Lecture 6 - Hydrogels and Smart Polymers
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Hydrogels and Smart Polymers
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is a hydrogel?
• Materials that are composed of hydrophilic, crosslinked polymer chains
– Crosslinks: covalent bonds, physical entanglement, hydrogen bonds or strong van der Waals, crystallites that bind two or more polymer chains
– Water-swollen, extremely high water content
What are the classifications of hydrogels?
– Homopolymer hydrogels
– Copolymer hydrogels
– Interpenetrating polymeric hydrogels
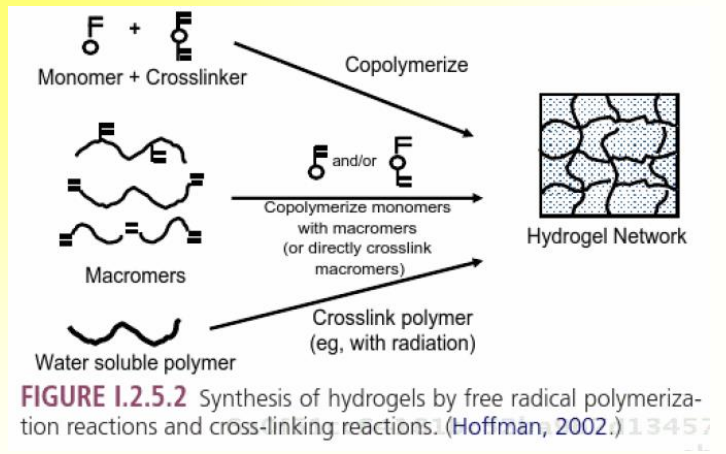
How are hydrogels prepared?
– Synthesize in dry state and put in water
– Synthesize in aqueous solution and further swell in water
Mechanisms of reactions:
• Chemical cross-linking
• Photopolymerization: UV
• Irradiative cross-linking: Electron beam, gamma, X-rays via free radical reactions
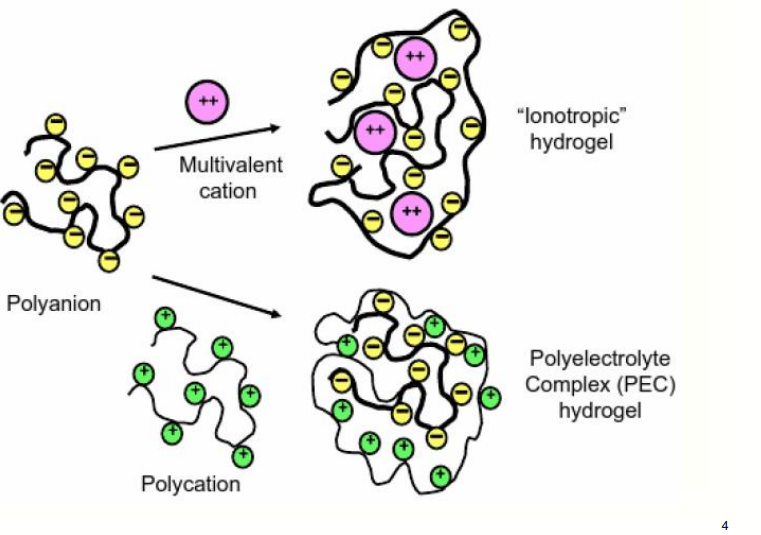
What are the two types of ionic hydrogels?
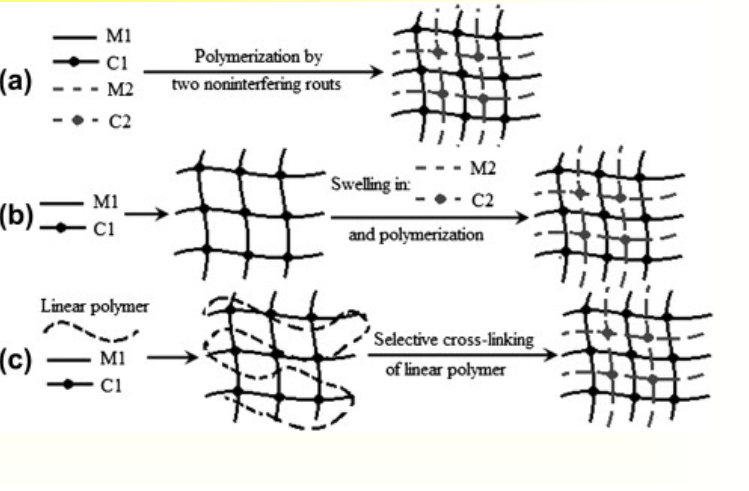
Methods for Interpenetrating Network
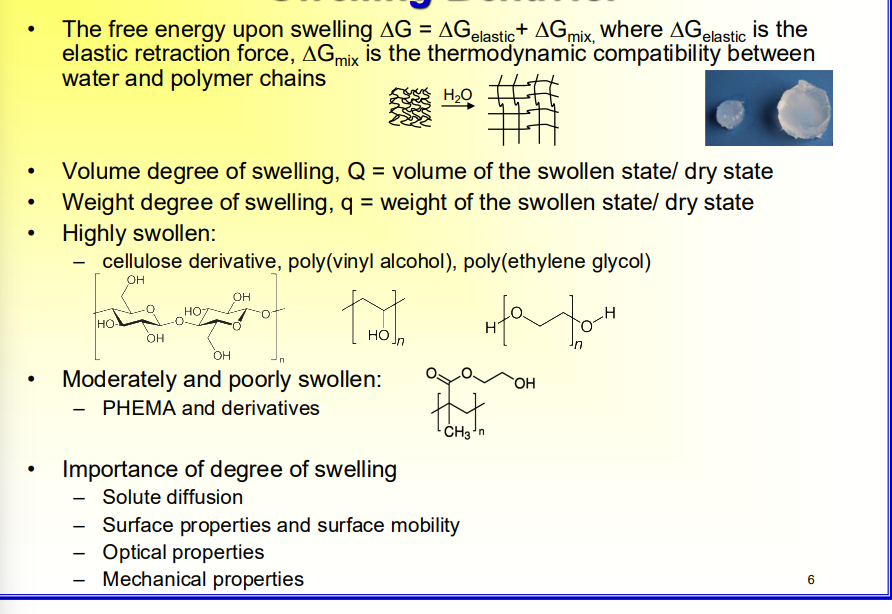
What are some characterisitics of swollen hydrogels??
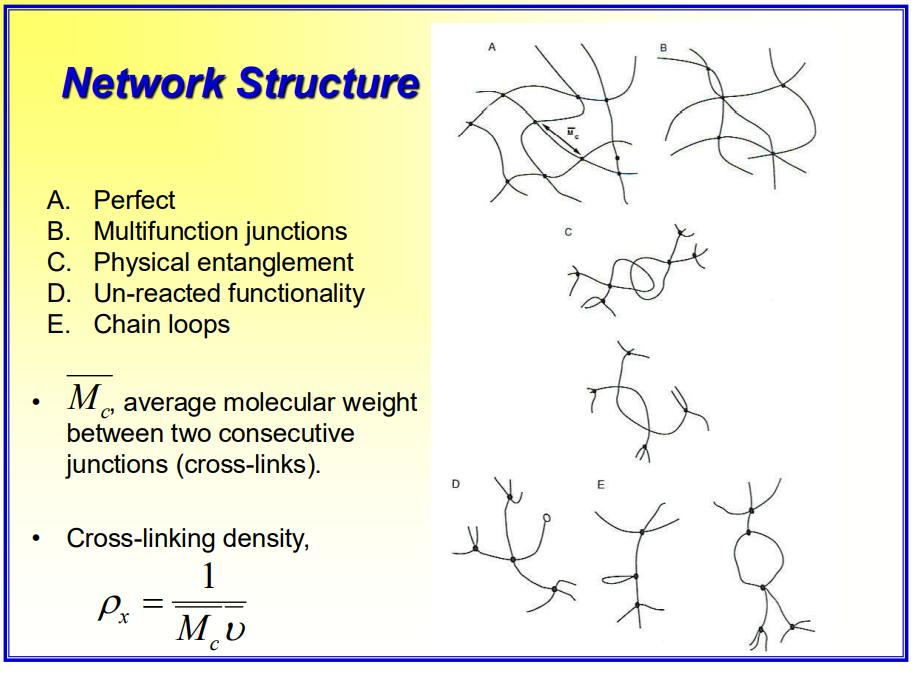
What are different types of network structures you can get after doing a polymerization and crosslinking?
What are some advantages of hydrogel use?
• Closely mimic mechanical properties of soft tissue
– Can be modulated for specific tissue or application
• May be polymerized into any desired geometry
• Free diffusion of cellular nutrients and waste products
• In situ polymerization possible
– Facilitates localized delivery of the material
– Gel conforms to the geometry of the wound or defect
• Mechanisms of polymerization allow incorporation of bioactive signals or bio-responsive domains
– Cellular growth or guidance cues
– Enzymatic degradation domains
How are biomolecules etched/added to hydrogels?
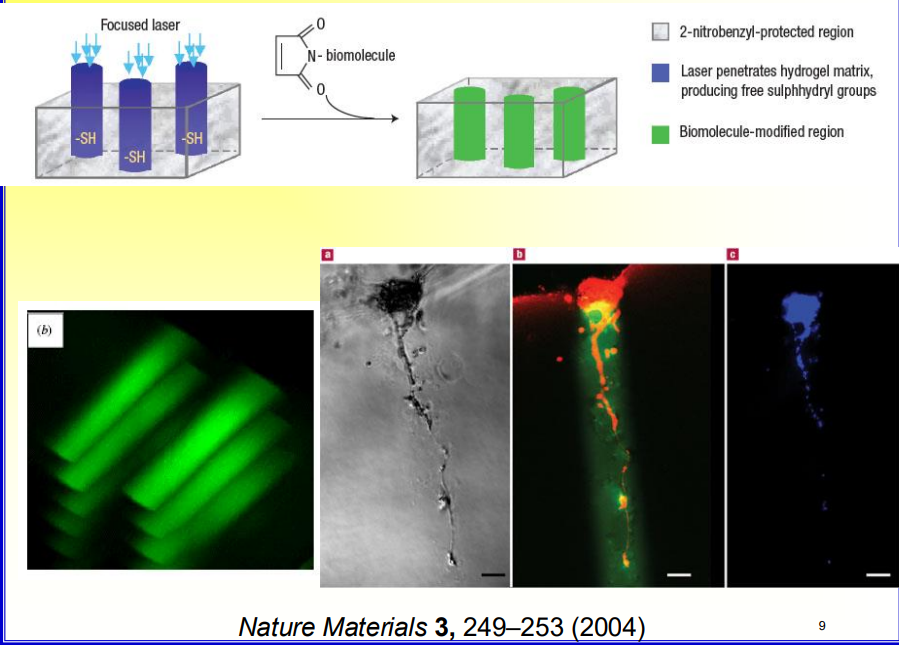
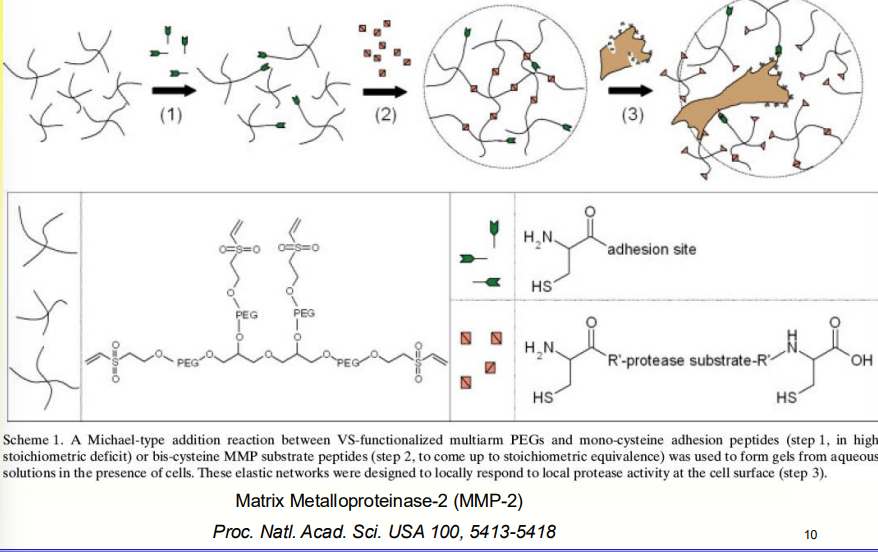
Cell Responsive Hydrogel
Incorporate domains in a gel that only respond to specific enzymes that are released by the target regenerative cells
start with Polyethylene Glycol and add an adhesion molecule (peptide) that encourages cells to stick to the gel
Not a gel yet; no crosslink
Add crosslink
crosslink desinged to have protease in the middle and two functional groups on the end (thiol + vinyl) which reacts quickly to protease
What are some applications of hydrogels?
• Biocompatible and blood compatible biomaterials
– PVA, Polyacrylamide, PHEMA, PEG
• Wound healing adhesive
• Cartilage
• Skin
• Nerve repair
• Carrier for cell transplantation
• Pharmaceutical
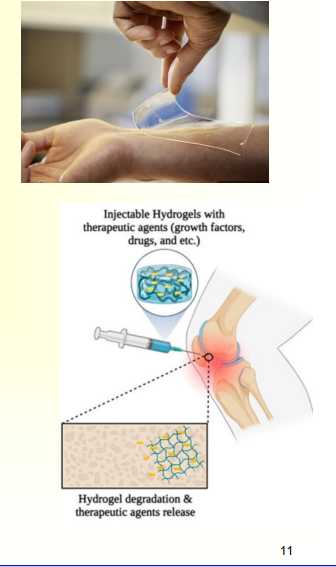
Intelligent or smart hydrogels
• Environmentally responsive, show drastic change in swelling due to changes in pH, temperature, ionic strength, nature and composition of swelling agent, enzymatic chemical reaction, electrical and magnetic stimuli
• Critical point
• Reversible
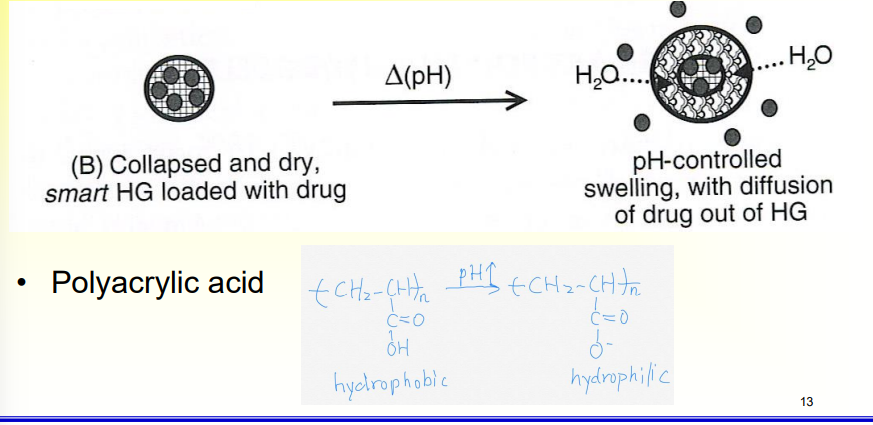
pH Sensitive Hydrogels
• Containing acidic or basic pendant groups →which ionize at appropriate pH or ionic strength → ^ swelling
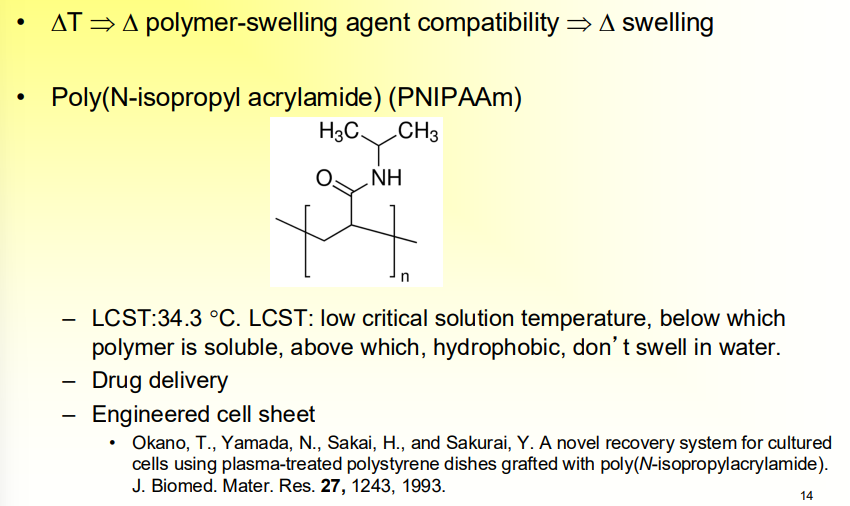
Temperature Sensitive Hydrogels
When there is a temperature change, the polymer and water compatibility changes
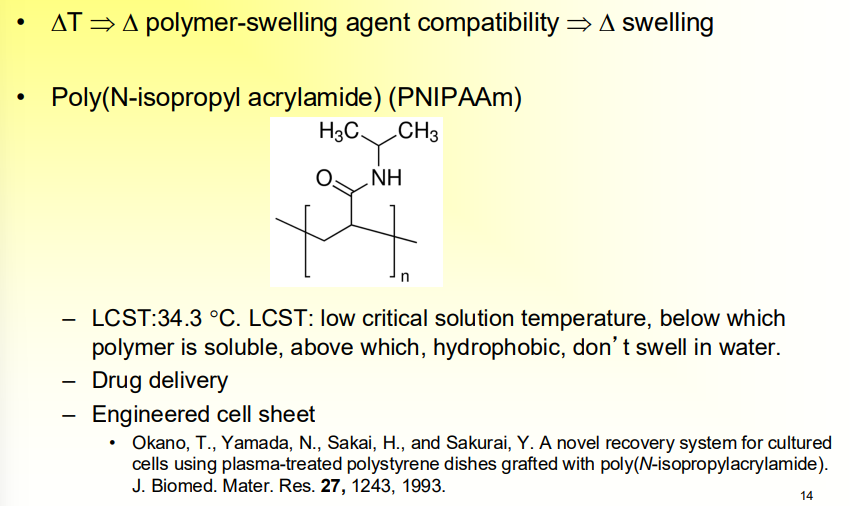
PNIPAAm
A popular temperature sensitive polymer hydrogel
changes properties depending on temperature
Smart Polymers that respond to biostimuli
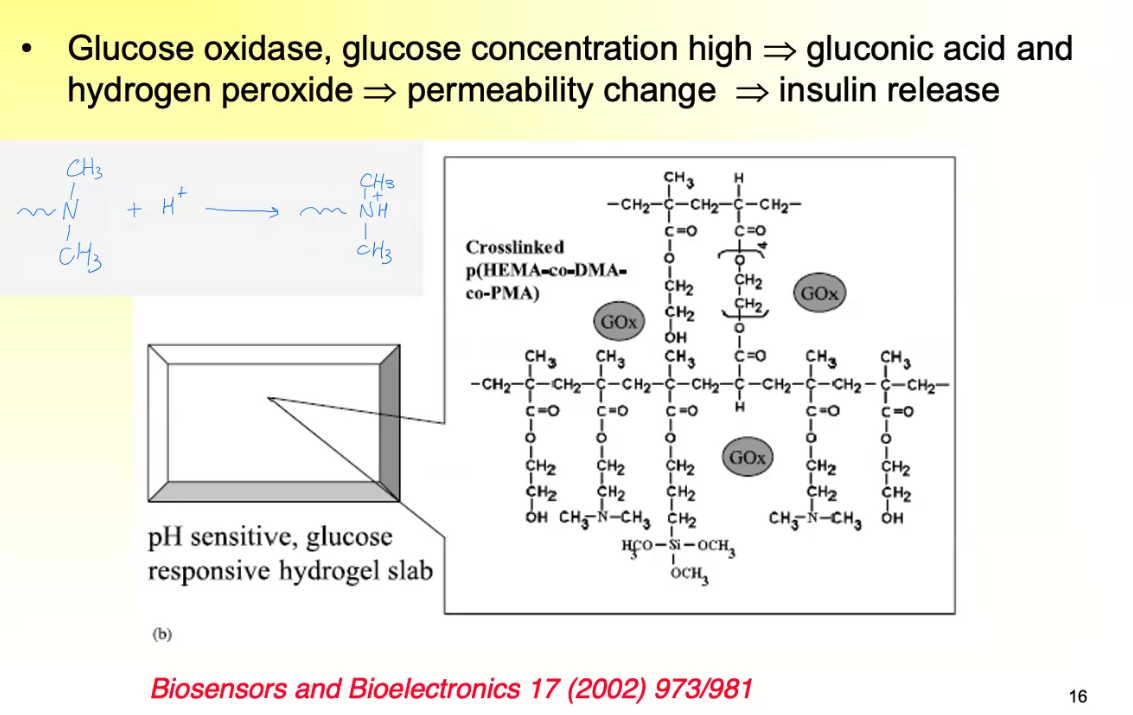
What are conducting Polymers?
Specialized polymer, not necessarily hydrogel. Typically, polymers aren’t conductive
Some are, because of a contribution along the backbone of the polymer chain that allows electrons to travel down the backbone chain
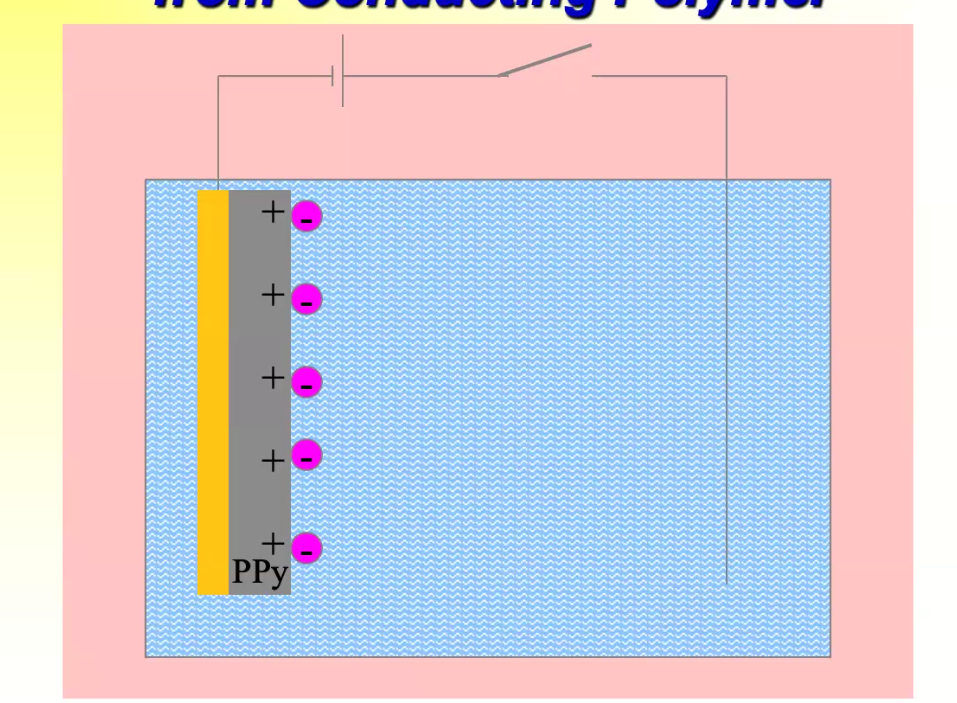
Eg. Polypyrrole - Electrically Conductive and active
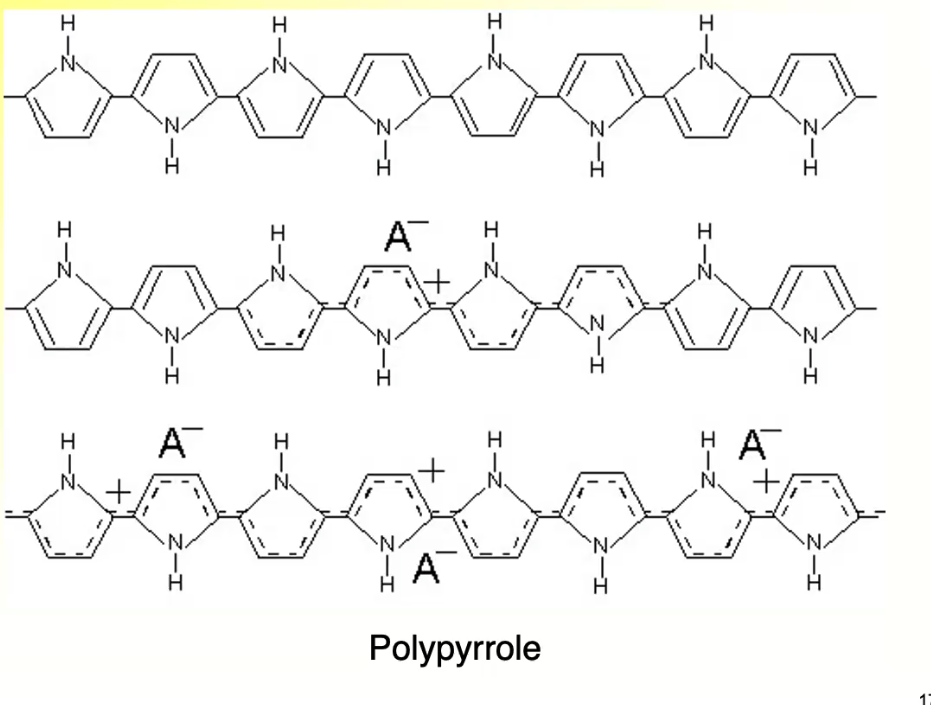
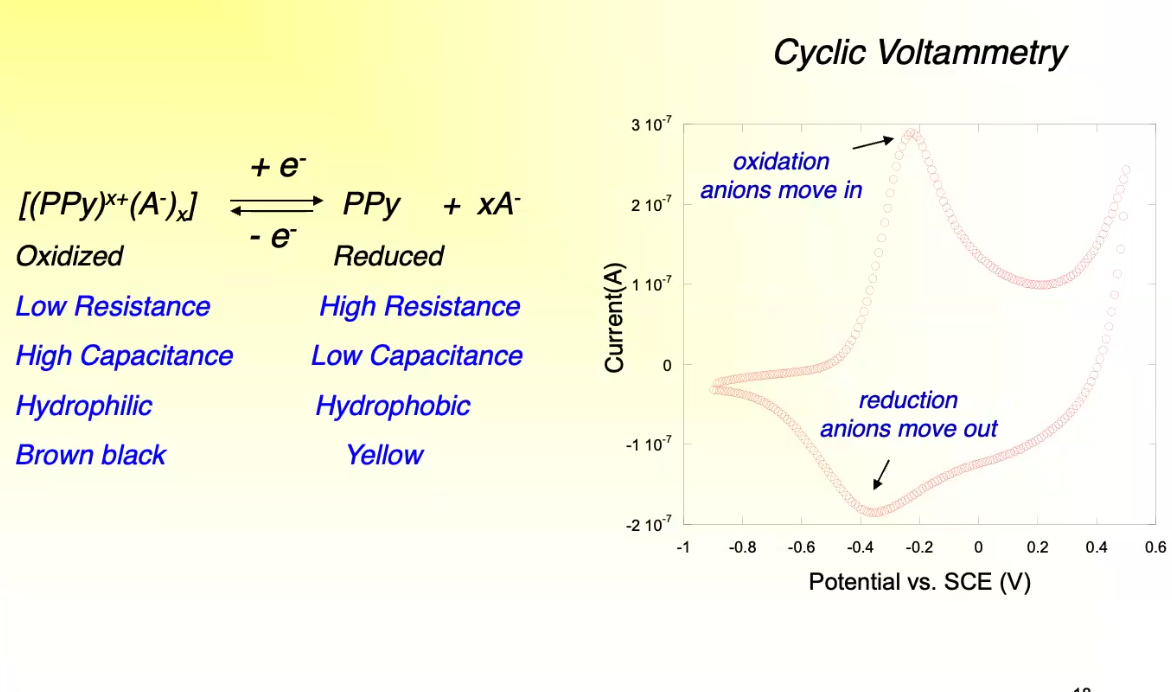
Polypyrrole Reversible Redox Reaction
To be made conductive, it needs to be positive charge, and be doped with a negatively charged ion
can be converted to a reduced state, and releases ion
two states have very different properties
Polypyrrole Drug Release from conducting polymer
Polypyrrole bounded by negatively charged ions
if ion is drug molecule, you can make electrically controlled drug release methods