Biology Final (Scientific Literacy, Ecology, Energy)
5.0(5)
5.0(5)
Card Sorting
1/82
Last updated 7:56 PM on 12/17/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
1
New cards
What are the six characteristics of life?
\-respond to environment
\-grow and develop
\-reproduction
\-maintain homeostasis or keeping things constant
\-complex chemistry
\-cells
\-grow and develop
\-reproduction
\-maintain homeostasis or keeping things constant
\-complex chemistry
\-cells
2
New cards
responding to the environment
It means to detect changes in an environment. For example: stepping on a turtle (the turtle will move)
3
New cards
reproduction
Producing offspring, asexually (an exact copy of organism) or sexually (different)
4
New cards
maintaining homeostasis/keeping things constant
keeping things relatively stable on the inside regardless of the conditions around them
For example: humans maintain a stable internal body temperature
For example: humans maintain a stable internal body temperature
5
New cards
complex chemistry
Consisting of large, complex molecules and undergo many complicated chemical changes to stay alive
For example: metabolism
For example: metabolism
6
New cards
ecology
The study of the relationship between organisms and their environment
7
New cards
lag phase
slow population growth due to low number of individuals to mate
8
New cards
exponential phase
plenty of resources and mates lead to rapid growth
9
New cards
carrying capacity
the maximum number of of individuals an ecosystem can hold
10
New cards
Parasitism
a relationship between two organism where one is benefitted and one is harmed
11
New cards
Commensalism
a relationship between two organisms where one is benefitted and the other is not harmed nor benefitted
12
New cards
Mutualism
a relationship between two organisms where both are benefitted
13
New cards
What is the food pyramid with each trophic level?
\-quaternary consumers (carnivores)
\-tertiary consumers (carnivores)
\-secondary consumers (carnivores)
\-primary consumers (herbivores)
\-primary producers (plants)
\-tertiary consumers (carnivores)
\-secondary consumers (carnivores)
\-primary consumers (herbivores)
\-primary producers (plants)
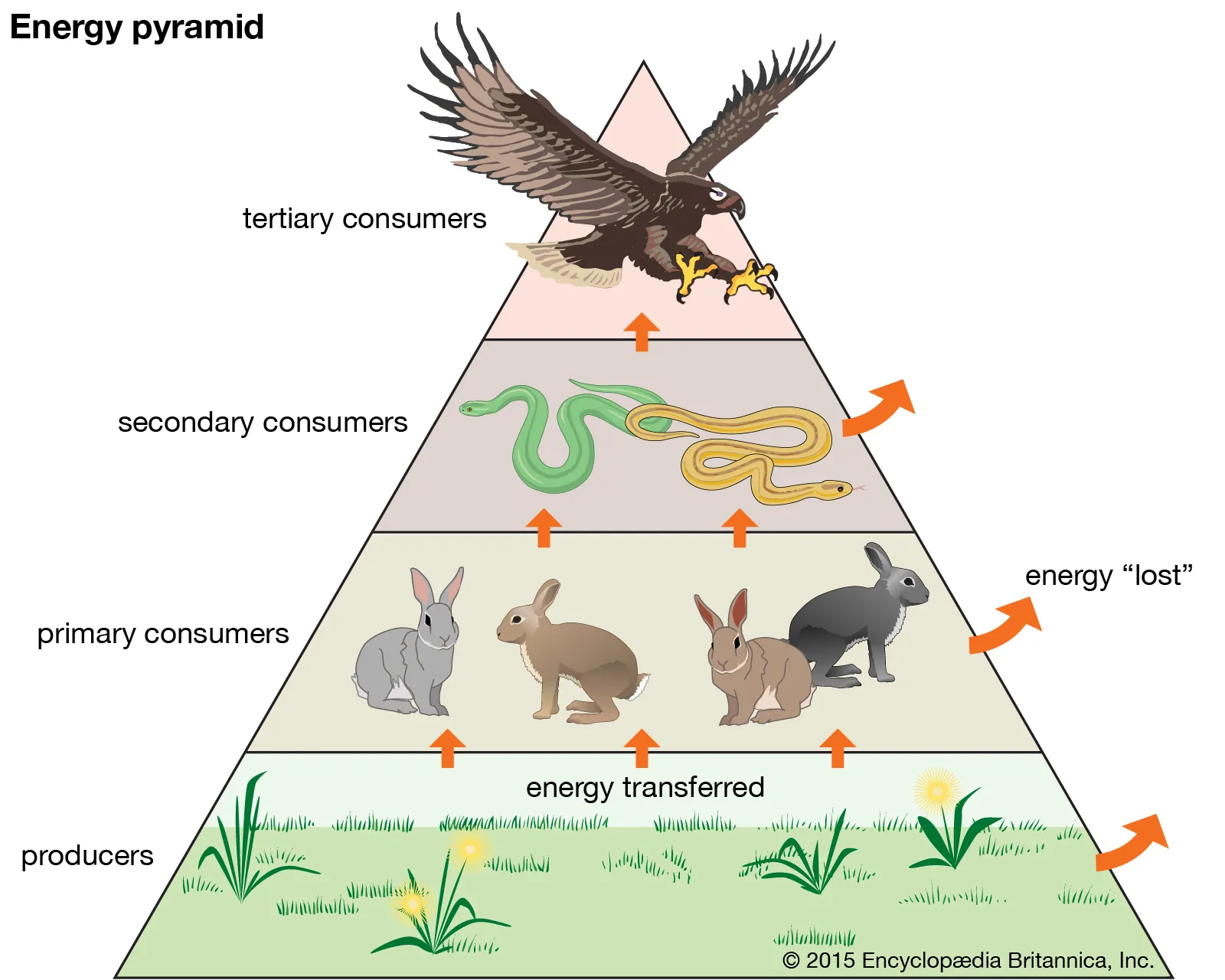
14
New cards
niche partitioning
one species will naturally be better suited to a niche and the other will adapt to occupy a slightly different niche
15
New cards
Competitive exclusion
One species will naturally be better suited to a niche and cause the other species to decline and go extinct
16
New cards
Keystone species
A species that has a huge effect on the biodiversity of its ecosystem
17
New cards
How much energy is passed from one trophic level to the next?
10%
18
New cards
What do animals use the rest of the 90% of energy for?
* Homeostasis (breathing)
* Moving
* Dying
* Moving
* Dying
19
New cards
What determines global climate patterns?
Input of solar energy and the planet’s movement in space
20
New cards
Why do equatorial regions get hotter?
They receive sunlight more directly
21
New cards
Why are equatorial regions moister?
Ascending moist air releases moisture doldrums. The sun makes all the water evaporate and that causes heavy rainfall.
22
New cards
How are deserts created/found?
The dry air goes away from the equator created dry deserts. They are found away from the equator.
23
New cards
What is the most distinguishing feature for each of the biomes?
Temperature and precipitation
24
New cards
What are the 9 biomes?
* desert
* Tropical rainforest
* Taiga
* Deciduous forest
* Savana
* Grassland
* Arctic tundra
* Alpine tundra
* Chaparral
* Tropical rainforest
* Taiga
* Deciduous forest
* Savana
* Grassland
* Arctic tundra
* Alpine tundra
* Chaparral
25
New cards
What are 3 ways organisms could divide or partition a niche so there is no exclusion?
* compete for different food sources
* Forage at different times
* Forage in different areas
* Forage at different times
* Forage in different areas
26
New cards
trophic cascade
happens when keystone species have an indirect impact has a positive influence on organisms for outside of its own food chain.
For example: Wolves positively affect elk, grass, trees, birds, beavers, and more
For example: Wolves positively affect elk, grass, trees, birds, beavers, and more
27
New cards
What are the building blocks of all living things?
The four macromolecules
* carbohydrates
* Proteins
* Nucleic acids
* Lipids
* carbohydrates
* Proteins
* Nucleic acids
* Lipids
28
New cards
What is the purpose of carbohydrates?
Provides the body with glucose
29
New cards
What is the purpose of nucleic acid
Stores energy
30
New cards
What is the purpose of lipids?
energy source, genes, dna
31
New cards
Photosynthesis
Process where plants transform light energy and reactants into chemical energy that can be sued to do work
32
New cards
Cellular respiration
Something organisms use to obtain chemical energy needed
33
New cards
What is aerobic cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration using oxygen
34
New cards
What is anaerobic cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration without oxygen
35
New cards
What is the equation for photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 6H20 → C6H12O6 + 6O2
36
New cards
What is the equation for cellular respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 +6H2O + ATP
37
New cards
How is energy transformed in photosynthesis?
1) light (kinetic)
2) electrons (chemical)
3) proton gradient (potential)
4) moving protons (kinetic)
5) ATP (chemical)
2) electrons (chemical)
3) proton gradient (potential)
4) moving protons (kinetic)
5) ATP (chemical)
38
New cards
What happens one the thylakoid creates its end product?
It will be used in the calvin cycle (LIR)
39
New cards
Where does the calvin cycle take place?
Stroma
40
New cards
What is the first step of LDR?
UV rays from the sun hit the pigments in photosystem 2 which causes water to split.
41
New cards
What is the second step of LDR?
The electrons are energized by light energy from the sun
42
New cards
What is the third step of LDR?
Electrons are captured by electron carries
43
New cards
What is the fourth step of LDR?
Electrons are passed from acceptor to acceptor like a relay race. As this occurs, the electrons are loosing energy
44
New cards
What is the fifth step of LDR?
The energy from the electrons is used to pull H+ from the stroma into the lumen.
45
New cards
What is the sixth step of LDR?
a proton gradient is created in the lumen
46
New cards
What is the seventh step of LDR?
The protons are under enormous pressure to esacpe
47
New cards
What is the eighth step of LDR?
The protons escape by rapidly moving through the enzyme ATP synthase
48
New cards
What is ATP synthase?
The enzyme that makes ATP
49
New cards
What is the ninth step of LDR
The moving protons are used to spin the turbine in ATP synthase
50
New cards
What is the tenth step in LDR
The spinning turbine is used to add a phosphate to ADP, making ATP
51
New cards
What is the 11th step in LDR?
The electrons are received by photosystem 1 where they are re-energized by light
52
New cards
What is the 12th step in LDR
Newly energized electrons are passed along 3 electron carries and then loaded onto NADP+ to make NADPH
53
New cards
What is the 13th step in LDR?
Now the ATP and NADPH will carry usable energy from the thylakoid to the stroma to be used in the calvin cycle
54
New cards
What is the first step of the calvin cycle?
5C sugar is combined with CO2 by the enzyme RuBisCo to produce a 6C sugar, which is very unstable
55
New cards
2nd step of calvin cycle?
The 6c sugars breaks into two 3c units
56
New cards
3rd step of calvin cycle?
The energy from ATP and the electrons from NADPH are then used to rearrange 3c units
57
New cards
4th step in calvin cycle?
The carbon reorganizer is a series of reactions that reforms the 5c sugars and sets aside 1 carbon to be used in glucose
58
New cards
5th step in calvin cycle?
The cycle must occur 6 times to produce glucose
59
New cards
What is the purpose of cellular respiration?
To convert energy stored in glucose C6H12O6 to energy in the form of ATP
60
New cards
What is the first step of cellular respiration?
Glycolysis (no oxygen needed)
61
New cards
Where is the glycolysis located
cytoplasm
62
New cards
What is the purpose glycolysis?
Splits glucose into 2 pyruvates
63
New cards
What is second step in cellular respiration?
the kreb cycle
64
New cards
Where is the kreb cycle located?
Matrix of mitochondria
65
New cards
What is the purpose of the kreb cycle?
Pyruvate’s broken down to acquire electrons
66
New cards
What is the third step of cellular respiration?
Electron transport chain
67
New cards
Where is the ETC located?
The inner membrane of the mitochondria
68
New cards
What is the final electron acceptor in the chain is reduced to water
Oxygen
69
New cards
The electron transport chain yields how many ATP for each molecules of glucose
28 ATP
70
New cards
An experimenter is testing the effects of the drug Y on blood pressure. Which of the following would be the independent variable?
* Heart Rate
* Blood pressure
* Amount of drug Y
* Heart Rate
* Blood pressure
* Amount of drug Y
Amount of drug Y
71
New cards
Another name for the independent variable is
Manipulated
72
New cards
Another name for dependent variable is
Responding
73
New cards
What is the ultimate source of energy in an ecosystem?
Sun
74
New cards
What type of competition is between members **within** a species.
Intraspecies Competition
75
New cards
What type of energy is the energy of movement?
Kinetic
76
New cards
What type of energy is present because of an object's position or structure?
Potential
77
New cards
What type of energy is found in the bond between atoms of a larger molecule?
chemical
78
New cards
What type of reaction releases energy and involves breaking a larger molecule into smaller ones?
Exergonic
79
New cards
What molecule is the all purpose energy source for almost every reaction in a cell?
ATP
80
New cards
The goal of photosynthesis is to make glucose. What are the two molecules of chemical energy that are made in the LDR so they can be used in the LIR to make glucose?
ATP and NADPH
81
New cards
Where do the Light Dependent Reactions (LDR) take place?
Thylakoid
82
New cards
What substance is able to absorb light energy?
Pigments and chlorophyll
83
New cards
Light energy is used to split water and then is first converted into what energy?
Energized electrons