Module 2 (Completed) - Chapters 4 & 5
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
151 Terms
Define output (or national product).
The value of a nation’s total production of goods and services
True or False: The value of national product is equal to the value of national income.
True
Define national income.
The value of total output and the value of income claims generated by the production of that output
Define nominal national income (or current-dollar national income).
The total value of goods and services produced in the economy, representing total output, or national income, measured in dollars
What are the 2 ways in which a change in nominal national income can occur?
Change in physical quantities
Producing more goods and services leads to increase in nominal national income
Change in prices
Increase in prices leads to increase in nominal national income
Define real national income (or constant-dollar national income).
The value of individual outputs, not at current prices, but at a set of constant prices from some base period
Shows the extent to which change in national income is due to change in quantities or change in prices
True or False: Changes in real national income from one year to another reflect only changes in quantities.
True
Define GDP (gross domestic product).
A measure of national income in either real or nominal terms
True or False: Any changes in Y (real national income) are driven by changes in the quantity of goods produced.
True
Real GDP shows 2 kinds of movement: ______ and ______.
Real GDP shows 2 kinds of movement: long-term economic growth and short-term fluctuations.
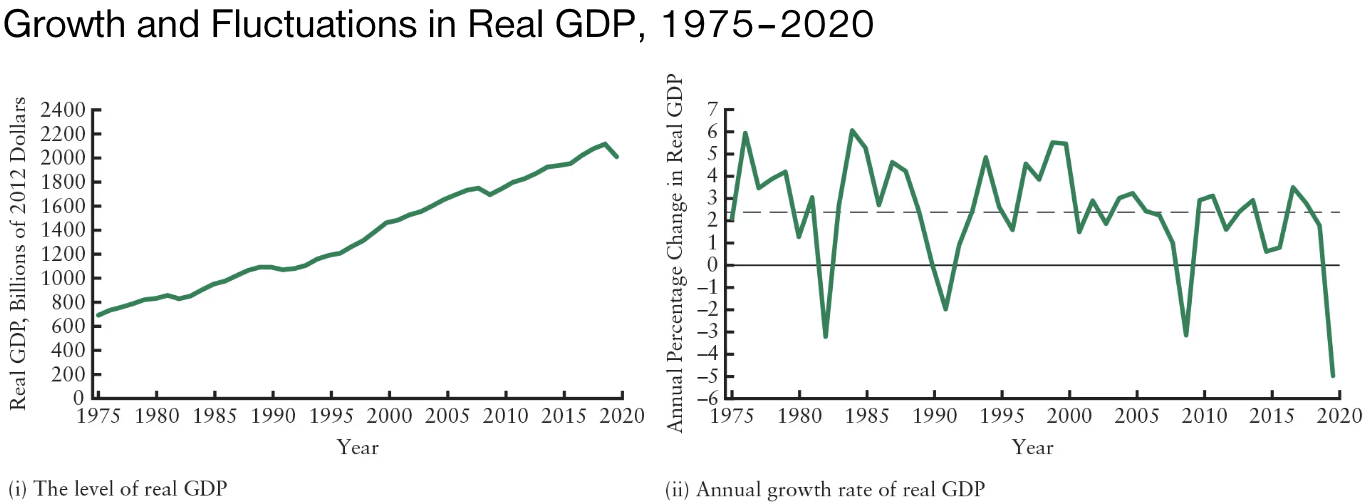
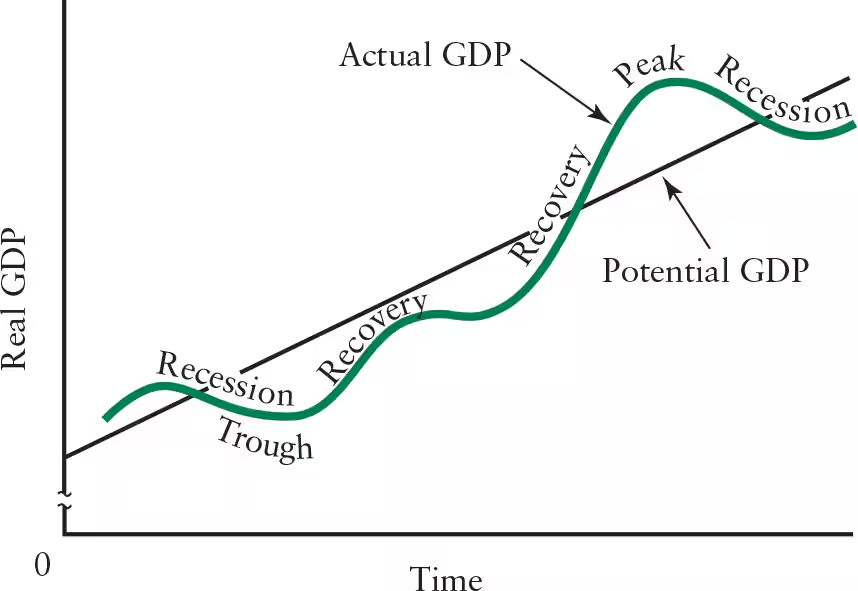
Define recession.
A period in which there is a decline in real GDP (downturn in economic activity)
Decline in output, employment and household incomes, investments, and profits
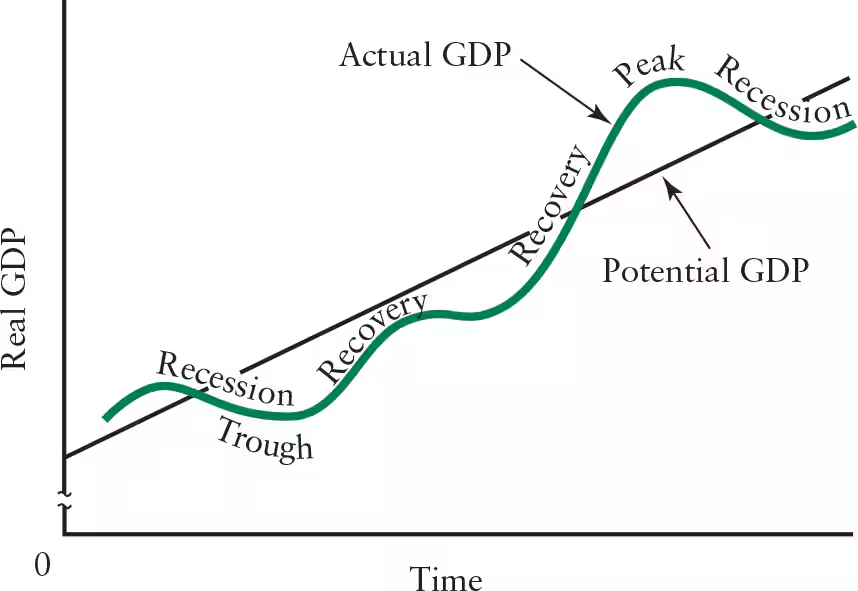
Define the business cycle.
The continual ebb and flow of business activity that occurs around the long-term trend
A single cycle usually includes an interval of quickly growing output, followed by an interval of slowly growing or even falling output
Variations in business cycles occur in duration and magnitude
Define trough (business cycle).
The lowest point in the business cycle, characterized by unemployed resources and a level of output that is low in relation to the economy’s capacity to produce
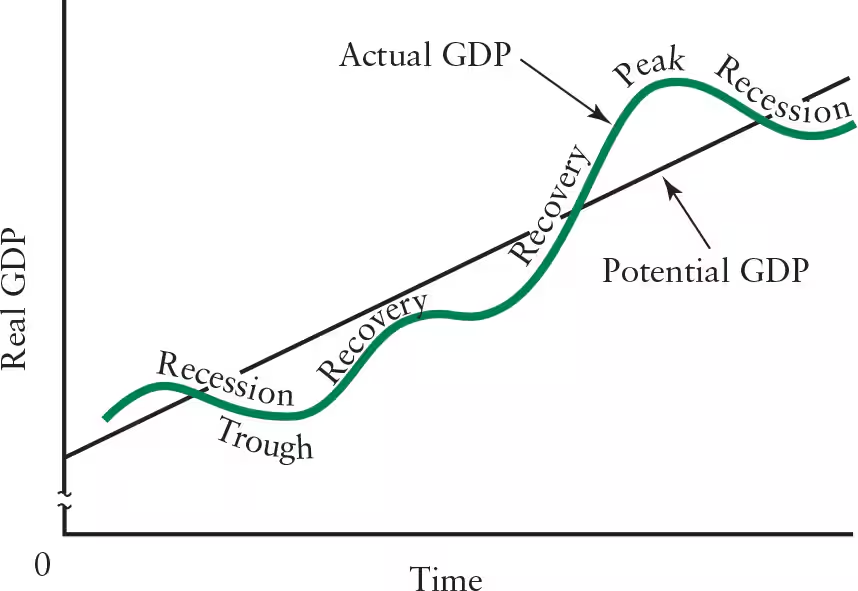
Define recovery (business cycle).
The process of moving out of a trough, characterized by increase in production, investments, employment, income, and consumer spending
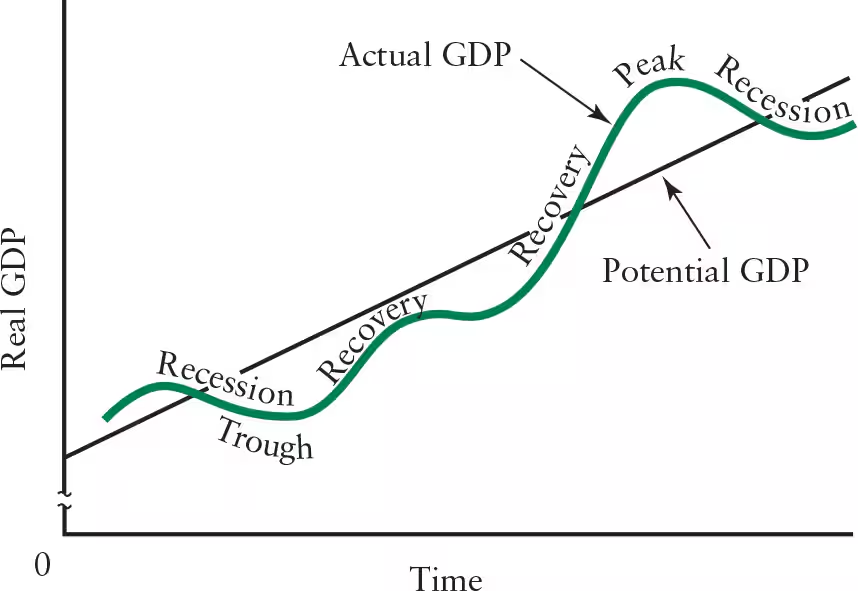
Define peak (business cycle).
The highest point in the business cycle
Existing productive capacity is used to the highest degree
Labour shortages and shortages of raw materials are likely
Increase in prices results in businesses remaining profitable
Define depression.
A deep and long-lasting period of recession
Define slump (business cycle).
The entire falling half of the business cycle
Define boom (business cycle).
The entire rising half of the business cycle
Define potential output.
The level of output the economy would produce if all resources (land, labour, and capital) were fully employed
Y is used to denote the economy’s actual output, and Y* is used to denote potential output
Define output gap.
The difference between actual output and potential output, computed as Y — Y*
When actual output is ______ than potential output (______), the output gap measures the market value of goods and services not being produced because the economy’s resources are not fully employed.
When actual output is less than potential output (Y < Y*), the output gap measures the market value of goods and services not being produced because the economy’s resources are not fully employed.
Define recessionary gap.
An output gap in which actual output is less than potential output (Y < Y*)
When actual output is ______ than potential output (______), the output gap measures the market value of production in excess of what the economy can produce on a sustained basis.
When actual output is more than potential output (Y > Y*), the output gap measures the market value of production in excess of what the economy can produce on a sustained basis.
Define inflationary gap.
An output gap in which actual output exceeds potential output (Y > Y*)
Results in upward pressure on wages and prices
Inflationary gap could be due to longer working hours or factories operating extra shifts
If more output is to be produced, either more workers must be used in production (rise in ______) or existing workers must produce more (rise in ______).
If more output is to be produced, either more workers must be used in production (rise in employment) or existing workers must produce more (rise in productivity).
Define employment.
The number of adults (defined in Canada as persons aged 15 and over) who have jobs, including those who are self-employed
Define unemployment.
The number of adults who are not employed but who are actively searching for a job
Define labour force.
The total number of people who are either employed or unemployed
Define unemployment rate.
The number of unemployed people expressed as a fraction of the labour force
What is the formula for calculating unemployment rate?
Unemployment Rate = Number of People Unemployed / Number of People in the Labour Force X 100
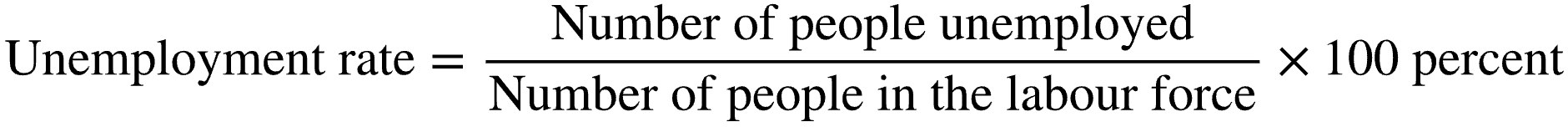
When the economy is at potential GDP, there is ______.
When the economy is at potential GDP, there is full employment.
What are the 2 reasons for unemployment when the economy is at potential GDP?
Frictional Unemployment: unemployment caused by the normal turnover of labour
Constant turnover of individuals in given jobs, leading to constant change in job opportunities
Structural Unemployment: mismatch between the structure of the supplies of labour and the structure of the demands for labour
Mismatch between the characteristics of people seeking employment and the characteristics of available jobs
Define cyclical unemployment.
A type of unemployment that rises and falls with the business cycle
Full employment is said to occur when the only employment is ______ and ______, a situation that corresponds to actual GDP being ______ to potential GDP.
Full employment is said to occur when the only employment is frictional and structural, a situation that corresponds to actual GDP being equal to potential GDP.
What is an example of seasonal fluctuations in unemployment?
Individuals employed in the fishing industry are often unemployed during the winter
Ski instructors are often unemployed in the summer
Unemployment is a cause for concern because it involves economic waste of ______.
Unemployment is a cause for concern because it involves economic waste of potential output.
Define productivity.
A measure of the amount of output that the economy produces per unit of input
Define labour productivity.
The amount of real GDP produced per unit of labour employed
The amount of labour employed could be measured as the total number of employed workers or by the total number of hours worked
______ is the largest cause of rising material living standards over long periods of time.
Productivity growth is the largest cause of rising material living standards over long periods of time.
Higher productivity explains why current workers’ real incomes (purchasing power of their earnings) are so much higher than for workers in the past
Define inflation.
The increase in the average prices of goods and services over a period of time
Define price level.
The average level of all prices in the economy
Price level is represented by the symbol P
Define rate of inflation.
The rate at which the price level is rising
What is the formula for calculating the rate of inflation?
Rate of Inflation = (CPI2 — CPI1) / CPI1 X 100
CPI1: previous CPI (consumer price index)
CPI2: current CPI
Define price index.
A measure of the price level that averages the prices of various goods and services according to how important they are
What is the formula for calculating price index?
Price Index = (Cost of Basket in Current Year / Cost of Basket in Base Year) X 100
Define consumer price index (CPI).
The best-known price index in Canada
Measures the average price of goods and services bought by the typical Canadian household
True or False: A price index is a pure number—it does not have any units.
True
When constructing a price index, units (in dollars) are eliminated because the price index shows the price of goods at a specific time relative to some base period
Price of goods (base year) is set to 100
Since the price level is measured with an ______, its value at any specific time has meaning only when it is compared with its value at some other time.
Since the price level is measured with an index number, its value at any specific time has meaning only when it is compared with its value at some other time.
By comparing the general price level at different times, price index (such as CPI) allows us to measure the ______.
By comparing the general price level at different times, price index (such as CPI) allows us to measure the rate of inflation.
The value of the CPI in April 2021 was 140.0. In April 2020, the value of the CPI was 135.6. What is the rate of inflation during that one-year period, expressed in percentage terms?
Rate of Inflation = (140.0 — 135.6) / 135.6 X 100
Rate of Inflation = 3.2%
True or False: The rate of inflation measures the annual rate of increase in the price level.
True
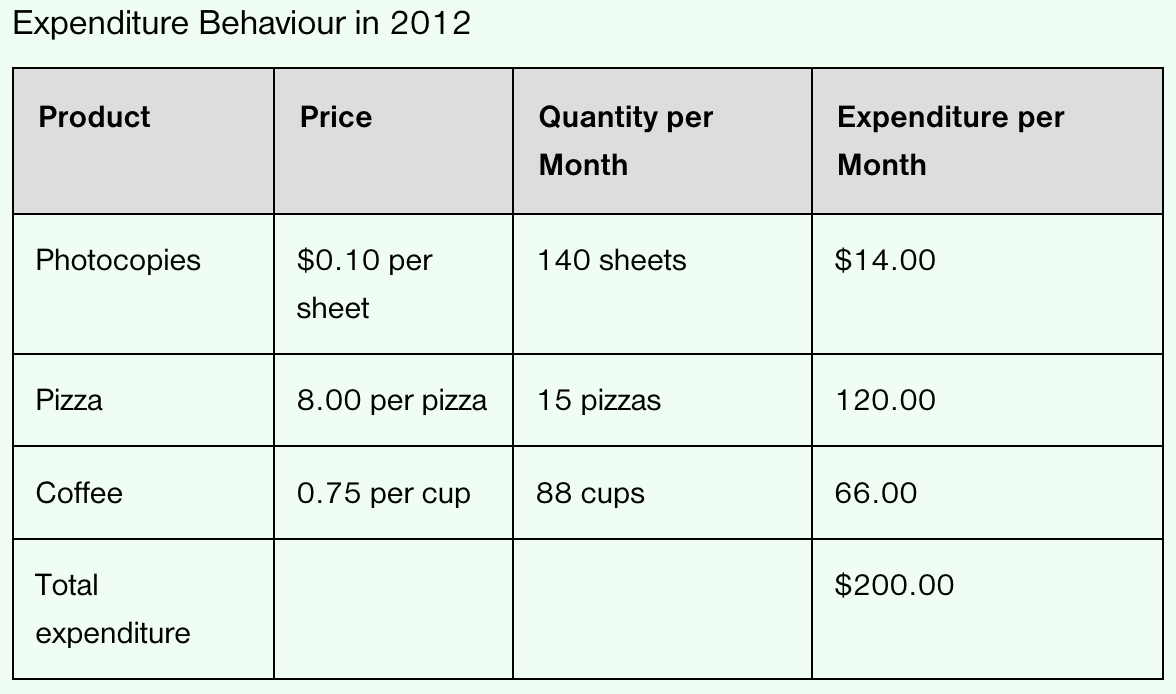
Assume that a survey of student behaviour in 2012 showed that the average university student consumed only 3 goods—pizza, coffee, and photocopying. By 2022, the price of photocopying has fallen to 5 cents per copy, the price of pizza has increased to $9.00, and the price of coffee has increased to $1.00. If 2021 is the base year for the “student price index,” what is the value of the index in 2022?
Student Price Index = (0.05 X 140 + 9.00 X 15 + 1.00 X 88) / (0.10 X 140 + 8.00 X 15 + 0.75 X 88) X 100
Student Price Index = 230 / 200 X 100
Student Price Index = 115
Goods cost $100 in 2012 (base year)
Goods cost $115 in 2022 (current year)
Define purchasing power of money.
The amount of goods and services that can be purchased with a given amount of money
True or False: The purchasing power of money is negatively related to the price level.
True
Ex: if the price level doubles, a dollar will buy only half as much
Inflation reduces the real value of anything whose ______ value is fixed in dollar terms.
Inflation reduces the real value of anything whose nominal value is fixed in dollar terms.
Explain the relationship between inflation and the purchasing power of money.
Inflation reduces the purchasing power of money.
Explain the distinction between anticipated inflation and unanticipated inflation.
Anticipated Inflation: if households and firms anticipate inflation over the coming year, they can adjust nominal prices and wages to maintain their real values
Inflation will have fewer real effects on the economy
Unanticipated Inflation: generally leads to more changes in the real value of prices and wages
Define interest rate.
The price that is paid to borrow money for a stated period of time
Expressed as a percentage amount per year per dollar borrowed
Ex: interest rate of 5% per year means that the borrower must pay 5 cents per year for every dollar that is borrowed
Define prime interest rate.
The interest rate that banks charge to their best business customers
Define bank rate.
The interest rate that the Bank of Canada (Canada’s central bank) charges on short-term loans to commercial banks (such as the Royal Bank or the Bank of Montreal)
Define nominal interest rate.
The amount of interest paid expressed in money terms
Define real interest rate.
The amount of interest paid expressed in terms of purchasing power
The more the price level rises, the worse off the lender will be and the better the transaction will be for the borrower
What is the formula for calculating real interest rate?
Real Interest Rate = Nominal Interest Rate — Inflation Rate
The burden of borrowing depends on the ______ rate of interest, not the ______ rate of interest.
The burden of borrowing depends on the real rate of interest, not the nominal rate of interest.
True or False: A nominal interest rate of 8% with a 2% rate of inflation (real interest rate of 6%) is a greater real burden on borrowers than a nominal rate of 16% with a 14% rate of inflation (real interest rate of 2%).
True
Higher real interest rate means the borrower repays more value over time
______ benefit from negative real interest rates.
Borrowers benefit from negative real interest rates.
A ______ represents the flow of credit between lenders and borrowers, with the interest rate representing the price of this credit.
A loan represents the flow of credit between lenders and borrowers, with the interest rate representing the price of this credit.
True or False: Banks play a crucial role in the credit market by acting as intermediaries between the households and firms that have available funds and the households and firms that require funds.
True
Define exchange rate.
The number of units of domestic currency required to purchase one unit of foreign currency
Ex: 1 Canadian dollar = 0.68 euros
Ex: 1 euro = 1.47 Canadian dollars
Define foreign exchange.
Foreign currencies or claims on foreign currencies (such as bank deposits, cheques, and promissory notes) that are payable in foreign money
Define foreign-exchange market.
The market in which currencies are traded, at a price expressed by the exchange rate
Define depreciation.
A rise in the exchange rate
Ex: it takes more Canadian dollars to purchase one unit of foreign currency
Define appreciation.
A fall in the exchange rate
Ex: it takes fewer Canadian dollars to purchase one unit of foreign currency
Define trade-weighted exchange rate.
The weighted-average exchange rate between a home country and its trading partners, where the weights reflect each trading partner’s share in the home country’s total trade
Define net exports (or trade balance).
The difference between exports and imports
Net Exports (Trade Balance) = Exports — Imports
The depreciation of the Canadian dollar leads to a(n) ______ in exports.
The depreciation of the Canadian dollar leads to a(n) increase in exports.
The weaker Canadian dollar makes products less expensive for foreign buyers
The depreciation of the Canadian dollar leads to a(n) ______ in imports.
The depreciation of the Canadian dollar leads to a(n) decrease in imports.
The weaker Canadian dollar implies a higher Canadian-dollar price for foreign goods
True or False: If the CPI increases from 110 to 121, the inflation rate is 10%. Therefore, a nominal interest rate of 12% implies a real interest rate of 2%.
True
Inflation Rate = (121 — 110) / 110 X 100
Inflation Rate = 10%
Real Interest Rate = 12% — 10%
Real Interest Rate = 2%
Define double counting (or multiple counting).
The error that occurs when estimating a nation’s output by adding all sales of all firms
If we added up the values of all sales, the same output would be counted every time that it was sold by one firm to another
Provide an example of double counting.
The local baker uses flour that is the output of the flour milling company; the flour milling company uses wheat that is the farmer’s output
If we added the total value of output, we would be counting the value of wheat three times, the value of flour twice, and the value of bread once
Define intermediate goods.
Outputs of firms that are used as inputs by other firms
Define final goods.
Products that are not used as inputs by other firms
True or False: In general, it is extremely difficult to distinguish between final goods and intermediate goods.
True
Define value added.
The amount of value that firms and workers add to their products, over and above the costs of purchased intermediate goods
What is the formula for calculating value added?
Value Added = Sales Revenue — Cost of Intermediate Goods
True or False: Payments to factors of production (such as workers’ wages or profits paid to owners) are not purchases from other firms (intermediate goods), and therefore, are not subtracted from the firm’s sales revenue when calculating value added.
True
True or False: Value added is equal to the sum of national income/factor payments (payments owed to the firm’s factors of production).
True
Value added is calculated as the difference between sales revenue (output) and cost of intermediate goods (input)
The remaining value (value added) is then distributed among the factors of production (labour income and profits)
The sum of all values added in the economy is a measure of the economy’s total ______.
The sum of all values added in the economy is a measure of the economy’s total output.
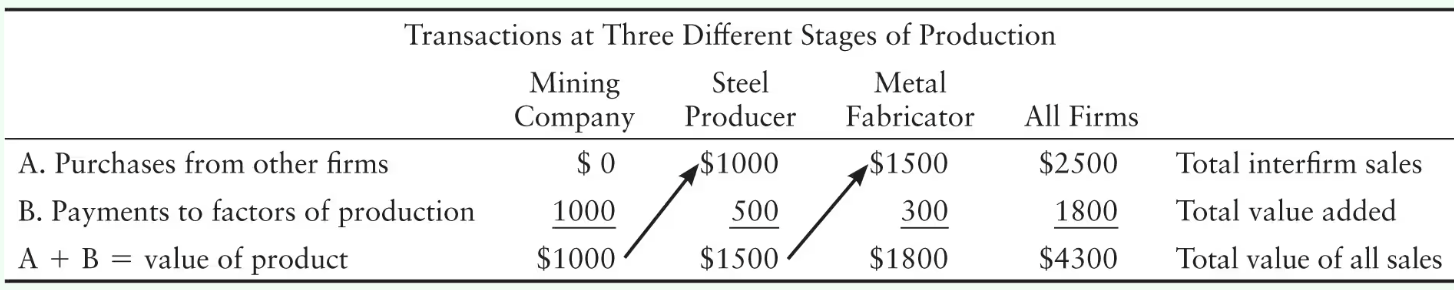
The mining company produces iron ore valued at $1,000. This firm’s value added is ______. The mining company sells iron ore to the steel producer who produces steel valued at $1,500. This firm’s value added is ______ because the value of goods has increased by _____ as a result of the firm’s activities. The steel producer sells steel to the metal fabricator who produces folding chairs valued at $1,800. This firm’s value added is ______.
The mining company produces iron ore valued at $1,000. This firm’s value added is $1,000. The mining company sells iron ore to the steel producer who produces steel valued at $1,500. This firm’s value added is $500 because the value of goods has increased by $500 as a result of the firm’s activities. The steel producer sells steel to the metal fabricator who produces folding chairs valued at $1,800. This firm’s value added is $300.
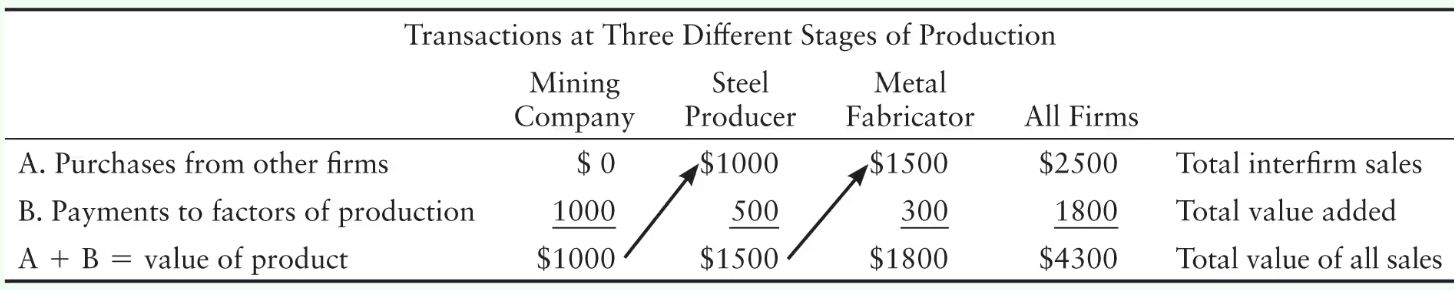
The mining company produces iron ore valued at $1,000. The mining company sells iron ore to the steel producer who produces steel valued at $1,500. The steel producer sells steel to the metal fabricator who produces folding chairs valued at $1,800. What is the value of the final goods?
$1,800
Find the value of the final goods either by counting only the sales of the last firm or by taking the sum of the values added by each firm
The value of domestic output is ______ the value of expenditure on that output. It is also ______ the total income generated by producing that output.
The value of domestic output is equal to the value of expenditure on that output. It is also equal to the total income generated by producing that output.
National income is ______ national product.
National income is equal to national product.
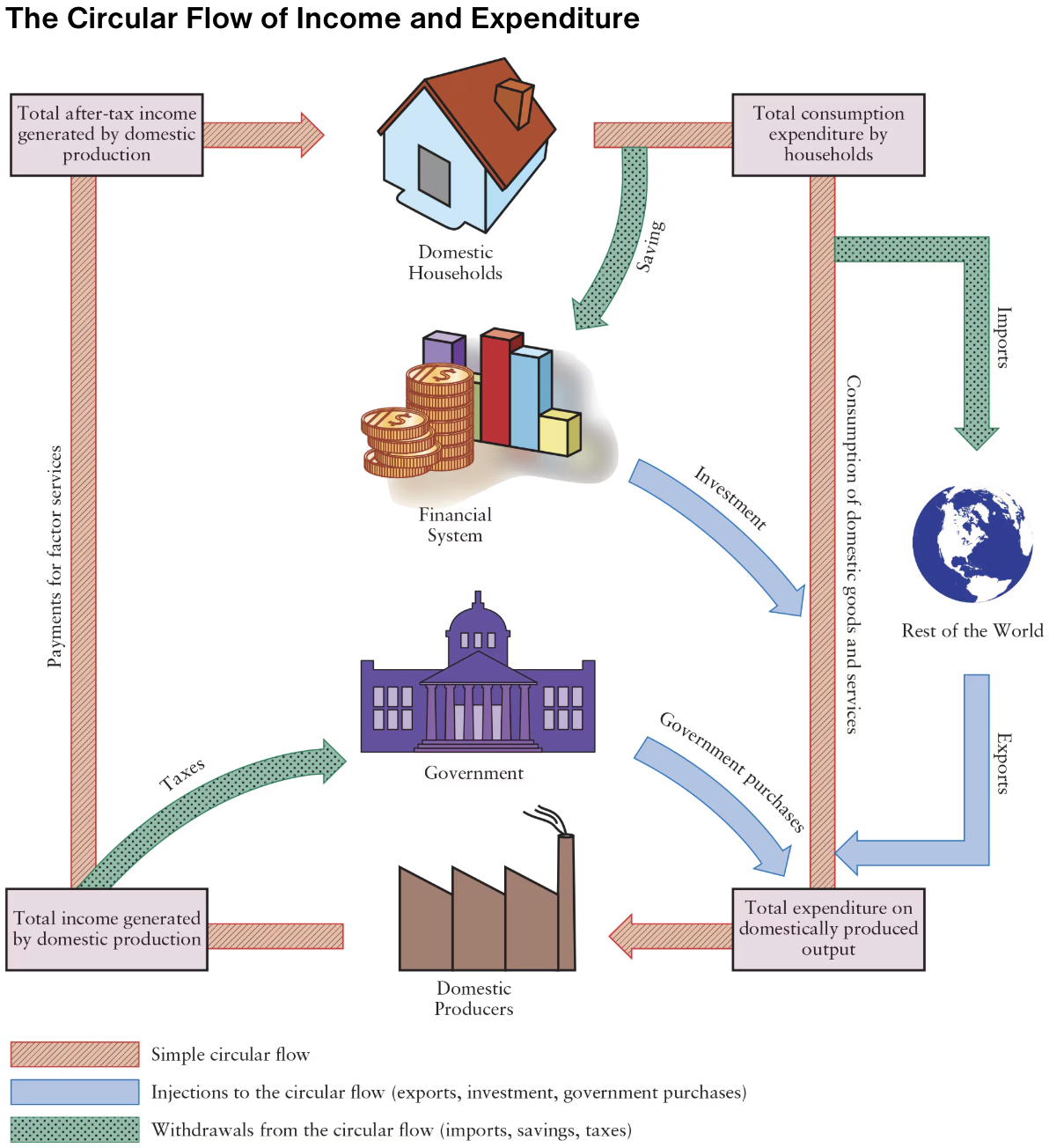
What are injections to the circular flow of income and expenditure?
Exports
Investment
Government purchases
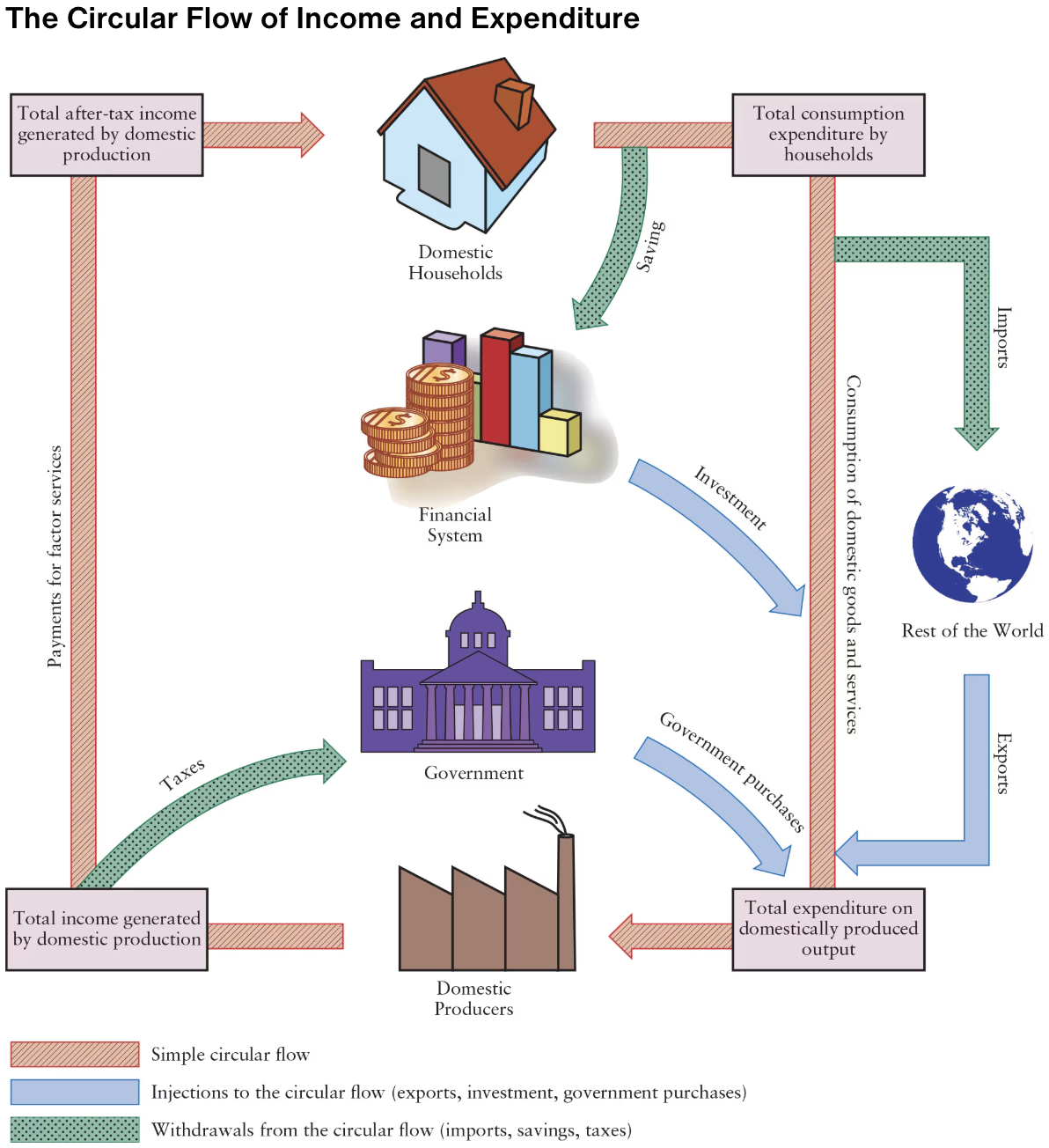
What are withdrawals from the circular flow of income and expenditure?
Imports
Saving
Taxes
What are the 3 ways of measuring national income?
Adding up the value of all domestic output (goods and services produced in the economy)
This requires the concept of value added
Adding up the total flow of expenditure on domestic output
Adding up the total flow of income generated by domestic production
Define GDP on the expenditure side.
When GDP is calculated by adding up total expenditure on components of output
Define GDP on the income side.
When GDP is calculated by adding up all the income generated by the act of production
True or False: GDP calculated from the income and expenditure sides are conceptually identical, differing only because of errors in measurement.
True
What are the 4 categories of expenditure?
Consumption (C)
Investment (I)
Government purchases (G)
Net exports (NX)
Define consumption expenditure.
Expenditure on all goods and services sold to their final users (households or businesses) during the year
Actual measured consumption expenditure is denoted by the symbol Ga
Ex: haircuts, clothing, cars