Week 7: Aggression
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
What is the definition of aggression according to Scherer et al. (1975)?
Behaviour intended to harm another of the same species.
According to Bandura (1973), how is aggression operationalised?
As behaviour resulting in personal injury or destruction of property.
What are methods of operationalising aggression?
Analogues of behaviour, such as punching a doll (Bandura et al. 1963).
Signal of intention, e.g. body language
Self-ratings, e.g. aggression questionnaires
Rated by others
Indirect spreading rumours
What does the frustration-aggression hypothesis propose?
Frustration is caused by being prevented from achieving a goal.
This, in turn, leads to aggression.
Frustration is regarded as the foundation of aggression.
This aggression is seen as a cathartic release (psychological release) of pent-up feelings, which can reduce the drive for further aggression
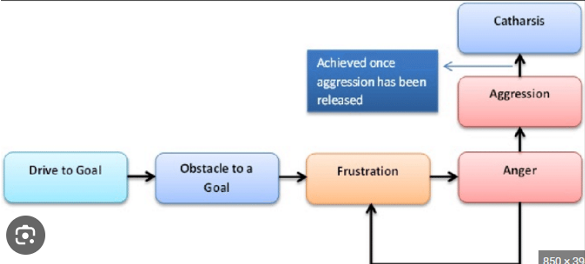
What can frustration lead to according to later revisions of the frustration-aggression hypothesis?
Various responses, not just aggression, and aggression may be displaced onto a more convenient target.
What is the role of the environment in aggression according to Kenrick et al. (2003)?
The behavioural manifestation of a genotype depends critically on inputs from, and reactions to, the environment.
What was the main finding of Bandura's Bobo Doll Experiment?
Children who observed aggressive behaviour were more likely to imitate that behaviour.
Describe the 4 conditions of Bandura’s Bobo Doll study
1. Adult was physically aggressive towards the doll (live)
2. Adult was physically aggressive towards the doll (video)
3. Adult was physically aggressive towards the doll (cartoon)
4. Control condition: adult didn't perform any aggressive behaviour towards the doll, neutral behaviour
What are the four mediational processes in Bandura's social learning theory?
Attention, Retention, Motor reproduction, and Motivation.
Outline Straus et al’s (2003) study on spanking children
Longitudinal study over 2 years
Recorded how often the child was spanked (0-3+/week)
Positive relationship between frequency of spanking and anti-social behaviour of the child
Children who were not spanked showed less aggressive behaviour after 2 years
What was the outcome of Anderson et al. (2003) study on violent lyrics?
Violent lyrics triggered aggressive associations and contradicted the cathartic hypothesis, since listening to violent lyrics should lessen aggressive thinking.
Outline Black and Bevan’s (1992) study on violent films
Naturalistic experiment conducted in a real-world cinema
129 adults
Montreal
Participants watched one film considered to be aggression and one non-violent
Participants who watched the violent film rated themselves higher on an aggression questionnaire and vice versa
What was the placebo effect observed in Begue et al. (2009) study?
Males acted more aggressively when they believed they consumed an alcoholic cocktail, even though it was non-alcoholic.
Controlled naturalistic field experiment - conducted in a bar
Studied males only - 115/116 pps
Male students given non-alcoholic cocktail as well as an alcoholic cocktail
Thought it was alcoholic (placebo effect)
Acted more aggressively with the placebo.
Even the connotations of alcohol can lead to an increase in aggression
What is prosocial behaviour according to Wispe (1972)?
Behaviour that has positive social consequences and contributes to the well-being of another person.
What is the common experience before acting prosocially?
A state of arousal followed by empathy.
How can empathy be learned ?
Through giving instructions, using reinforcement, and exposure to models.
What is the definition of helping behaviour?
Helping is intentional and benefits another living being or group.
What is the significance of Bandura's social learning theory in relation to aggression?
It emphasises that aggression can be learned through observation and imitation.
What does the term 'displacement' refer to in the context of aggression?
Redirecting aggression towards a more convenient target when the original source is too powerful or abstract.
What is the role of reinforcement in Bandura's theory?
Reinforcement influences the likelihood of a child reproducing aggressive behaviour.
What did Bandura's study reveal about gender differences in aggression?
Later research found that males were more aggressive than females.
What is the relationship between empathy and prosocial behaviour?
People often fail to act prosocially if they are actively engaged in avoiding empathy.
What is the impact of violent media on aggression according to the studies mentioned?
Exposure to violent media can increase aggressive thoughts and behaviours.
What is the importance of cognitive processes in Bandura's social learning theory?
Cognitive processes and abilities are crucial for understanding how aggression is learned and reproduced.
What is altruism?
An act meant to benefit another person rather than oneself; true altruism is selfless.
What hypothesis suggests that people believe they get what they deserve?
Just world hypothesis.
How do mood states affect prosocial behavior?
Good moods increase the likelihood of helping, while bad moods lead to internal focus.
What is image-reparation in the context of prosocial behavior?
Helping to make amends after causing harm or feeling guilty.
What is the negative state relief model?
Helping others in order to reduce one's own bad mood if they are feeling bad or guilty, which is hedonistic rather than altruistic.
What personality traits predict prosocial behavior?
Agreeableness, self-transcendence, and empathic self-efficacy.
What did Mikulincer et al. find regarding attachment and altruism? *
Those securely attached are more likely to be compassionate and altruistic.
According to Amato (1983), how does population size affect helping behaviour? *
Helping behaviour decreases as population size increases.
What is terror management theory?
The idea that the fundamental human motivation is to reduce the fear of death.
What did Baumeister et al. (1988) find about leadership and helping behavior?
Leaders helped more (80%) than followers (35%) in a simulated group task.
How does sexual attraction influence helping behavior?
More physically attractive individuals receive more help.
What is kin selection in evolutionary psychology?
The bias to help blood relatives to propagate one's own genes.
What is mutualism in the context of prosocial behavior?
Cooperative behavior that benefits both the co-operator and others.
What role does empathy play in altruism according to Patricia Oswald (1996)? *
Empathy requires perspective taking and is vital for altruistic behaviour.
How does experience with stressful situations affect empathy?
People with prior experience empathise more with others undergoing similar situations.
What did Rushton and Teachman (1978) find about modeling in children?
→ Boys aged 8-11 years watched an adult who played a game to win tokens.
Adult generously donated some to a later child: very emotional story behind them, e.g. poverty etc
Child played the same game after the adult had
Boys who observed positive reinforcement for generosity were more likely to donate tokens.
Outline Bryan and Test’s (1967) study of models on adults
Modelling can also work for adults - adult only study
Condition 1 – driver passed a woman whose car had a flat tyre and was being helped by a man. The driver then passed another woman by her car needing assistance
Condition 2 – the driver just passed the 2nd car where there was no model
Drivers in condition 1 were 50% more likely to help
Explained that we need modelling to promote positive behaviour in adults
Outline Hornstein’s (1970) study on modelling and emotional responses
People observed a model returning a lost wallet
Condition 1 – Model was pleased to help
Condition 2 – Model showed no strong emotion
Condition 3 – Model was displeased at the bother of having to help
Participants then found a ‘lost’ wallet
Condition 1 helped more than 2 which helped more than 3
Learning by vicarious experience: vicarious reinforcement
How do prosocial video games affect behaviour according to Gentile et al. (2009)? *
Prosocial content increases helping behaviour, while violent content increases hurting behavior.
What effect does listening to prosocial music have on behaviour?
It increases spontaneous helping behaviour.
What is prosocial music?
Music that, when listened to, increases spontaneous helping behavior.
What effect do prosocial videos have on behavior?
They increase helping behavior and make prosocial thoughts more accessible.
What case study sparked research on the bystander effect?
The murder of Kitty Genovese.
Outline the Kitty Genovese murder case study
Late one night in March 1964, Kitty is walking home after work
In a respectable neighbourhood within Queens in New York
In the half an hour it took to kill her, no one helped
30 mins later, anonymous call, didn’t want to “get involved”
38 people hear the screams, but did not act
Media: Apathy? Indifference? Moral callousness?
What is the bystander effect?
The phenomenon where people are less likely to help in an emergency when others are present.
How does the number of bystanders affect helping behavior?
The greater the number of bystanders, the less likely it is that anyone will help.
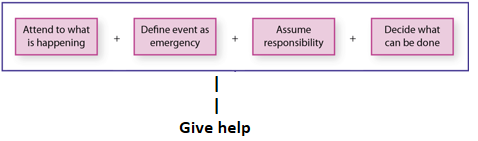
What are the characteristics of an emergency situation?
It involves danger, is unusual, cannot be anticipated, and requires instant action.
What is diffusion of responsibility within the bystander effect?
The tendency to pass the responsibility to act to other available people.
What is audience inhibition within the bystander effect?
The fear of making a social blunder that prevents individuals from helping.
What role does social influence play in the bystander effect?
The passive behaviour of others can serve as a model for how to act.
What did meta-analyses reveal about the bystander effect?
It becomes weaker in dangerous situations and when bystanders are familiar with the victim.
What is the bystander intervention?
When an individual breaks out of the role of a bystander and helps another person in an emergency.
What is the bystander-calculus model? *
A model that describes how bystanders evaluate the costs and benefits of helping.
What are the three stages of the bystander-calculus model? (Piliavin) *
Physiological arousal,
Labeling the arousal as an emotion
Evaluating the consequences of helping.
Pandas Love Eating
What are the four motives for helping others?
Egoism - acting in ways which benefit yourself
Altruism - acting to help others, even if it costs you something
Collectivism - prioritising the group over the individual
Principlism - making decisions based upon ethical principles
Outline Latane and Darley's 1968 study?
Male students in interview room
Smoke began to pour for 6 mins
Alone: 75% took action
2 strangers 38% took action (bystander effect)
2 passive confederates 10% took action (bystander effect)
Presence of others can inhibit people from responding to an emergency
What was the outcome of Latane and Rodin's 1969 study? *
Helping behaviour decreased as the number of bystanders increased.
What did Darley and Latane's 1968 study on seizures reveal?*
Help rates decreased as the number of bystanders increased.
What is bystander apathy?
The phenomenon where individuals do not help in emergencies due to the presence of others.
What is the reciprocity principle in prosocial behavior?
The expectation to help those who have helped us.
What is the social responsibility norm?
The expectation to help those in need without regard to future exchanges.
What is the significance of familiarity with the victim in helping behavior?
Familiarity increases the likelihood of helping.
What did the study involving participants watching a victim in distress reveal?
Helping decreased as diffusion of responsibility, social influence, and audience inhibition increased.
What is the impact of shared social identity on helping behavior?
Expectation of later interaction or shared identity increases helping behavior.
What are the limits to the bystander effect?
Familiarity with the victim and expectation of shared identity can increase helping.
Outline Latane and Darley’s 5 stage cognitive model of bystander intervention (1970)
Angry Dragons Always Dance Gracefully
What did Gaertner and Dovidio study about bystander apathy (1977)
Gaertner and Dovidio (1977) found that people are less likely to help in an emergency when others are present, due to diffusion of responsibility—each person assumes someone else will act.
Found that female pps were slightly inclined to help black confederate when no other help was available
Helping behaviour significantly decreased when the number of bystanders increased
What did Latane and Darley discover about the bystander effect (1976)?
Latane and Darley (1976) found that people are less likely to help in an emergency when others are present, showing the bystander effect—as the number of witnesses increases, individual responsibility to act decreases