Heterogeneous Transformations
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
What are the benefits of a heterogeneous catalyst?
Ease of separation
Easier use in flow reactors (more efficient, safer, higher ratio of catalyst to reagents)
Shape selectivity (pore size)
What is the benefit of catalysts with multiple surface sites?
You can have different properties in different areas of the catalyst surface eg hydrophilic/ hydrophobic, bronsted acid, amphoteric sites (both acidic and basic), lewis acidic.
What is the IUPAC definition of
A) Micropores
B) Mesopores
C) Macropores
A) < 2.0 nm
B) 2-50 nm
C) > 50 nm
What is the benefit of pores in a catalyst?
Increased surface area so more active sites
Define heterogenisation
Attaching a homogeneous catalyst to a solid surface.
What is the role of (MeO)3SiR in heterogenisation?
Adds an organic group to an inorganic support.
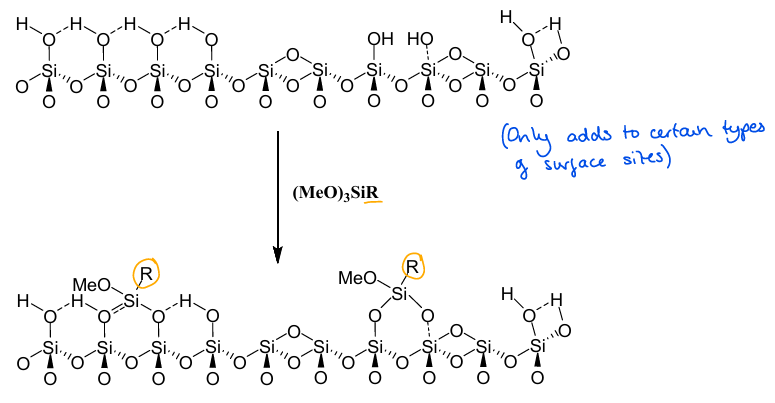
What are the two methods of heterogenisation?
1) Grafting to the surface with (MeO)3SiR
2) Direct synthesis of catalytic groups into the support
What are the benefits of solid sulphonic acid?
High loading (2-3 mmolg-1)
Bronsted acidity
High surface area
Ease of separation as heterogeneous catalyst
Recyclable with no loss of activity
What are the disadvantages of solid sulphonic acid?
Catalyst formation has production steps which increases the PMI of the process (more waste produced)
What are the disadvantages to using AlCl3 in Friedel Crafts reactions?
Produces very acidic waste and is too reactive to be recovered.
What are the benefits of using solid supported AlCl3 in Friedel Craft reactions?
No toxic aqueous waste produced
Faster and simpler process
Lower excess of benzene required
Lower PMI
Catalyst is reusable
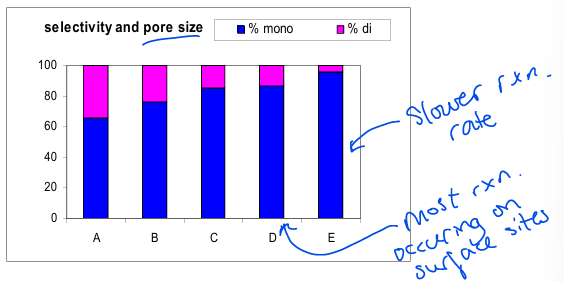
What is shape selectivity
When the size of the pore dictates which products are favoured. Eg smaller pore means less di-substituted products
Why is a catalyst required for amide formation? Which catalyst is used?
The traditional (non-catalysed) method involves heating acid and amines together. This requires an activating agent (such as SOCl2) which is rarely recoverable.
Silica is used because it makes the process safer (less toxic than SOCl2 etc.), is reusable and is easily removed
What are the benefits of flow chemistry?
Good temperature control (higher surface area)
Smaller reaction volumes so smaller accidents
Larger catalyst to reagent ratio
Good mixing
Once the flow begins, it is low maintenance
Unreacted reagents can be cycled back around
What is the general make-up of zeolites?
SiO2 framework, with some Si replaced with Al.
Al isomorphous substitution gives acidity.
The lattice has an overall negative charge so requires counterions.
What is the aperture diameter?
The size of the pore entrance.
What is the typical aperture diameter of a zeolite pore?
< 1 nm
generally just large enough for small aromatic molecules
What are the disadvantages to zeolite synthesis?
High temp. and moderate pressure
NaX (sodium salt) waste
Template is burned out, meaning poor AE & PMI
What are the advantages to zeolite synthesis?
Zeolites are almost indestructible so last for several years - high TON - synthesis negatives are outweighed
What are the two types of zeolite structure?
Pentasil and truncated octahedron
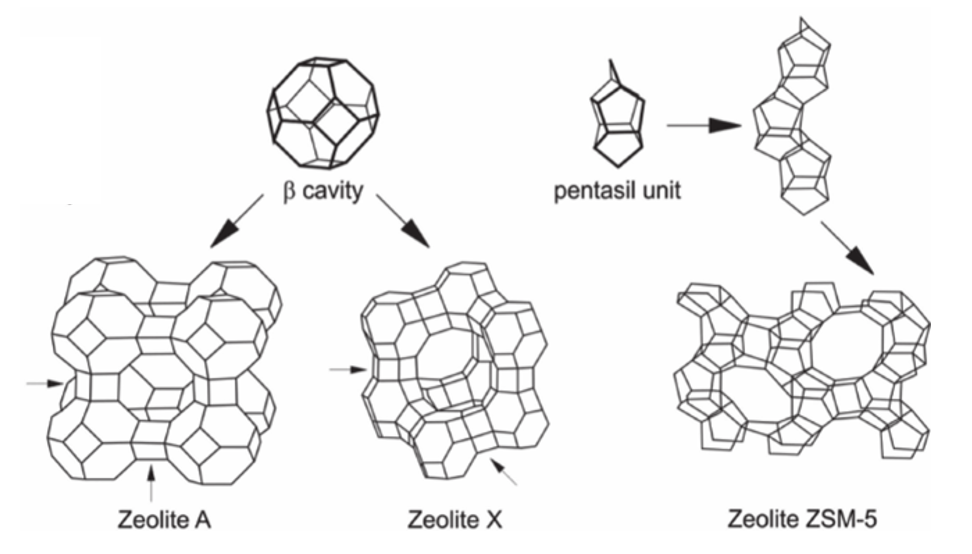
Name this zeolite structure
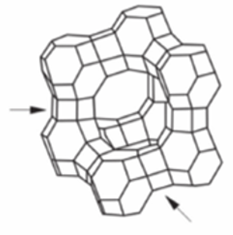
Faujasite
What is the impact of replacing a Si with Al in a zeolite?
Al gives a framework charge of -1 so a positive counterion is required. This is typically Na from the synthesis, which can then be replaced with Ca/ Mg etc to soften water
What impact does the positive counterion have on a zeolite?
Can impact pore size
How do you produce a zeolite with a H+ counterion?
Add NH4Cl to introduce a NH4+ counterion, then reflux to remove ammonia
How do you measure the acid strength and concentration of acid sties of a zeolite?
Measure Tdes (temp. of desorption) - a higher temperature means a stronger acid site
The amount of ammonia released suggests the number of acid sites
This is called temperature-programmed desorption (TPD)
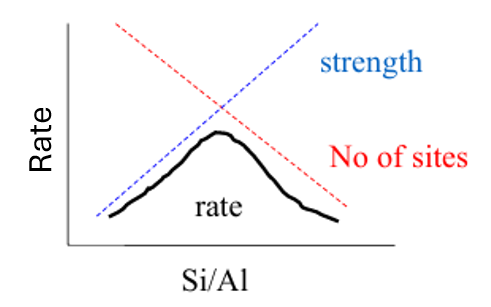
What is the relationship between Al content and the strength of the acidic sites?
More Al means weaker acidic sites, but more of them
What is the term for the acidity level when there’s few Al sites?
Superacidic
How does Tdes in the desorption of ammonia from a zeolite (TPD) dictate the acidity?
A higher Tdes (temp of desorption) indicates a more acidic zeolite
What is the main application of zeolites?
Cracking of crude oil
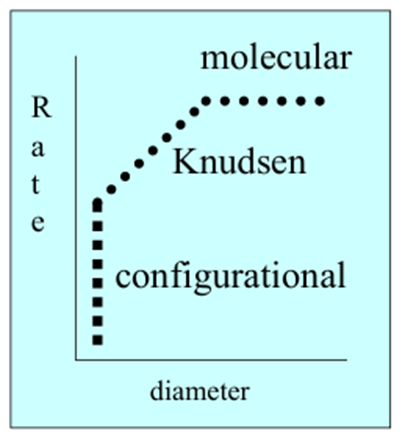
What is the general shape of this graph?
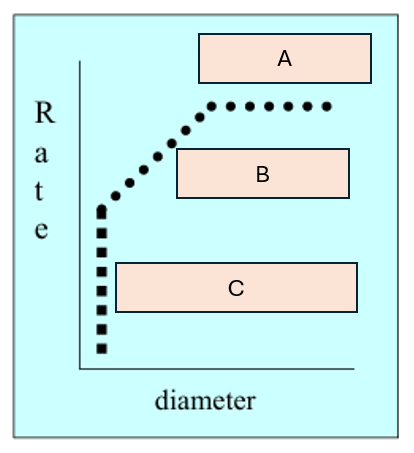
What is behind boxes A-C
A) Molecular
B) Knudsen
C) Configurational
Describe molecular diffusion
When the pores are much larger than the molecule so diffusion rate is constant with increasing pore size
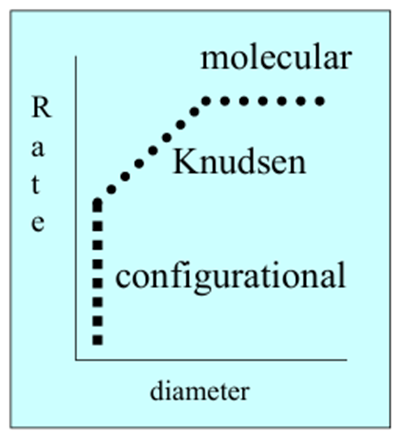
Describe Kudsen diffusion
When pores are sightly larger than the molecules so diffusion rate increases proportionally with pore size
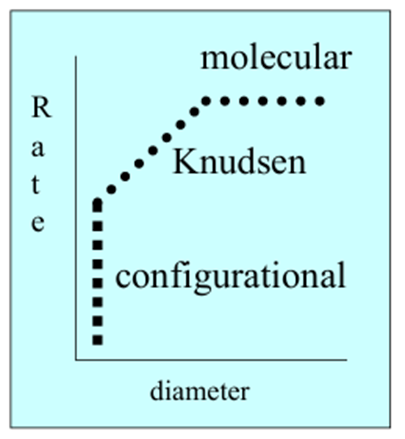
Describe configurational diffusion
When the pores are similar in size to the molecules so the diffusion rate is determined by the orientation of the molecules
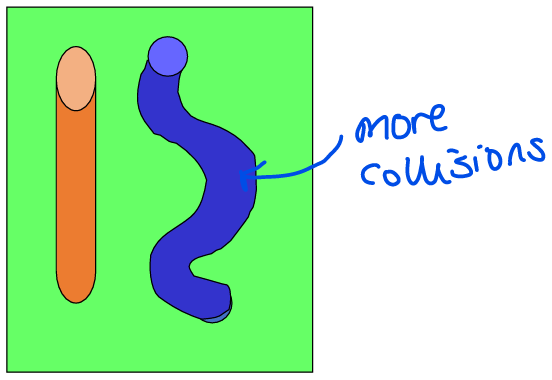
Define tortuosity
The level of twisting/winding of a pore
What is the name of the red region?
Stationary layer/ Boundary layer/ Hydrodynamic layer
Discuss how different factors impact diffusion across the boundary layer.
A less viscous solvent has a thinner boundary layer, hence faster diffusion.
Mixing the system increases the transport through the stationary layer by increasing the shear forces.
What factors is diffusion dependent on?
Pore size and hydrodynamic layer thickness
(not temperature)
How can you test whether the rate is diffusion controlled (dependent)?
Use the Arrhenius equation to find the activation energy, if Ea is low then diffusion is controlling the rate
How can you test whether hydrodynamic layer diffusion or pore diffusion controls the rate?
If you increase the stirring, the hydrodynamic layer gets thinner. If hydrodynamic diffusion is controlling rate then increased stirring should increase the rate. If not, pore diffusion is the rate controlling factor
What are the 3 types of shape selectivity?
Reactant selectivity - reagents are too small to diffuse into the pore
Product selectivity - product is too large to leave the pore so kills the catalyst or breaks down
Transition state selectivity - reagent molecules need to orientate correctly to form the transition state, which may not be possible depending on pore size
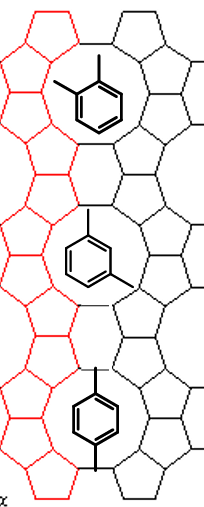
Which of these products is favoured and why? What is this called?
1,4 product because it is the narrowest, so can diffuse most easily out of the pore. This is product selectivity.
What type of hydrocarbon from crude oil does H-ZSM5 selectively react and why? What is this called?
Linear alkanes because they are narrower, so can fit into the pores, whereas branched alkanes cannot. This is reagent selectivity.
What is the first step in catalytic cracking of hydrocarbons?
Protonation of a secondary carbon to give a pentavalent carbon (carbocation)
What is the benefit of using C as a support for a metal catalyst?
It is easily recoverable by combustion.
Describe a Langmuir Hinshelwood mechanism
When A and B adsorb competitively to the surface, react while bound and then desorb
Describe an Eley-Rideal mechanism
When A adsorbs and B reacts with adsorbed A
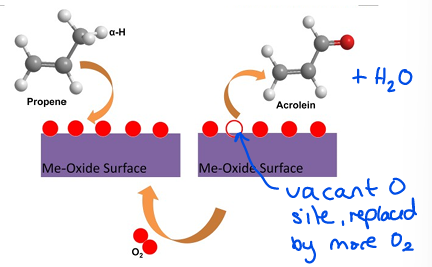
Describe a Mars van Krevelen mechanism
When A adsorbs, then leaves with a surface atom (eg. Oxygen). B replaces the surface atom.
Draw an example of a Langmuir Hinshelwood mechanism
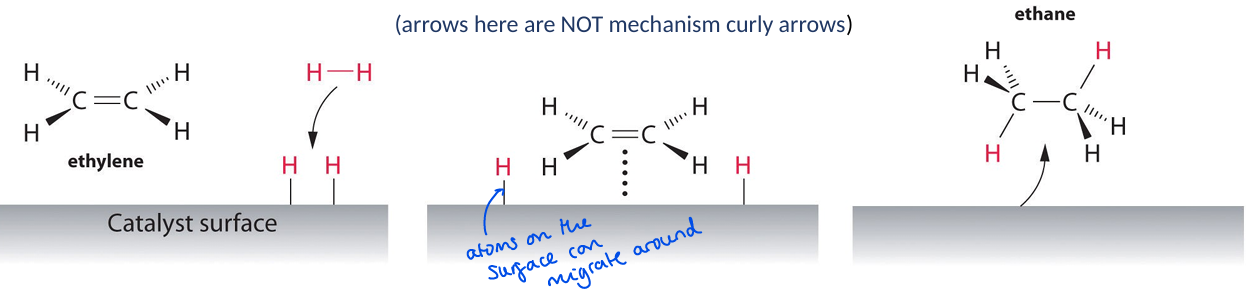
Draw an example of an Eley Rideal mechanism. What is the key difference here to LH
Increasing O2 concentration just increases rate, until all surface sites are occupied when the rate flattens out
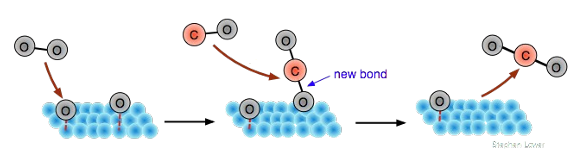
Draw a Mars van Krevelen mechanism
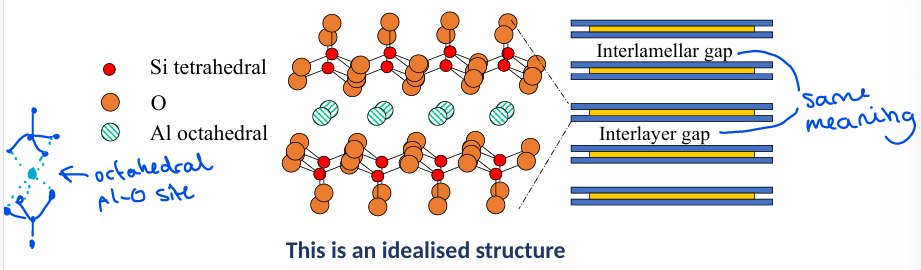
What is the general structure of a bentonite clay?
Uncharged material made up of three layer groups. Sometimes the Si or Al is replaced by other metals which can give the layers charge, so a cation adds to the interlayer gap to balance this
How can you alter the properties of a clay (2D material)?
Dehydration or ion exchange of the interlayer cation decreases the interlayer gap. A smaller cation (higher charge density) leads to a more active site in the layer, but a smaller interlayer gap. This reduces the rate of diffusion and hence, slow catalysis.
What is the issue with using high charge density cations in 2D materials? What can this lead to?
Narrowing of the interlayer gap. It can cause the interlay gap to become so small that it collapses. This can be avoided using pillaring cations
When might a pillaring cation be necessary?
When using a high charge density cation in an interlayer gap (this is the most catalytically active type of cation, so they’re desirable to use). They can cause the layers to collapse so a pillaring cation can hold the layers apart.
How can you produce zeolites with pores larger than 1 nm? What would be the benefit of this?
A template can be used in the synthesis process, this is called Micelle Templated Silicas (MTS). Long chain amines or polyethers organise into structures which the zeolite forms around.
This allows larger molcules to diffuse into the catalyst and react. This method also allows you to add various catalytic groups to the inside of the pore.
What reagent do you add to produce a zeolite around a -NH2 micelle?
Si(OR)4 (hydrated to give Si(OH)4)
What reagent do you add to produce a zeolite around a -NR3+ micelle?
Na2SiO4
How do you remove the template from a zeolite after synthesis?
Burning, or an amine template can be washed out
Define amorphous
Having no defined structure (not crystalline)
What is the difference between zeolite walls and MTS walls?
MTS walls are amorphous (zeolite walls are crystalline) so adding Al doesn’t make it as acidic as a zeolite wall
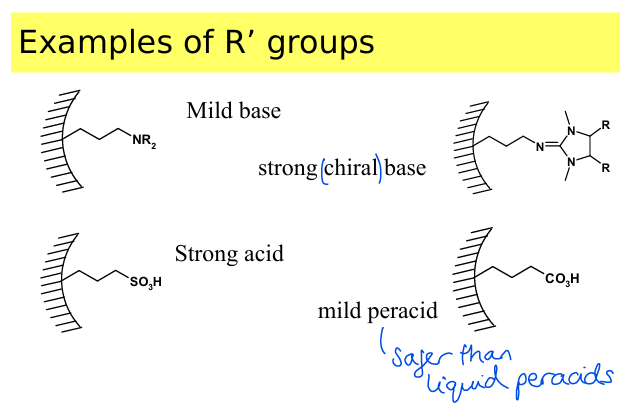
What are some examples of types of R groups that can be added in organically modified MTS? What are the benefits of this?
Mild base, strong chiral base, strong acid, mild peracid.
Acidic and basic groups within a pore make the compound safer to handle and can aid in selectivity of a catalytic process
How can MTS be used to make a bifunctional catalyst?
The zeolite can be synthesised, then active sites added to the external surface. Then, the template can be removed and a different active site can be added to the internal walls.
This means that larger molecules will react with the external sites, and smaller molecules can diffuse into the pore to react with the internal active sites.
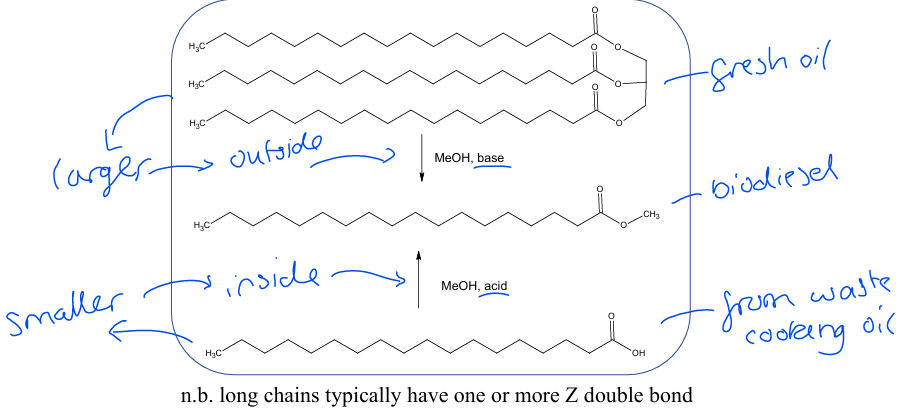
Give one example of an application of a bifunctional MTS catalyst
Converting waste cooking oil into biodiesel.
During use (heating), triglycerides in cooking oil break down into fatty acids.
These are smaller so can fit into the pore to react with the acidic internal sites.
The larger (unchanged) triglycerides react with the external basic sites.
This allows both components of used cooking oil to be converted into biodiesel.