skeletal muscle system
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
skeletal muscle
striated, voluntary, multinucleated ex: biceps, triceps and quadriceps and attached to bones

cardiac muscle
involuntary, striated, one or two nuclei per cell. intercelated discs
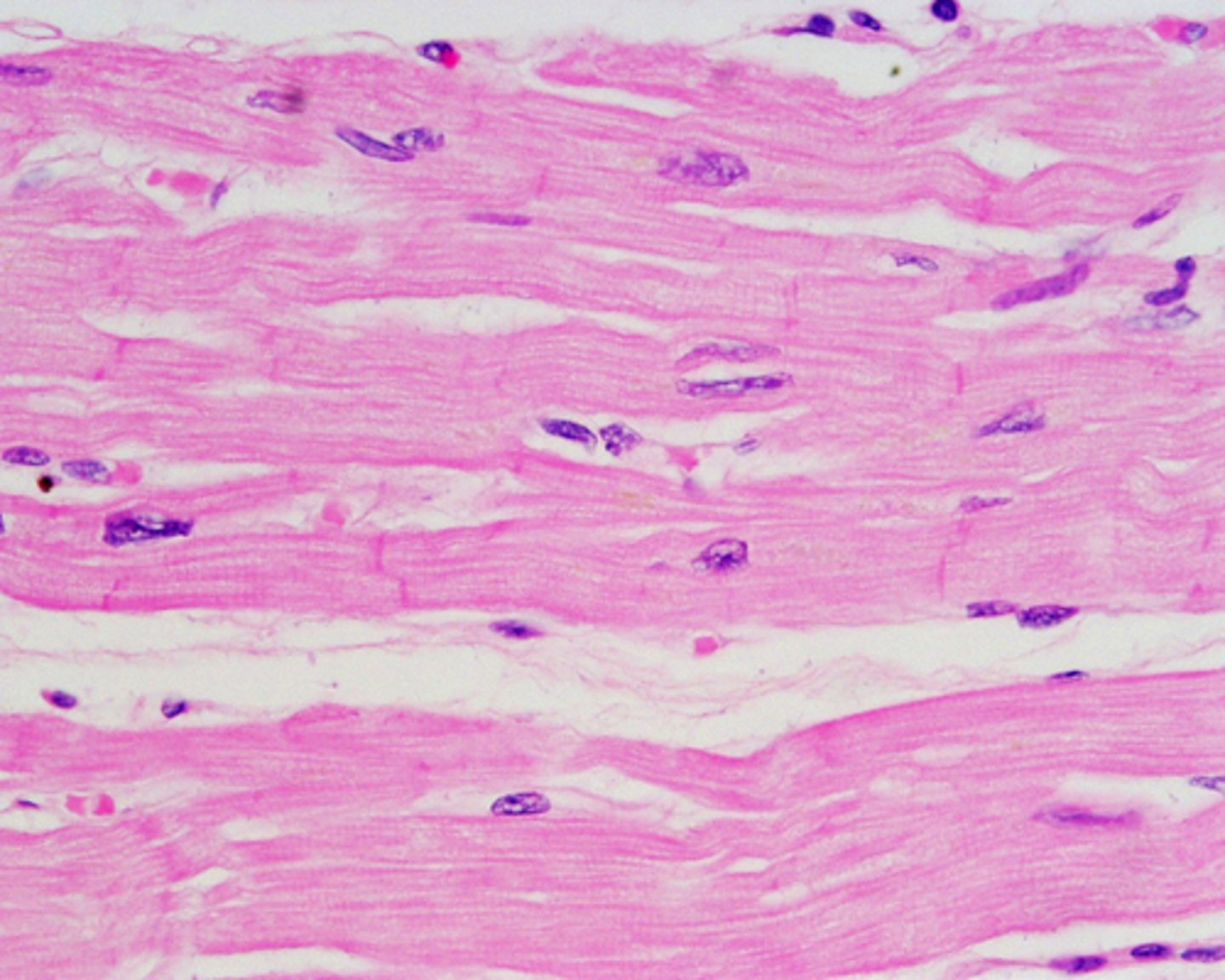
smooth muscle
involuntary, found in hallow organs, non-striated, uninucliated. slow contractions that last longer. ex: digestive tract and arteries
origin of skeletal muscle
the fixed attachment point of the muscle (doesn't move during contraction)
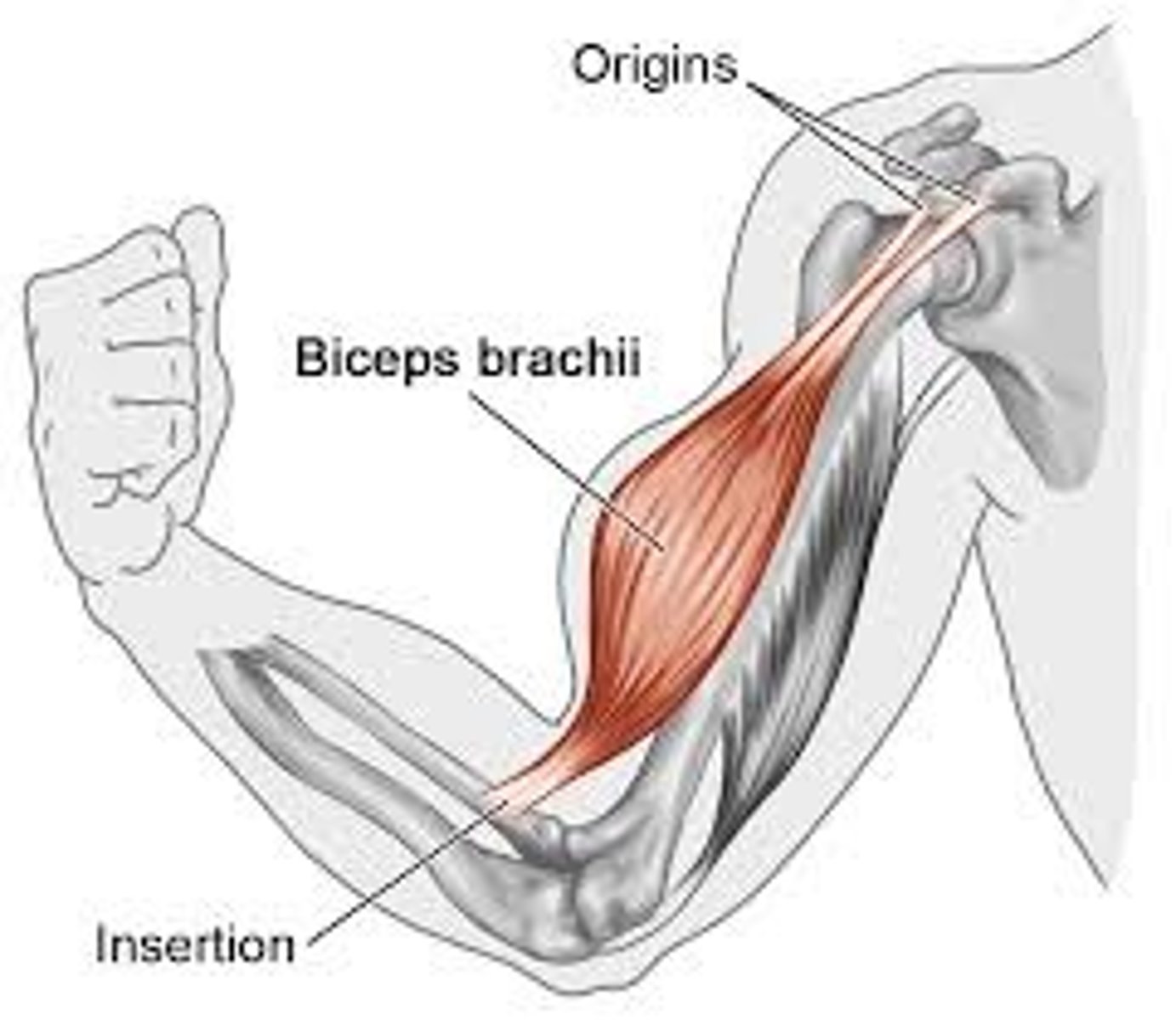
insertion
the moveable attachment point of the muscle ( moves during contraction
movement
when a muscle contracts, the insertion moves toward the origin
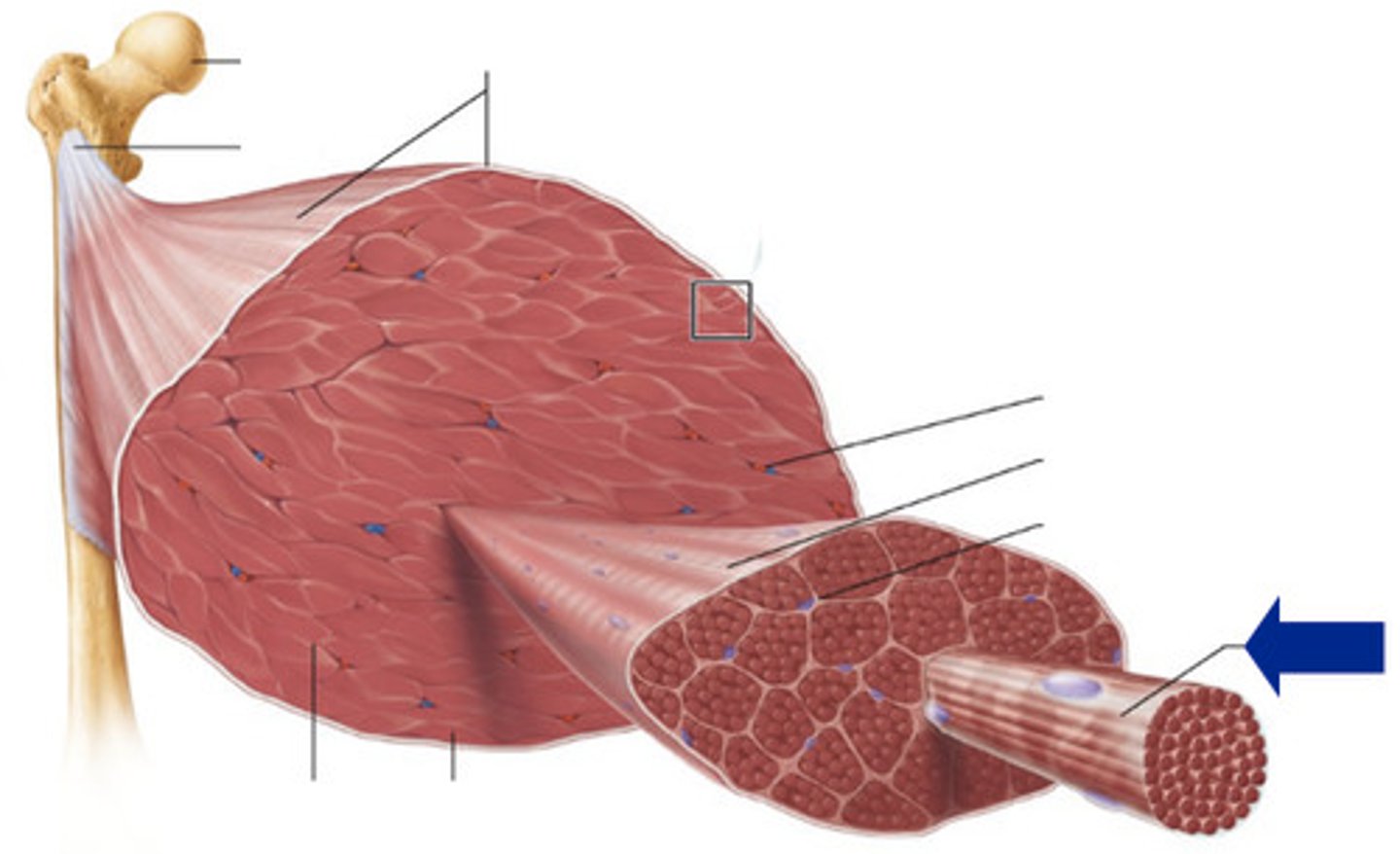
Epimysium
outer connective tissue layer that surrounds the entire muscle
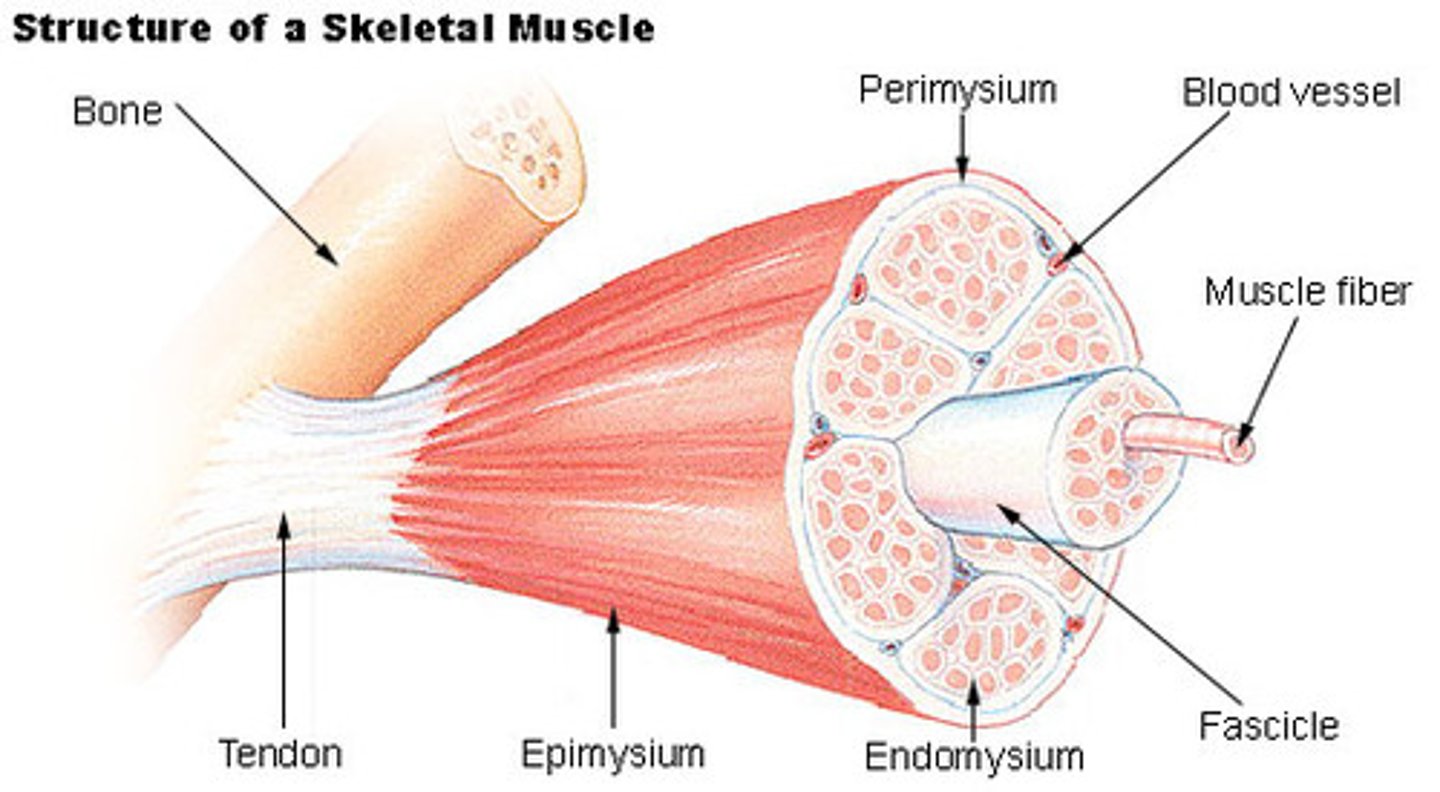
Perimysium
connective tussue that surrounds a bundle of muscle fibers called a fascicle
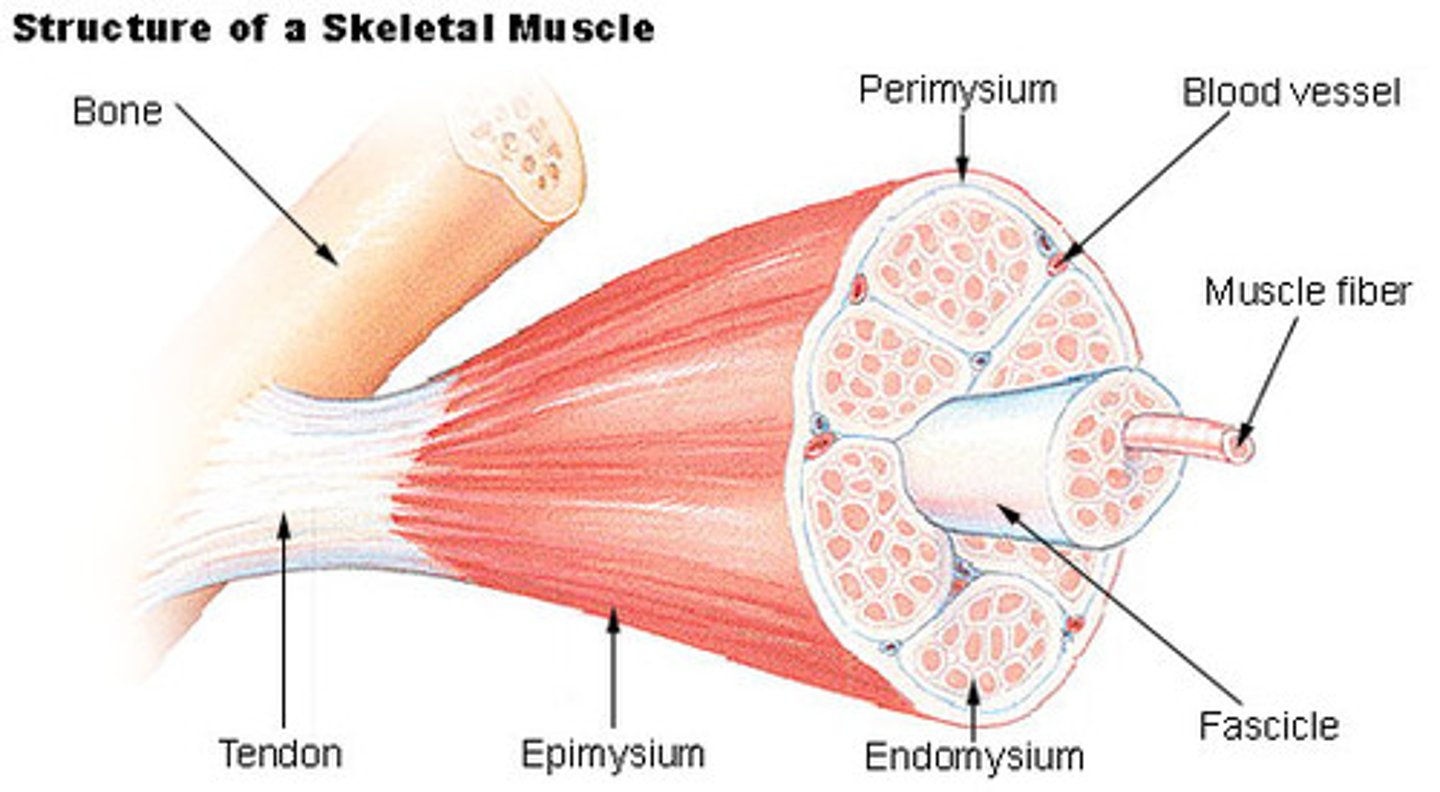
endomysium
connective tissue that surrounds invidual muscle fibers
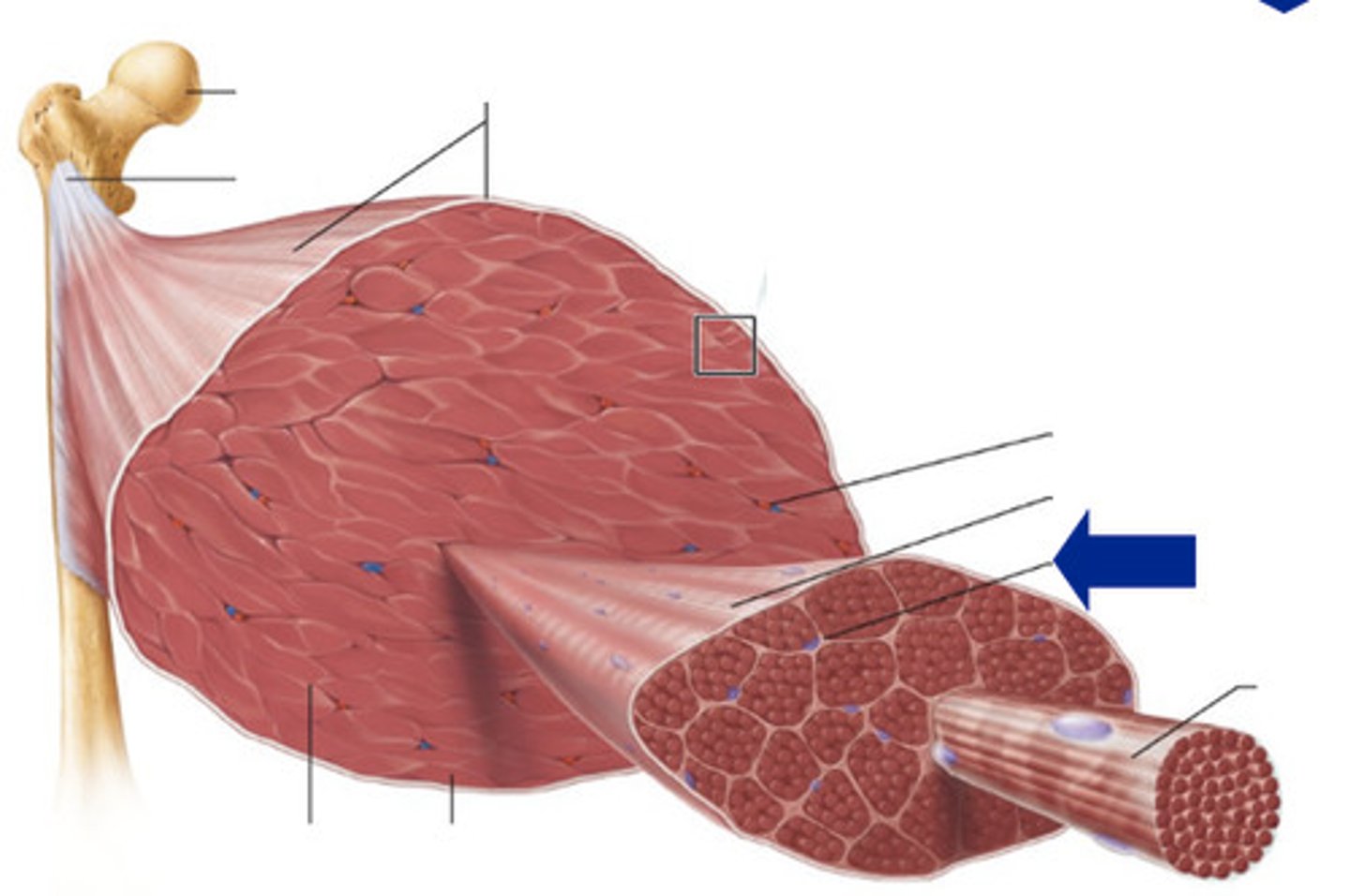
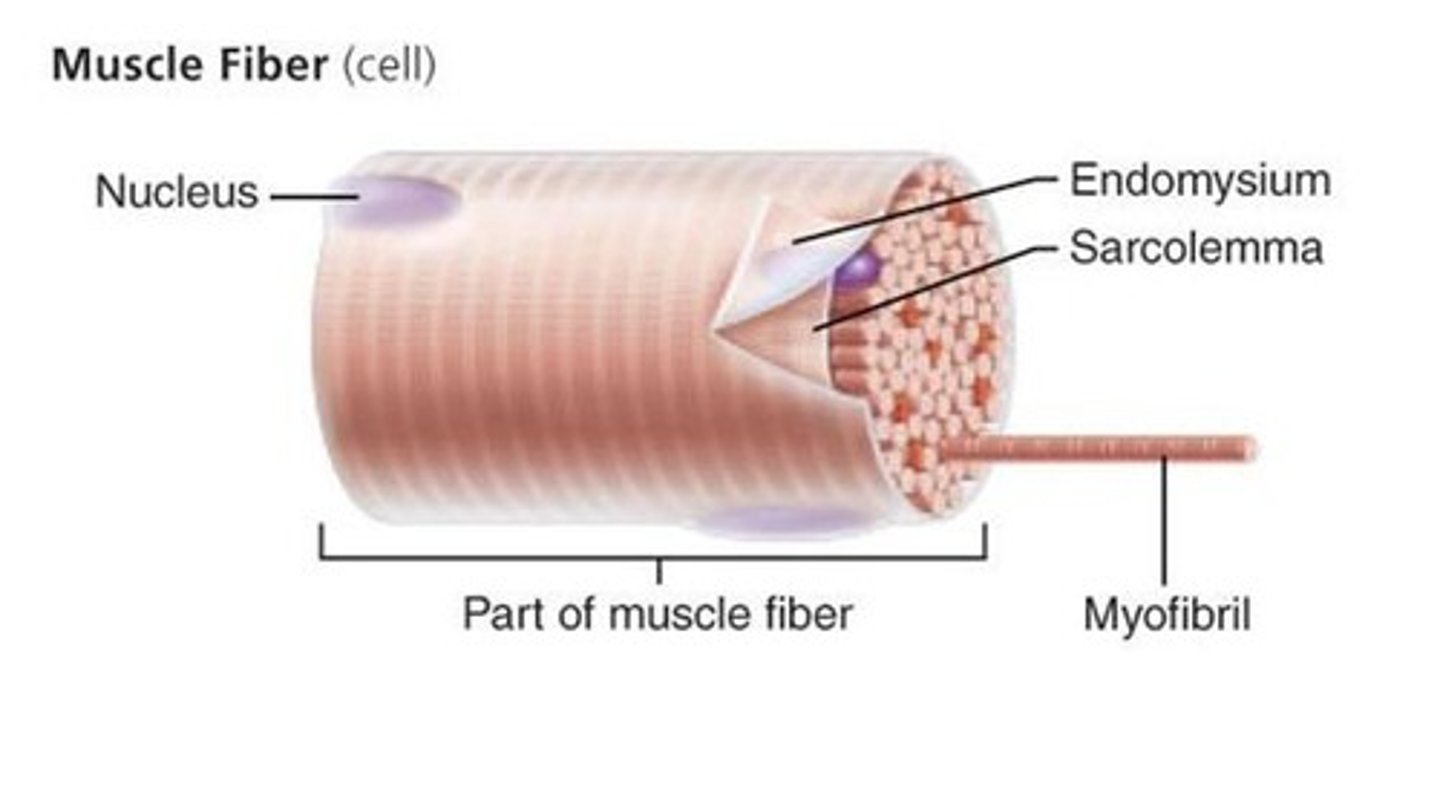
muscle fiber (cell)
contains multiple nuclei and mitochondria
Myofibrils
rod-like structures inside muscle fibers that allow contraction
sarcolemma
the cell membrane of a muscle fiber
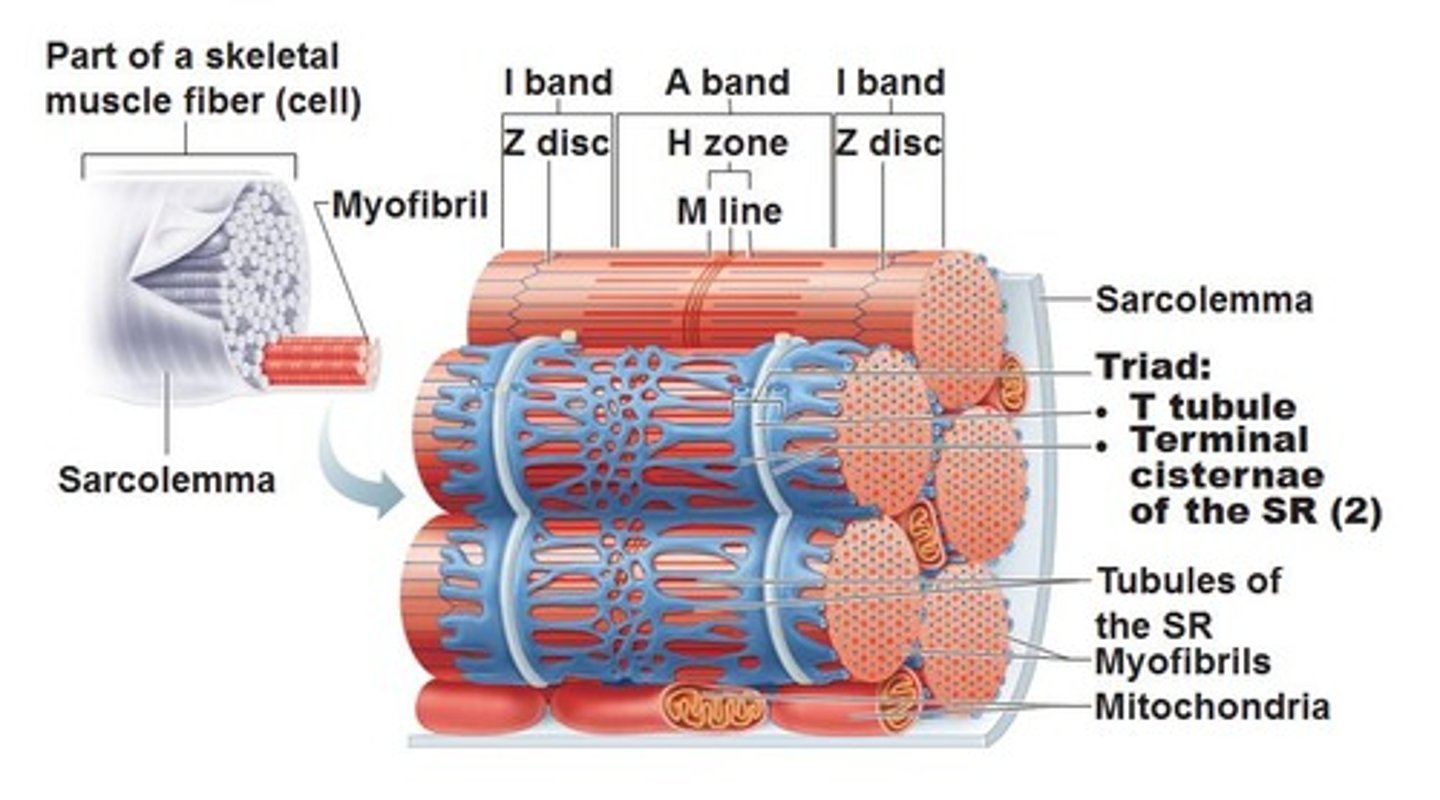
sarcoplasmic reticulum
stores calcium ions for contraction
T-tubules
channels that caryr electrical signals deep into the muscle
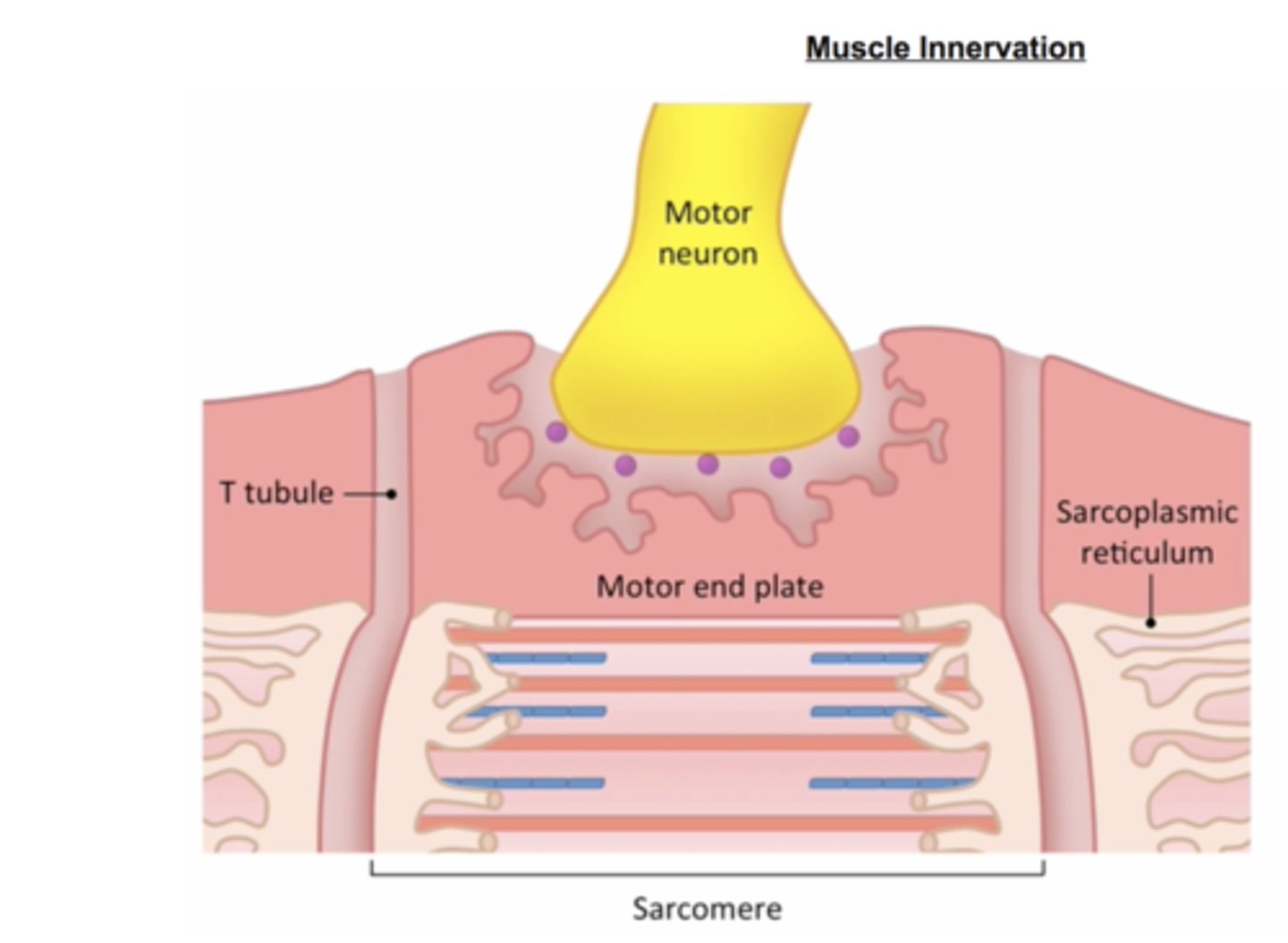
neuromuscular junction
Synapse between motor neuron and muscle fiber.
nerve signal arrives- a nerve impulse (action potential) reaches the axon terminal.
step 1
Acetylcholine (ACh) Release: The nerve releases ACh, a neurotransmitter, into the synaptic cleft.
step 2
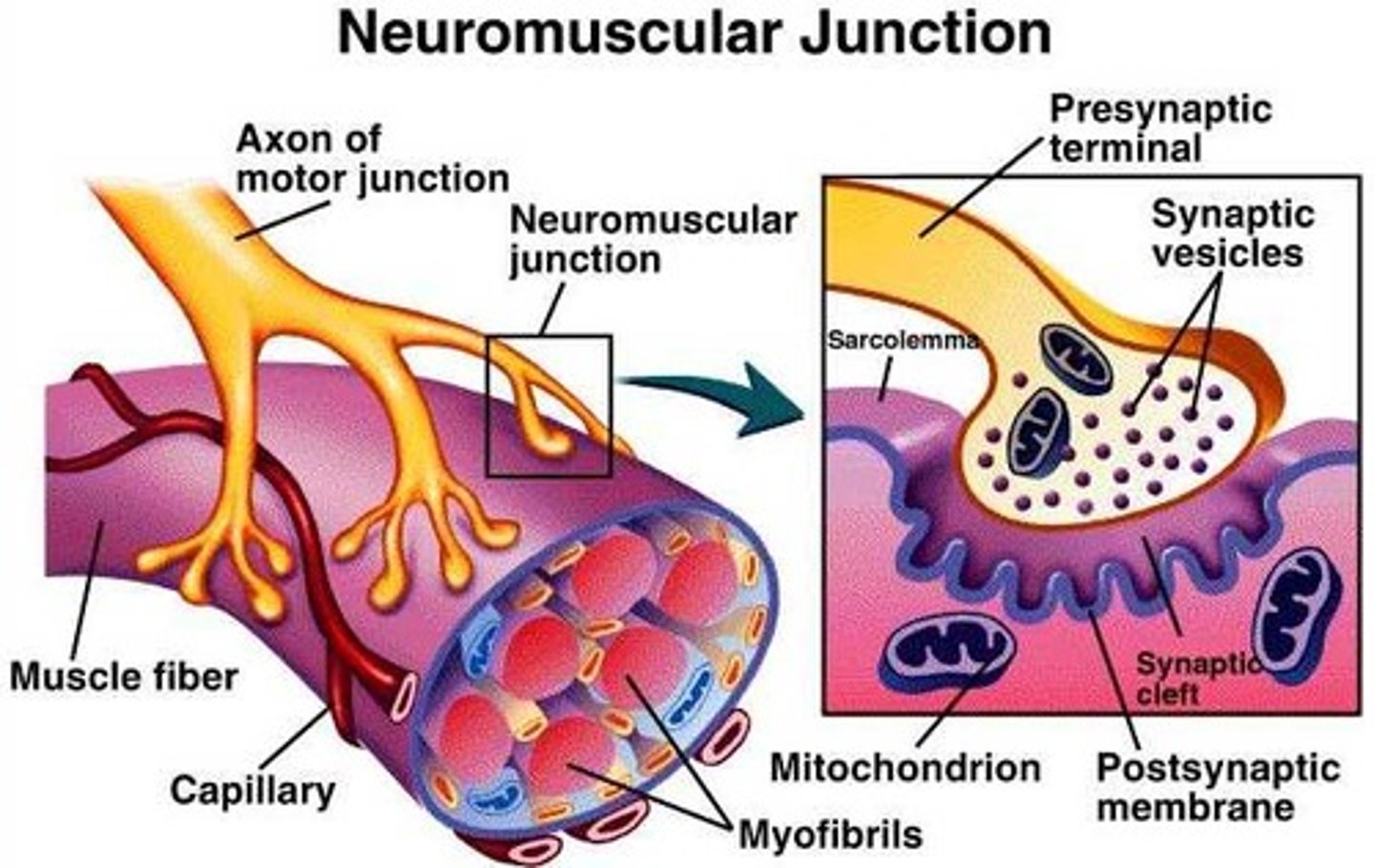
ACh Binds to Receptors: ACh binds to receptors on the motor end plate (part of the sarcolemma).
step 3
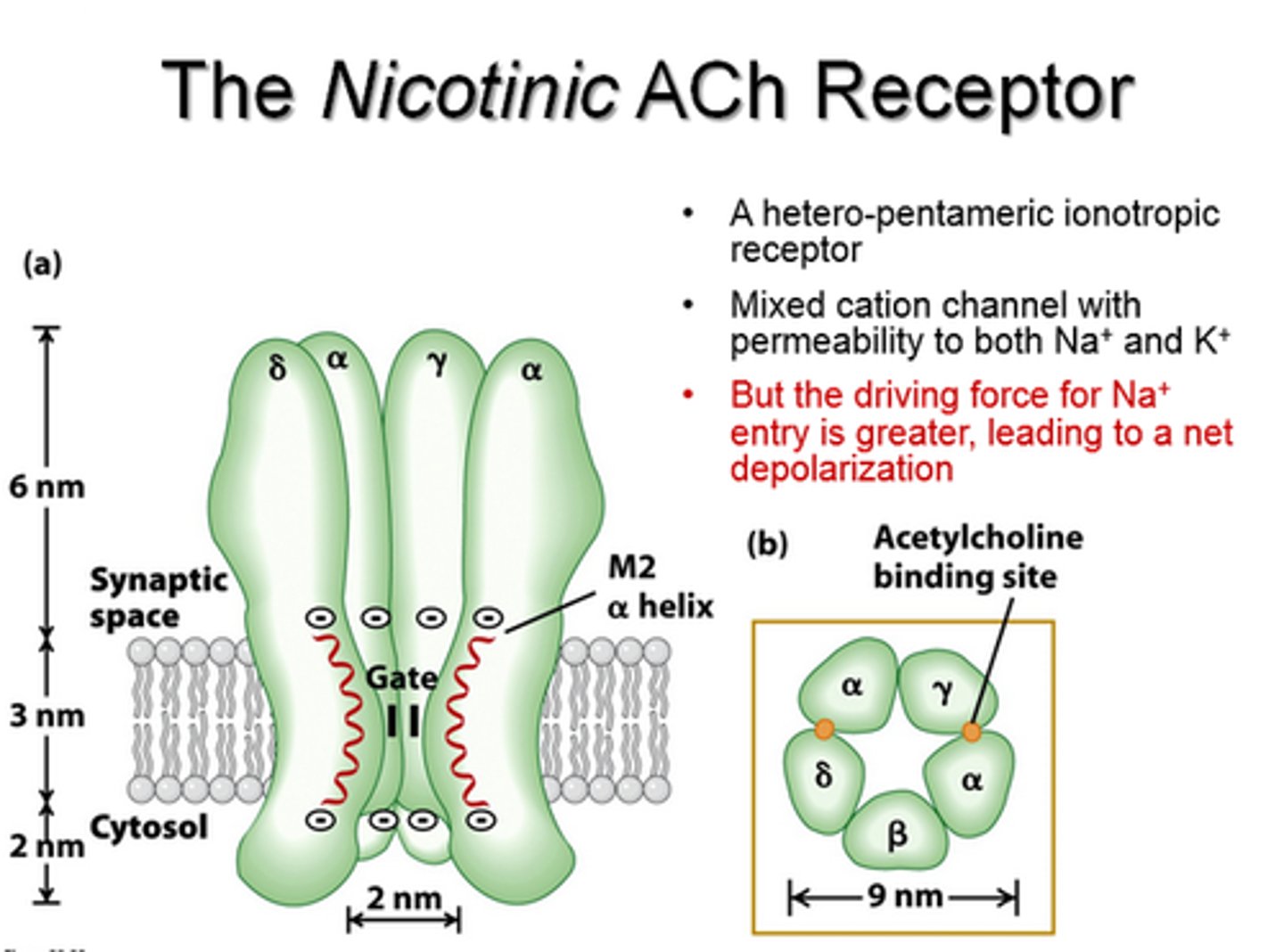
Sodium (Na⁺) Channels Open: Sodium ions rush into the muscle cell, triggering depolarization.
step 4
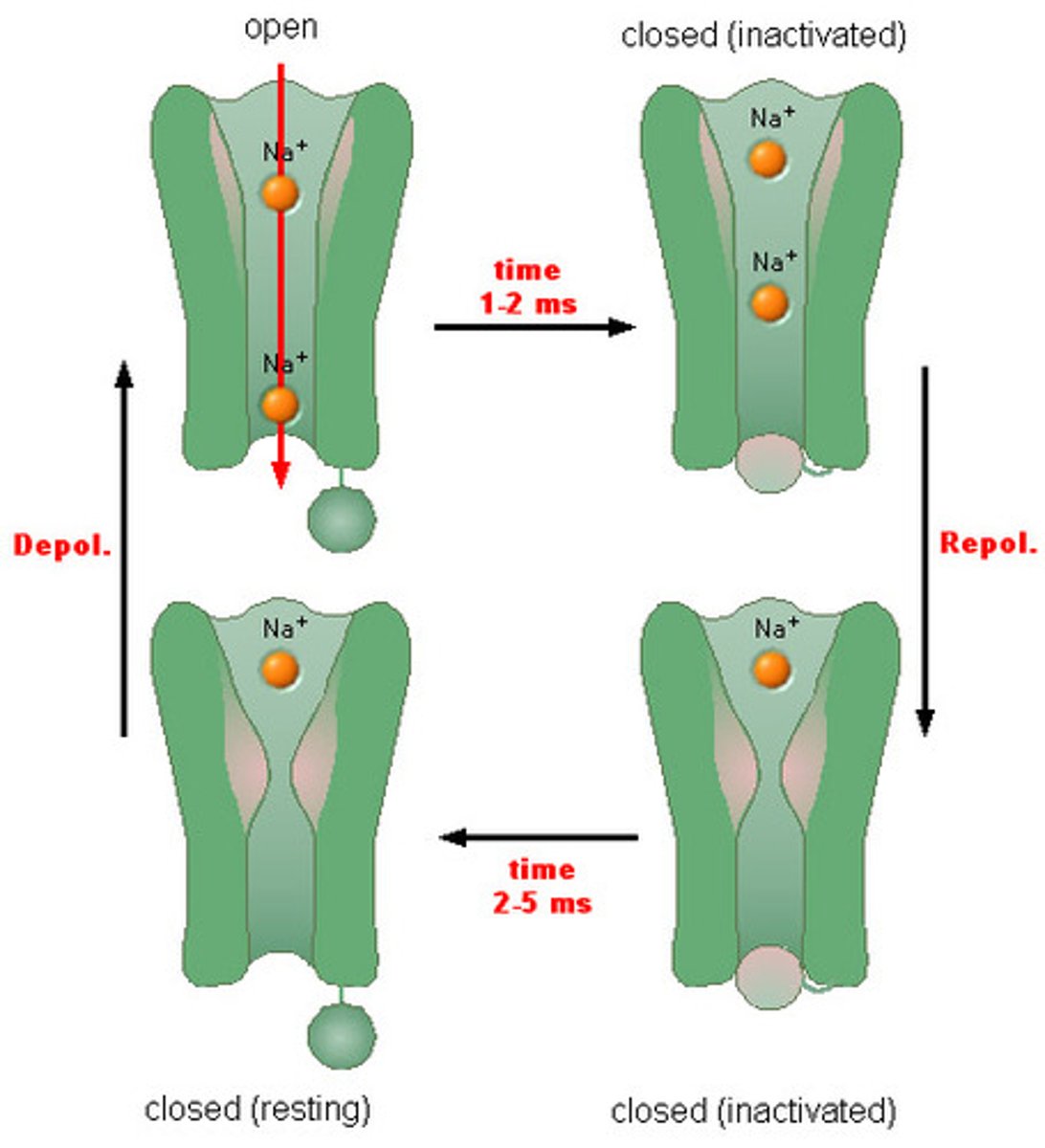
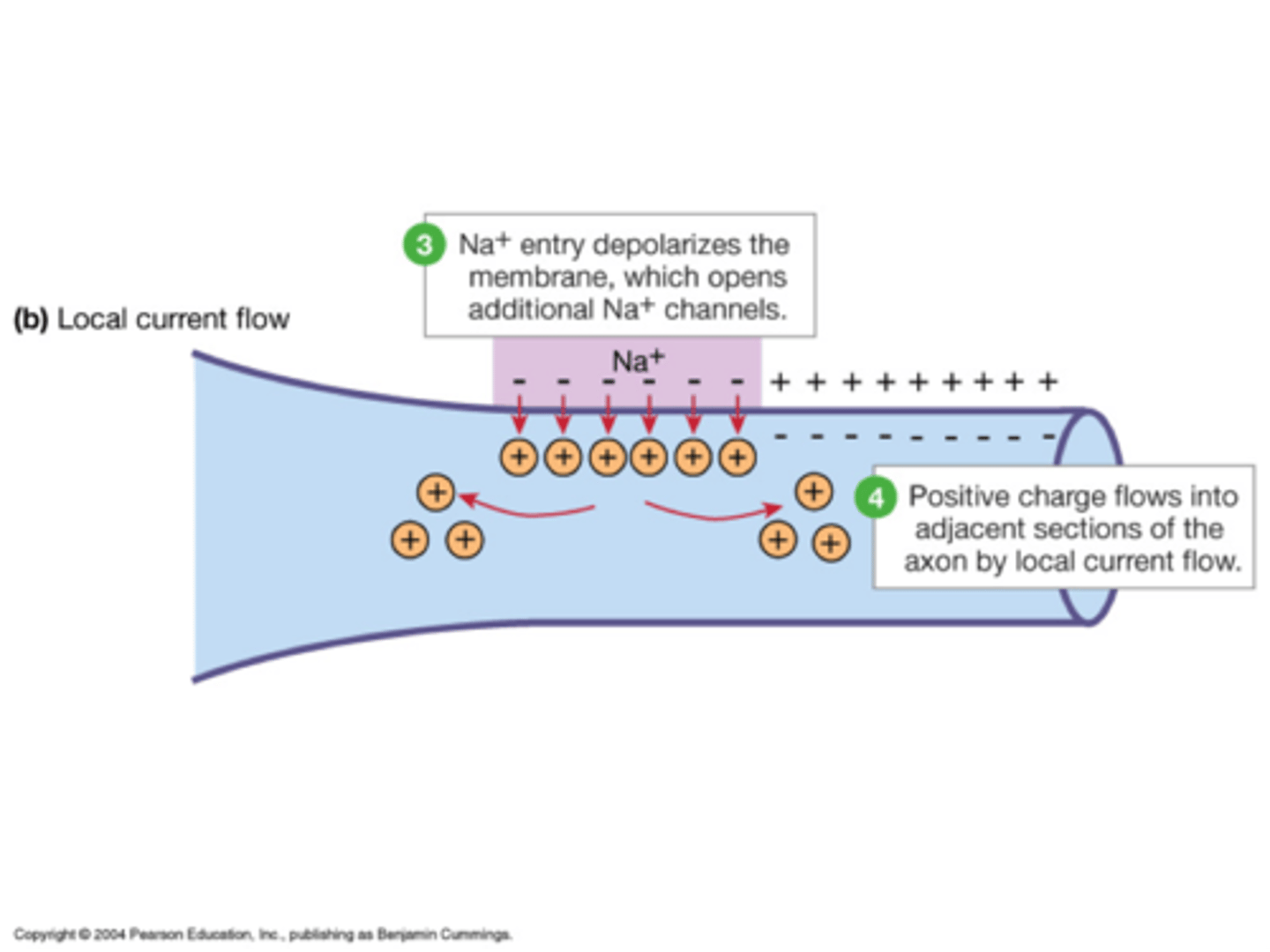
Action Potential Propagation: The electrical signal spreads along the sarcolemma and into T-tubules.
step 5
Calcium Release: The sarcoplasmic reticulum releases calcium ions, initiating contraction.
step 6
sarcolemma membrance potential
The sarcolemma's membrane potential is controlled by ion movement across the cell membrane.
resting potential
The cell's stable, negative charge when inactive (~ -70mV
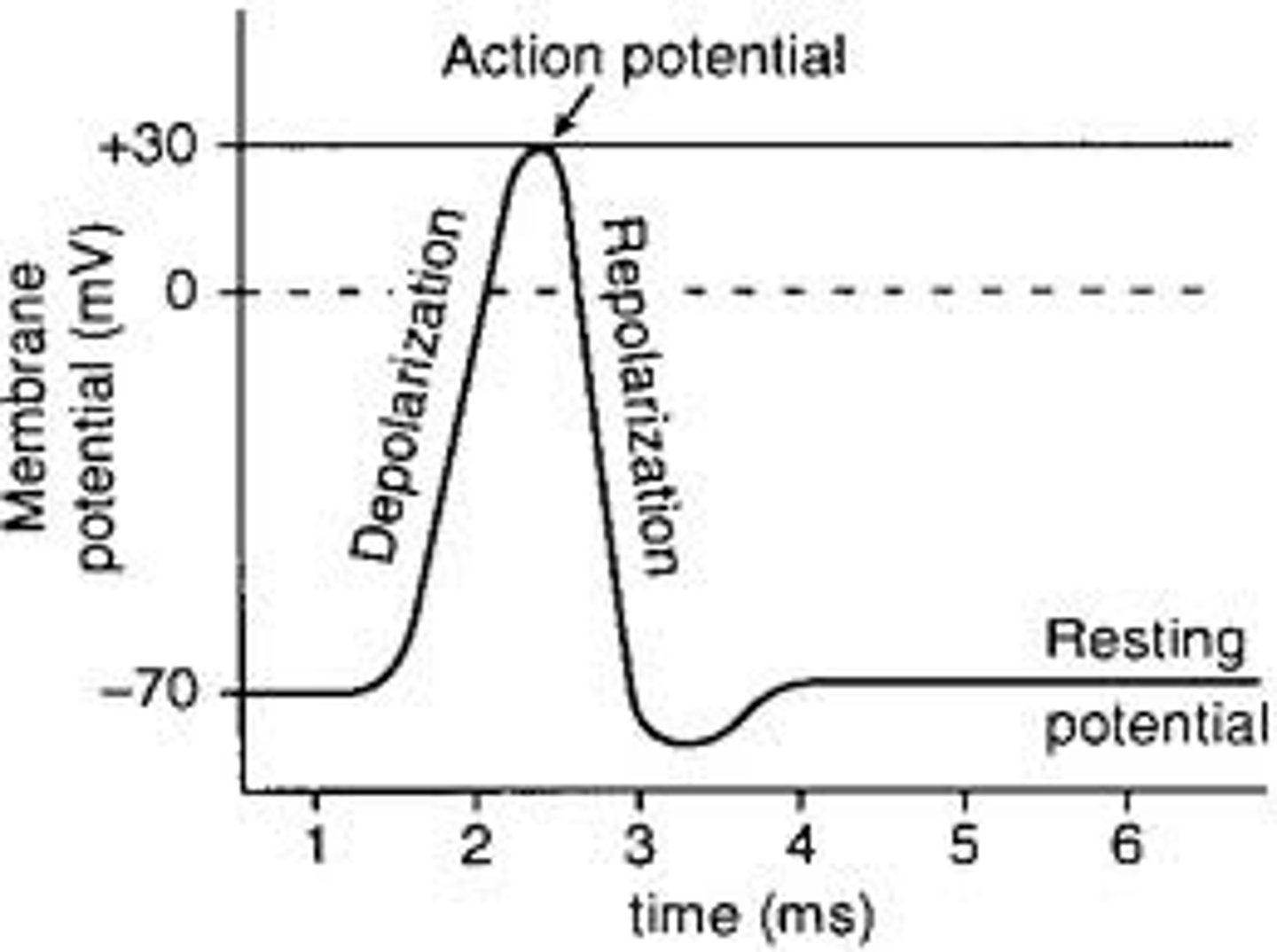
depolarization
Sodium (Na⁺) rushes into the cell, making the inside less negative.
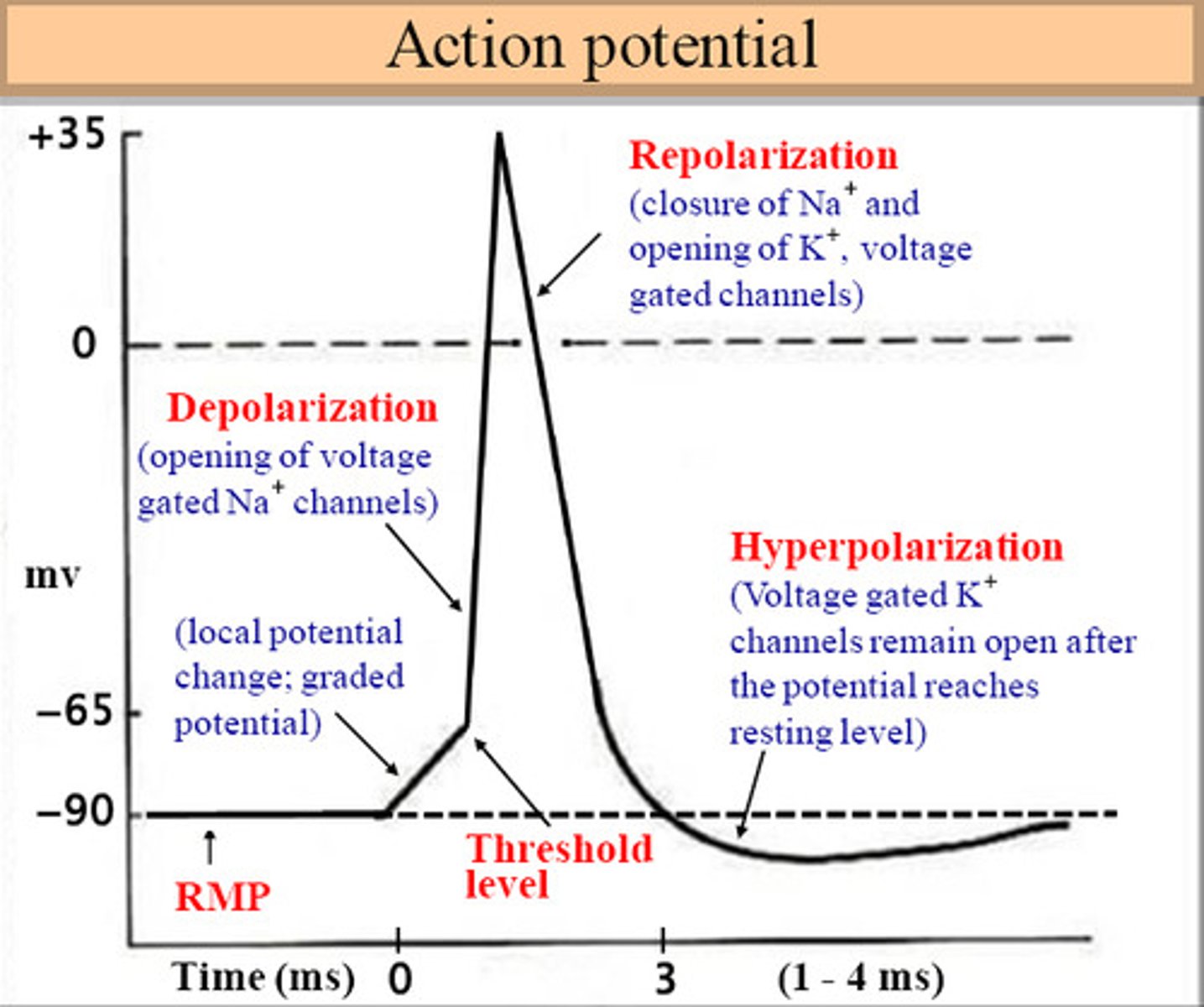
repolarization
Potassium (K⁺) rushes out of the cell, returning the inside to its negative state.
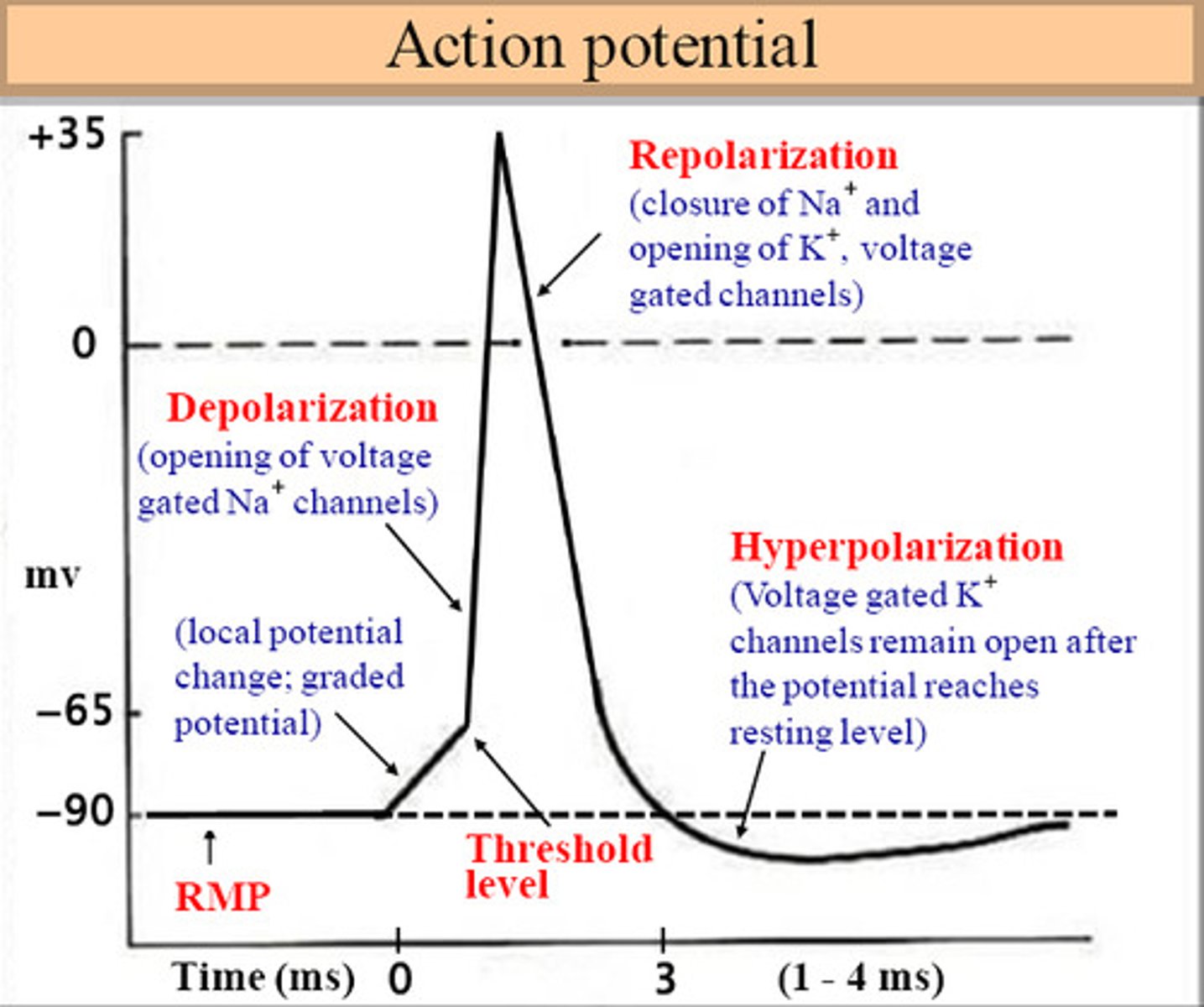
hyperpolarization
the cell becomes too negative before stabilizing
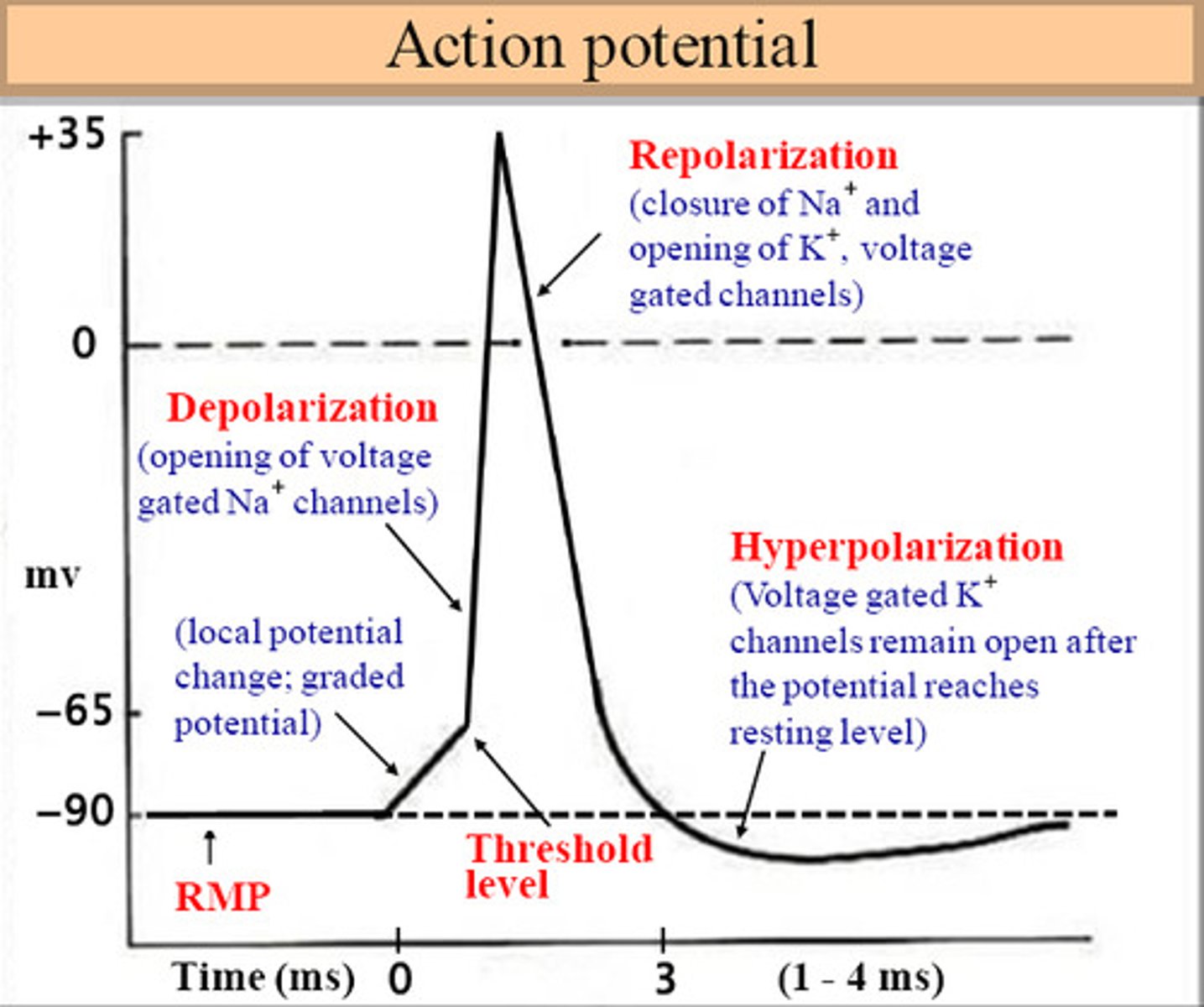
restoration of resting potential
The sodium-potassium pump restores the original ion balance.
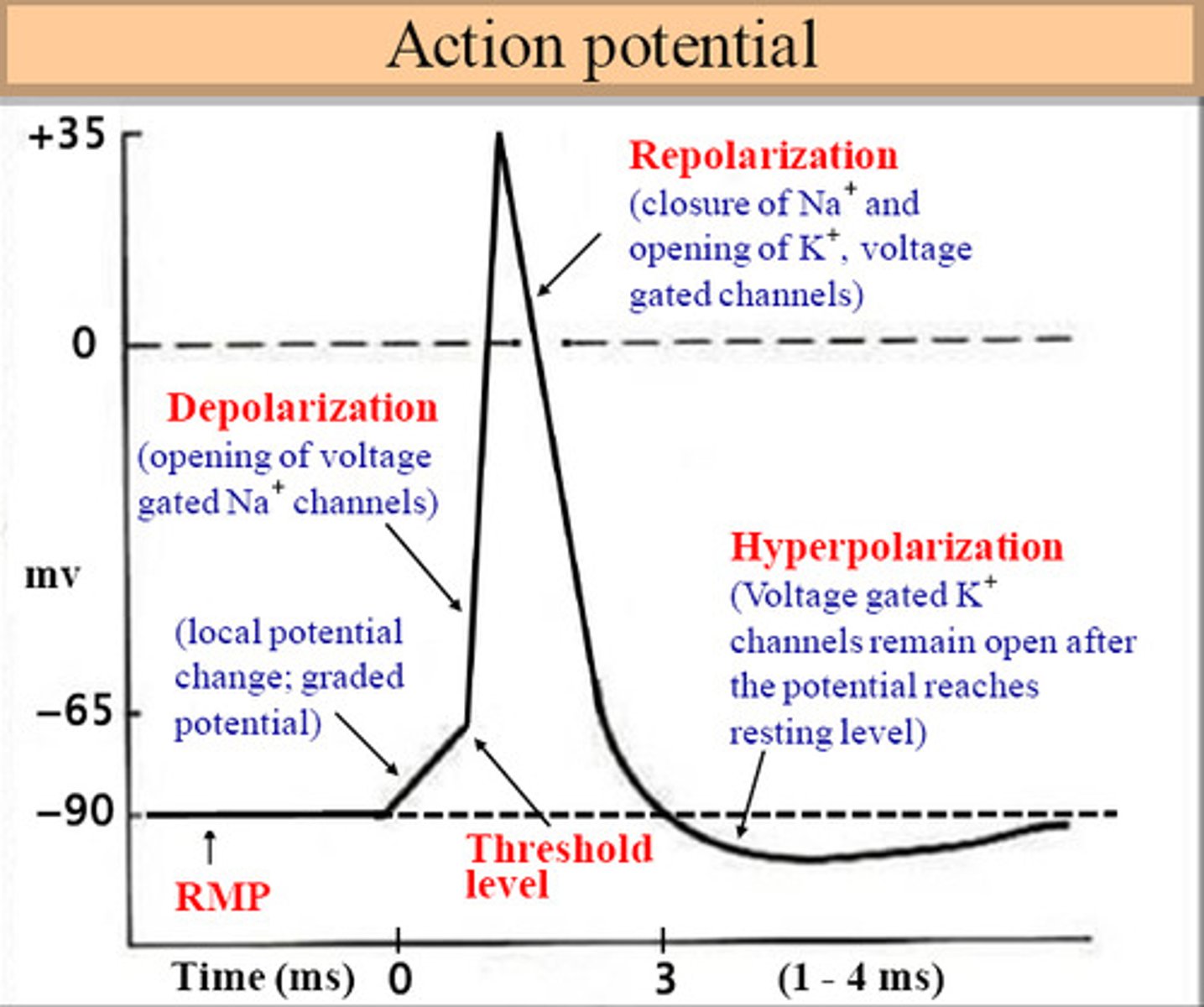
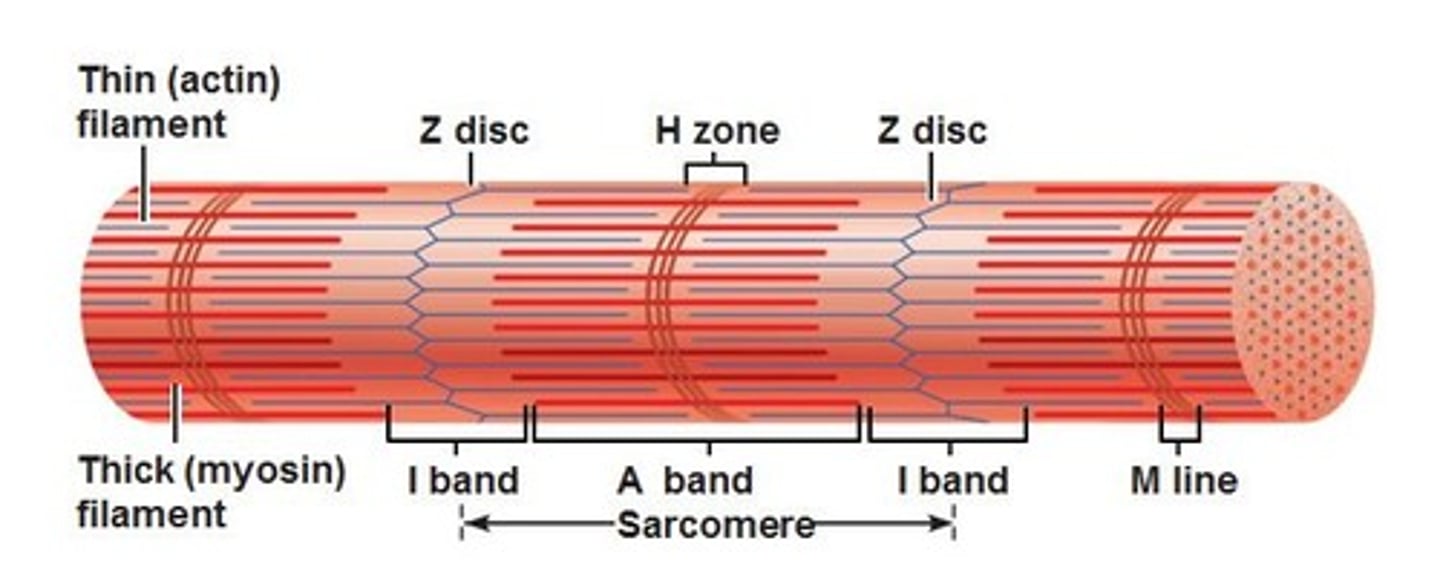
z-discs
boundary lines marking the ends of each sarcomere
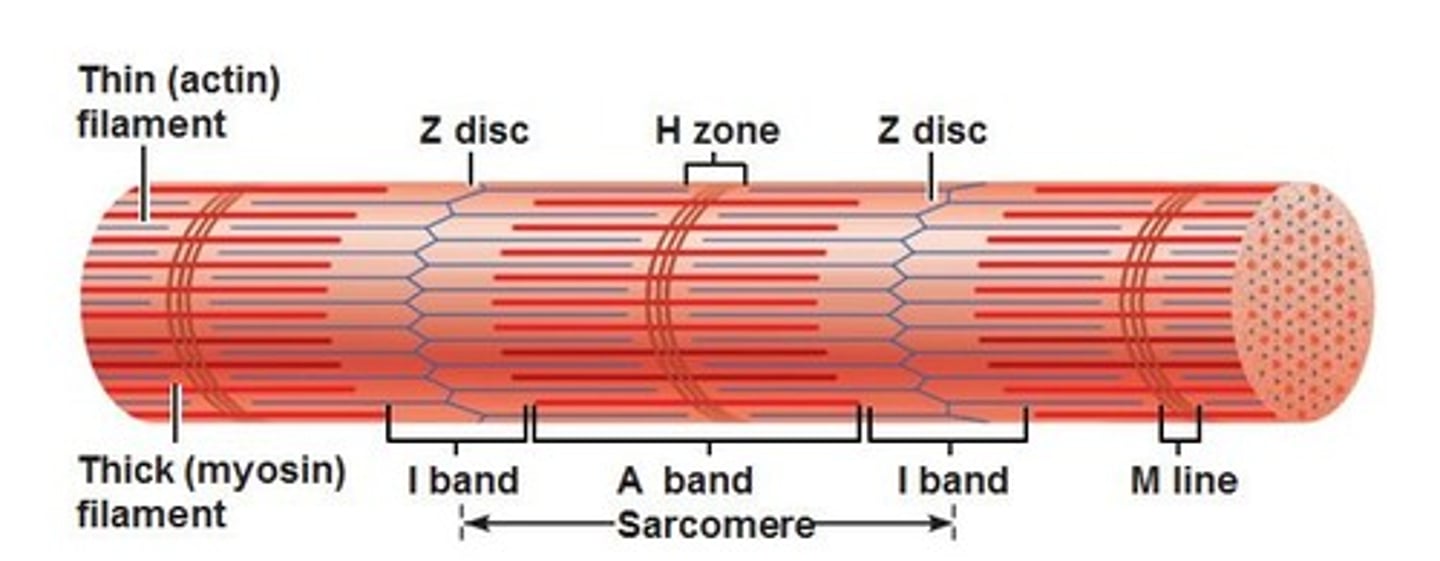
a-band
the dark area where thick filaments(myosin) are present
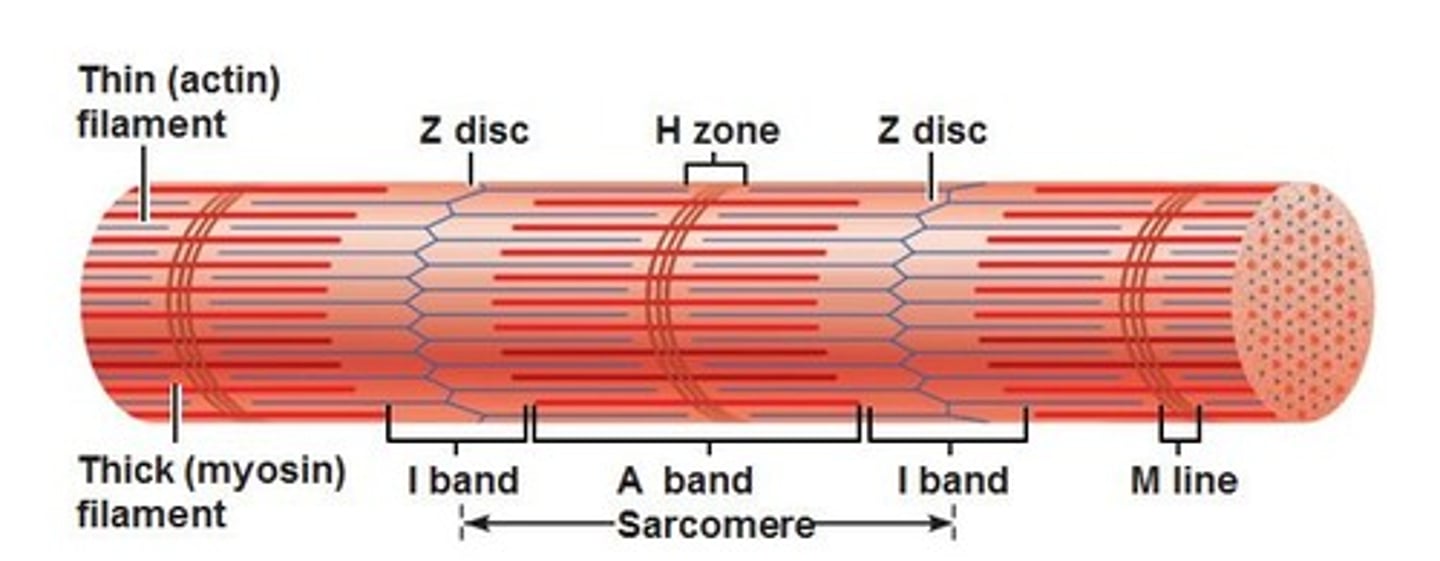
i-band
the light area containing think filaments (actin)
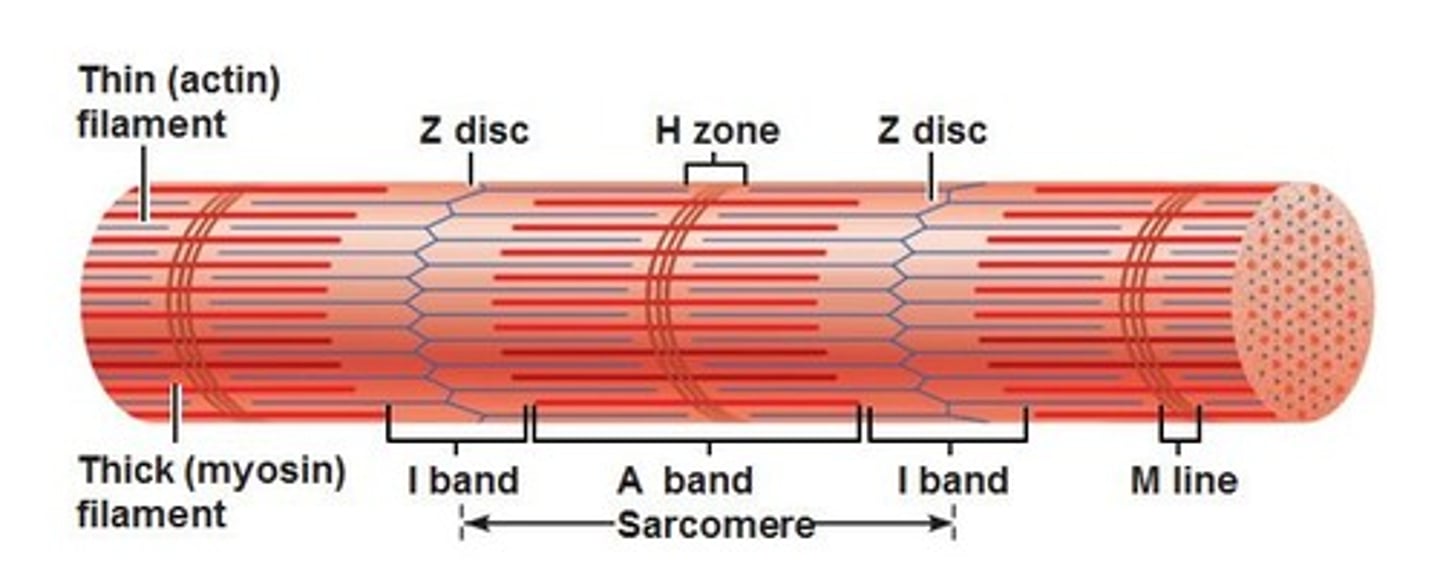
H-zone
the middle of the sarcomere that only contains myosin when relaxed
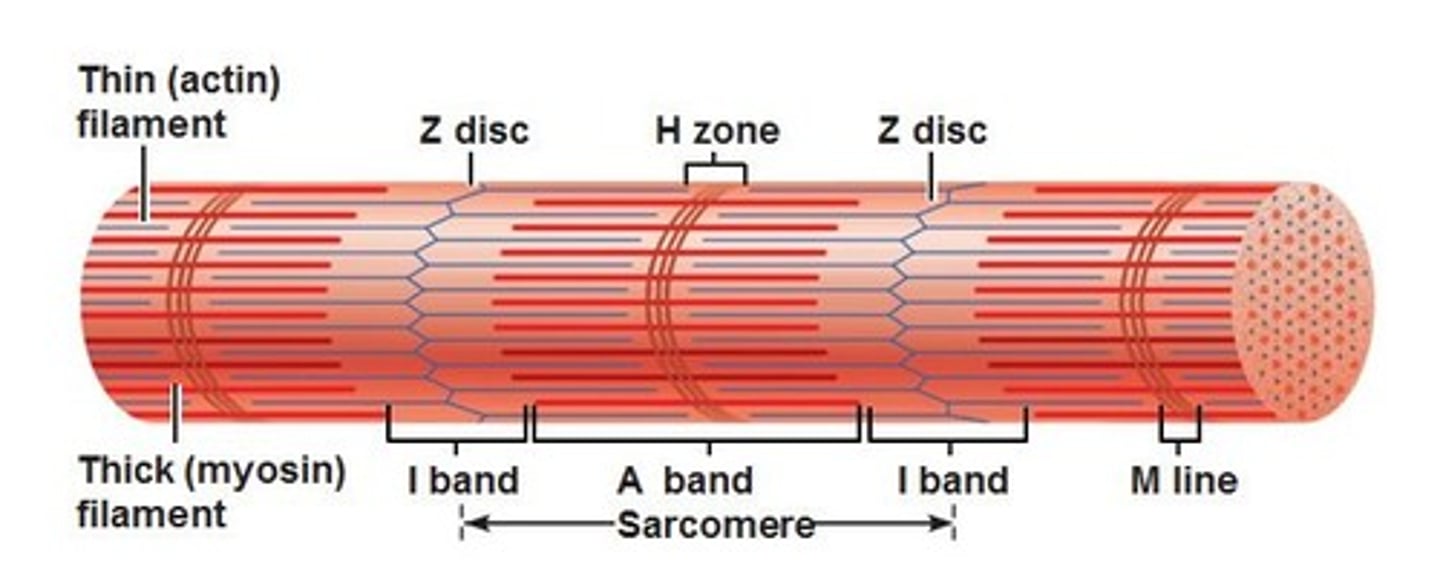
m-line
the center of the sarcomere that holds thick filaments together
sliding filament mechanism
Calcium Release: Calcium binds to troponin, which moves tropomyosin, exposing actin's binding sites.
Cross-Bridge Formation: Myosin heads attach to the exposed actin sites.
Power Stroke: Myosin heads pull actin toward the M-line, shortening the sarcomere.
ATP Attachment: ATP binds to myosin heads, causing them to detach from actin.
Cycle Continues: This process repeats, shortening the muscle fiber and causing contraction.
