AP HUG VOCAB Urban Development
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AP Human Geography Unit 6 Cities and Urban Land-Use Patterns and Processes
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
1
New cards
Settlement
A small community or village.
2
New cards
Urbanization
Movement of people from rural areas to cities.
3
New cards
Suburb
A residential district located on the outskirts of a city.
4
New cards
Urban Area
A central city and its surrounding built-up suburbs.
5
New cards
Site (as it applies to Urbanization)
The physical character of a place (climate, absolute location, unique features that allow for settlement)
6
New cards
Situation (as it applies to Urbanization)
The location of a place relative to other places (rivers, roads, connections, networks, telecommunication, relative location)
7
New cards
Central Place
A market center for the exchange of goods and services by people attracted from the surrounding area.
8
New cards
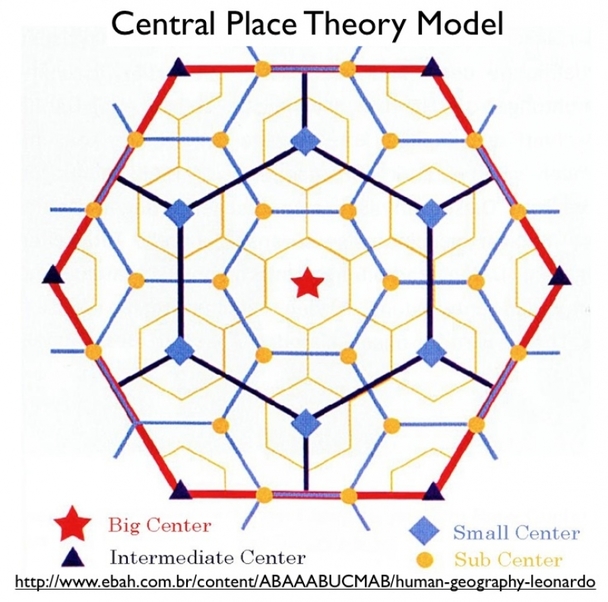
Central Place Theory
A theory that explains the distribution of services, based on the fact that settlements serve as centers of market areas for services; larger settlements are fewer and farther apart than smaller settlements and provide services for a larger number of people who are willing to travel farther.
9
New cards
Service
work that is performed for someone.
10
New cards
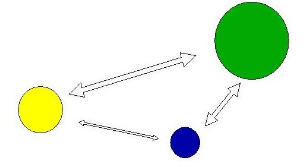
Gravity Model
A model that holds that the potential use of a service at a particular location is directly related to the number of people in a location and inversely related to the distance people must travel to reach the service.
11
New cards
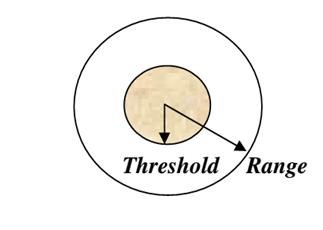
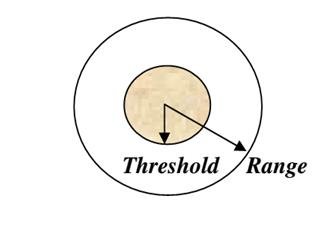
Range
The maximum distance people are willing to travel to use a service.
12
New cards
Market Area
The area surrounding a service from which customers are attracted
13
New cards
Threshold
The minimum number of people needed to support the service.
14
New cards
Central Business District (CBD)
The downtown or nucleus of a city where retail stores, offices, and cultural activities are concentrated.
15
New cards
Central City
An urban settlement that has been legally incorporated into an independent, self-governing unit known as a municipality.
16
New cards
Concentric Zone Model
A model of the internal structure of cities in which social groups are spatially arranged in a series of rings.
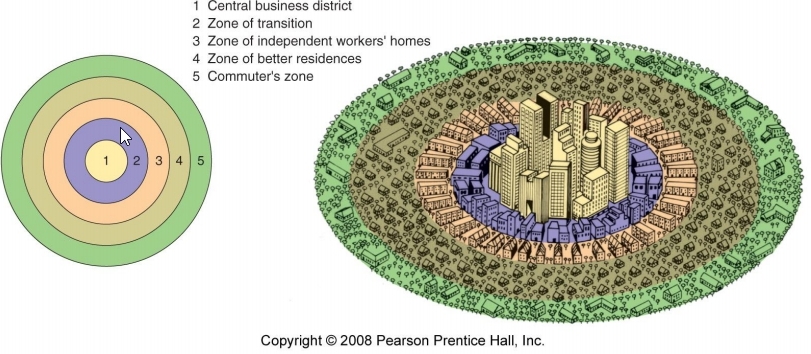
17
New cards
Galactic Model
A model of North American urban areas consisting of an inner city surrounded by large suburban residential and business areas tied together by a beltway or ring road.
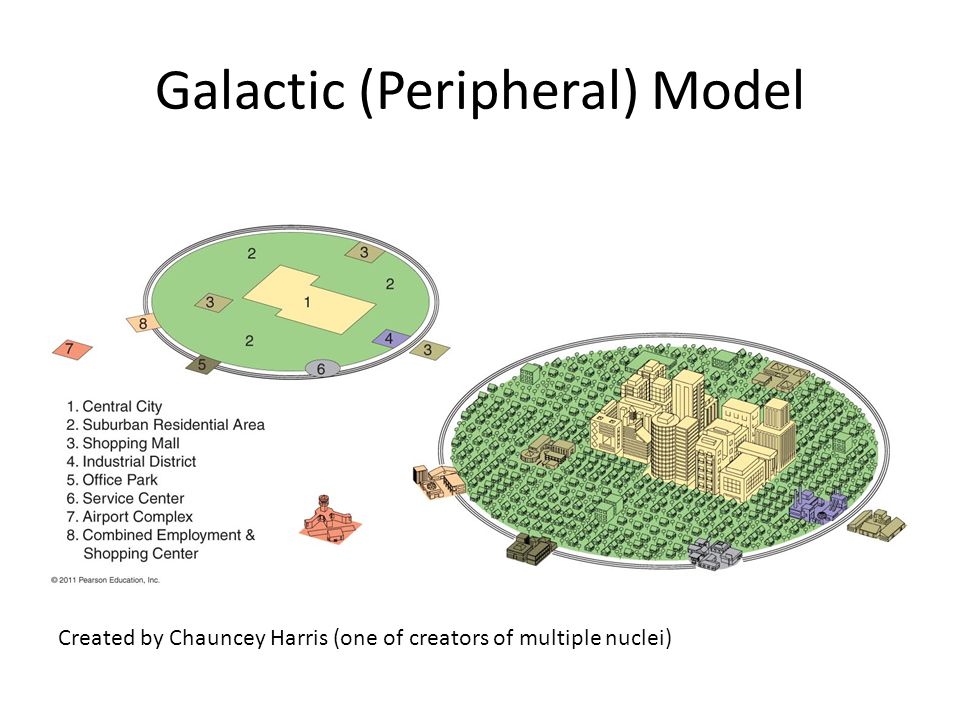
18
New cards
Multiple Nuclei Model
A model of the internal structure of cities in which social groups are arranged around a collection of nodes of activities.
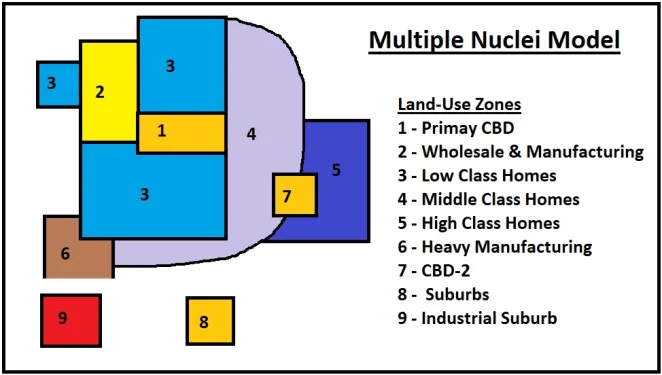
19
New cards
Sector Model
A model of the internal structure of cities in which social groups are arranged around a series of sectors, or wedges, radiating out from the central business district (CBD).
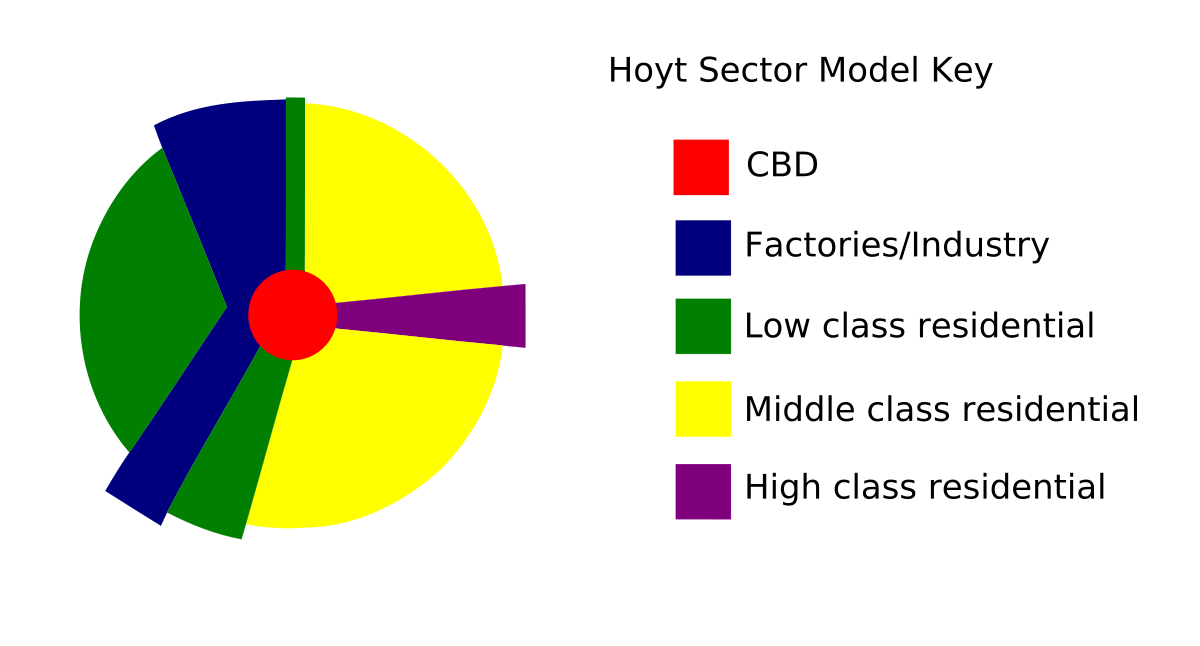
20
New cards
Informal Settlement
An area within a city in a less developed country in which people illegally establish residences on land they do not own or rent and erect homemade structures.
21
New cards
Hinterland
The area surrounding a central place, from which people are attracted to use the place's goods and services.
22
New cards
Edge City
cities that are located on the outskirts of larger cities and serve many of the same functions of urban areas, but in a sprawling, decentralized suburban environment.
23
New cards
Consumer Services
To provide services to individual consumers who desire them and can afford to pay for them.
24
New cards
Economic Base
A community's collection of basic businesses
25
New cards
Food Desert
An area characterized by a lack of affordable, fresh and nutritious food.
26
New cards
Global City
A former industrial center that has reinvented itself as a command center for global production.
27
New cards
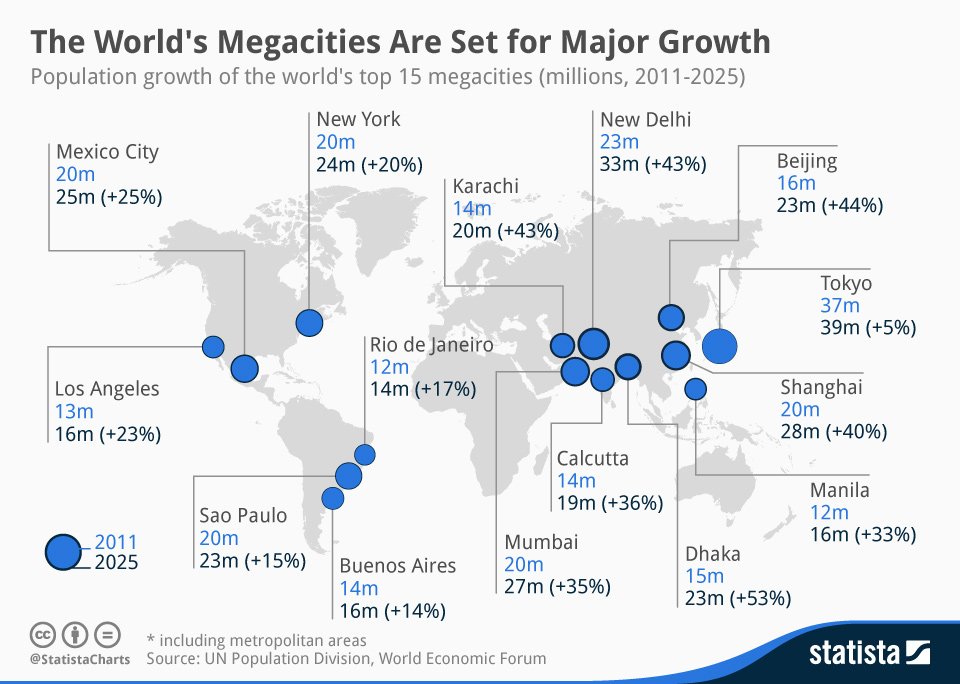
Megacity
City with more than 10 million people.
28
New cards
Metacity
A city with a population over 20 million.
29
New cards
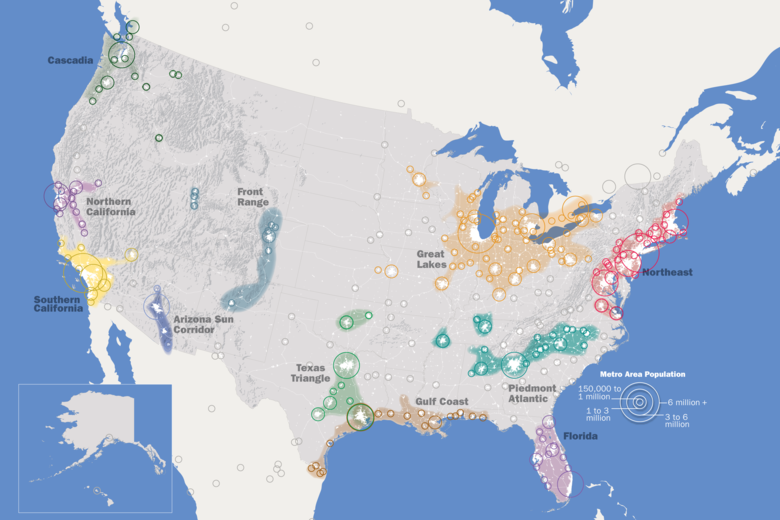
Megalopolis
Multiple cities linked together (Great Lakes, S CA, TX triangle, 3 bananas)
30
New cards
Exurbs
A district outside a city, especially a prosperous area beyond the suburbs.
31
New cards
Boomburbs
Rapidly growing suburb cities.
32
New cards
New Urbanism
Development, urban revitalization, and suburban reforms that create walkable neighborhoods with a diversity of housing and jobs (Seaside, FL and Pearl District, Oregon)
33
New cards
Con-urbanization
An extended urban area, typically consisting of several towns merging with the suburbs of one or more cities.
34
New cards
Primate City
The largest settlement in a country, if it has more than twice as many people as the second-ranking settlement.

35
New cards
Primate City Rule
A pattern of settlement in a country such that the largest settlement has more than twice as many people as the second-ranking settlement

36
New cards
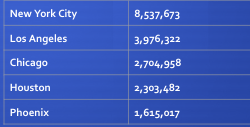
Rank Size Rule
In a model urban hierarchy, the idea that the population of a city or town will be inversely proportional to its rank in the hierarchy.
37
New cards
Basic Business
A business that sells its products or services primarily to consumers outside the settlement (typically gives area a primary function - Nashville and music/entetainment)
38
New cards
Business Service
A service that primarily meets the needs of other businesses, including professional, financial, and transportation services
39
New cards
Non Basic Business
Jobs that shift money within a city (teachers, dry cleaners, janitors, fire department)
larger cities have a higher % of this to support larger infrastructural needs, and these jobs are typically the same in all places
larger cities have a higher % of this to support larger infrastructural needs, and these jobs are typically the same in all places
40
New cards
Gentrification
A process of converting an urban neighborhood from a predominantly low-income renter-occupied area to a predominantly middle-class owner-occupied area.
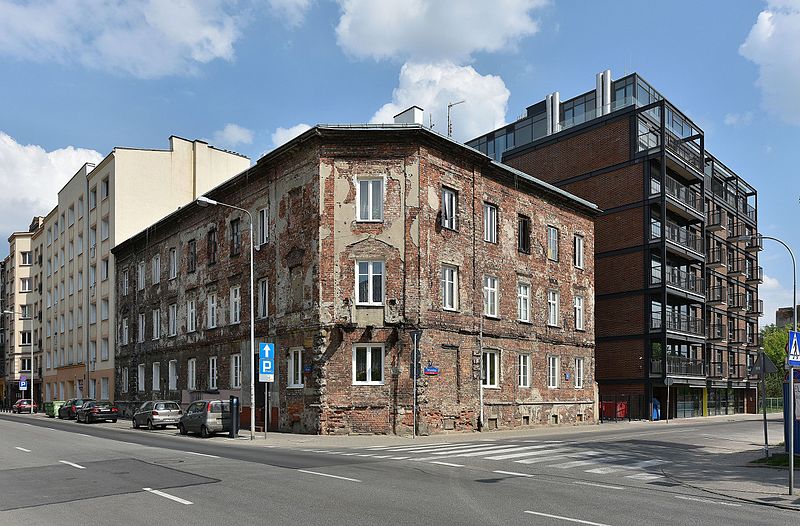

41
New cards
Shantytowns/Self Construction
Little towns consisting of shacks.
42
New cards
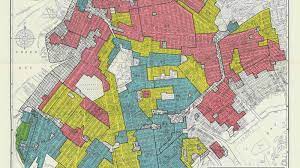
Redlining
A discriminatory real estate practice in North America in which members of minority groups are prevented from obtaining money to purchase homes or property in predominantly white neighborhoods.
43
New cards
Blockbusting
Illegal practice of inducing homeowners to sell their properties by telling them that a certain people of a certain race, national origin or religion are moving into the area.
44
New cards
Ghettoization
A process occurring in many inner cities in which they become dilapidated centers of poverty, as affluent whites move out to the suburbs and immigrants and people of color vie for scarce jobs and resources.
45
New cards
Green Belts
Areas around cities where suburban land uses are restricted; contains new development within an urban core to prevent sprawl
46
New cards
Mixed Development
A type of urban development that blends residential, commercial, cultural, institutional, or industrial uses, where these functions are integrated (joined) together, by public transport/routeways for example.
47
New cards
Public Housing
Housing owned by the government; in the United States, it is rented to low-income residents, and the rents are set at 30 percent of the families' incomes.
48
New cards
Public Service
Services offered by the government to provide security and protection for citizens and businesses.
49
New cards
Annexation
The adding of a region to the territory of an existing political unit.
50
New cards
Census Tract
An area delineated by the U.S. Bureau of the Census for which statistics are published; in urbanized areas, census tracts correspond roughly to neighborhoods.
51
New cards
Smart Growth
Legislation and regulations to limit suburban sprawl and preserve farmland.
52
New cards
Sprawl
Development of new housing sites at relatively low density and at locations that are not contiguous to the existing built-up area.
53
New cards
Functional Zonation
Division of a city into different regions or zones for certain purposes or functions.
54
New cards
Forward-Thrust Capital
A capital city created to develop an empty part of the country away from the core.
55
New cards
Urban Morphology
The study of the physical form and structure of urban places.