Price Discrimination
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Pros of price discrimination
Dynamic efficiency
Economies of scale
Some consumers benefit
Cross subsidisation
Cons of price discrimination
Allocative inefficiency
Inequalities
Anti-competitive pricing
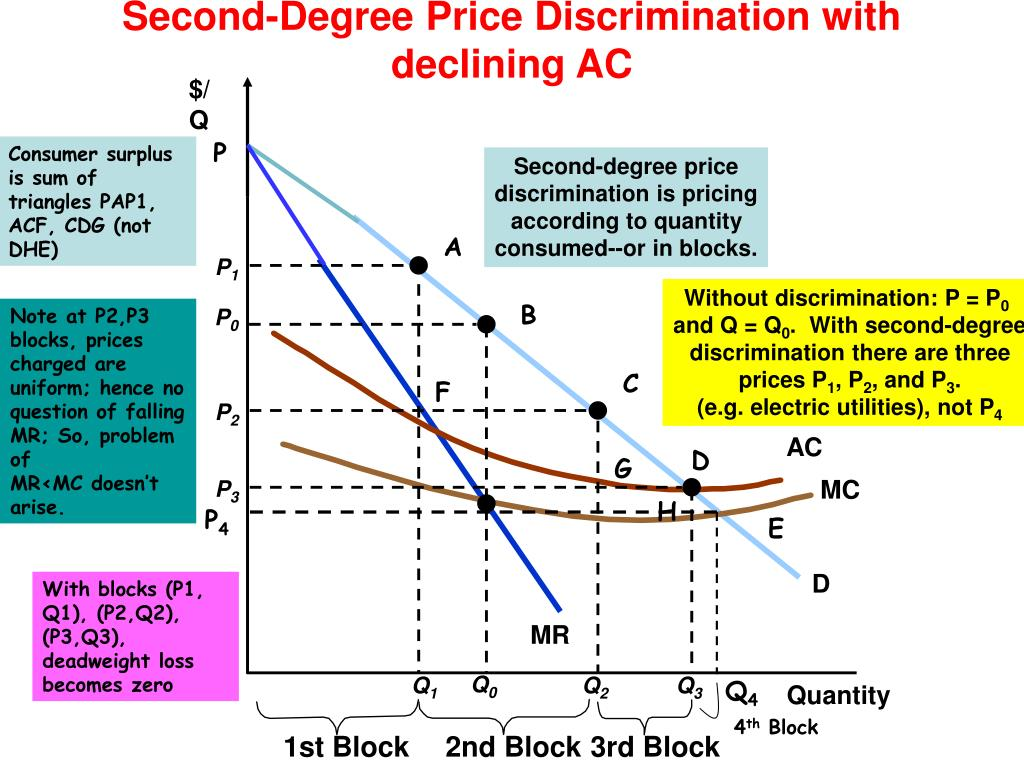
2nd degree price discrimination
The ability to gather information on every potential buyer is not present. Instead, companies price products or services differently based on the preferences of various groups of consumers
Normally applied through:
Quantity discounts, such as special offers to customers who buy in bulk over those who buy a single product
Buy-two-get-one offers
Coupons
Loyalty and rewards cards for frequent customers
Price discrimination
when firms sell the same good at different prices to different customers
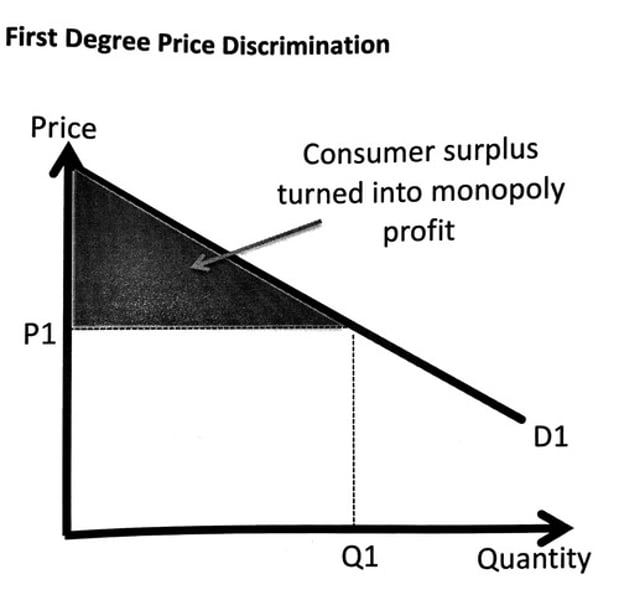
1st degree price discrimination
Charge every customer their maximum willingness and ability to pay; personalised pricing
3rd degree price discrimination
charging different prices for the same good to different groups of consumers e.g. peak and off-peak prices for tickets/ last minute prices, student prices
Conditions that enable price discrimination
1. Price making power
2. Information which can separate markets
3. Ability to prevent re-sale
1st degree price discrimination diagram
txt
2nd degree price discrimination diagram
txt
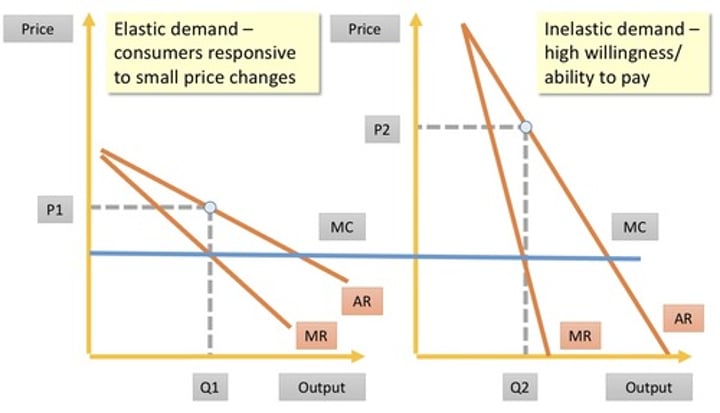
3rd degree price discrimination diagram
Blue line = MC, (e.g. right - peak ticket, inelastic price; left- off-peak ticket, elastic price)