USHH Chap 11-12 Test Jefferson to Missouri Compromise
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Election of 1800
Jefferson and Burr each received 73 votes in the Electoral College, so the House of Representatives had to decide the outcome. The House chose Jefferson as President and Burr as Vice President.

Jefferson's Goals and First Term (1801-1804)
Jefferson wanted to shrink the National debt, shrink the army, and call for unity. During his first term, trade tripled, Louisiana purchase, and there was no war.
"Midnight Judges"
The 16 judges that were added by the Judiciary Act of 1801 that were called this because Adams signed their appointments late on the last day of his administration.

Marbury v. Madison (1803)
This case establishes the Supreme Court's power of Judicial Review b/c John Marshall declared the writ of mandamus unconstitutional.

Election of 1804
Thomas Jefferson ran as a Democratic-Republican and Charles Cotesworth Pinckney ran as a Federalist. Jefferson easily defeated Pinckney. George Clinton won for Vice President. This marked the death of the Federalist party.

Jefferson's Second Term (1805-1809)
Jefferson was popular and easily won the election in 1804, but foreign policy problems plagued it. The war between England and France led to more attacks on US trade ships the British navy impressed more than 1000 American merchant sailors per year from 1803 to 1807 jefferson was frustrated with his inability to get England or France to stop attacking US ships
Impressment
British practice of taking American sailors and forcing them into military service

Orders in Council (Britain)
No neutral ships can trade w/ Fr nor its allies (eg. Spain)

Imperial Decrees (France)
No neutral ships can trade w/ Br nor its territories
USS Chesapeake
US warship, the British thought that the ship might be carrying deserters of the British navy so they fired cannons at the sloop, killing 3 Americans and wounding others. 4 deserters were found on the ship and one was hanged.

Embargo Act of 1807
This act issued by Jefferson forbade American trading ships from leaving the U.S.

Election of 1808
the Democratic-Republican candidate James Madison defeated Federalist candidate Charles Pinckney.
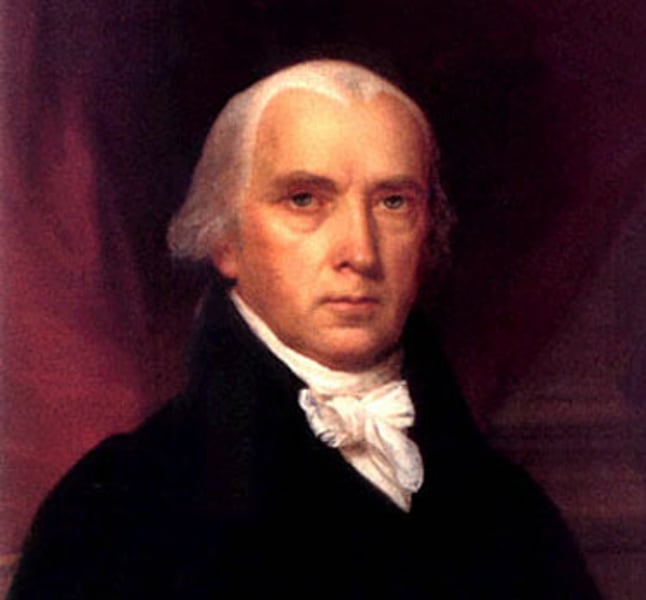

Macon's Bill #2 (1810)
It lifted all restrictions on trade and promised France and England that if either nation would lift their trade restrictions, the U.S. would trade only with that nation (the U.S. would not trade with the other nation). France accepted first.

war hawks (1811-1812)
New, young Southerners and Westerners who were eager for war with Britain. They had a strong sense of nationalism, and they wanted to takeover British land in North America and expand.

Tecumseh and the Prophet
Two Shawnee brothers, Tecumseh and Tenskwatawa, welded a far-flung confederacy of all the tribes east of the Mississippi. The Prophet was discredited by attacking a much larger American army, and Tecumseh was killed in the Battle of the Thames. Their actions were in response to the flood of western-bound settlers and resulted in Indian unity and cultural revival. The death of Tecumseh ended the hope of an Indian confederacy.

Battle of Tippecanoe (1811)
U.S. forces - led by William Henry Harrison - defeated Tecumseh's confederacy then burned its headquarters at Prophetstown.
Historical Significance:
Tecumseh's confederacy allied with the British during the War of 1812; Harrison emerged as a war hero.

William Henry Harrison
Military leader during the War of 1812 with remarkable achievements like the defeat of the Indian Confederacy,

1812 Offensive Phase
3- pronged attack on Canada
US attacks Montreal, Niagara, and Detroit (All Fail)
US Navy Successful (USS Constitution defeats HMS Guerrierre off Boston Coast)
1813 Offensive Phase
Battle of Chippewa Falls- Winfield Scott defeats the British at Niagara - no surrender
Battle of Thames- William H Harrison defeats Brits (Tecumseh killed)
US soldiers burn York (Capital bldgs)
1814 Defensive Phase
British: 3-pronged Attack
Lake Champlain: Battle of Plattsburgh
Br invade Chesapeake
Treaty of Ghent (1814)
Ended the War of 1812. Did not address grievances that led to the war (stalemate for both sides).

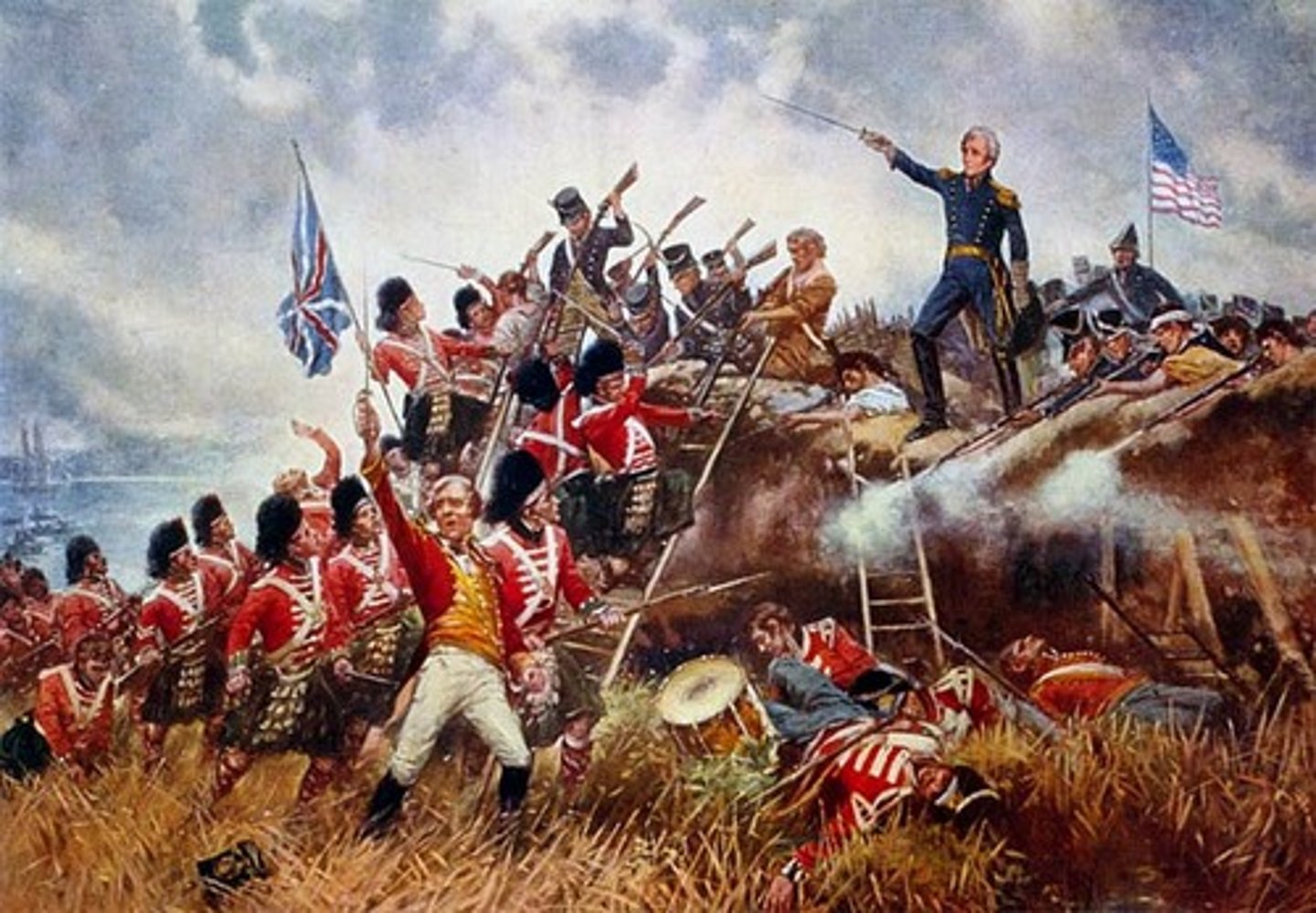
Battle of New Orleans (1815)
Famous battle the occurred AFTER the War of 1812 is finished ironically. Battle that made Andrew Jackson a war hero- he was able to bring together Americans and inspire them to fight the Brits.

Hartford Convention (1814)
A meeting of Federalist delegates from New England inspired by Federalist opposition to the War of 1812; contributed to the death of the Federalist Party during the "Era of Good Feelings". They wanted to make constitutional changes and make individual peace with Britain.

Death of Federalists
-Federalists lose 6 straight elections
-Their anti-war stance was seen as disloyal
-Country had grown too rural to care about Federalist policies (favors rich)
-By 1820 they are done! They don't even have a candidate for President!

Era of Good Feelings (1815-24)
Period of strong nationalism, economic growth, territorial expansion under the presidency of James Monroe. Only one major political party at the time (Republican)

The American System (1815)
Henry Clay's economic plan for America. Government adopted tariffs and national bank, but rejected call for internal improvements (said it was unconstitutional)

Henry Clay
A northern American politician. He developed the American System as well as negotiated numerous compromises.

Bonus Bill of 1817
Securing funding for roads and canals was hard. This bill was passed by Congress to give states $1.5 million for internal improvements, but it was immediately vetoed by Pres. Madison. In his opinion, he believed states should pay for their own improvements.

Market Revolution & Impact on America
Steamboats, factories, canals, railroads
West- Cheap Land
Cheap land = more opportunities for weath

The panic of 1819
Economic panic caused by extensive speculation and a decline of European demand for American goods along with mismanagement within the Second Bank of the United States. Often cited as the end of the Era of Good Feelings.

Missouri Compromise of 1820
Allowed Missouri to enter the union as a slave state, Maine to enter the union as a free state, prohibited slavery north of latitude 36˚ 30' within the Louisiana Territory (1820)
Marshall Cases (3)
mcculloch vs maryland (1819)
supreme court case that strengthened federal authority and upheld the constitutionality of the bank of the united states by establishing that the state of maryland did not have power to tax the bank.
cohens vs virginia (1821)
case that reinforced federal supremacy by establishing the right of the supreme court to review decisions of state supreme courts in questions involving the powers of the federal government.
gibbons vs ogden (1824)
suit over whether new york state could grant a monopoly to a ferry operating on interstate waters. the ruling reasserted that congress had the sole power to regulate interstate commerce.
Marshall cases (2)
Fletcher v. Peck (1810)
Supreme Court case which protected property rights and asserted the right to invalidate state laws in conflict with the Constitution
Dartmouth College v. Woodward (1819)
This decision declared private corporation charters to be contracts and immune form impairment by states' legislative action. It freed corporations from the states that created them.