Biology Topic 5- Movement of organic solutes through the plant
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Another test !!! YIPPIEEE (help)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What type of mixture is referred to when the term “assimilates” is used?
Sucrose and Amino acids
Where do assimilates, such as sucrose and amino acids, move to/from?
They move from sources to sinks in phloem sieve tubes.
source:
A site in the plant that provides food for the sink/any area of a plant in which sucrose is loaded into the phloem
sink:
A site in the plant that receives food from the source/any area where sucrose is taken out of the phloem
sieve tube:
tube formed from sieve tube elements lined up end to end
What are Assimilates?
compounds made by the plant as a result of assimilation.
What is the process of assimilation?
When the plant converts its inorganic nutrients into organic compounds. Then, during photosynthesis, inorganic carbon dioxide and water are converted, using energy, to organic solutes (like sugars).
Plants use nitrates obtained from the soil to help make amino acids.
True or False?
True
Examples of “sources”?
leaves and storage organs, such as tubers
Examples for “sinks”?
buds, flowers, fruits, roots and storage organs
In phloem, what are the two most important types of cells for transport?
sieve tube elements & companion cells
Unlike xylem vessels, sieve tubes are made of living cells.
True or False?
True
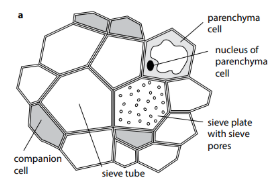
How do you recognize the sieve plate in a diagram?
By the pores in the middle of the sieve plate.
What are the cells specialized for transport of assimilates?
phloem sieve tube elements
How does phloem sap move in sieve tubes?
It moves by mass flow, which moves organic solutes, and occurs due to differences in pressure.
What type of prosses is needed to create the pressure differences needed for mass flow?
Active transport, which uses energy, unlike the transport in xylem.
What is Translocation?
It’s the movement of assimilates from the source to the sink.
What is the liquid inside phloem sieve tubes is called?
Phloem Sap or just Sap
How does water enter the sieve tube element?
by osmosis!!!
Explain mass flow in phloem sap down a hydrostatic pressure gradient from source to sink.
1) at the source, sucrose enters phloem sieve tube.
2) lowers water potential.
3) draws extra water into sieve tube by osmosis.
4) increases hydrostatic pressure.
5) At sink, sucrose leaves phloem sieve tube.
6) Water follows osmosis trajectory.
7) hydrostatic pressure at the source is higher than at the sink.
8) fluid/phloem sap moves from source to sink down pressure gradient by mass flow.
How do companion cells transfer assimilates to phloem sieve tubes?
sucrose is loaded into phloem sieve tubes by companion cells using proton pumping and the co-transporter mechanism in their cell surface membranes
How are Hydrogen ions (H+) pumped out of the companion cell and into its cell wall?
By a proton pump, using ATP.
What happens loading sucrose into phloem?
1) Hydrogen ions (H+) are pumped out of the companion cell into its cell wall, by a proton pump using ATP.
2) concentration of H+ builds up in the apoplastic pathway outside the companion cell.
3) hydrogen ions move back into the companion cell down their concentration gradient, through a co-transporter protein.
4) Sucrose molecules are carried through co-transporter molecule into the companion cell, against the concentration gradient for sucrose.
5) Sucrose concentration increases in companion cell
6) Sucrose diffuses from the companion cell into sieve tube element through plasmodesmata.
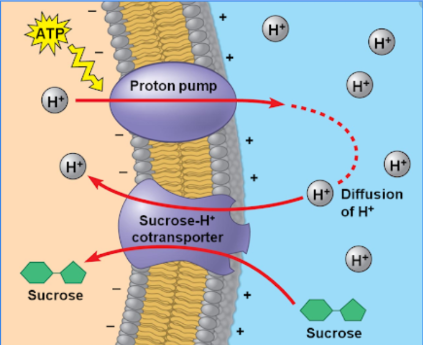
The entry of sucrose into the phloem sieve tube is passive but the whole process is sometimes described as ‘active loading’.
True or false??
True!
How does sucrose move into companion cell from source cell?
By active transport.
ATP is used to fuel the transport. This is done by pumping protons (hydrogen ions) out of the companion cell.
Fill in the space:
As the protons diffuse back into the __________, they pass through a ___________ protein that allows both ________ and sucrose molecules to enter the cell.
companion cell, co-transporter, protons.
How does Sucrose move from the companion cell into the sieve tube element?
By diffusion down the concentration gradient through plasmodesmata.
What does the presence of sucrose in the phloem sieve element cause?
It lowers the water potential. Water enters sieve tube by osmosis from surrounding cells.
What does the addition of water produce inside the phloem sieve element?
It produces a higher hydrostatic pressure, causing phloem sap to move by mass flow down this pressure gradient, through the phloem sieve elements and through the sieve pores.
(From source to sink.)