Neurophysiology - PNS Afferent
1/203
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
204 Terms
CNS is and contains
Central Nervous System
Brain and Spinal Cord
PNS is and contains
Peripheral Nervous System
Cranial and Spinal Nerves and Sensory Organs
Schematic of the Nervous System
1. Sensory Information
2. Goes to receptors
3. Afferent division
4. Goes to CNS (brain and spinal cord)
5. Efferent Division
6. Somatic or Autonomic nervous system
3 classes of receptors in PNS
Exteroceptors
Proprioceptors
Interoceptors
Exteroceptors sense
Sense the external environment
somatic (general) and special senses
Special Senses
vision, hearing, taste, smell, equilibrium (walking)
Proprioceptors sense
Positional Senses
ex) sensing the position of muscle or organ in space
- position and state of the muscle (ex: if its tensed or not)
Interoceptors sense
visceral (deep) senses or internal senses
- blood ph, stomach pain, blood pressure
nothing of the nervous system schematic occurs without
sensory information
afferent division deals with
sensory information that comes in
efferent output is to control effectors of the body via
nerves
somatic nervous system
motor neurons
- skeletal muscles
(biceps, quads, etc).
autonomic nervous system divisions
sympathetic and parasympathetic
sympathetic and parasympathetic control which body parts?
everything other than skeletal
- smooth & cardiac muscle, exocrine and endocrine glands, fat
enteric nervous system is a
self contained system dealing with the digestive organs
how many cranial nerve pairs?
12
- most are just afferent/efferent, few are mixed
How many spinal nerve pairs?
31
- all are mixed, both afferent and efferent
3 types of cartilage
Highland, Fibril, Elastic
Highland cartilage
most abundant
fibril cartilage
least abundant but strongest
elastic cartilage
flimsy, present in ears and nose
intervertebral disks are made of
fibrocartilage/ fibril
hole between a vertebrae
veritable foramen
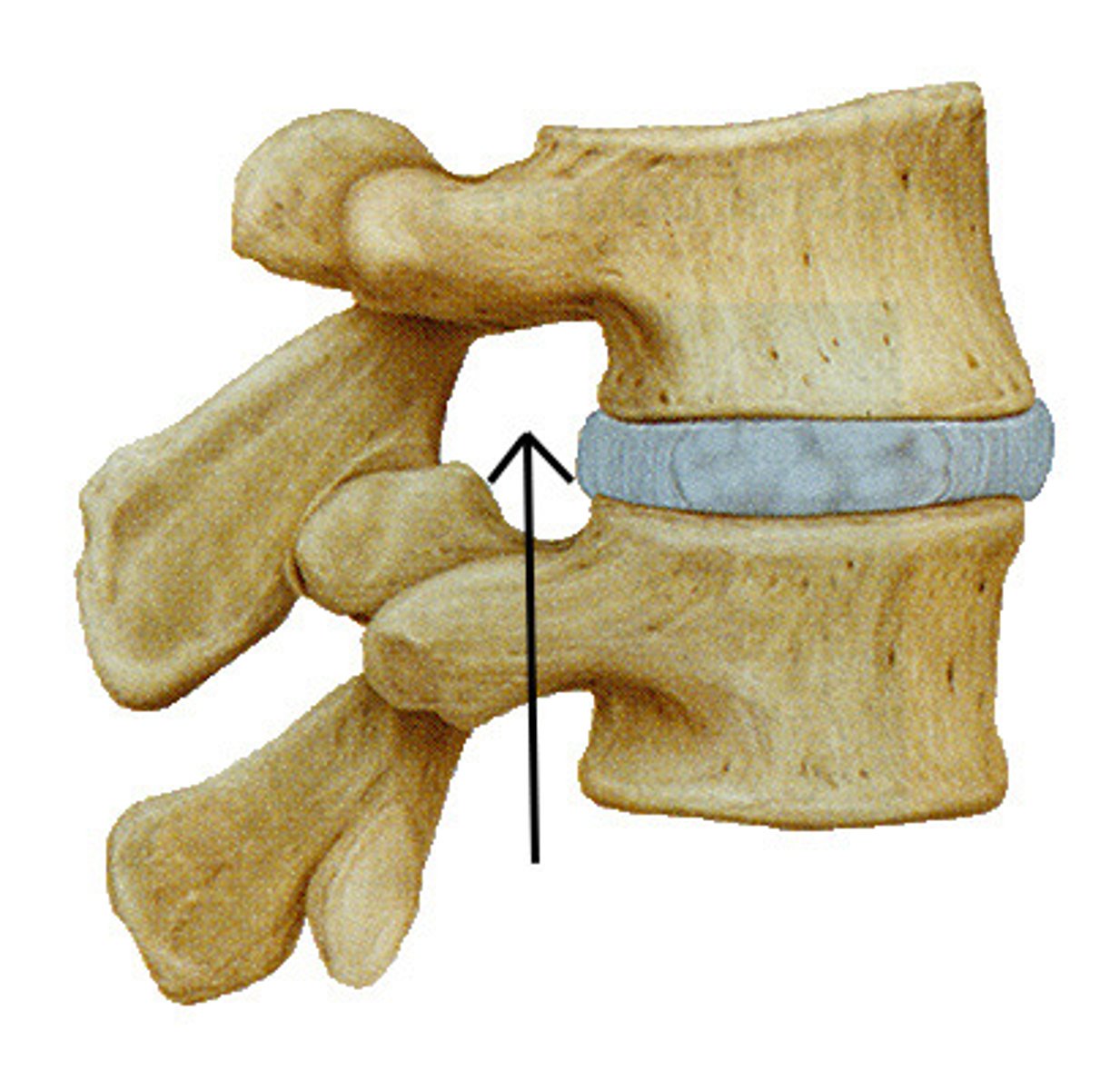
what is in the veritable foramen
where spinal nerves come/exit
sciatica
inflammation of the sciatic nerve, may be rubbing against the bone or pinched
ppl w/ spina bifida have...
their lamina (back) of vertebrae naturally exposed
herniated disk
cartilage breaks and rubs on the nerve in the veritable foramen
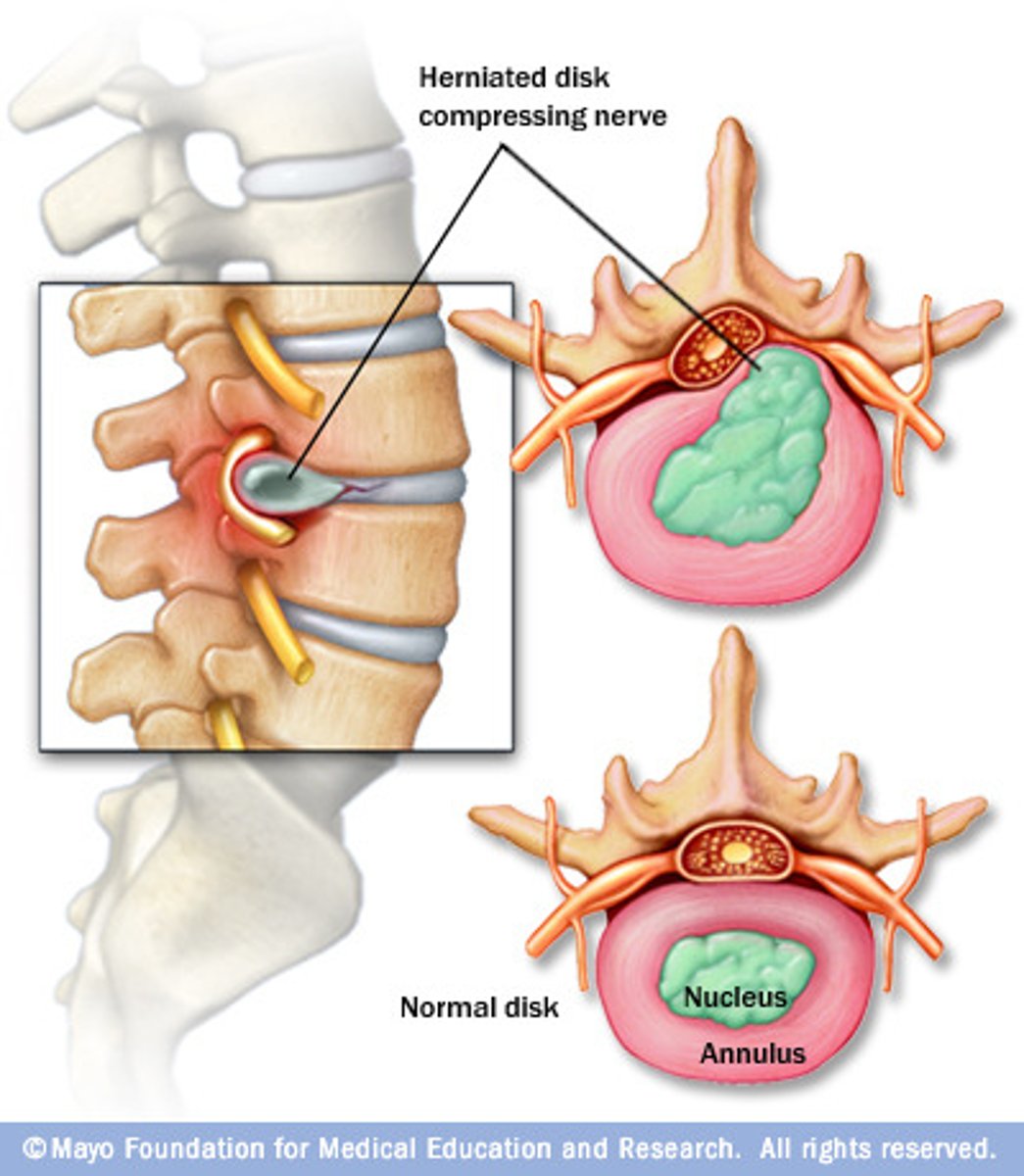
Thinning disk
fibroblast make less connective tissue as you age, thinning between vertebrae
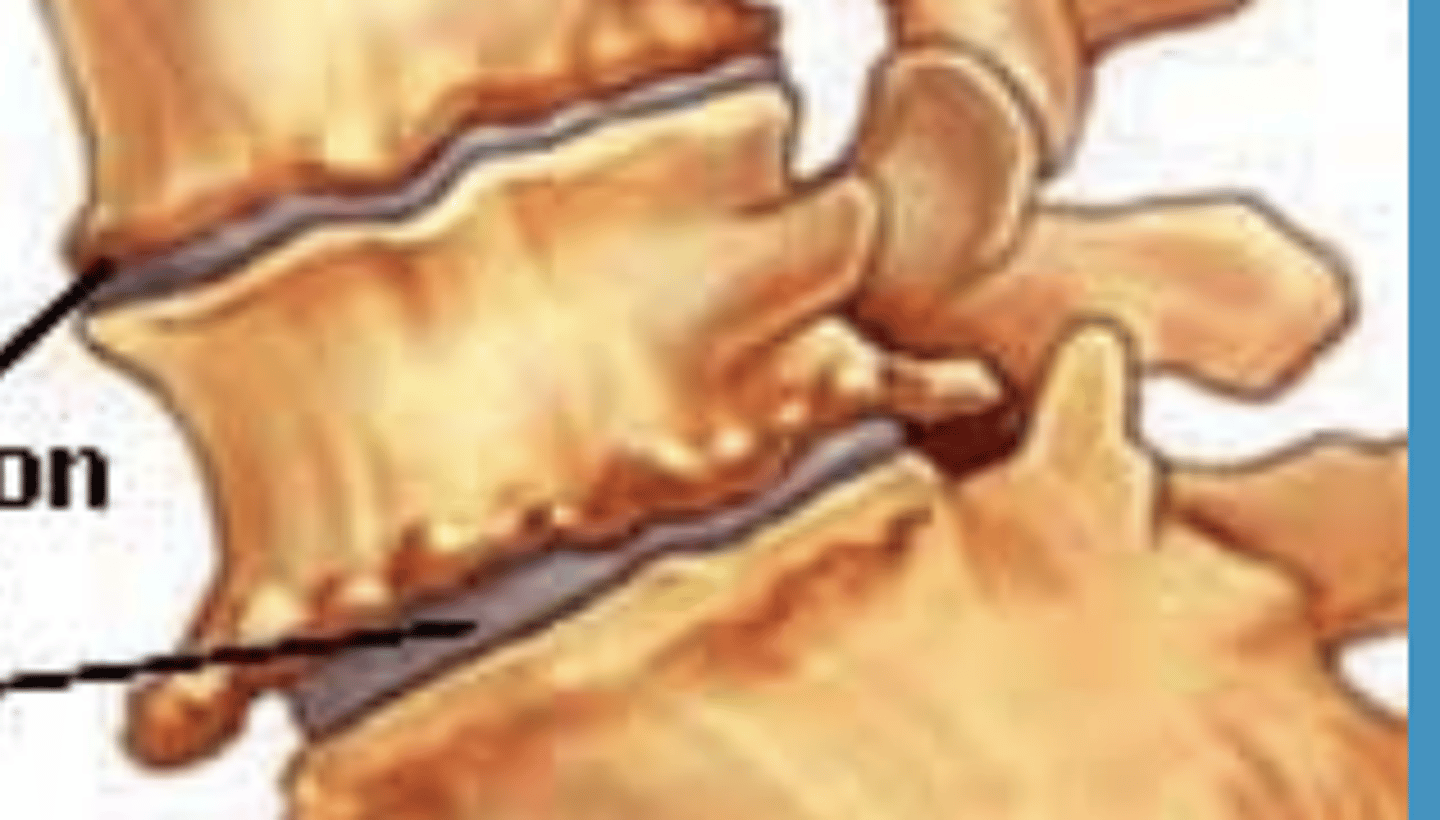
Disk degeneration with osteophyte formation
bone forms which obliterates the cartilage and space lessens

What are in the intervertebral disks?
Glycoproteins/proteoglycans
what do Glycoproteins/proteoglycans do
they have negative charges and attract water inside the disk
- constant water drag inside keeps our disks hydrated and thick
spinal stenosis
narrowing of the spinal canal with compression of nerve roots
Dorsal root ganglion contains
cell bodies of sensory unipolar neurons
dorsal ramus and root contains
sensory neurons
ventral ramus and root
motor neurons
both ventral and dorsal ramus form
fuse together to form the spinal nerve
all of the sensory information goes to the back or front of spinal cord?
back of the spinal cord
explain how sensory info goes through the spinal cord
1. sensory info comes through the dorsal ramus
2. passes by the dorsal root ganglion containing the unipolar cell bodies
3. goes to the rootlet, spinal nerve, then spinal cord to CNS
4. neuron comes out of spinal cord through ventral rootlets (motor info)
5. then goes to spinal nerve, then ventral root to body
spinal reflex arc (finger on stove)
1. stimulus activates receptor (ex) finger on stove
2. sensory neuron sends action potentials
3. sensory info goes to the spinal cord via interneuron, cell bodies of neurons in the dorsal root ganglia
3.5. collateral neuron sends info to the brain
4. motor neuron is activated tells the body to do something (ex: contract biceps)
5. response occurs (ex: you take your hand off stove)
motor neuron cell bodies
located in ventral gray matter of brain stem unlike sensory neuron cell bodies
gray matter looks gray bc
of all the cell bodies it has
All sensory info is processed on the...of the brain
opposite side of the brain
ex) right hand pain processed in left cortex
therefore you remove your hand from pain before your brain knows, this is a protective mechanism
Ipsilateral
info travels on the same side of spinal cord but crosses to the other side in the brain stem
ex) touch
Contralateral
goes across the spinal cord and then up to brain stem
ex) pain and temperature
5 types of receptors
mechanoreceptors, chemoreceptors, thermoreceptors, osmoreceptors, photoreceptors
Mechanoreceptors
need a mechanical stimulus that opens a channel and causes depolarization - sends APs to brain
tactile receptors
for touch
nociceptors
pain receptors
Baroreceptors
pressure receptors
ex) changes in blood pressue, present in carotid artery in neck
Proprioceptors receptors
monitor the position and movement of skeletal muscles and joints
auditory receptors
hearing
equilibrioceptors
equilibrium and balance (walking)
Chemoreceptors include
olfactory receptors, gustatory, and nociceptors
olfactory receptors
smell
gustatory receptors
taste
Thermoreceptors
temperature cold and hot
nociceptor is a
multi-modality receptor
mechanoreceptor and chemoreceptor and thermoreceptor
Osmoreceptors
detect the osmolarity of body fluids (ISF)
photoreceptors
detect vision
tonic receptors
slowly adapting receptors that respond for the duration of a stimulus
- as long as stimulus is there, graded potential continues, action potential is still there but is less
ex) paper cut
phasic receptors
fast adapting
- stimulus is sustained, but graded potential and action potential disappear
- touch, smell, wearing a shirt
somatic (general) senses include
Touch, vibration, pressure, stretch, pain, and temperature
- all located in the skin
3 layers of skin
epidermis, dermis, hypodermis
hypodermis is
a layer of fat beneath the skin
free nerve endings are present in the...
epidermis, detect pain and temp, are dendrites
Merkel's disks
respond to light touch
- in epidermis
- single cell neurons
Meissner's corpuscles
light touch
- connected to hair follicles
- in dermis
Pacinian (lamellated) corpuscles
deep pressure and vibration
- in hypodermis
Ruffini corpuscles
detect stretch
- in dermis
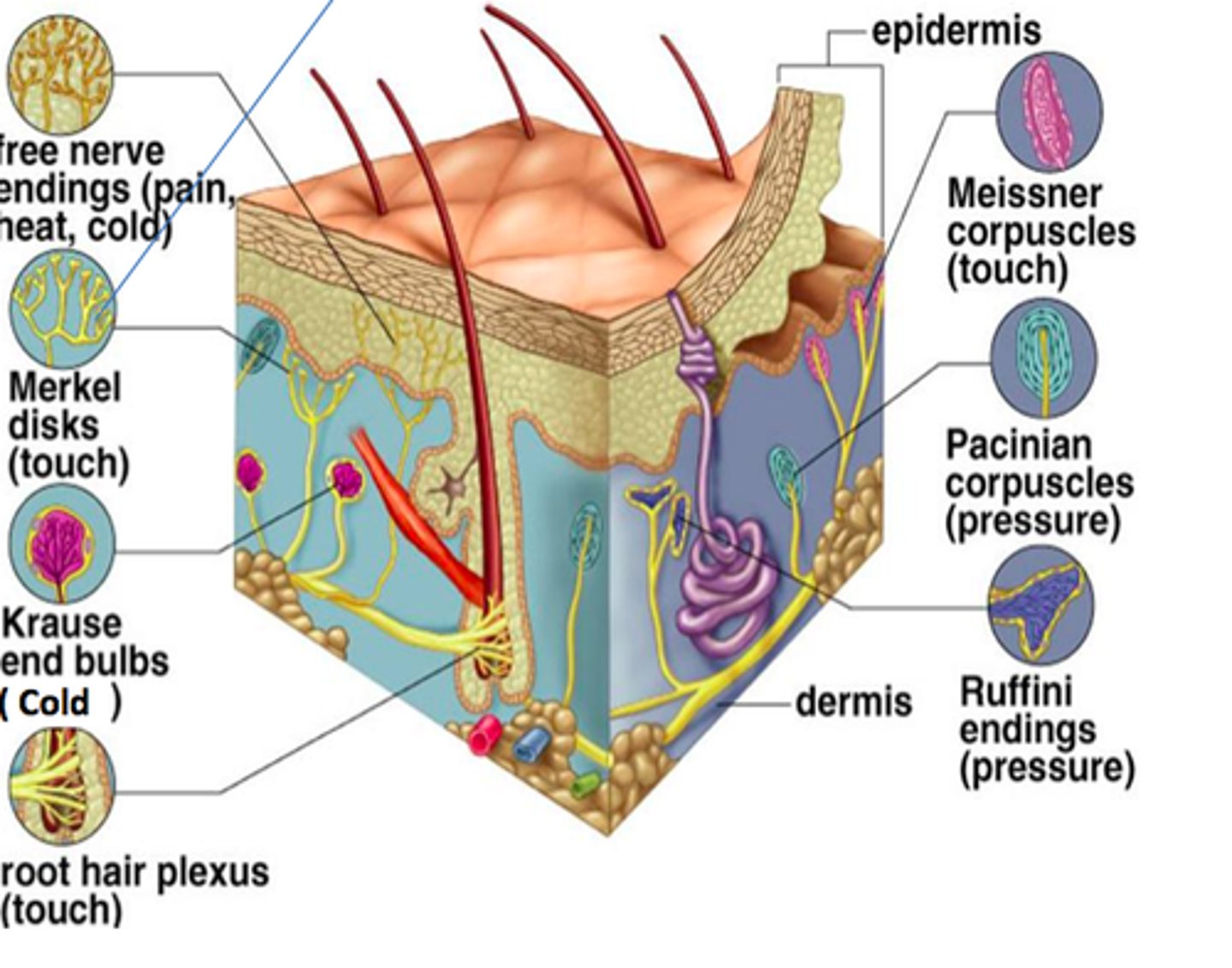
Nocicieption means
pain
analgesia
reducing pain
Antihistamines, what they do
blocks histamine - vasoconsrict your blood vessels
- and histamines vasodilate blood vessels so your nose dries up and blood pressure goes down. Vasodilates so WBCs can go fight it
Antihistamines examples
Benadryl and Zyrtec
NSAIDS, what they do and examples
Blocks prostaglandin
- reduces inflammation which reduces pain because less fluid pressure on neuron
NSAIDs examples
- aspirin and ibuprofen
local anesthetics, what they do
Block voltage gated sodium channels
- no action potentials sent to brain, no pain
local anesthetics examples
articaine and lidocaine
Opiates, what they do
Reduce pain both the brain and spinal cord- endogenous (internal)
opiates examples
endorphines, morphine
Chilli peppers what do they do
Blocks substance P, reduces pain
What does substance P do?
enhances perception of pain, increases histamine
example of chilli peppers
capsaicin
referred pain
pain that is felt in a location other than where the pain originates
referred pain example
- cross talk between neurons in the heart and in the skin and they both travel up to the brain
Phantom pain
pain felt in a body part that is no longer there
why does phantom pain occur?
Stimulus can come from anywhere along the neuron not just the receptor
At the roof of your nasal cavity you have
Olfactory epithelium
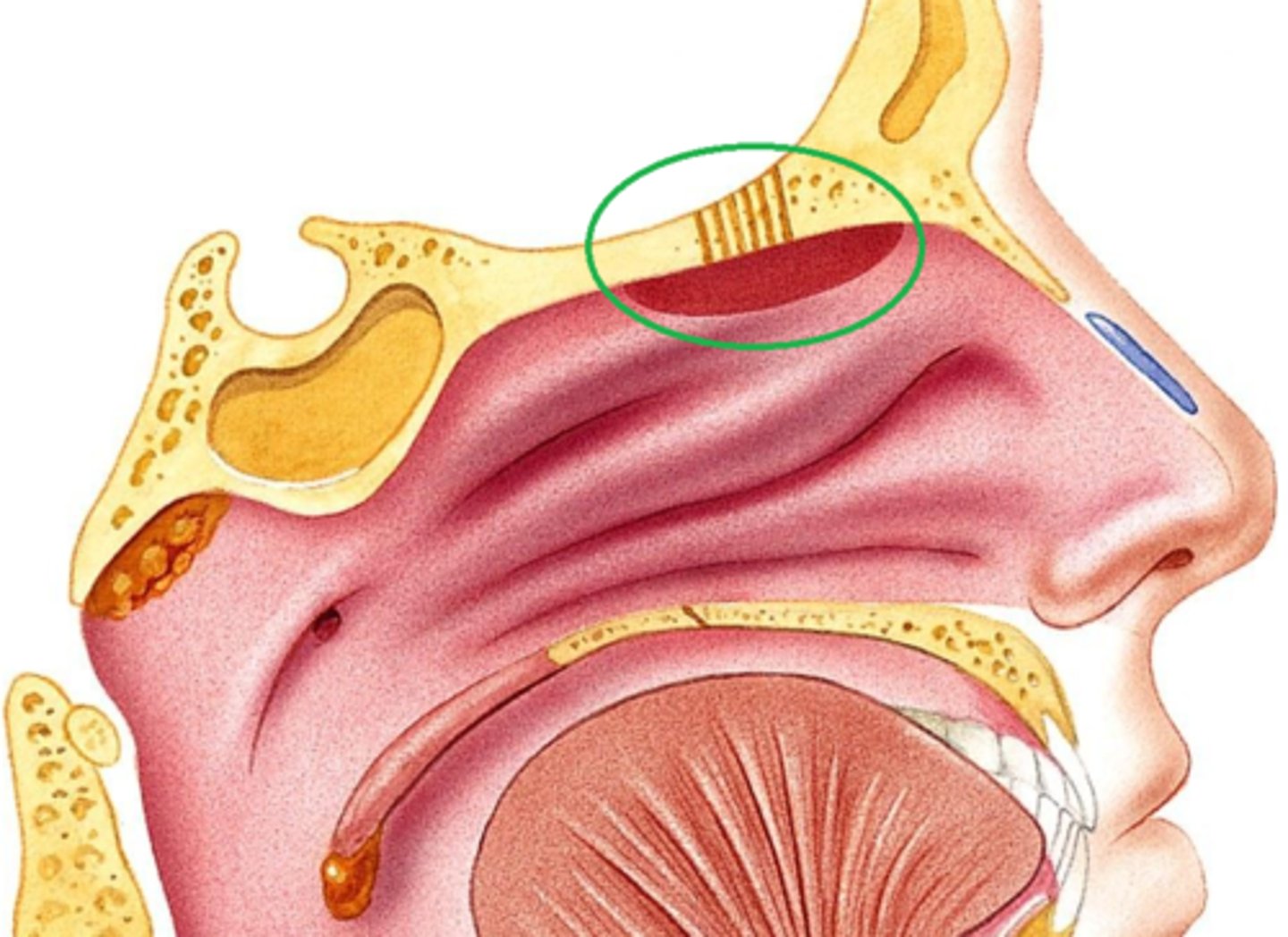
supporting cells in nose
sustentacular cells, glial like cells
cribriform plate
A bony structure riddled with tiny holes, separates nose from brain
Holes in the cribiform plate are called
olfactory foreman
olfactory nerve fibers go through the...
holes in the nasal cavity
we have the ability to regenerate... in the nose due to
neurons in the nose due to stem cells
how the olfactory nerves sends info to the brain?
1. olfactory nerves go to your skull into the brain
2. nerve synapse in brian with secondary neurons
olfactory cilia
olfactory cilia or dendrites that contain receptor proteins
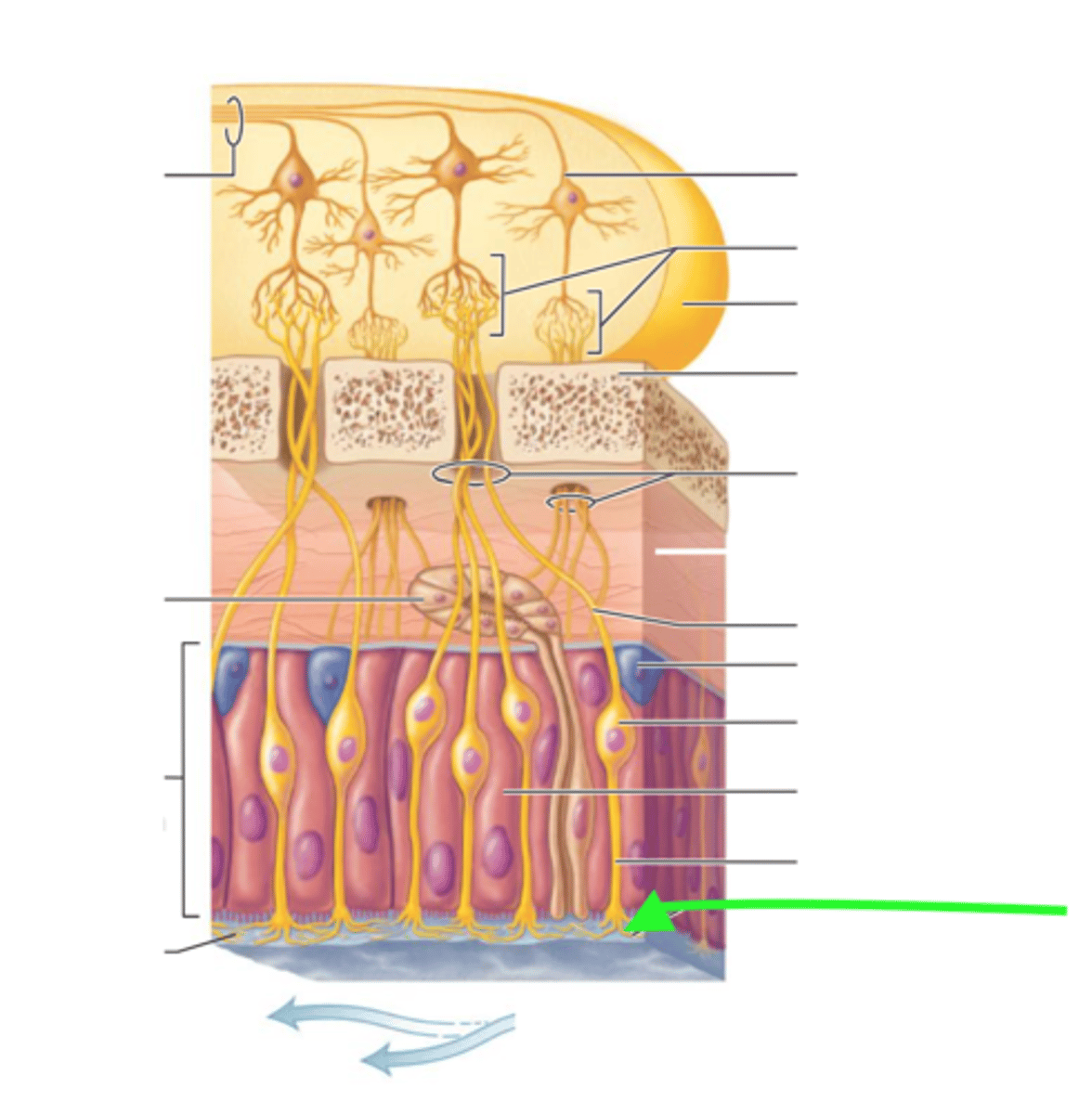
oderent molecules
dissolve in fluid and bind to receptors to activate them
sense of taste
gustation
5 tastes
sweet, sour, salty, bitter, umami
what is umami
glutamate
what is spicy? is it a taste?
not a taste, it is a thermal response so it uses unipolar neurons
bumps on the tongue are
papillae, not taste buds