Session 8: Viral Infections and Cancer
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Cancer
Disease of inappropriate cell proliferation
Oncogene
Genetic material that carries the ability to induce cancer
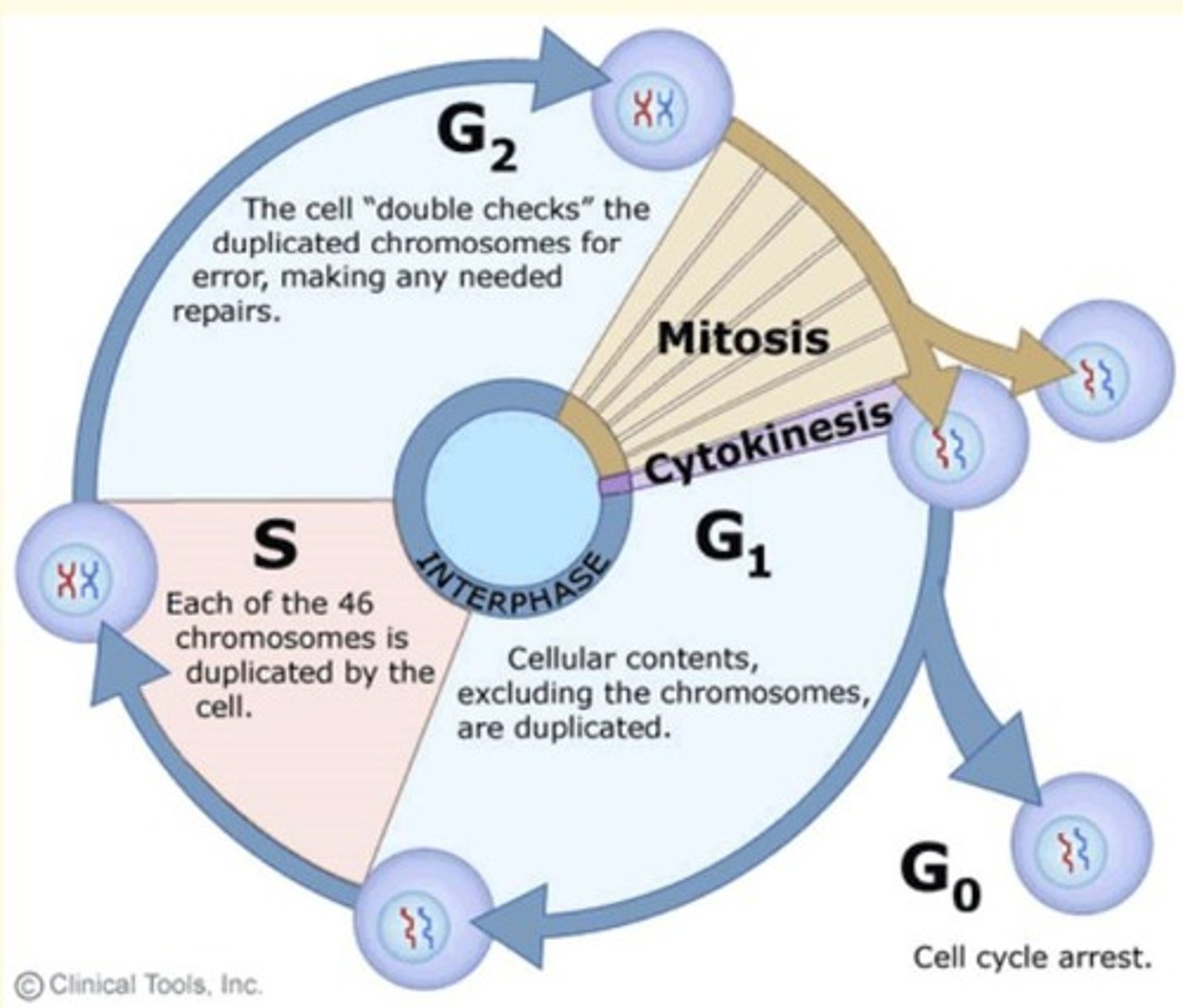
Cell cycle
series of events in which a cell grows, prepares for division, and divides to form two daughter cells
Oncovirus
Virus that causes cancer
DNA viruses capable of causing human cancers
- Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
- Human Papilloma virus (HPV)
- Hepatitis B virus (HBV)
- Human herpes virus
RNA viruses capable of causing human cancers
- Human T lymphotropic virus type 1
- Hepatitis C viruses
Genital warts are caused by ___
Human papillomavirus (HPV)
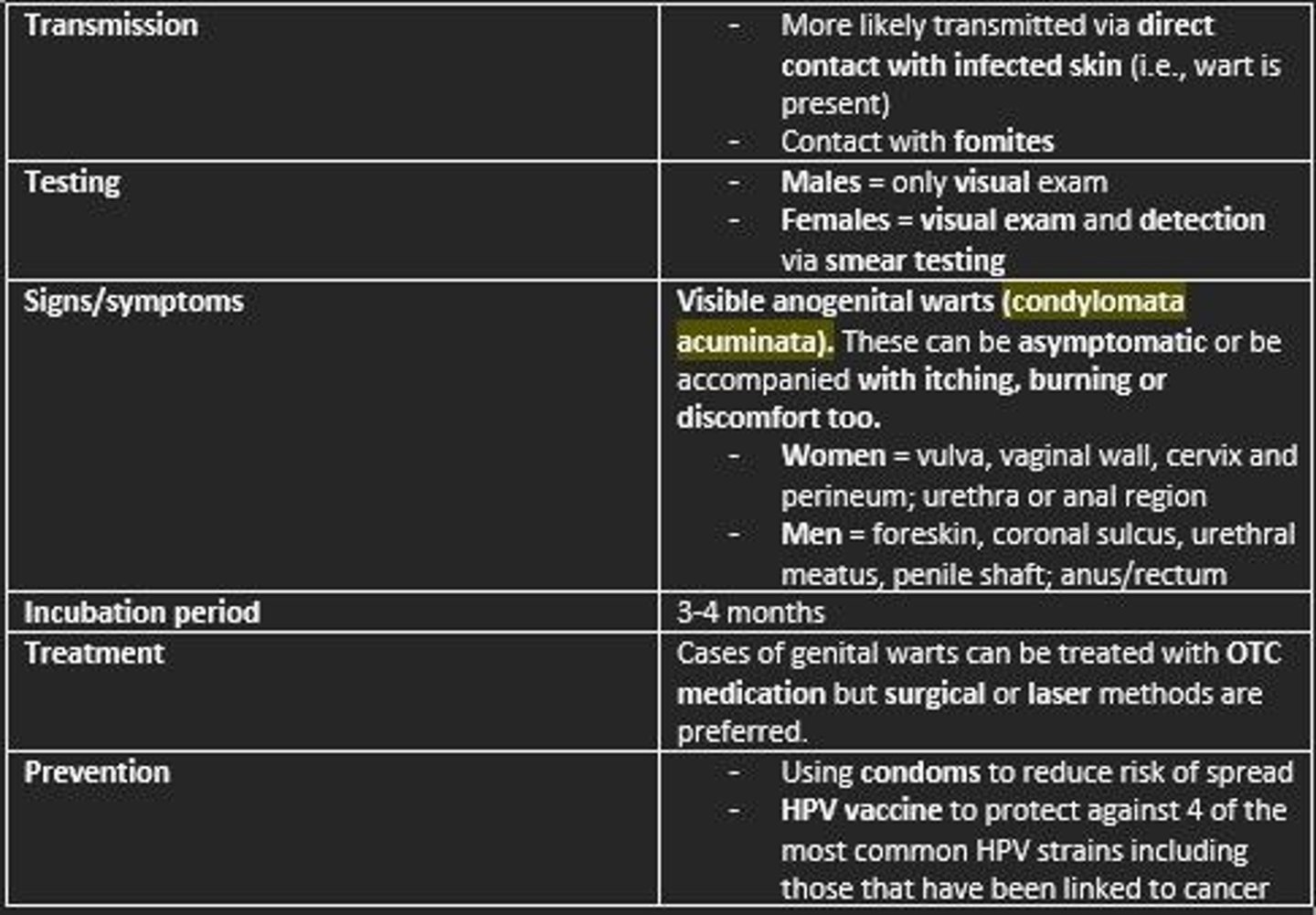
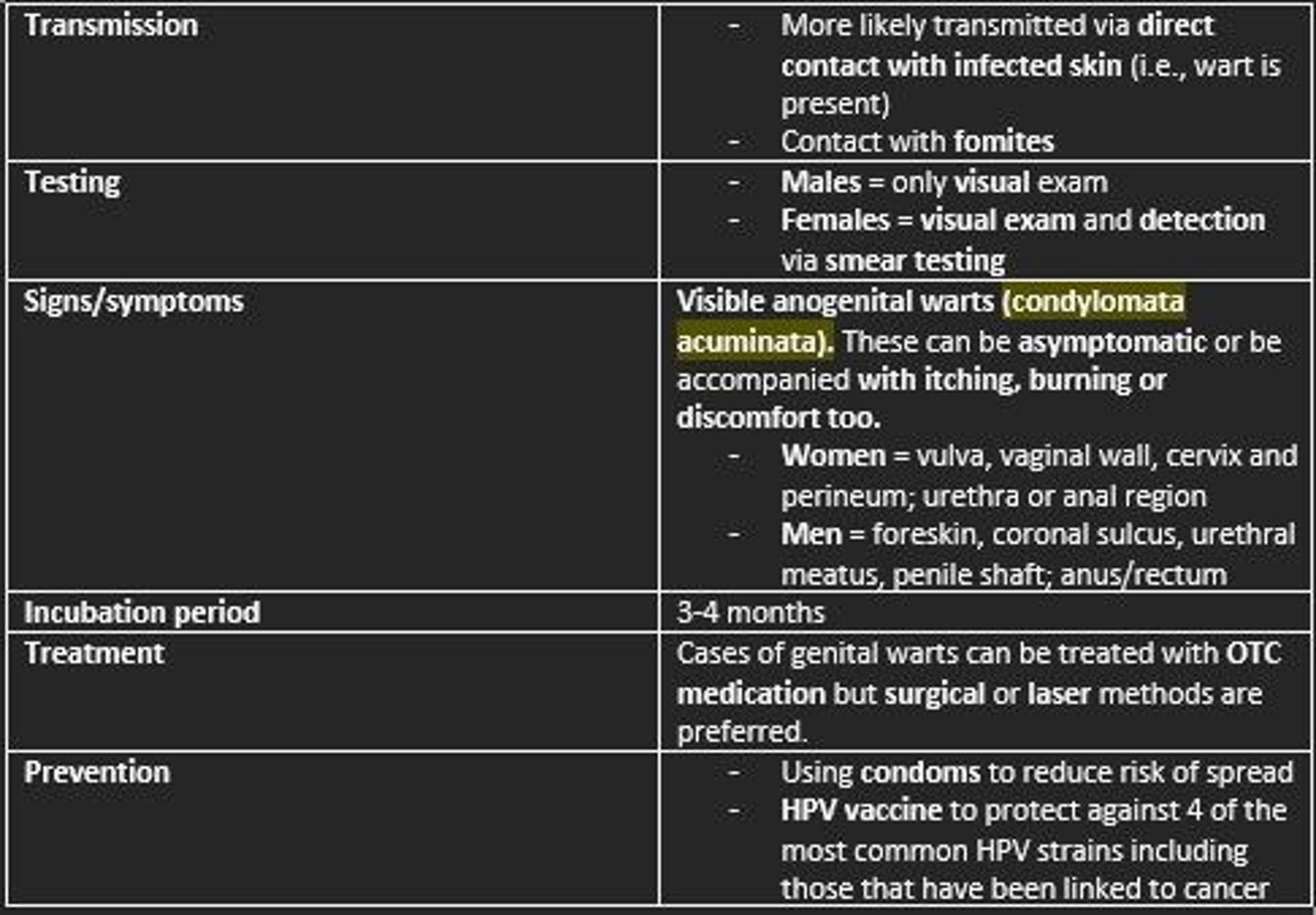
HPV is spread via...
- Direct contact with individuals (infected skin)
- Fomites
HPVs invade the skin/mucous membranes of the penis, vagina or anus.
Once inside the cells, HPV replicates. Over 1/2 of HPVs can permanently integrate into cells chromosomes.
Hijacking of human host cells occurs to produce viral ___ and ___ proteins can trigger cancer, especially if the host already has the Herpes virus.
HPVs invade the skin/mucous membranes of the penis, vagina or anus.
Once inside the cells, HPV replicates. Over 1/2 of HPVs can permanently integrate into cells chromosomes.
Hijacking of human host cells occurs to produce viral E6 and E7 proteins can trigger cancer, especially if the host already has the Herpes virus.
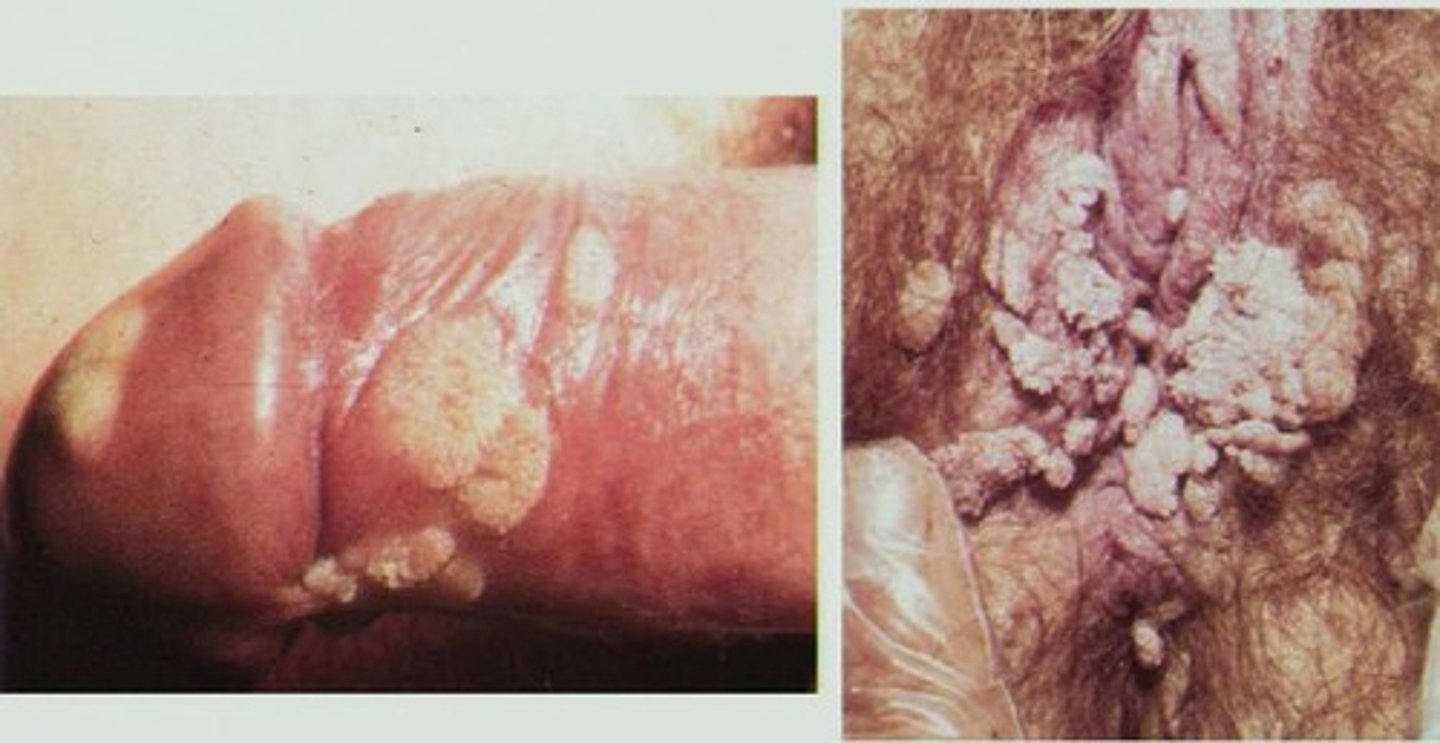
Signs/symptoms of HPV
Females = growths on the vulva, vaginal wall, cervix and perineum
Males = warts on the penis, foreskin, coronal sulcus, urethral meatus, penile shaft
Both sexes = warts in or on the anus, and the skin around the groin between the thigh and pelvis
Condyloma acuminata = branching, cauliflower-like masses
The warts can be asymptomatic or be accompanied with...
- Itching
- Burning
- Discomfort
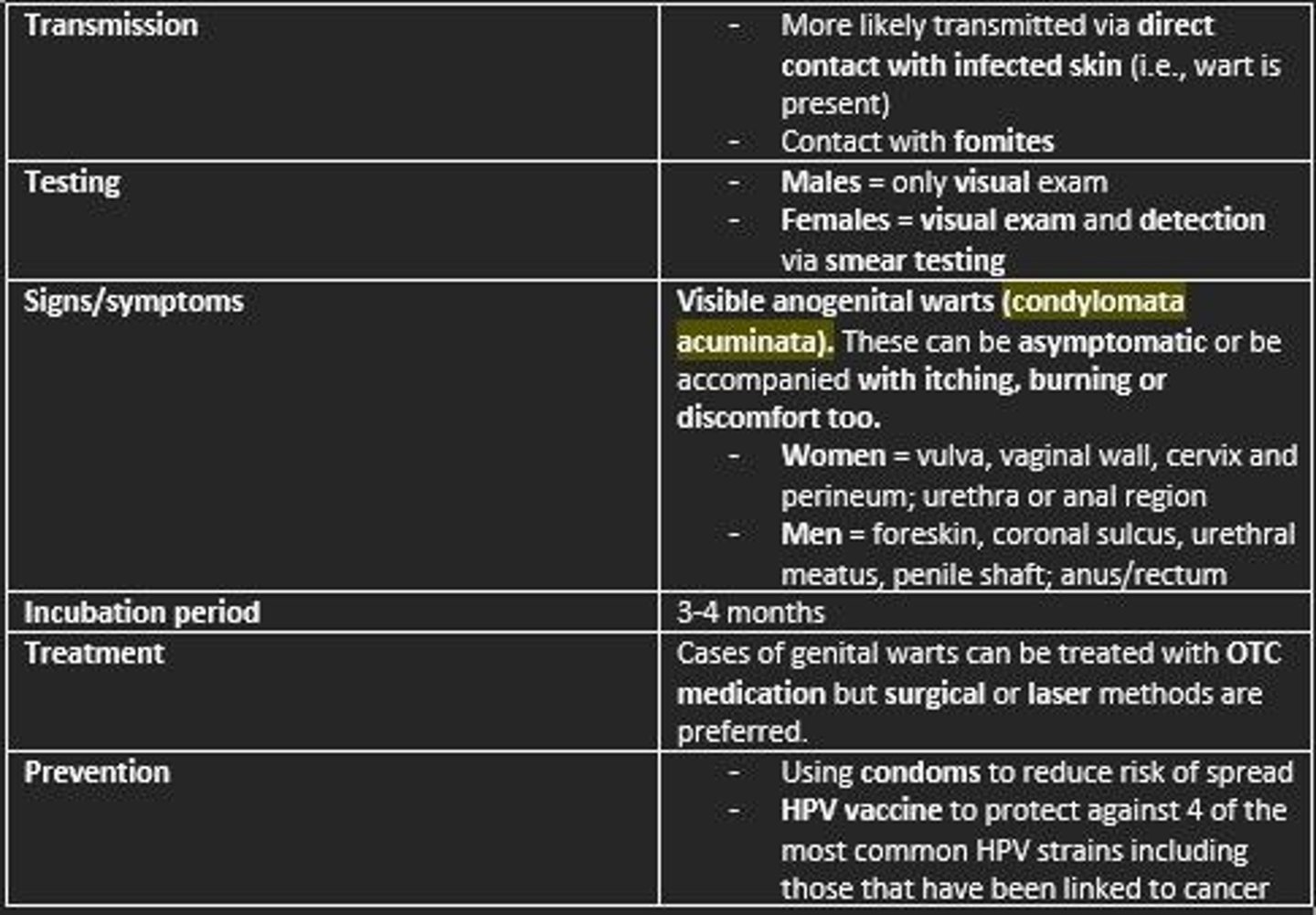
Incubation period of HPV
3-4 months
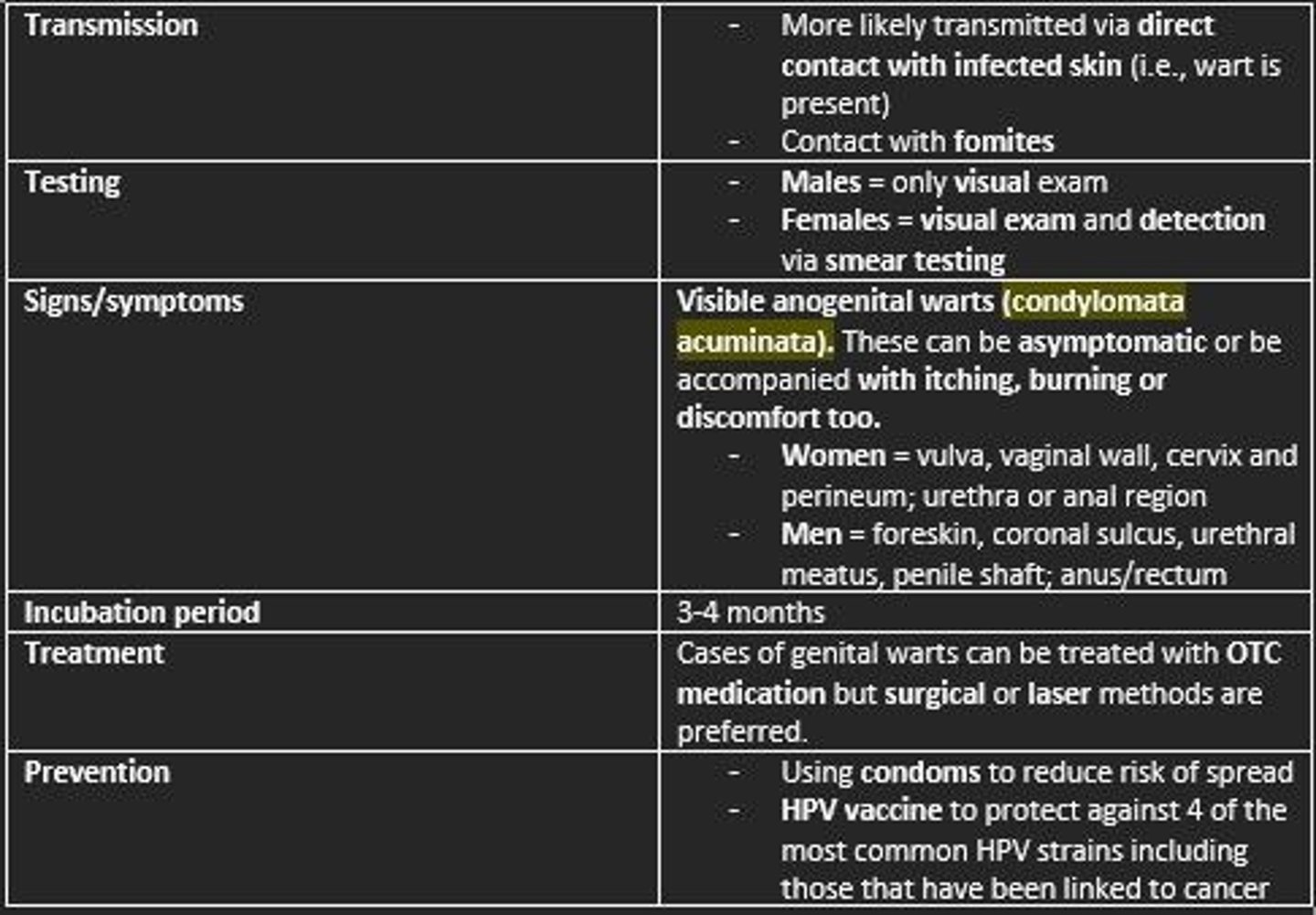
Treatment of HPV
- OTC medication
- Surgical or laser methods are preferred
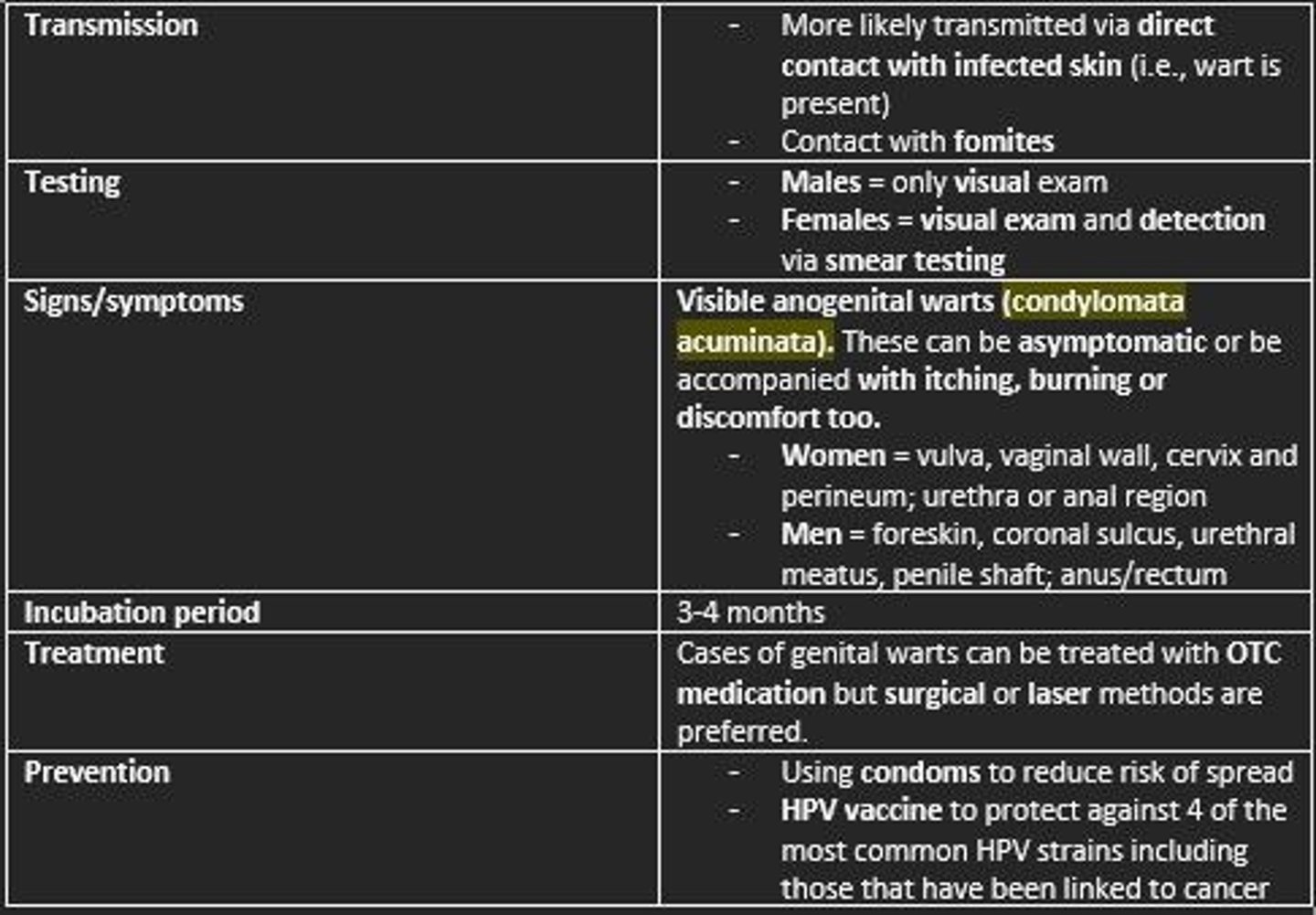
Prevention of HPV
- HPV vaccine
- Using protection during sex (condoms)
Untreated HPV
- Transmission to sex partners/newborns
- Warts can grow and spread if left untreated
- May cause cervical cancer
- Block openings from anus, vagina or urethra
Cervical cancer results from Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia (CIN) which appears to be caused by infection with human papillomavirus (HPV) types ___, ___, ___, ___, ___, or ___.
Cervical cancer results from Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia (CIN) which appears to be caused by infection with human papillomavirus (HPV) types 16, 18, 31, 33, 35 or 39.
Which HPV types are associated with benign warts (low risk of cervical cancer)?
HPV types 6 and 11
Which HPV types are associated with invasive carcinoma (high risk of cervical cancer)?
HPV types 16 and 18
Which HPV type is most common in squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)?
HPV type 16
Which HPV type is most common in adenocarcinoma?
HPV type 18
Risk factors for cervical cancer
Younger age at intercourse
High lifetime number of sex partners
Cigarette smoking
Immunodeficiency
Oral contraceptives
STDs
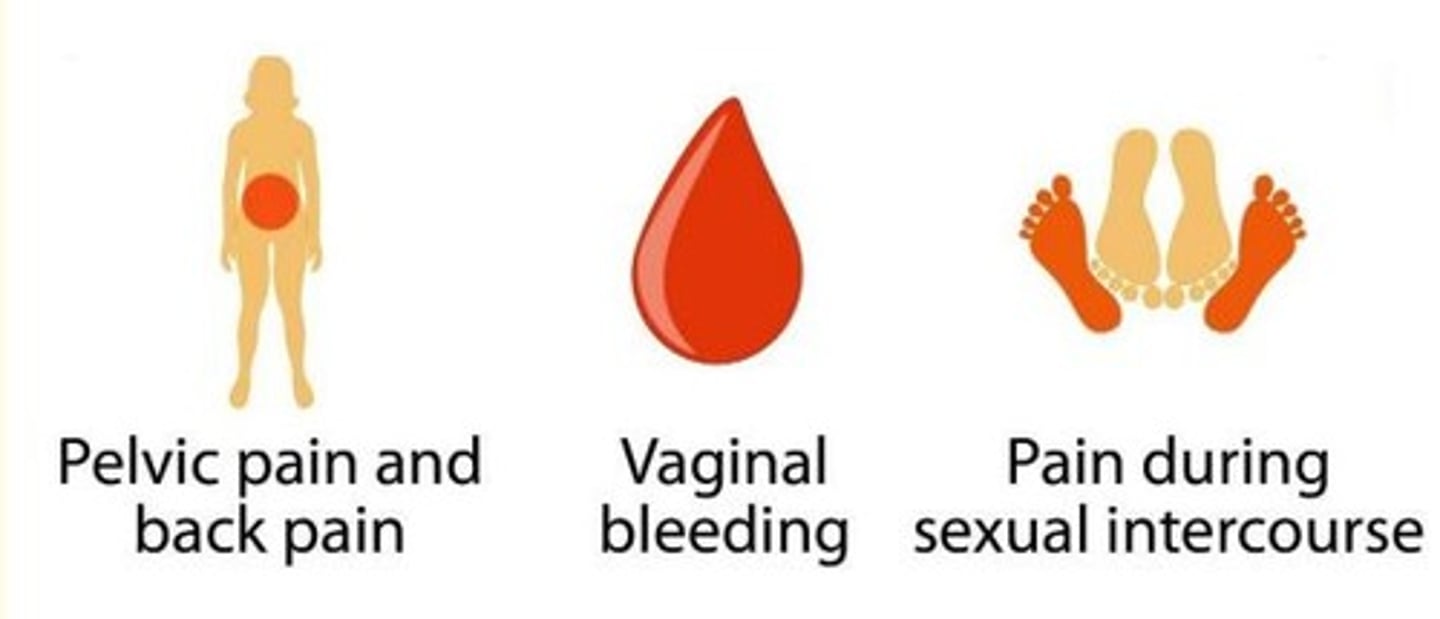
Symptoms of cervical cancer
- Asymptomatic
- Irregular vaginal bleeding +/- foul-smelling discharge
- Pain during sex
- Pelvic pain/back pain
For more widespread cancers...
- Back pain
- Leg swelling
- Obstructive uropathy
Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia (CIN) is graded as...
1) Mild cervical dysplasia
2) Moderate cervical dysplasia
3) Severe dysplasia and carcinoma in situ
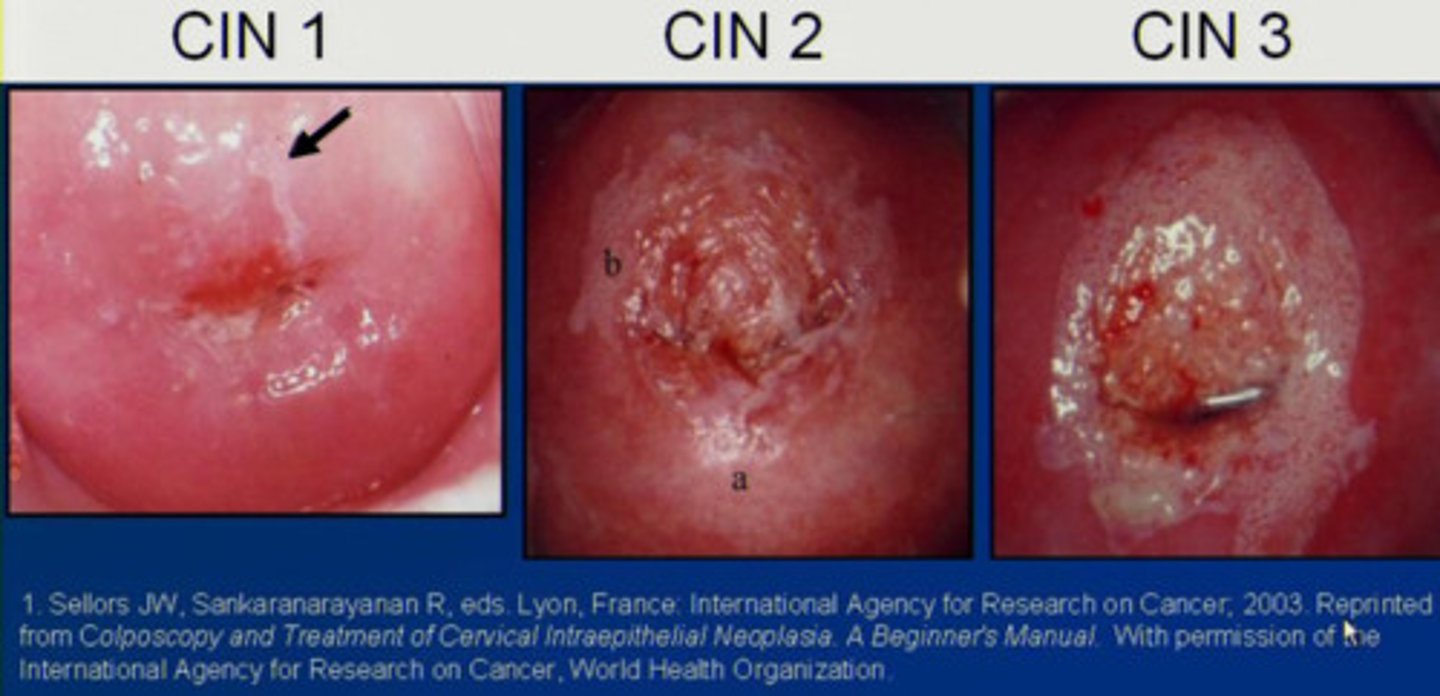
Risk varies on Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia (CIN) grading...
Low risk = CIN 1
High risk = CIN 2 & 3
HPV type 6 and 11
Benign warts
Low risk
HPV type 16 and 18
Mainly found in CIN 2 & CIN 3 and invasive carcinoma
High risk
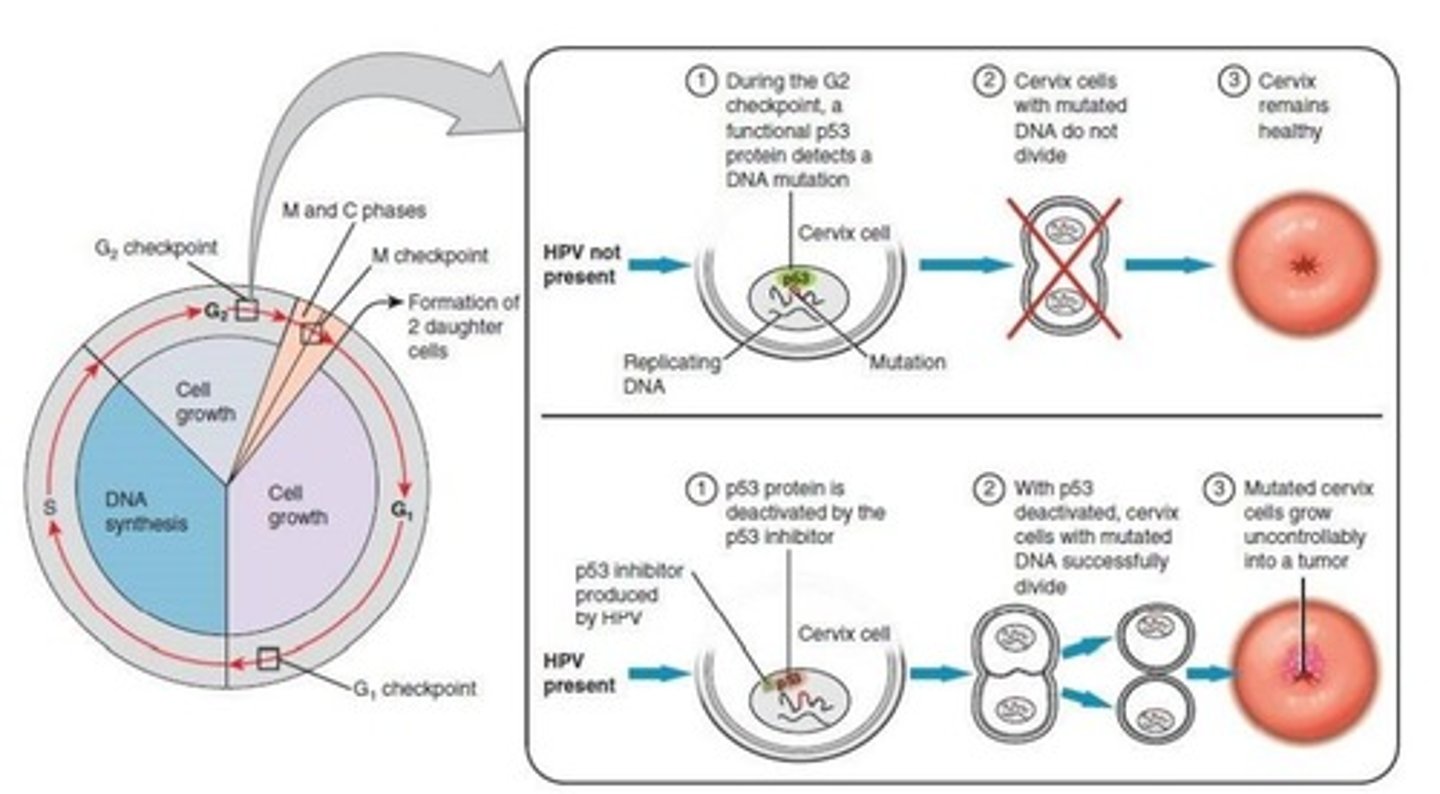
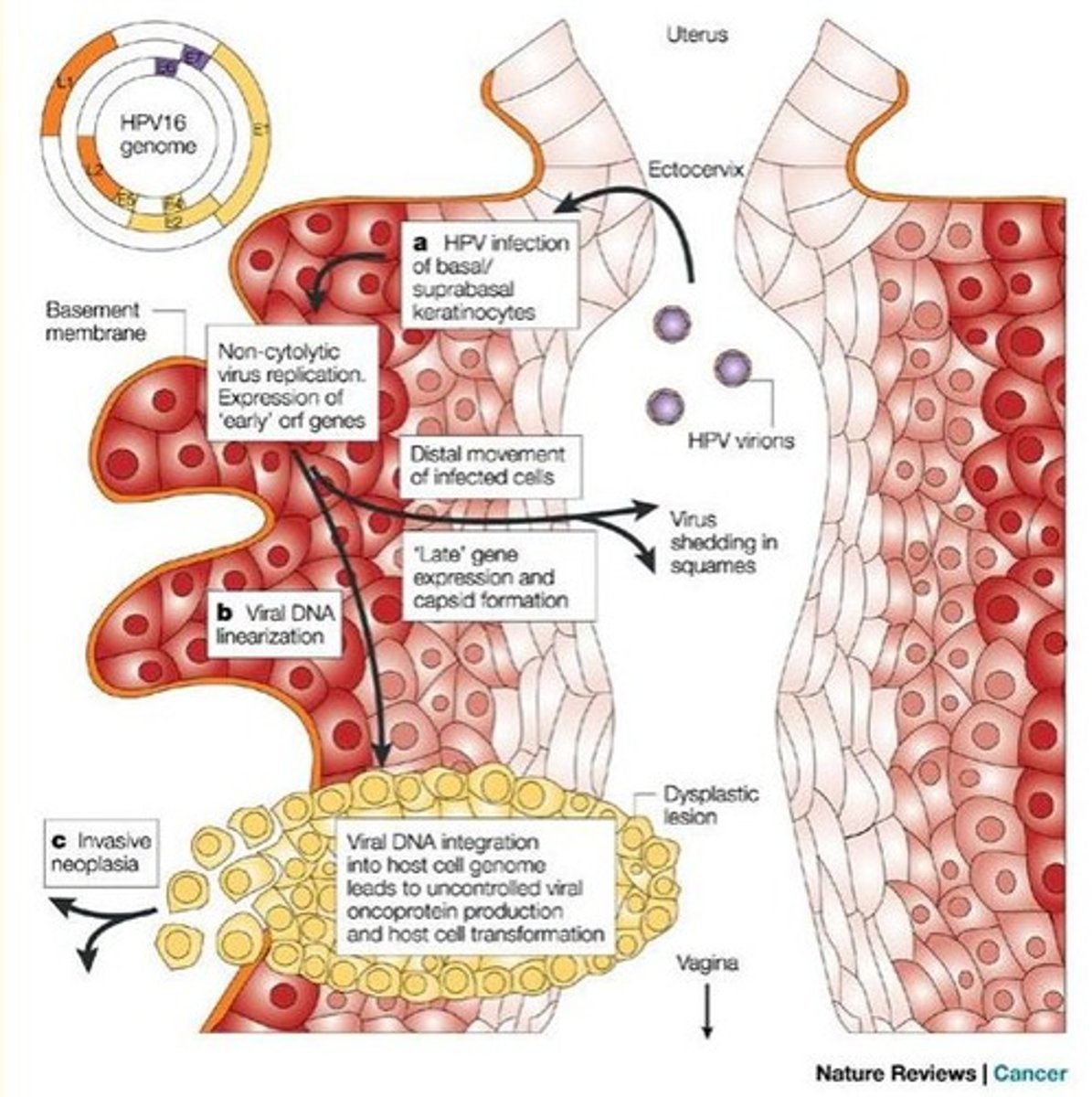
Mechanism of HPV action
- HPV infection causes viral DNA to integrate into host DNA
- Alterations in genes can lead to carcinogenesis
1) Loss of function of tumor suppressor genes
2) Enhanced expression of oncogenes
3) Genetic rearrangement
HPV infection interferes with normal cell cycle, probably by altering cell cycle checkpoints
How does E6 and E7 gene products (viral proteins) lead to unregulated unimpeded cell growth in HPV infection?
The ‘hijacking’ of the human cell to produce viral E6 and E7 proteins can trigger cancer, especially if the host already has Herpes virus.
- E6 gene product binds to human p53 tumor suppressor protein to impede cell growth
- E7 anti-apoptotic effect through mutations in p53 protein
- Unregulated, unimpeded cell growth (cancer transformation)
Cervical screening
Prevention of cervical cancer by detecting and treating early
- Sample of cells taken from woman's cervix for analysis
- Speculum used to open woman's vagina and use of spatula to sweep around the cervix
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) histology
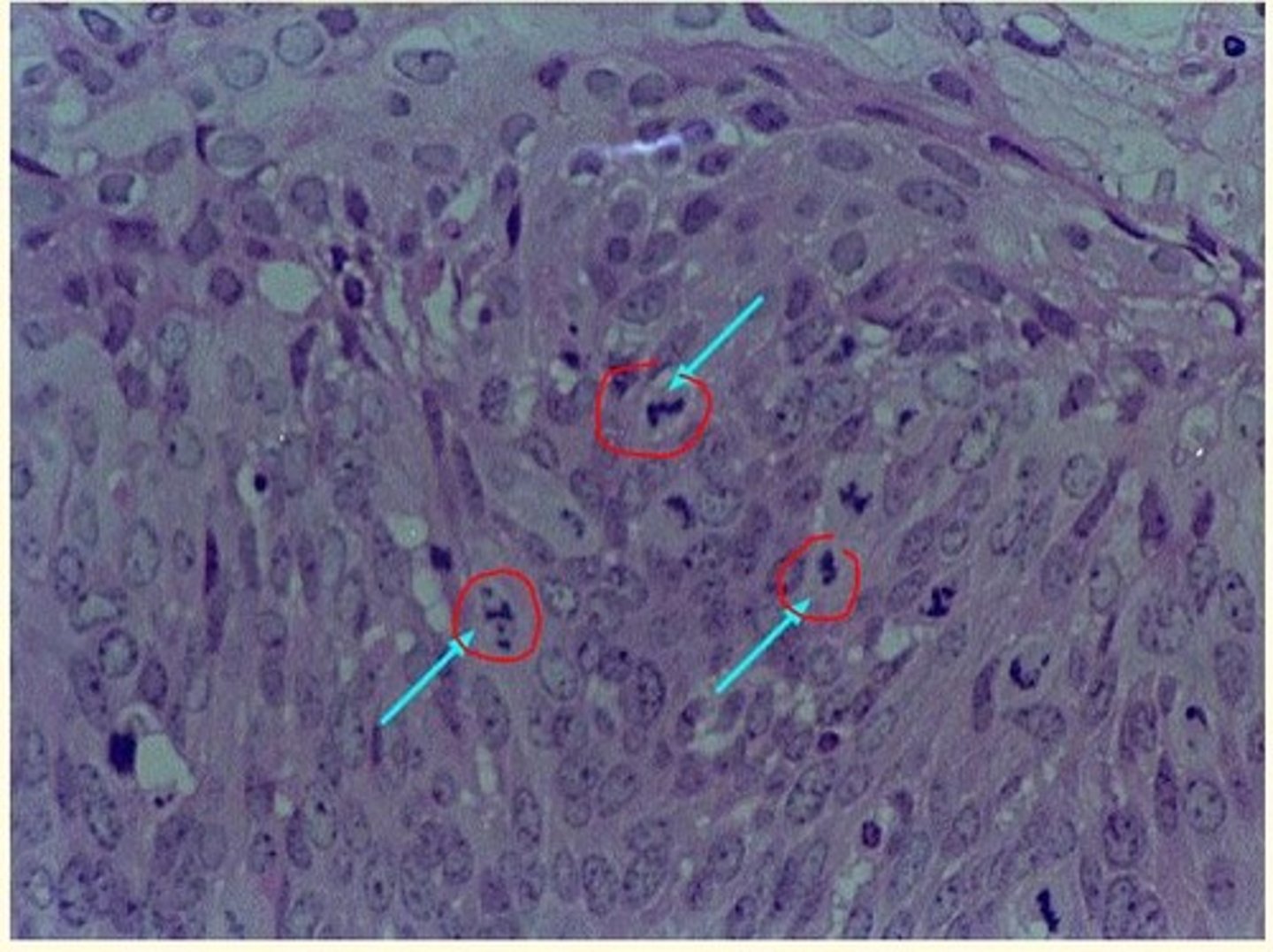
Grading the neoplasm...
If the neoplasm is well differentiated and resembles the parent normal tissue, the neoplasm is ___ grade. This implies it will grow ___.
Grading the neoplasm...
If the neoplasm is well differentiated and resembles the parent normal tissue, the neoplasm is low grade. This implies it will grow slowly.
Grading the neoplasm...
If the neoplasm is poorly differentiated and doesn't resemble the parent normal tissue, the neoplasm is ___ grade. This implies it will grow ___.
Grading the neoplasm...
If the neoplasm is poorly differentiated and doesn't resemble the parent normal tissue, the neoplasm is high grade. This implies it will grow quickly.
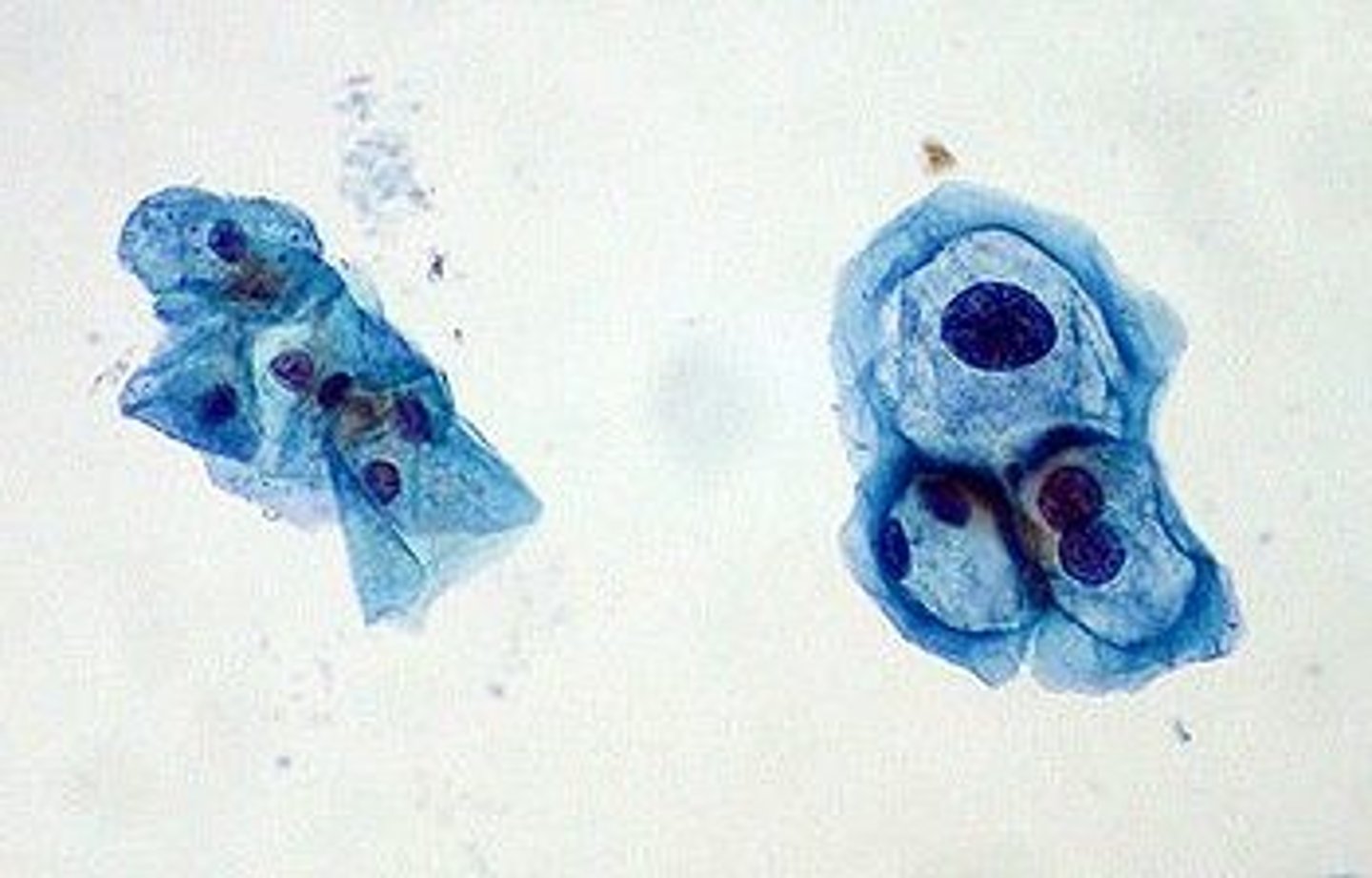
Koilocyte
A squamous epithelial cell infected with HPV
Large, flat cell with large nucleus and clearing around nucleus
If high-risk HPV and cell changes are found in a patient, what are the next steps of investigations for cervical cancer?
- Invite patient for colposcopy
- Biopsy
If invasion is deep, the prognosis is serious - because the likelihood of further spread increases dramatically
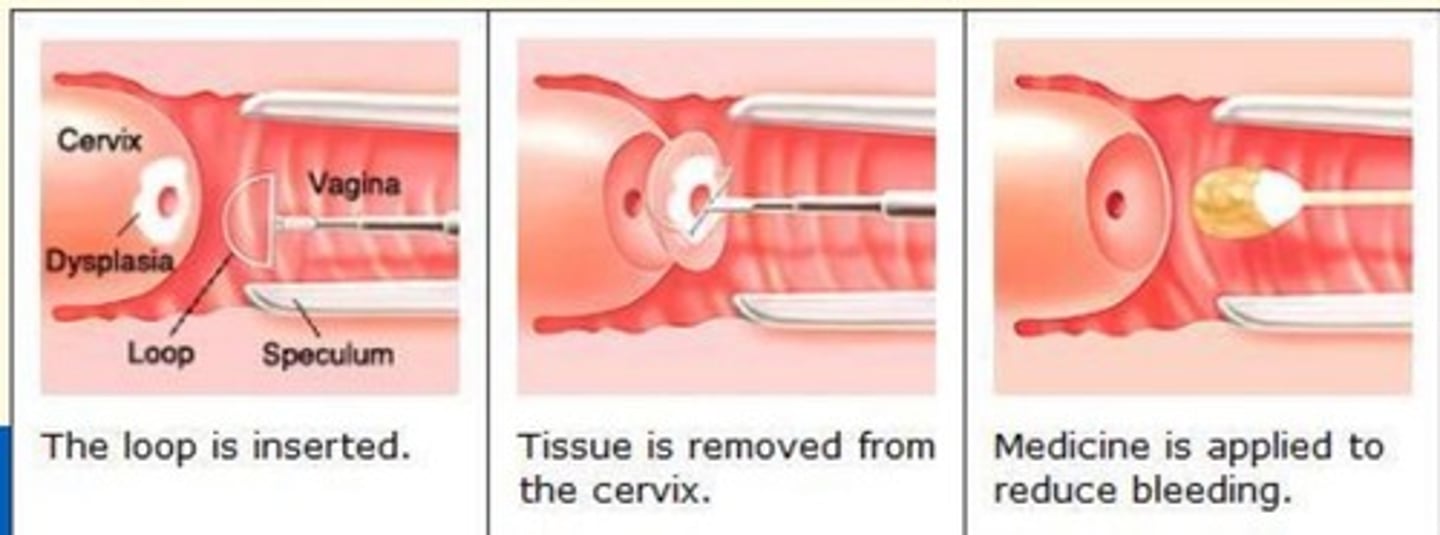
Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure (LEEP)
Gynecologic procedure that uses a thin, low-voltage electrified wire loop to cut out/remove abnormal tissue in the cervix or vagina
Name two cancers that HPV infection has been linked to
- Oral cancer (25-35%)
- Anal carcinoma (>90%)
HPV-related oral cancer
25-35% of oral cancers are HPV-related
HPV-related oral cancers are most common in heterosexual men in their 40s and 50s.
Which type of HPV is the most common genotype detected in about 70% of anal cancers
HPV 16
Risk factors for developing anal cancer (HPV anal carcinoma)
- >50 years of age
- Having another type of cancer (penile, vaginal, cervical)
- Immunocompromised
- Regularly experiencing anal abnormalities (fistulas, soreness)
- Having multiple sex partners
- Engaging in receptive anal sexual activity
- Smoking
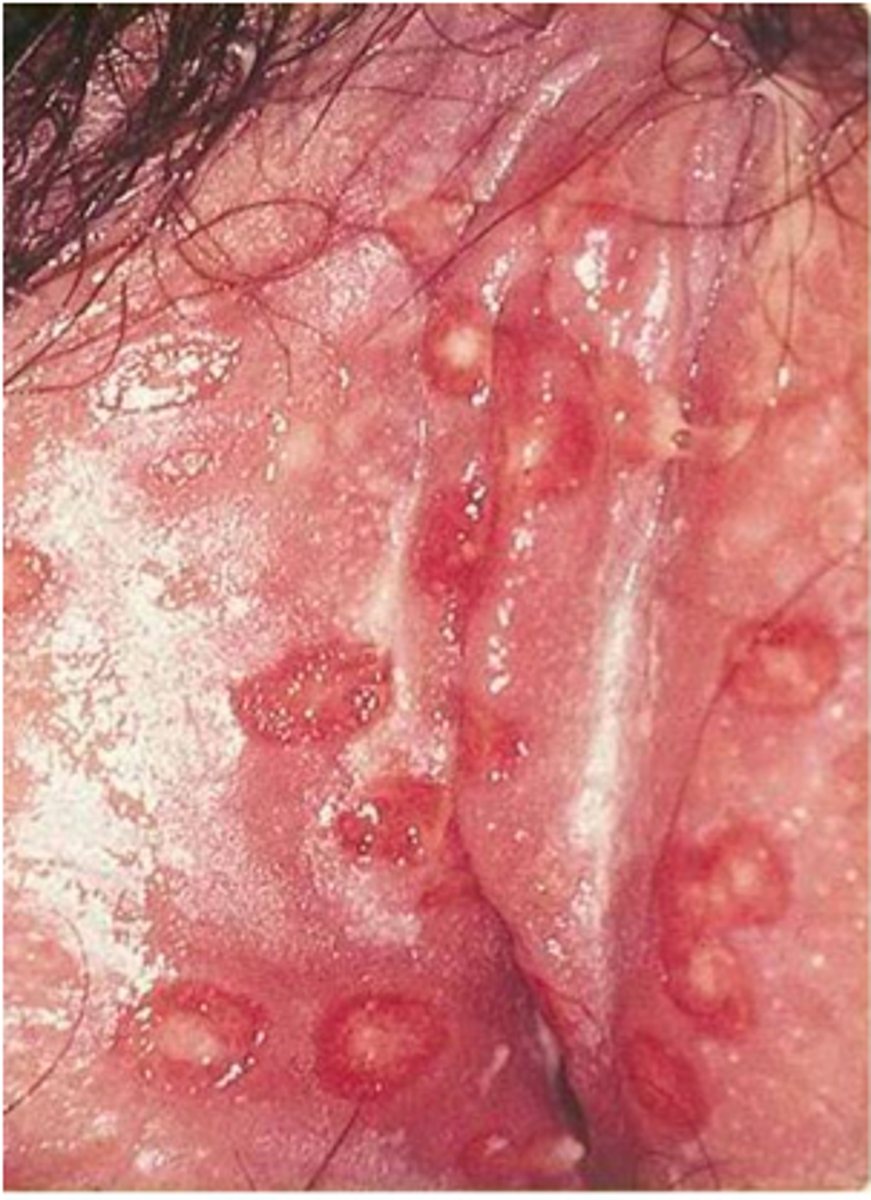
Genital herpes
A sexually transmitted infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. There are two human herpesviruses known to cause genital herpes.
Polyhedral enveloped double-stranded DNA viruses called HHV-1 and HHV-2 (or HSV-1 and HSV-2).
How does Herpes virus infect cells?
- Herpesvirus attaches to and fuses to host cell membrane
- The initial attachment of the virus triggers cascade of molecular interactions involving both the viral and host cell proteins and receptors.
- Penetration of viral nucleocapsid - viral DNA released into host cell
- New viruses are synthesised/assembled
- Virions use nuclear membrane to provide envelope & exit cell
- As HSV kills the epithelia, blisters filled with clear straw-coloured fluid form which eventually burst - releasing large numbers of virus particles which turn into an ulcer.
Transmission of genital herpes
HSV-1 can be transmitted non-sexually. HSV-2 is transmitted sexually.
The herpes lesions spread the virus particles to other sites on the patient's body or other individuals.
Is there a cure for genital herpes?
No, but antivirals (e.g., Acyclovir) can shorten and decrease the number of outbreaks.
Reduces number of herpes lesions and reduces the risk of spreading the disease between sexual partners or during childbirth.
What triggers outbreaks of genital herpes?
Stress, anxiety, high emotion
Genital Herpes symptoms
Men = blisters/sores; flu symptoms; or none
Women = blisters/sores; flu symptoms; or none
Vaccination against which virus has led to a significant decrease in the incidence of cervical cancer?
a) Influenza virus
b) Varicella-zoster virus
c) HIV
d) Hepatitis A virus
e) Human papillomavirus (HPV)
e) Human papillomavirus (HPV)