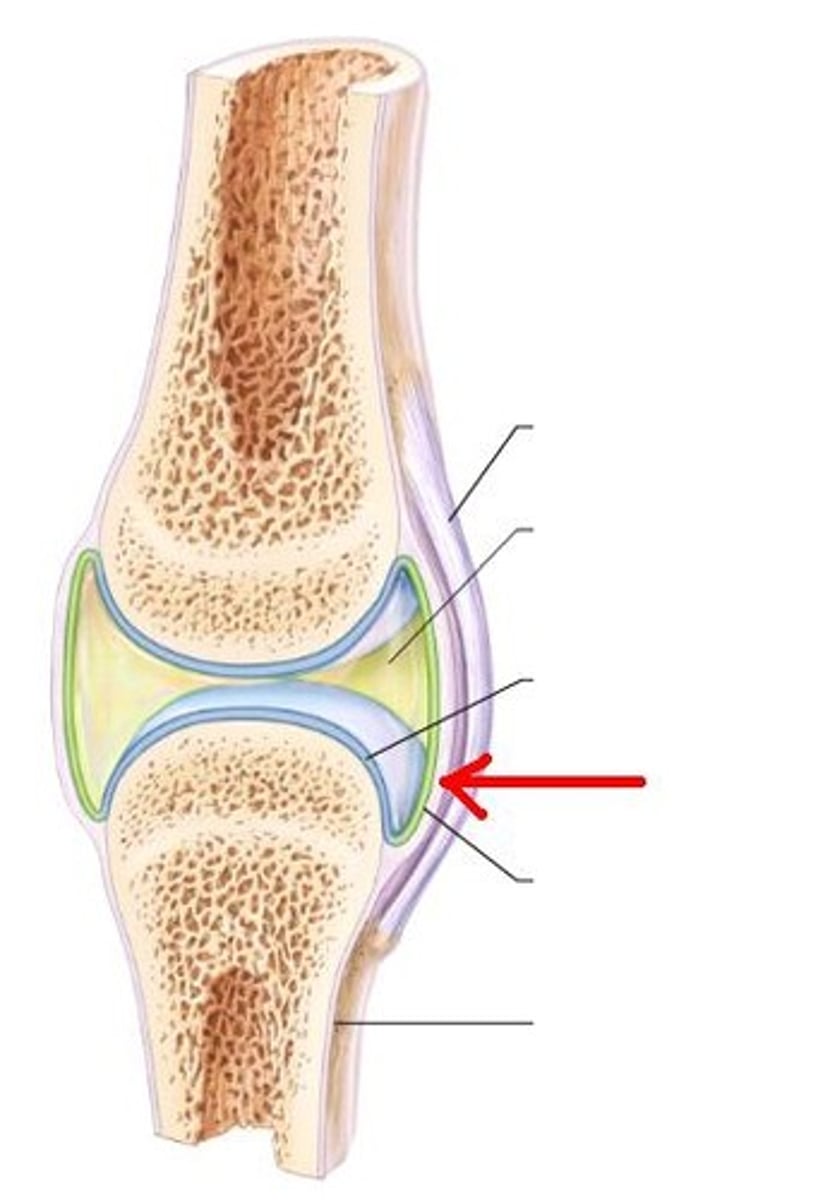
bursae
flattened fibrous sacs lined with synovial membrane and containing a thin film of synovial fluid
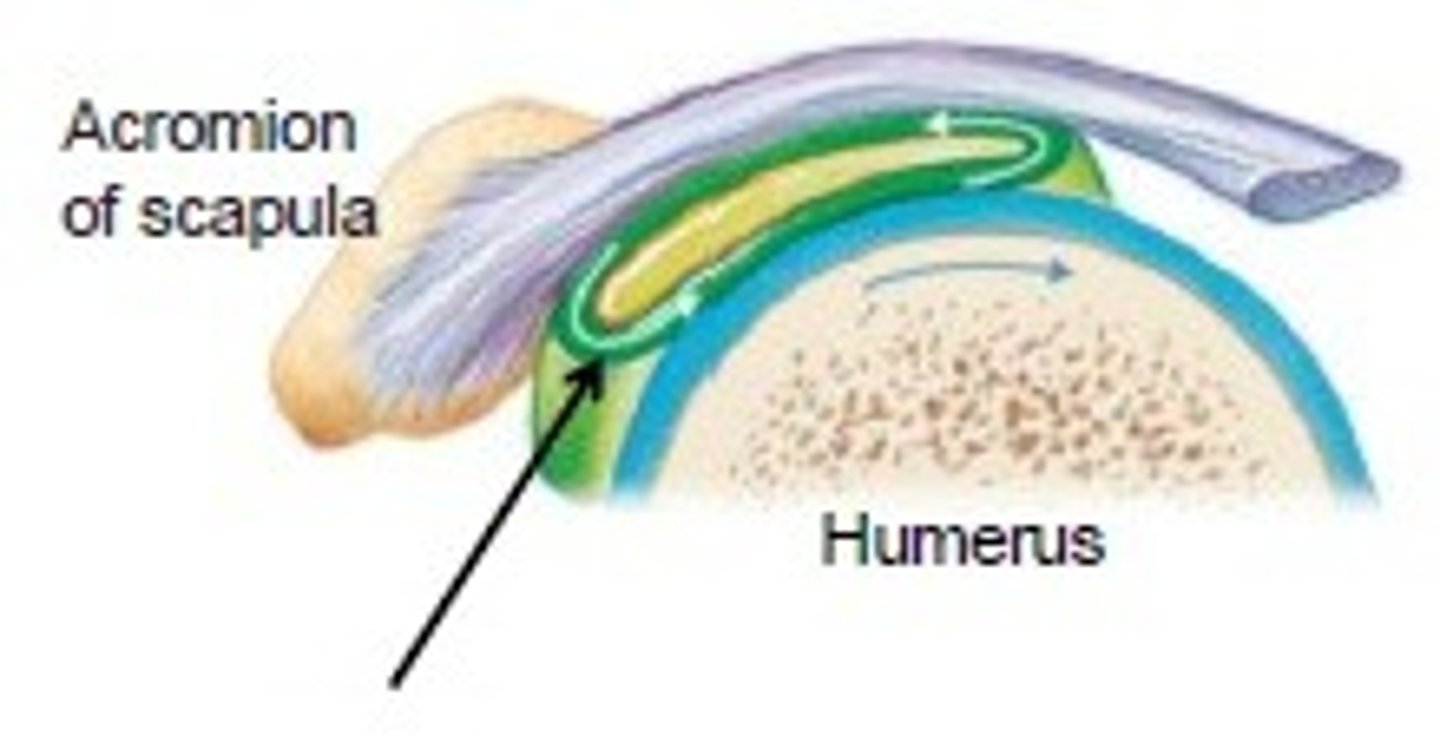
joint cavity
the space between two connecting bones
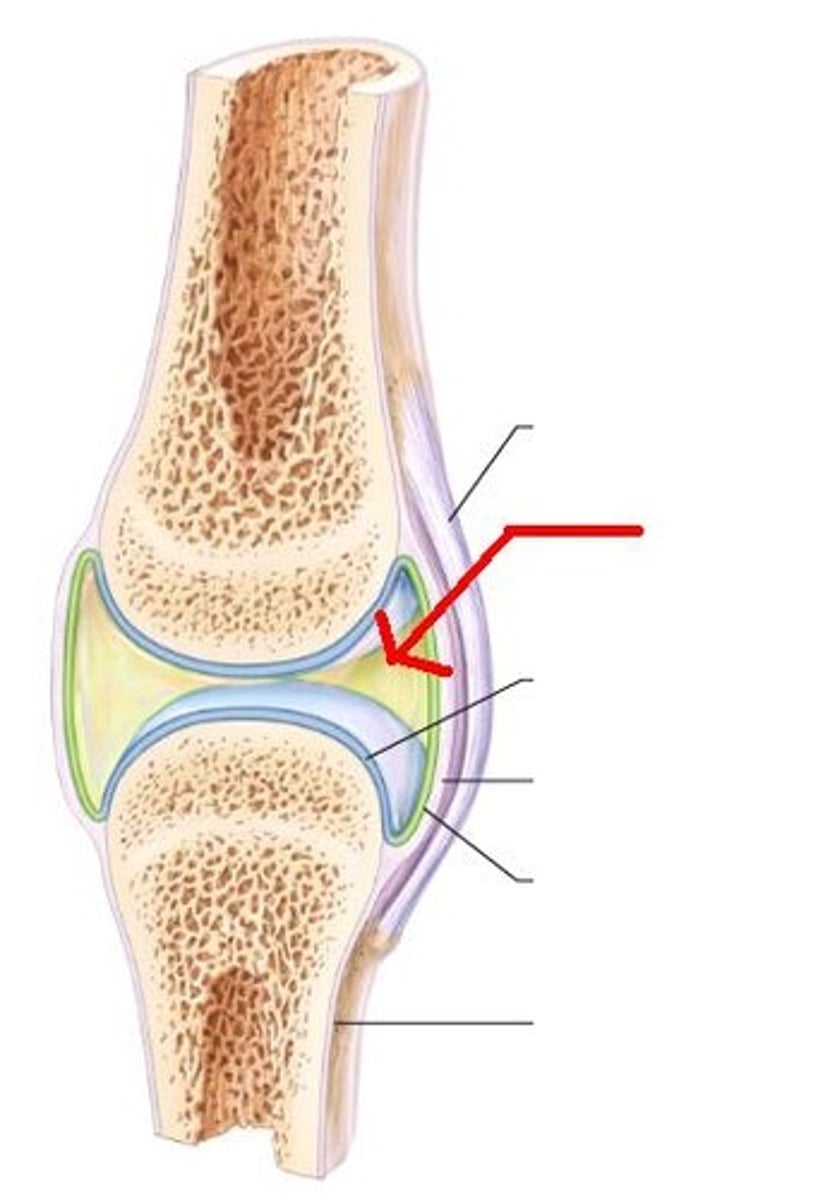
Hyaline (articular) cartilage
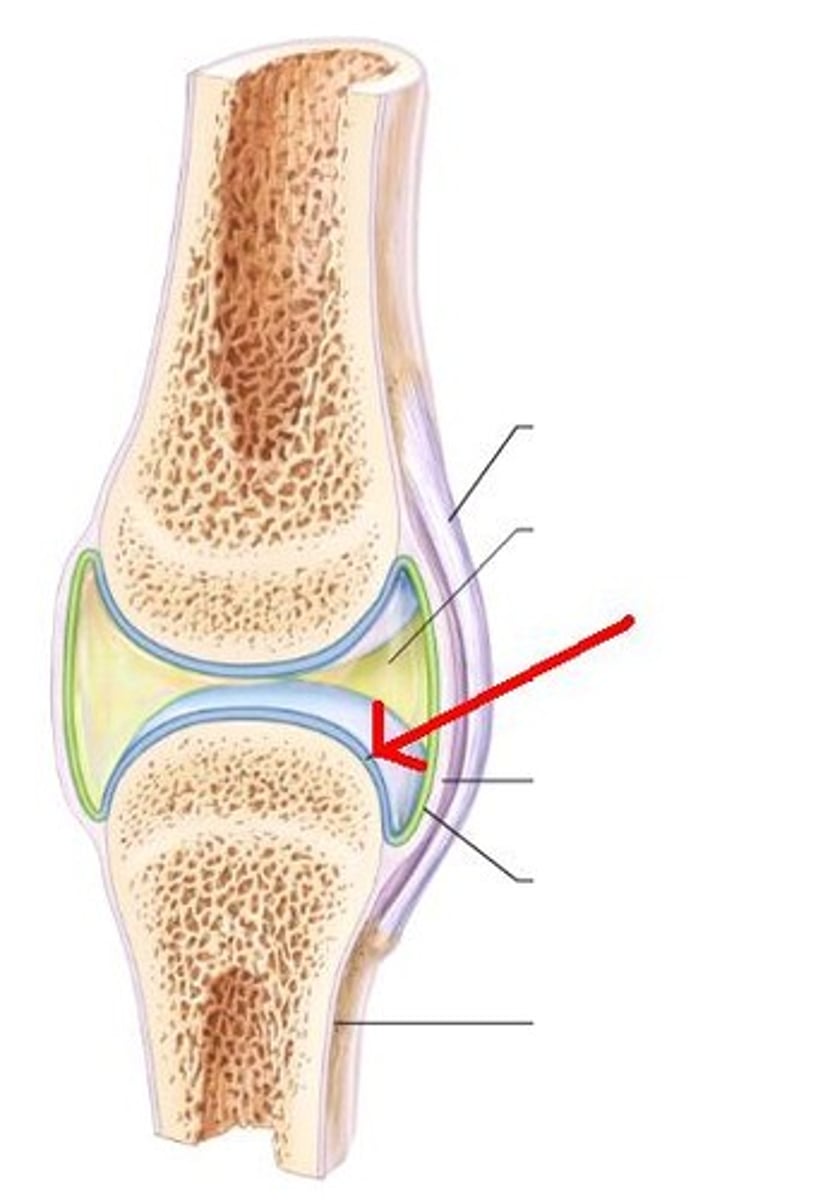
ligament
Connects bone to bone
synovial membrane
membrane lining the capsule of a joint
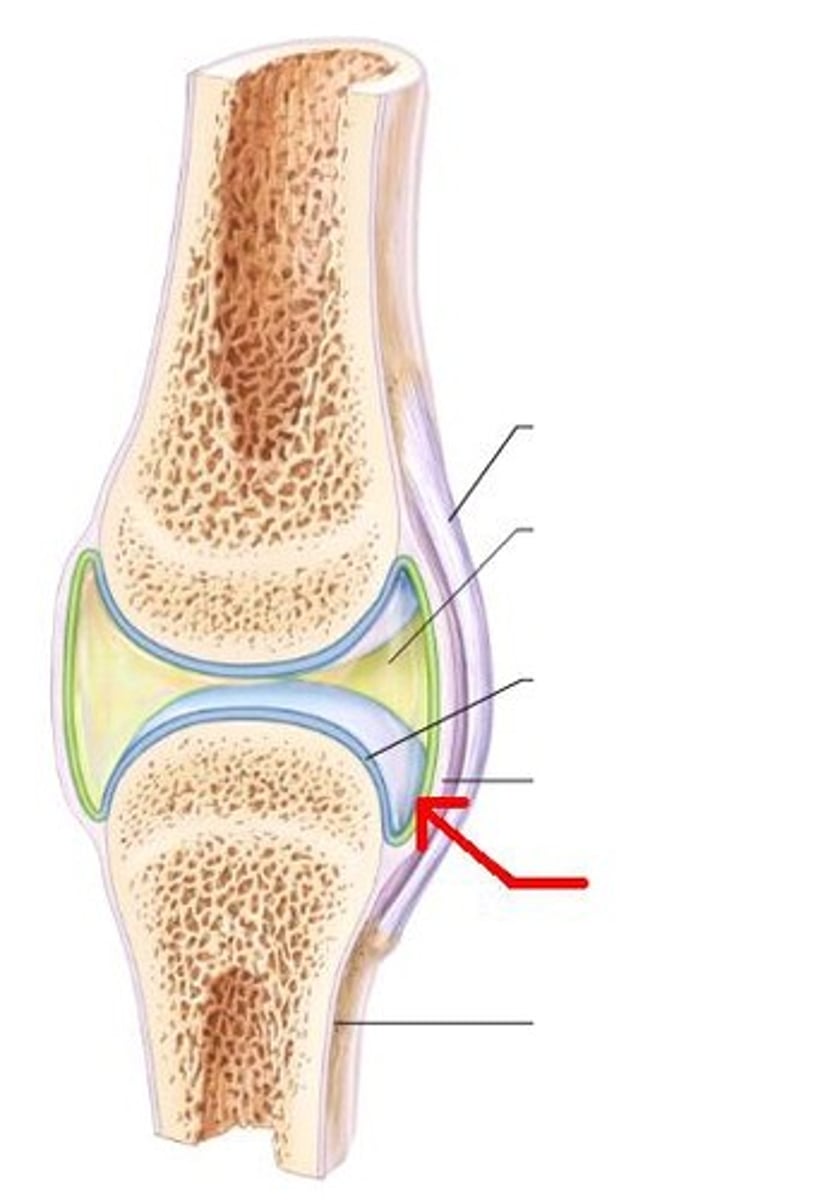
Fibrocartilage
Meniscus
fibrous layer
outer layer consisting of dense irregular connective tissue consisting of Sharpey's fibers that secure to bone matrix