ENG Exam 6.7-6.14
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Buoyancy
Upward force a floating/submerged object experiences
equal to the weight of water
Displacement
Weight of water displaced by the ship = actual weight of the ship (measured in tons).
Draft
vertical distance from the bottom of the ship (keel) to the waterline
How deep the ship sits in the water
Mean Draft:
The average of the forward and aft draft measurements.
Navigational Draft:
The deepest part of the ship, including things that stick out below the hull (like sonar domes, propellers, or rudders).
Used for safe clearance in shallow water.
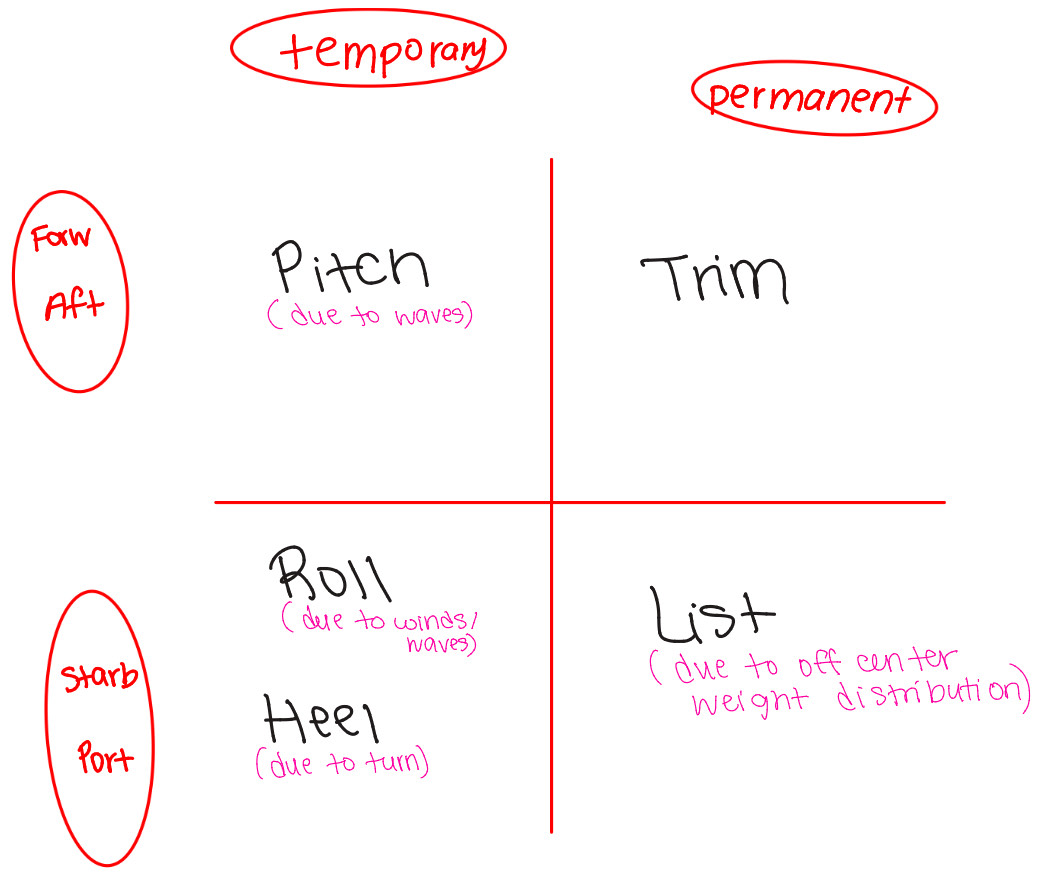
Trim
Permanent difference between forward and aft draft
Roll
Temporary inclination port or starboard due to wind or waves
Pitch
Temporary moving of bow or stern up or down due to wave action
List
Permanent Inclination to port or starboard
due to off-center weight distribution
Heel
Temporary inclination port or starboard due to turning
Sagging
Middle of ship sinks lower than bow/stern (compression at deck, tension at keel).
Hogging
Middle of ship rises above bow/stern (compression at keel, tension at deck).
Define COB and how it moves
Fallows waterline
It is the center of the underwater hull volume when viewed in transverse direction
It’s the point at which all buoyant forces can be considered to be acting in a vertical direction
Waterline moves up, so does the buoyancy moves up
Define COG and how it moves
Point where all ship's weight acts
Moves towards weight addition, and away from weight removed
GM (Metacentric Height)
Distance between Center of Gravity and Metacenter
Indicates stability:
Large GM = quick roll
Small GM = slow roll
Stability is reduced when: Fluid conditions
COG is high and off center
Free Surface
Free communication
Free Surface Effect
happens when a liquid (like fuel, water, or ballast) in a partially filled tank or compartment is free to move around like sloshing from side to side when the ship rolls or tilts.
When that liquid moves, it shifts the center of gravity, making the ship less stable. When gravity moves up the GM (metacentric height) becomes smaller.
Smaller GM means: It becomes easier to roll more or capsize.
wider the tanks worse the effect
Free Communication Effect
Occurs when:
Space is open to sea
partially flooded(not full)
Space is off-centerline
Water freely enters/leaves this shifts COG and virtual rise of COG this is bad for stability because center of gravity shifts unpredictably lowering and upping the GM
Compartmentalizing Benefits (using baffles)
Reduce Free surface Effect
Isolates Casualty
Maintains watertight integrity
Provides damage control zones
Material Conditions of Readiness (Fittings Classification)
X-RAY:
Least protection, inport, normal working hours, no threat
YOKE:
At sea/after hours
ZEBRA:
During General Quarters, fire, flooding, or battle
MODIFIED ZEBRA/YOKE:
Used in calm but cautious conditions.
CIRCLE X/Y/Z:
These allow some doors/fittings to be opened without special permission, even during higher conditions, but must be closed immediately after use.
DOG ZEBRA:
Used for darken ship
WILLIAM:
Sea suctions/ventilation (normally open for ship operation)
CIRCLE WILLIAM:
Closed during CBR (chemical/biological/radiation) attacks to protect air quality
Who is responsible for CCOL(Compartment Check-Off List)
Divo
posted at the entrances
Provide an itemized list and location of all DC fittings and the personnel responsible for the setting of material conditions of readiness
Temporary hull conditions/ Persistent hull conditions Chart
Compartment Numbers Label
1st number: Deck #
2nd number: Forward most aft
3rd number: Position relative to waterline
Last Letter: Compartment use
FR202: forward most frame
210: After most frame
S-5 S is division responsibility
5 is work center responsibility

3 Main Material Conditions of Readiness
X-RAY: in homeport
YOKE: import
ZEBRA: during battle, emergencies or General quarters
2 center gravity conditions
high
off center
Installed CO2
Charlie fire
found in paint lockers, flammable liquid rooms, electrical/machinery spaces
Fills the room with CO2 which removes oxygen so fire goes out
Halon 1301
Bravo fire (flammable liquids)
Found in engine rooms, generator spaces, boiler room, flammable storage areas
Chemically interrupts the fire reaction
Ventilation shut off automatically
60 sec delay if manned
30 sec if unmanned
Must wear SCBA
produces toxic gas like Cyanide
AFFF
Bravo fire
Found in Machinery rooms, fuel storage, Bottom of engine spaces
foam and sea water mixed to smoothe the fire
May produce Hydrogen sulfide gas
Hearing protection is required
Battle Dress
FRV Coveralls (flame-resistant)
Pant cuffs tucked into boots or socks
Life preserver worn or at station
Flash hood and flash gloves (protect skin from burns)
No metal, empty pockets
Everything buttoned up
Firefighter’s Ensemble (FFE)
Helmet – protects head from heat and falling stuff
Outer suit – flame- and steam-resistant
Gloves and boots – for burns and sharp debris
Flash hood – covers neck and face (gold = firefighting)
Protects from heat, steam, sharp objects, and more while actively fighting a fire
SCBA
It lets you breathe clean air in toxic or smoke-filled spaces.
Air tank (30 or 45 minutes of air)
Face mask with voice amp
Pressure regulator and harness
4500 PSI
EEBD
Your last-resort air supply for getting out of smoke or toxic areas — NOT for fighting fires.
10 minutes of air
Orange case, activates when you pull it out
Has mouthpiece and nose clip
Disposable – one-time use only
EEBA Allowances
Ship’s Complement 150%
Embarked Personnel 100%
Berthing Spaces 100%
(one EEBD per rack)
Engineering Spaces 200%
Two way to tell EEBD is ready for use
Gauge (green in color)
Orange
Not be expired
Electronic Box Fan
powered by electricity
Ventilating compartments during maintenance, cleaning, or cooling efforts.
Moves 3200 cubic feet of air /min
RAM 2000 Fan
powered by water
Provides ventilation in smoke-filled or confined spaces.
Moves 2000 cubic feet of air /min
Toxic
Atmosphere with harmful substances where exposure must stay below OSHA standards. Respirators required if above limits.
PEL (Permissible Exposure Limit):
Maximum amount of a substance personnel can be exposed to toxic gas without harm, set by OSHA.
LEL (Lower Explosive Limit)
Lowest concentration of a flammable gas that can ignite.
UEL( Upper Explosive Level)
Highest concentration of flammable gas that can ignite. Above this is too rich to burn.
IDLH (Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health): Any space where:
Flammable agents present above 10% of LEL
Oxygen greater then 22%
Oxygen less than 19.5%
Toxins high enough to prevent escape within 30 minutes without health effects
4 requirements of Fire Watch:
All sides of the hot work area must be watched
30-40-50 Rule
Stay on watch 30 min after work or until cool to the touch.
No hot work within 40 feet of painting/chemical cleaning.
Move flammables 50 feet from the work site.
Wear PPE (goggles, helmet, hearing protection, respirator if needed).
4 primary forms of radiation
Alpha
Beta
Gamma
neutron
Radiation Treatment
Time
Distance
Shielding
PPE
Gloves and Boot Covers
worn with JSLIST to protect hands and feel, used during MOPP 4 level
M50
Eye and respiratory protection against airborne contaminants
JSLIST
protective suit against CBRN threats (Chemical, Biological, Radiological, Nuclear).
Hot Work
Class II Hot Work:
Minimal amount of energy
Localized sparks
Damage Control Assistant (DCA) or Fire Marshal determines if fire watch is required
Class I Hot Work:
High amount of energy
Scattered sparks
Fire watch is required
MOPP Levels
0 Normal everyday operations
1 suspected CBR-N attack
2 possible CBR-N attack
3 probable CBR-N attack
4 imminent CBR-N attack
4 casualty power benefits
Preservation of watertight integrity
Simplicity of installation and operation
Flexibility of application
Interchangeability of parts and equipment
what are 4 loads you could power with casualty power
weapon system like CWIS
External Communications
DC Equipment
Lighting systems
Engineering Systems
Advantage of using bulkhead terminal and riser terminal
are used in shipboard electrical and piping systems to route cables or pipes through watertight bulkheads or decks without compromising the integrity of the compartment.
maintain watertight integrity of the ship
Quick Disconnection/Isolation
Safety & Compartmentalization
Minimizes Damage Propagation
casualty power loads connect all horizontal cable _____ to _______
LOAD to SOURCE
casualty power load
Refers to critical electrical equipment that must remain operational during an emergency (e.g., battle damage, power loss).
External Communications |
Fire Pump Motor Controllers |
CIWS / NSSM / RAM Systems |
Interior Comm Switchboards |
Lighting System Transformers |