Neurons and Neuronal Intergration
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Physiology exam 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
describe the three main parts of the neurons
the cell body - has the nucleus and the organelles
dendrites - projections of the cell body that receive the incoming signals
the axon - tubular structure that conducts the action potential away from the cell body and to other cells
describe the events of propagation of an action potential down the axon
describe the neuronal conduction and synapses
explain EPSP and IPSP, neuronal summation
the input zone
the dendrites, receives incoming signals from other neurons
the trigger zone
initiates action potentials at the axon hillock
the conducting zone
conducts the action potentials in undiminishing fashion, over long distances by the axon
the output zone
releases neurotransmitters that influence other cells at the axon terminals
Three main function regions of the neuron:
the receptive region
the dendrites and cell body
Three main function regions of the neuron:
the conducting region
the axon
Three main function regions of the neuron:
the secretory region
axon terminal
the all or nothing principle
AP happen in an all or nothing depending on the strength local potential of the stimulus, once an AP is stimulated it does not need another stimulus
absolute refractory period
the “hump” of the action potential where
Na channels are activated and K channels are activating slowly
then
Na channels are inactivated and K channels are activated
relative refractory period
the “dip” in the action potential
Na channels are in a resting state and K channels remain activated
AP velocity depends on
myelination of the fiber
fiber diameter
contiguous conduction
AP triggers a depolarization in a nearby membrane, then that one does it to another
domino affect
saltatory conduction
“skipping” the impulse along the nerve (on the myelinated sheaths)
50x faster than unmyelinated
AP does not have to be regenerated at myelinated section
myelin in the myelinated fibers are made by
schwann cells (PNS) and Oligodendrocytes (CNS)
Nodes of ranvier
voltage-gates Na channels concentrated between myelin sheaths
fiber diameter
influences the velocity of action potential propagation
increased diameter means there is less resistance, which increases the velocity
Synapses
the connection between two neurons (presynaptic, post synaptic, and extracellular space)
where do neurons terminate
either at the
muscle
gland
neuron
innervate
when a neuron terminates on another tissue
two types of synaptic connection
electrical (gap junctions)
chemical (neurotransmitters)
chemical synapses
chemical neurotransmitter is released from the presynaptic neuron and acts on the cell body or the dendrites of post synaptic neuron
synaptic knob
bulbous end of a neuron's axon that transmits signals to another cell
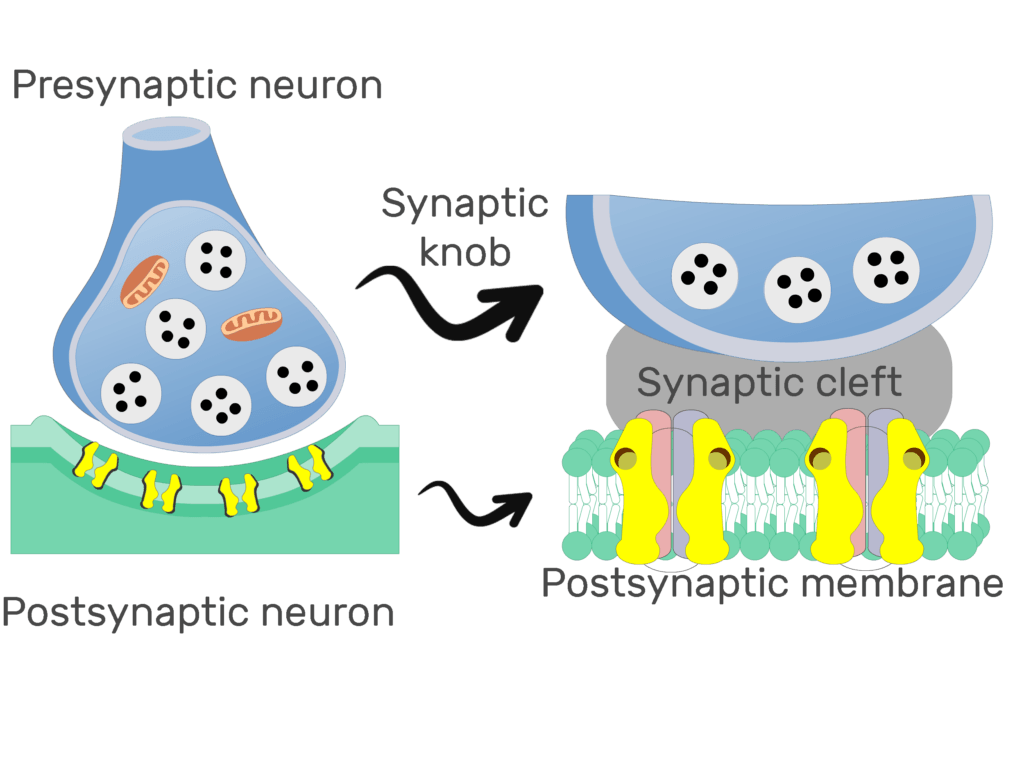
the synaptic vesicles
contain the neurotransmitters
the presynaptic neuron conducts the AP towards
the synaptic knob
the synaptic cleft
the space between the synaptic knob and the synaptic vesicles
release of the neurotransmitter from the presynaptic neuron effects
the AP firing of the post synaptic neuron
the neurotransmitters on the postsynaptic terminal
can be EITHER inhibitory or excitatory
Excitatory postsynaptic potential
EPSP
closer to threshold
inhibitory postsynaptic potential
IPSP
further away from threshold
EPSP and IPSP are both what kind of responses
graded responses
neural integration
postsynaptic neuron integrates all incoming information into single effect
can graded potentials summate?
yes
what does summate mean
to add together, unite, or summarize
grades potentials can summate to reach
threshold, and cause an action potential
temporal summation
The action of one EPSP makes the next EPSP more likely to elicit an AP
how can a second EPSP push the cell the threshold?
the membrane potential is still elevated from the first EPSP, so a second EPSP can push it from the elevated point
Spatial Summation
the actions of an EPSP or IPSP summating over a space or distance
the EPSP or IPSP can happen at the exact same time, but if they are not physically close enough together there will be no summation
synaptic cleft
space between the presynaptic neuron and the postsynaptic neuron