STD and Skin disorders
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What is the most commonly transmitted STI by gram - bacteria?
- chlamydia (c. trachomatis)
Majority of the chlamydia symptoms are asymptomatic, but ocularly adults can have a
*inclusion conjunctivitis, that can turn to a prolonged unresponsive conjunctivis (doesn't respond to antibiotics)
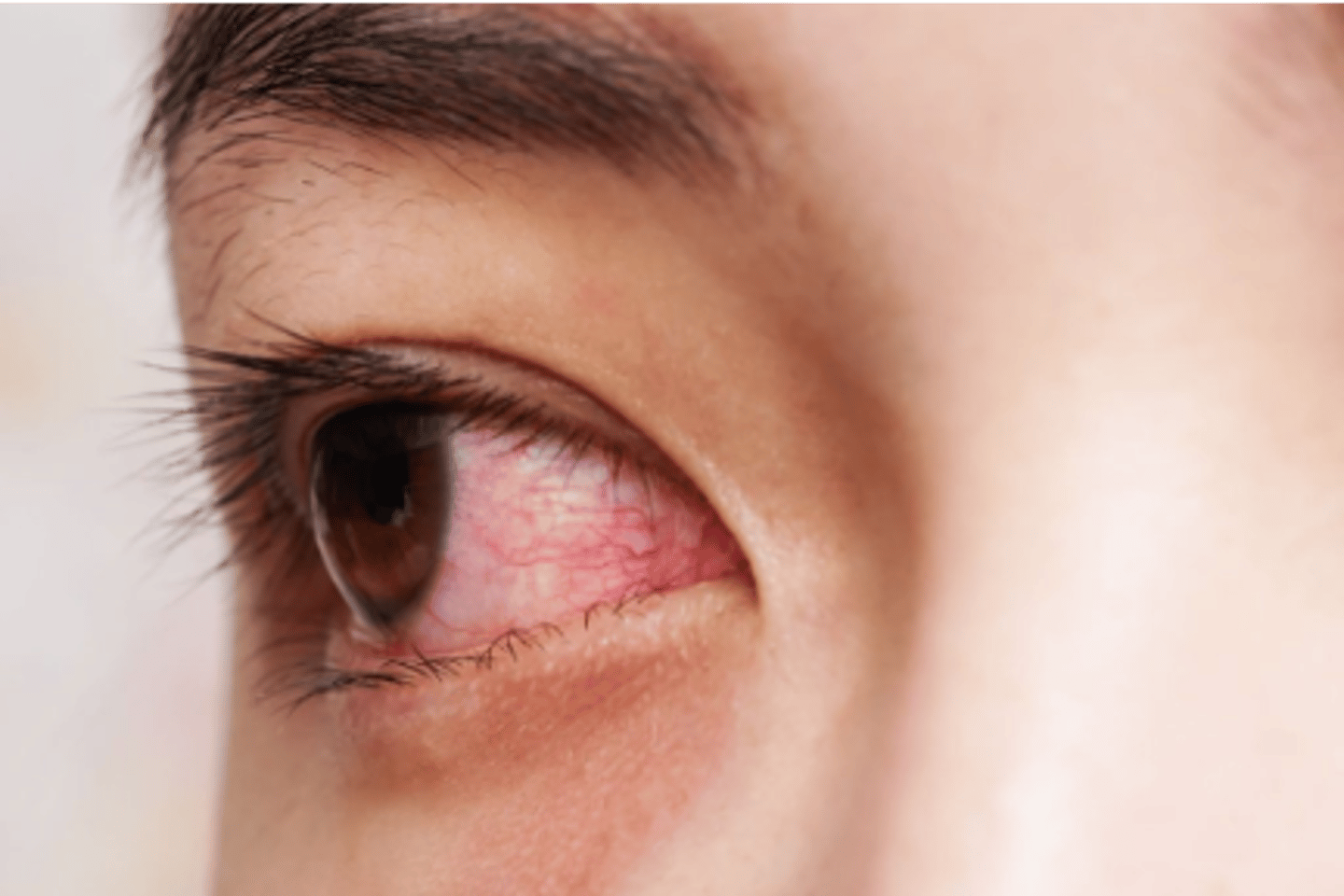
babies have a neonatal inclusion conjunctivitis,
- bilateral conjunctivitis that appears btwn day 4-15 w minimal to severe discharge
Doxycycline (100 mg bid x 7d) can be used to treat chlamydia
but it shouldn't be used in pregnant females!
(they can use azithro 1 g)
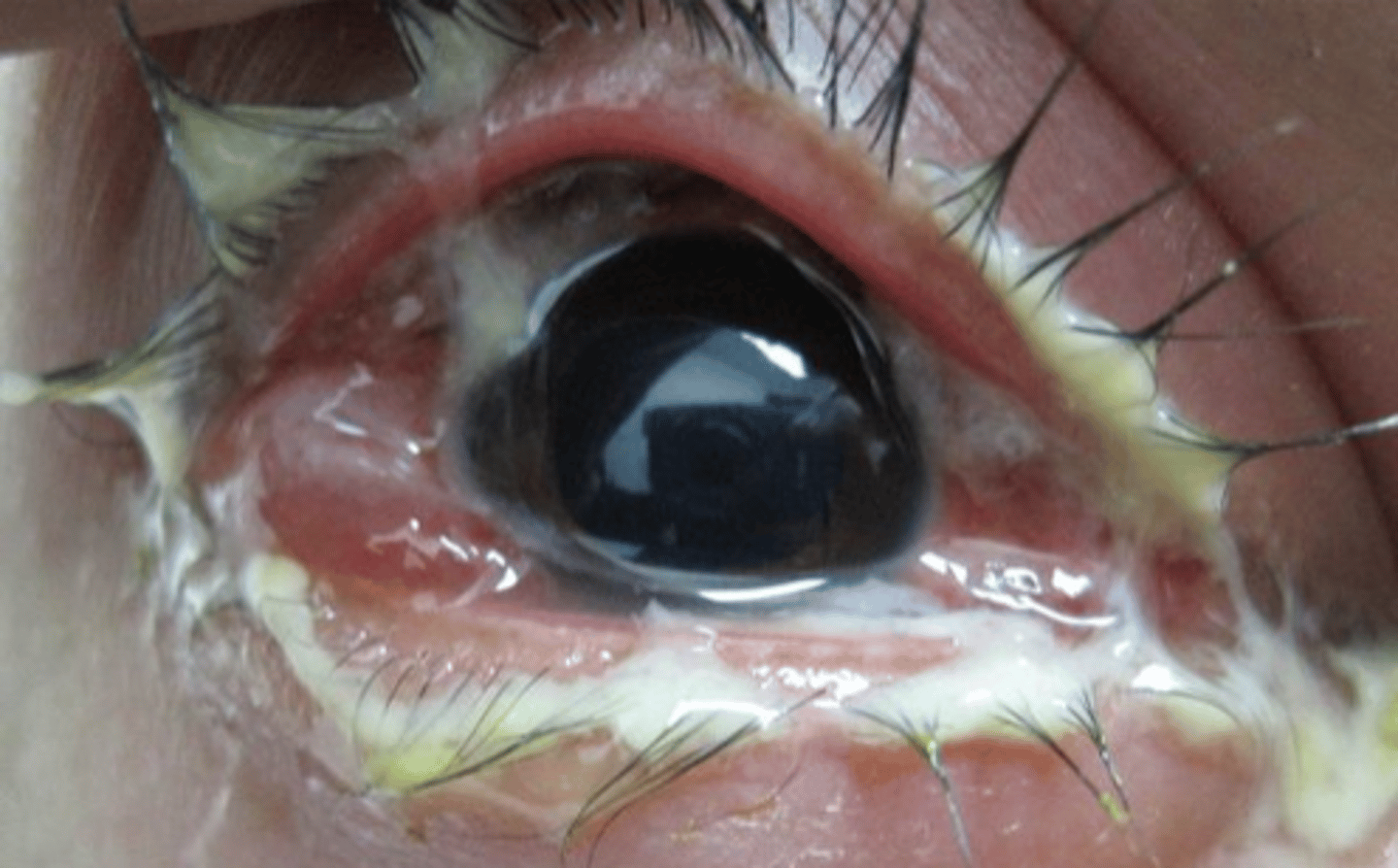
What is the second most prevalent STD caused by gram - bacteria?
gonorrhea (urethritis, cervicitis, epidymitis all observed in its bestie chlamydia too)
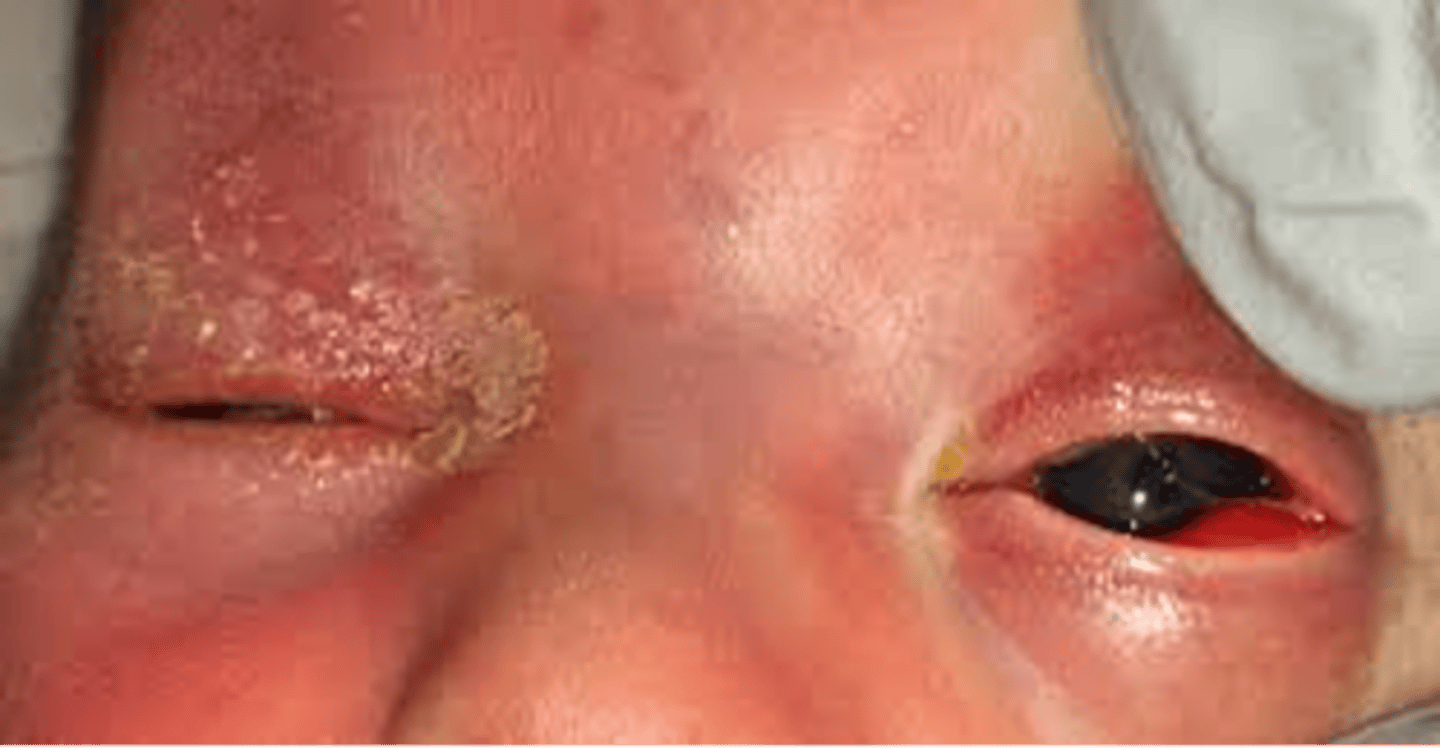
Main ocular complication with Gonorrhea
hint: "my eye just keeps pouring ______"
*hyperacute mucopurulent conjunctivitis (often w a concurrent urethritis)
Treat gonorrhea w
1 gram of ceftriaxone - single dose
Syphilis is a
- spirochete T. pallidum
- has 'hot spots' like OK
- disseminates in body through lymph
When is syphilis most infectious
during primary and secondary stages (early skin and mucous membrane)
What is neurosyphilis?
When syphilis spreads to the CNS. It can develop at any stage of the 4 stages of syphilis, but is more common in the tertiary (late) stage.
causing: mental changes, CN palsies EOMs, strokes, leg weakness
- typically occurs decades after infection
100% of patients with primary syphilis (red, painless chancres) will progress to secondary syphilis (disseminated syphilis) but
not all will be symptomatic
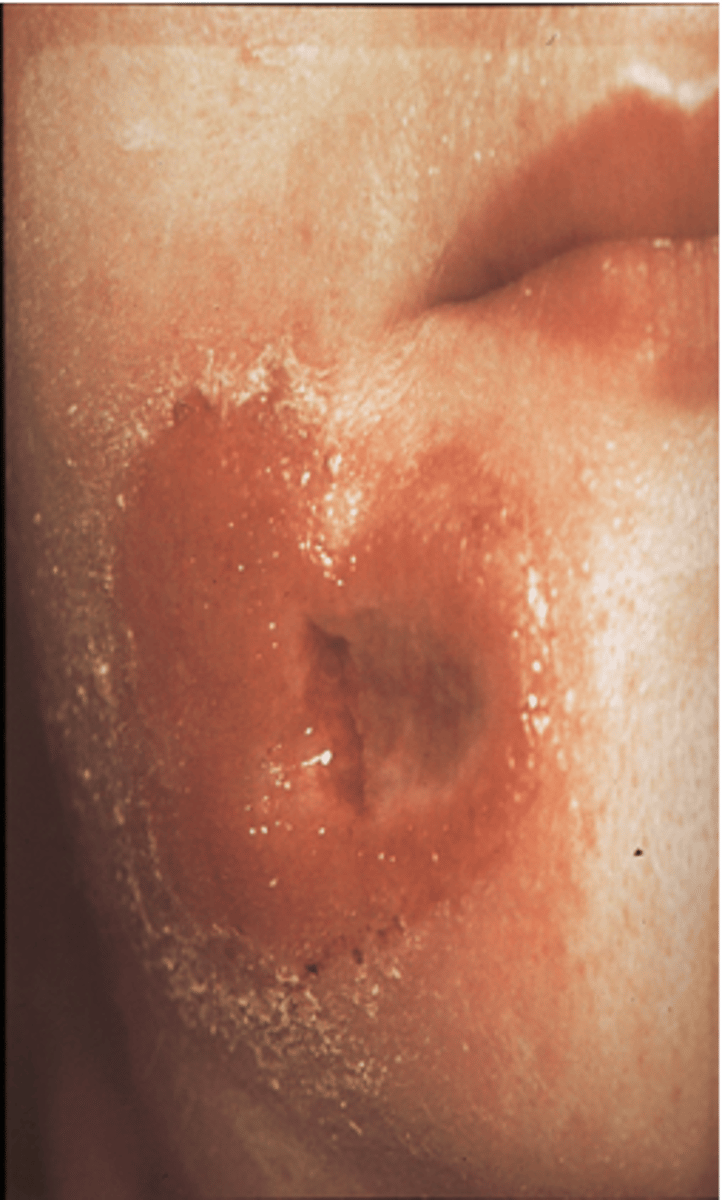
secondary syphilis
- occurs 1-3 mo and is when syphilis is systemic and not local anymore (skin and mucous lesions)
- can now test + for antibodies
- alopecia, flu- like symp., ocular syphilis (MOST common stage for ocular syphilis)
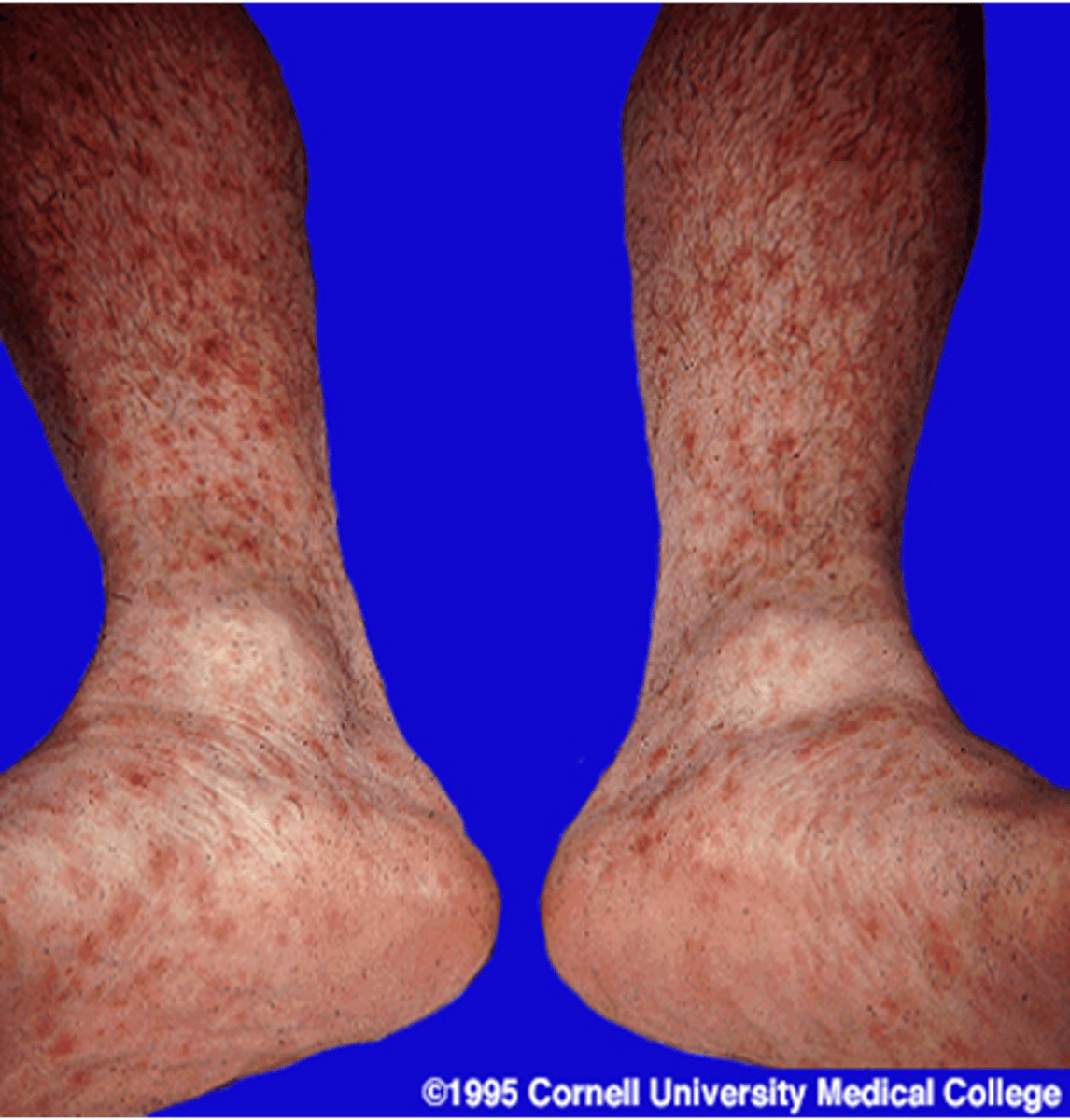
If left untreated (4-8 wks) syphilis can go through a symptom free period. aka latency period
early latency: can relapse
late latency: >1 year after secondary syphilis and rare relapse
Tertiary syphilis can affect any organ. We have two types:
1. benign (10-15 y): not affect vital organs but chronic phase includes "gummas"
2. cardiovascular (20-30 y): vascular inflammation. all pts <45 should get tested
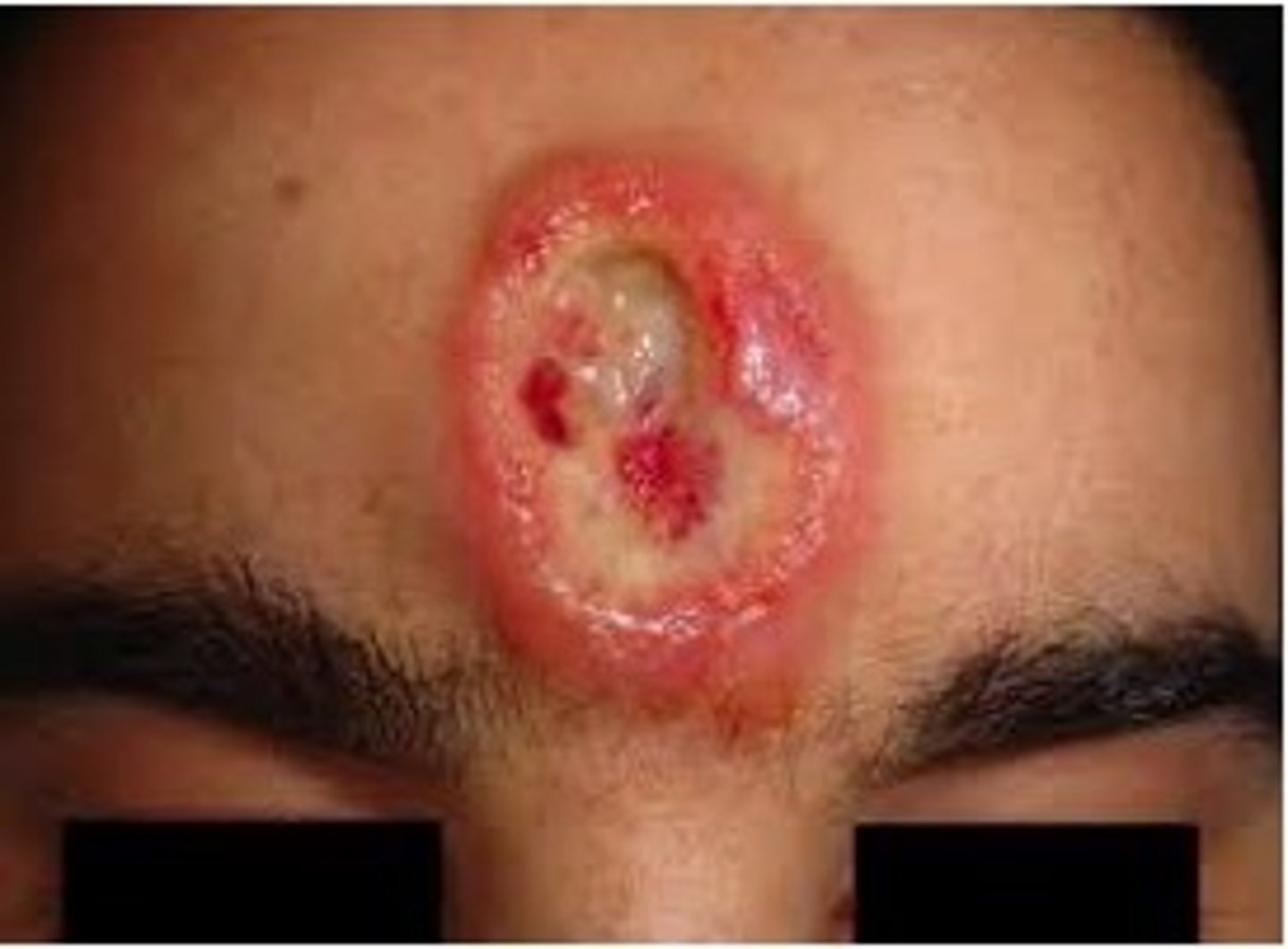
ocularly syphilis:
secondary: granulomatous pan-uveitis (only one that does NOT automatically classify as neurosyphilis)
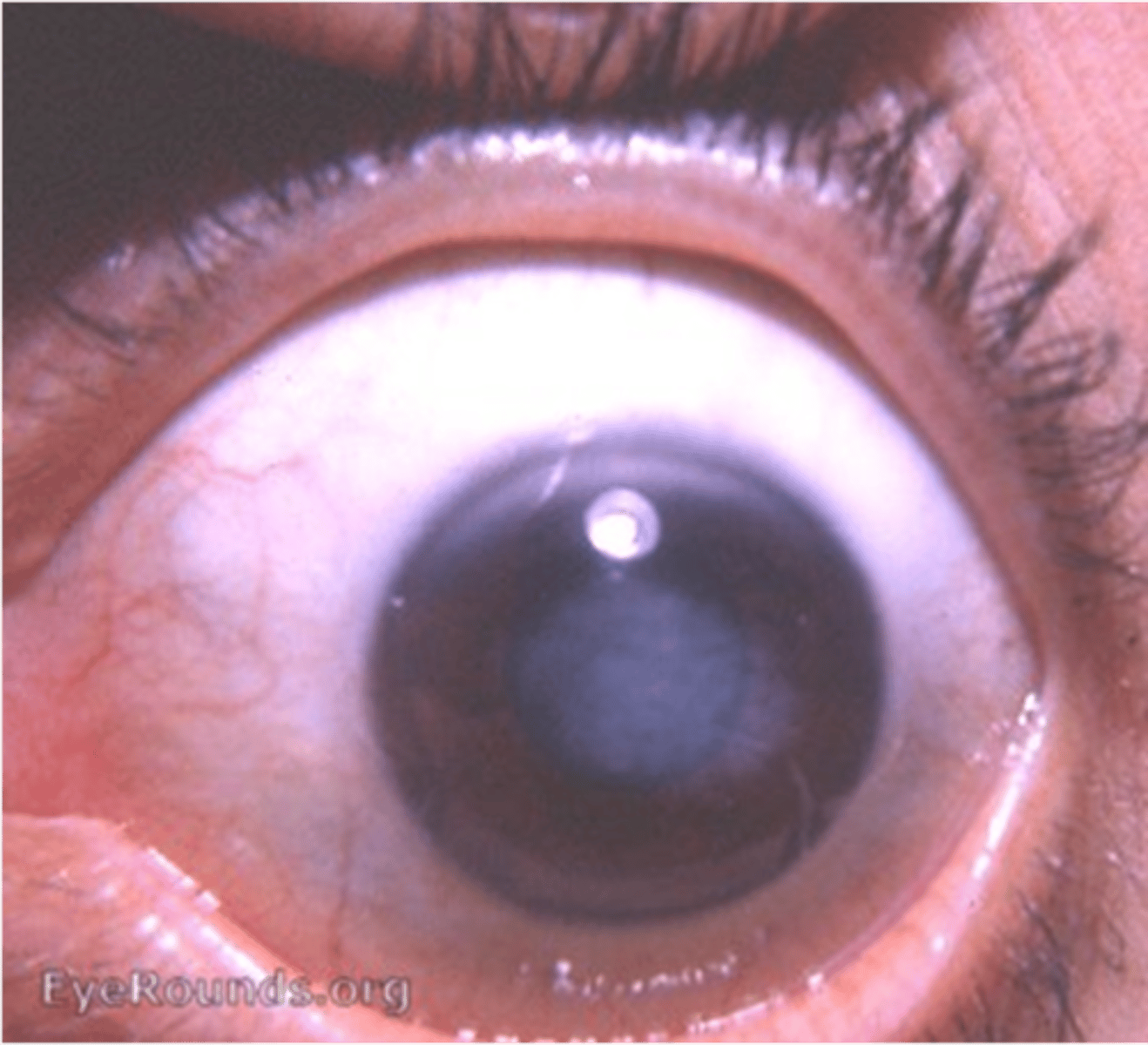
Neurosyphilis ocular effects:
- EOM palsies
- Pupil abnormalities (Argyll-Robertson Pupil)
-Chorioretinitis (Salt-and-Pepper Fundus - Congenital)
- Blepharoptosis
- Optic Atrophy
Congenital syphilis:
Hutchinson Triad
- defective teeth
- interstitial keratitis
- CN 8 deafness
HIV is prevalent in sub-sahara africa; what is the pathophysiology?
- Retrovirus infects T-helper (T4- lym. and helper) cells
- Virus uses the cell to make more viruses
- T4 cells are destroyed
- Without T4 cells, the immune system weakens
- Body can't fight infections
- Virus can stay hidden for years, but keeps growing silently
diagnostic tests for HIV
- ELISA and Western Blot (most sensitive for HIV)
CD4+ counts for HIV
lower levels = poorer health
- <200 is diagnostic as AIDS
- <50 is high risk AIDs
stages of AIDS
-initial: flu-like symptoms w no antibodies
- chronic: mo. to yr. w/o symptoms
- viral load cont. to increase and opportunistic infections will likely be COD (anorexia, dementia, diarrhea)
treat w antiretroviral therapy
Ocular manifestations of HIV --> AIDS.
- kaposi sarcoma (most common in AIDs)
- HIV retinopathy, uveitis, dry eye
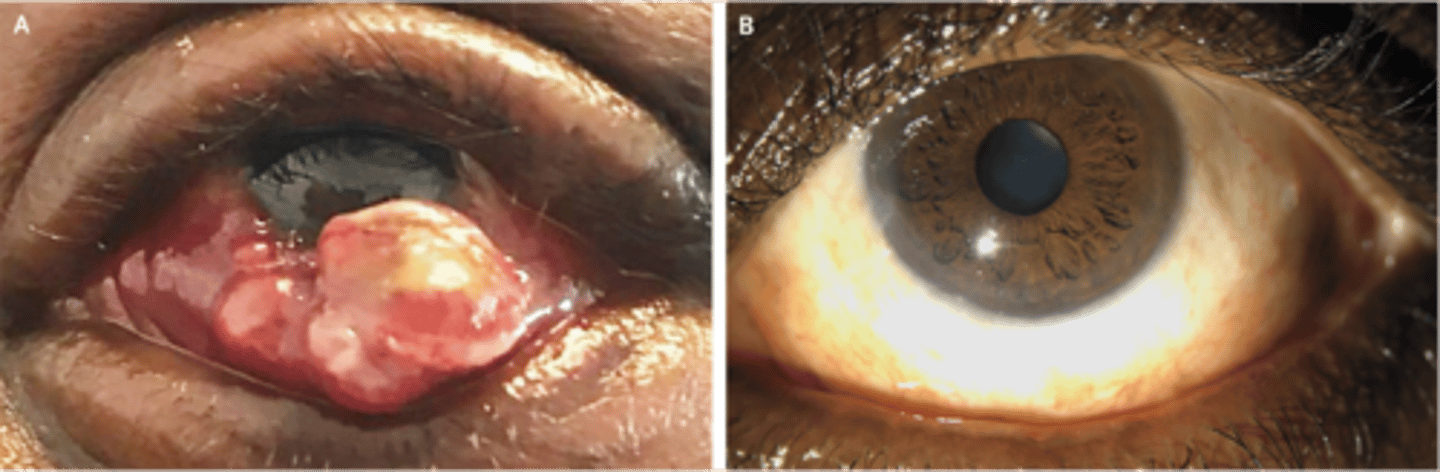
Herpes viruses are DNA viruses, while HIV is an RNA (retrovirus), what is Herpes Simplex
HSV-1 is above the belt.
- transmitted via bodily fluids
- 50-90% have hsv-1
- immune system can fight initial infection, but the virus remains dormant in ganglion cells (can come back up w stress)
HSV-1 reactivation complications
- fever blisters
- cold sores
- encephalitis, hepatitis, esophagitis
- ocular: epithelial keratitis (dendrite), stromal keratitis (haze in cornea), trabeculitis (IOP elevation), uveitis, conjunctivitis
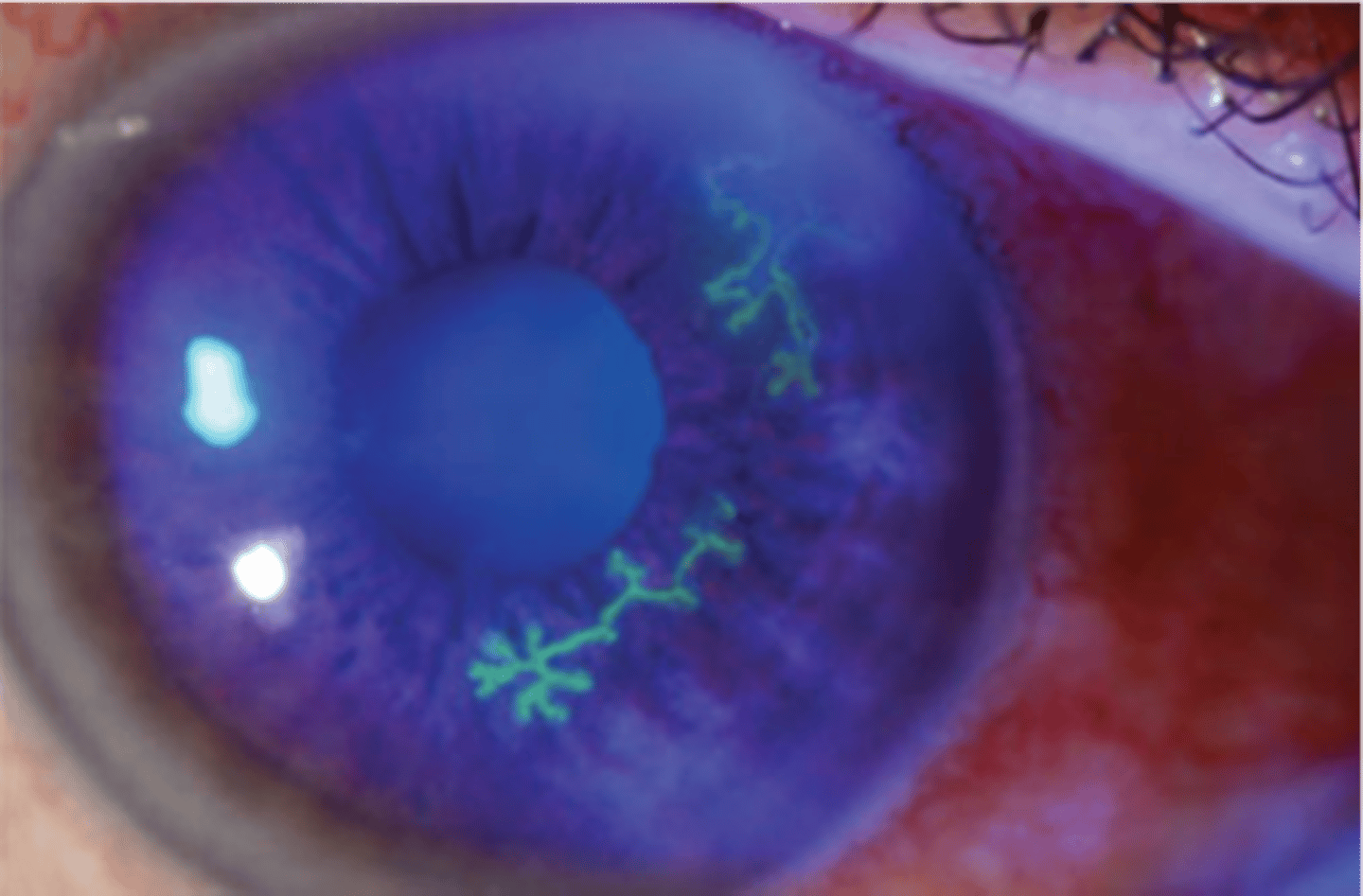
How do you treat HSV-1?
- w a "cyclovir" by 1/2 the dose for zoster
What is varicella zoster?
- virus that causes chicken pox and shingles (lesion contact spreads these)
varicella zoster: Chicken pox is primary (diffuse) infection
herpes zoster: shingles is a reactivation (both causes skin lesions)
Chicken pox is ___________, while shingles is
diffuse; only in one dermatome
vaccination for varicella zoster (chicken pox) reduces the risk of developing
- zoster and post-herpetic neuralgia
Zoster is shingles and ocularly manifests as
- hypoaesthesia
- keratitis
- uveitis
- dermatome pain
- do not examine HZO pts when you are pregnant!
Herpes zoster can have a burning, painful infection follow called
cranial neuralgia - often postherpetic
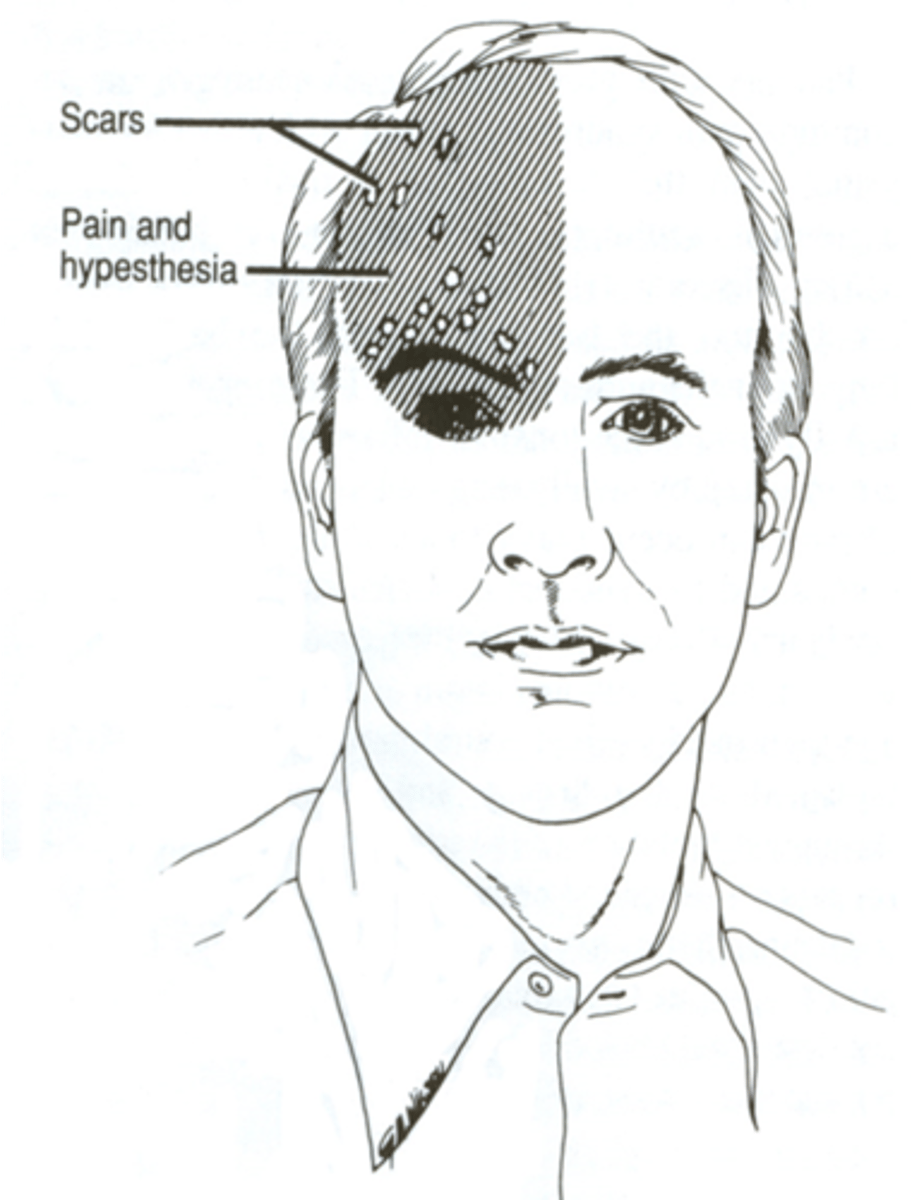
Tick borne-Illnesses: lyme disease and alpha-gal
Lyme disease is a
spirochete b. burgdoferi transmitted via ticks and is the leading cause of vector borne disease in US
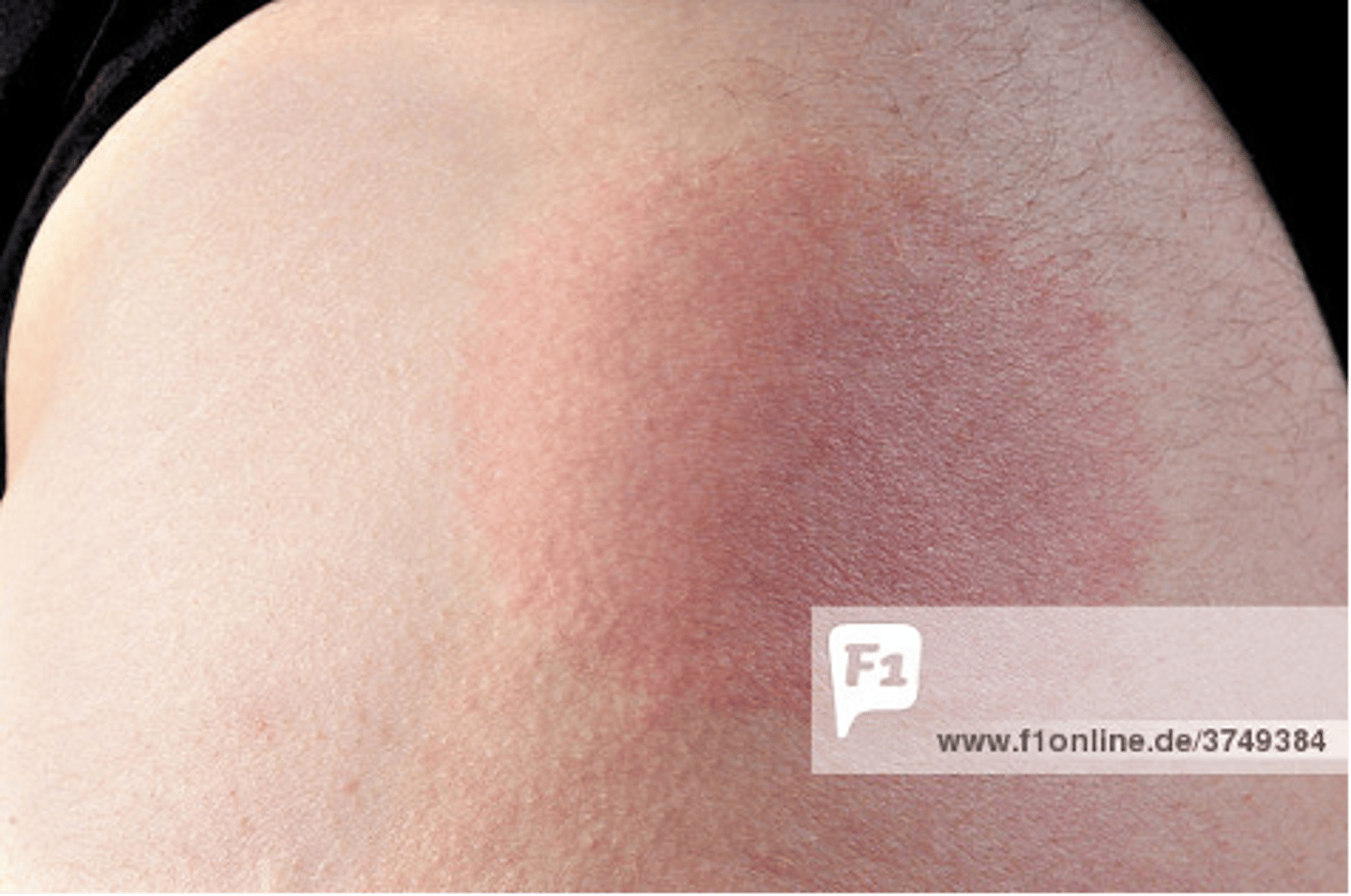
Lyme disease stages:
1. early localized disease: erythema migraines
2. early disseminated disease: joints, heart (+), nervous system
3. late disease: lyme arthritis
dx: IgA and IgG
tx: doxy
Rare ocular for lyme but
late - pupil abnormalities, CN palsies (3,4,6)
Alpha Gal is
IgE response to alpha-gal carbohydrate in meats, gelatins, and milk transmitted from a -lone star tick bite.
- avoid animal products to treat (eye drops too)
Rosasea: redness and rhinophyma, ocularly presents as
- Lid margin telangiectasia - Chronic dryness (MGD) - Corneal neovascularization - Often have comorbid demodex blepharitis
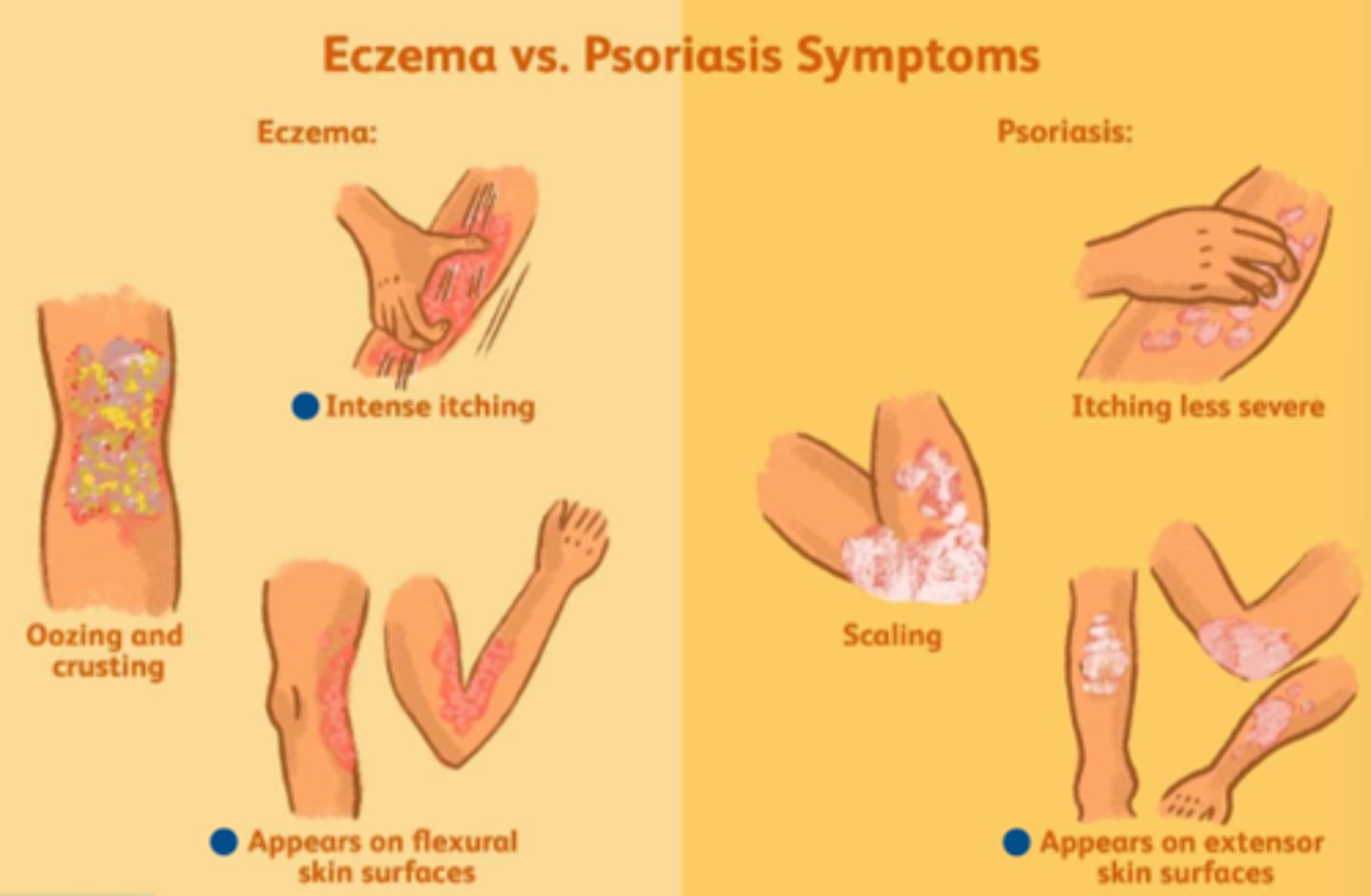
psoriasis (plaques) and eczema (atopic dermatitis - red patches) are both skin disorders that seem similar what can ezcema cause
- blepharitis (ezcema is most common in kids)
Steven Johnsons syndrome is most likely from
- medication (Dr. Miller)
- 1st 8 wks sulfa drugs
- **** mucosal erosin in mouth and conj.
Cellulitis is a
- bacterial infection of deep dermis and subQ in old people
Port wine stains are congenital but sturge-weber syndrome is a port -wine stain w a vascular hemartoma, ocularly we watch for
- glaucoma so CHECK IOPs!
Most common cause of skin cancer is
basal cell carcinoma
If a child has pediculosis in their eyelash
- call the police and report abuse
Can optometrist cut cancer?
- NOOOO but you can biopsy a benign lesion
The precursor to squamous cell carcinoma (more aggressive than basal cell but less aggressive than a melanoma) is
actinic keratosis (slow growing pre-malignant)
High-risk lesion feature
- macarosis (hair loss)
- asymmetric
- spontaneous bleeding
- itching
- eyelids: extend past the gray line
A neoplasia is NEW GROWTH
- if it is well-differentiated it will have a highly specific structure, grow slow, and less likely to be cancer
Oncogenes (allow mutated cells to grow) while, Tumor suppressor genes
- regulate cell growth and promote apoptosis (BRCA)